skeletal muscle, smooth muscle, cardiac muscle
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
skeletal muscle structure
striated
multinucleated (many nuclei per cell)
long, cylindrical fibers
under voluntary control
skeletal muscle function
produces body movements
maintains posture
generates head
skeletal muscle location
attached to bones by tendons
skeletal muscle special properties
fast contraction
fatigues relatively quickly
required neural stimulation to contract
Skeletal muscle anatomy
CT sheaths
Epimysium
Perimysium
Endomysium
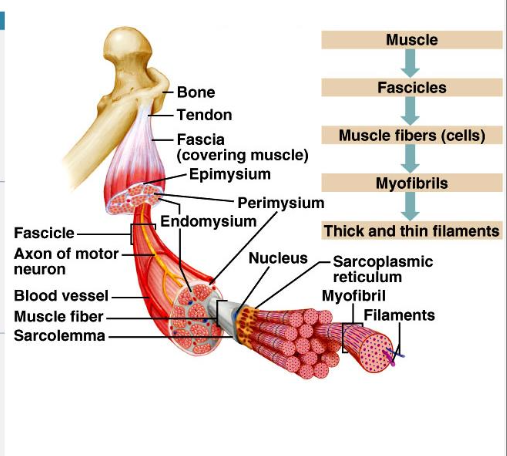
CT sheaths - Skeletal Muscle
support cells and reinforce whole muscle
epimysium
dense irregular CT surrounding entire muscle; may blend with fascia
perimysium
dense irregular CT surrounding fascicles (groups of muscle fibers)
endomysium
fine reticular fibers surrounding each muscle cell (= muscle fiber)
Skeletal muscle anatomy - attachments
muscles span joints and attach to bones in at least two places
insertion
origin
insertion
attachment to movable bone
origin
attachment to immovable/less movable bone
attachments can be…
direct or indirect
direct (fleshy)
epimysium fused to periosteum (bone) or perichondrium (cartilage)
ex: intercostals
indirect
connective tissue wrappings extend beyond muscle as ropelike tendon or sheetlike aponeurosis
Skeletal Muscle Microanatomy - Specialized features
sarcolemma
Sarcoplasm
Glycosomes
Myoglobin
Modified organelles
myofibrils
sarcoplasmic reticulum
T-tubules
sarcolemma
muscle fiber plasma membrane
sarcoplasm
muscle fiber cytoplasm
glycosomes
glycogen storage
myoglobin
O2 storage
myofibrils
rodlike
densely packed, rodlike elements - one muscle fiber can contain 1000s (~80% of muscle cell volume)
myofibril features: striations, sarcomeres, myofilaments (thick - myosin; thin - actin)
sarcoplasmic reticulum
calcium storage
T tubules
transport
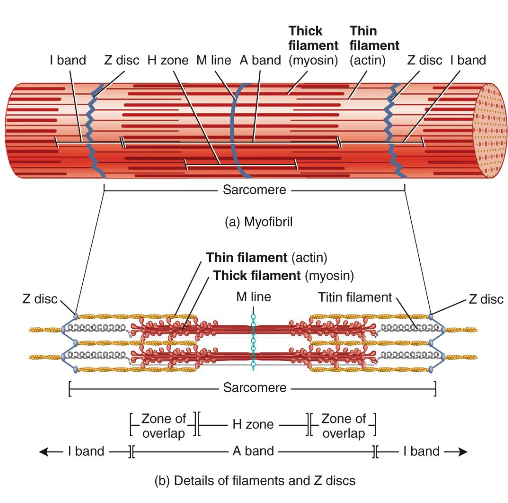
Sarcomere
smallest contractile unit (functional unit) of muscle fiber
Individual sarcomere formation
individual sarcomeres align end to end along a myofibril, like boxcars of a train
striations
myofilaments
striations
stripes formed from repeating series of dark and light bands along length of each myofibril
myofilaments
orderly arrangement of actin (thin) and myosin (thick) myofilaments within sarcomere
Components of a sarcomere
Z discs: narrow, plate-shaped regions of dense material that separate one sarcomere from the next
A band: dark, middle part of sarcomere that extends entire length of thick filaments and includes those parts of thin filaments that overlap thick filaments
I band: lighter, less dense area of sarcomere that contains remainder of thin filaments but no thick filaments. A Z disc passes through center of each I band
H zone: narrow region in center of each A band that contains thick filaments but no thin filaments
M line: region in center of H zone that contains proteins that hold thick filaments together at center of sarcomere
contractile proteins
proteins that generate force during muscle contractions
myosin
contractile protein that makes up thick filament; molecule consists of a tail and two myosin heads, which bind to myosin-binding sites on actin molecules of thin filament during muscle contraction
actin
contractile protein that is the main component of thin filament; each actin molecule has a myosin-binding site where myosin head of thick filament binds during muscle contraction
what happens during contraction
heads link thick and thin filaments together, forming cross bridges
regulatory proteins
proteins that help switch muscle contraction process on and off
tropomyosin
regulatory protein that is a component of thin filament; when skeletal muscle fiber is relaxed, tropomyosin covers myosin-binding sites on actin molecules, thereby preventing myosin from binding to actin
troponin
regulatory protein that is a component of thin filament; when calcium ions (Ca2+) bind to troponin, it changes shape; this conformational change moves tropomyosin away from myosin-binding sites on actin molecules, and muscle contraction subsequently begins as myosin binds to actin
what happens when calcium ions bind to troponin
it causes troponin to change shape - troponin’s shape change pulls on tropomyosin, which exposes binding sites on actin
sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR)
network of smooth endoplasmic reticulum tubules surrounding each myofibril
stores and releases Ca2+
transverse (T) tubules
tubes formed by protrusion of sarcolemma into cell interior - increases muscle fiber’s surface area
