Apologia Advanced Biology Module 8
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Gray Matter
Collections of neuron cell bodies and their associated neuroglia
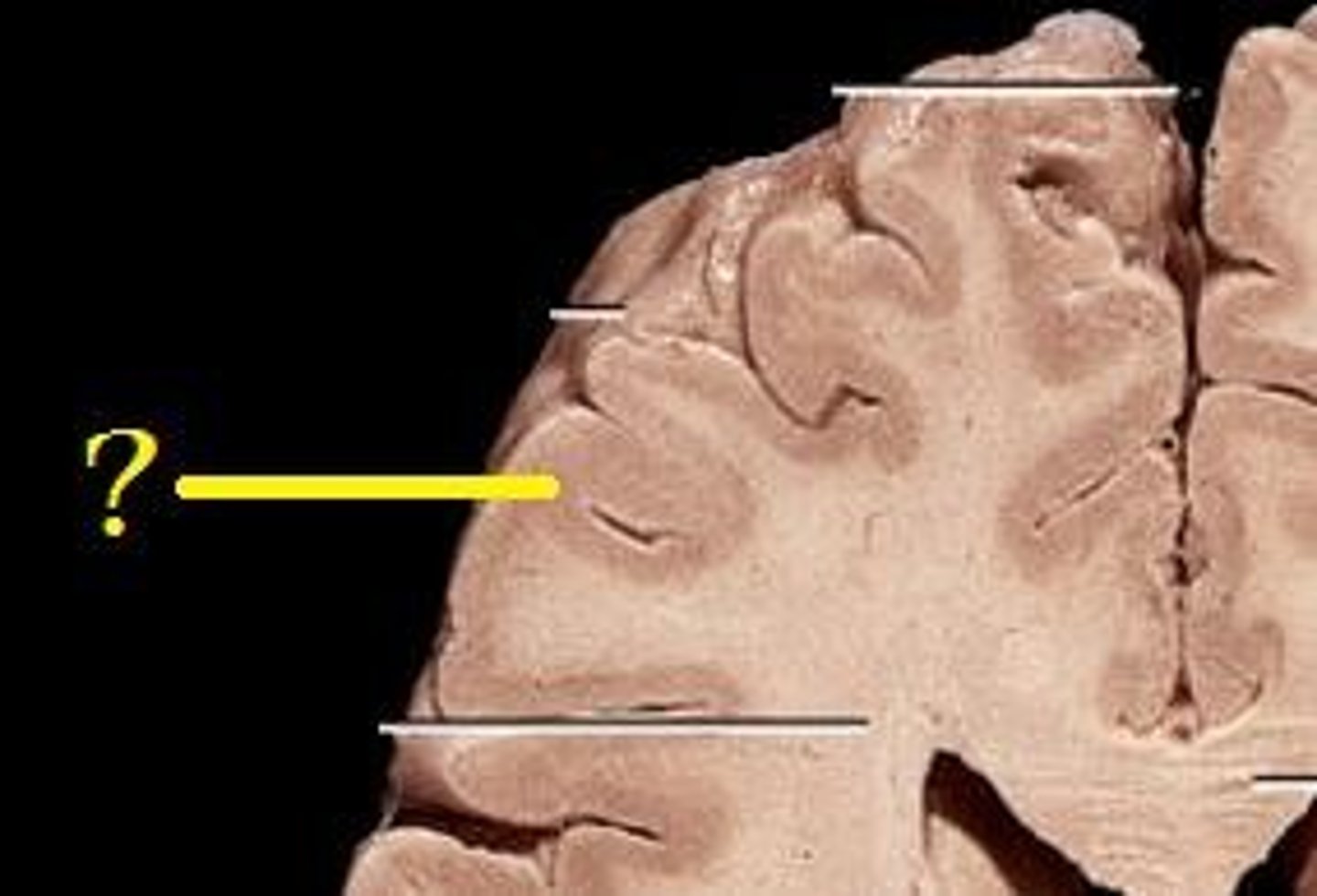
White matter
Bundles of parallel axons and their coverings