T tubules allow
electrical nerve transmissions to reach interior of cell
skeletal muscle fiber type is based on
speed of contraction
metabolic pathways used for ATP synthesis
oxidative - use aerobic pathways (red)
glycolytic - use anaerobic glycolysis (white)
skeletal muscle fibers can be classified into three types
slow oxidative fibers (red)
fast oxidative fibers (red-pink)
fast glycolytic fibers (white)
slow oxidative fibers (red)
low intensity, endurance activities (ex: maintaining posture)
fast oxidative-glycolytic fibers (red pink)
medium-intensity activities (ex: sprinting or walking)
fast glycolytic fibers (white)
short term intense or powerful movements (ex: hitting a baseball)
human muscles are
typically a mix (pink)
genes can determine percentage of fast and slow fibers
can also change with physical conditioning
cardiac muscle cells are usually
relatively small, usually 1 nucleus, can be branched
are there sarcomeres present in cardiac muscle
yes - causes striations
T tubules in cardiac muscle
wider and less numerous; SR simpler (no triads)
what is the release of Ca2+ triggered by in muscle cells
extracellular calcium
what type of respiration does cardiac muscle use
AEROBIC respiration only
large energy reserves
large numbers of mitochondria
abundant myoglobin
cardiac muscle cells contain
intercalated discs
gap junctions - electrically connect cells
desmosomes - keep cells from pulling apart
cardiac muscle can contract without
neural stimulation (automaticity)
pacemaker cells within the heart
cardiac muscle - system can make alterations to
rate of pacemaker cells
amount of tension in each contraction
cardiac muscle - contractions last
10 times as long as skeletal muscle
longer refractory periods
no fatigue
cardiac muscle - properties of the sarcolemma differ
twitches cannot undergo summation - no tetanic contractions
smooth muscle is found
in walls of most hollow organs
smooth muscle forms
sheets, bundles, or sheaths around other tissues
smooth muscle can
shorten and stretch to a greater extent
smooth muscle is arranged as
either single-unit (visceral) or multi-unit fibers
smooth muscle fiber shape
spindle shaped - thin and short
smooth muscle fiber - nucleus and striations
only 1 nucleus, no striations
smooth muscle lacks
connective tissue sheaths - endomysium only
SR and T tubules of smooth muscle
less elaborate SR and no T tubules
SR does store intracellular Ca2+, but most calcium used for contraction has extracellular origins
Troponin and tropomyosin in smooth muscle
no troponin complex, but does contain tropomyosin
what protein binds Ca2+ in smooth muscle
calmodulin
thin and thick filaments - smooth muscle characteristics
thin and thick filaments arranged diagonally
fewer thick filaments
spirally arranged, causing smooth muscle to contract in a corkscrew manner
smooth muscle contains a lattic-like arrangement of
non contractile intermediate filaments - resists tension
dense bodies in smooth muscle
anchor filaments to sarcolemma - like Z discs of skeletal muscle
what happens during contraction of smooth muscle
areas of sarcolemma between dense bodies bulge outward - cell looks puffy
functional characteristics of smooth muscle - sarcolemma
contains pouchlike infoldings (caveolae) that contain numerous Ca2+ channels that open to allow rapid influx of extracellular Ca2+
functional characteristics of smooth muscle - sarcolemma organization
organized into 2 layers of tightly packed fibers sheets oriented at right angles to each other
functional characteristics of smooth muscle - sarcolemma alternating contractions and relaxations of layers
alternating contractions and relaxations of layers mix and squeeze substances through lumen of hollow organs
smooth muscle contractions
slow, synchronized contractions and slower to relax - but maintains contraction for long periods with less fatigue
gap junctions in smooth muscle
transmit action potentials from fiber to fiber
some smooth muscle cells are
self-excitatory (depolarize without external stimuli) - act as pacemakers for muscle sheets
rate and intensity of contraction in smooth muscle cells
rate and intensity of contraction is modified by neural and chemical stimuli
how does smooth muscle respond to stretch
responds to stretch only briefly, then adapts to new length
this enables organ to temporarily store contents
smooth muscle contraction length
can contract when between ½ and 2x resting length
allows organ to have huge volume changes without becoming flabby when relaxed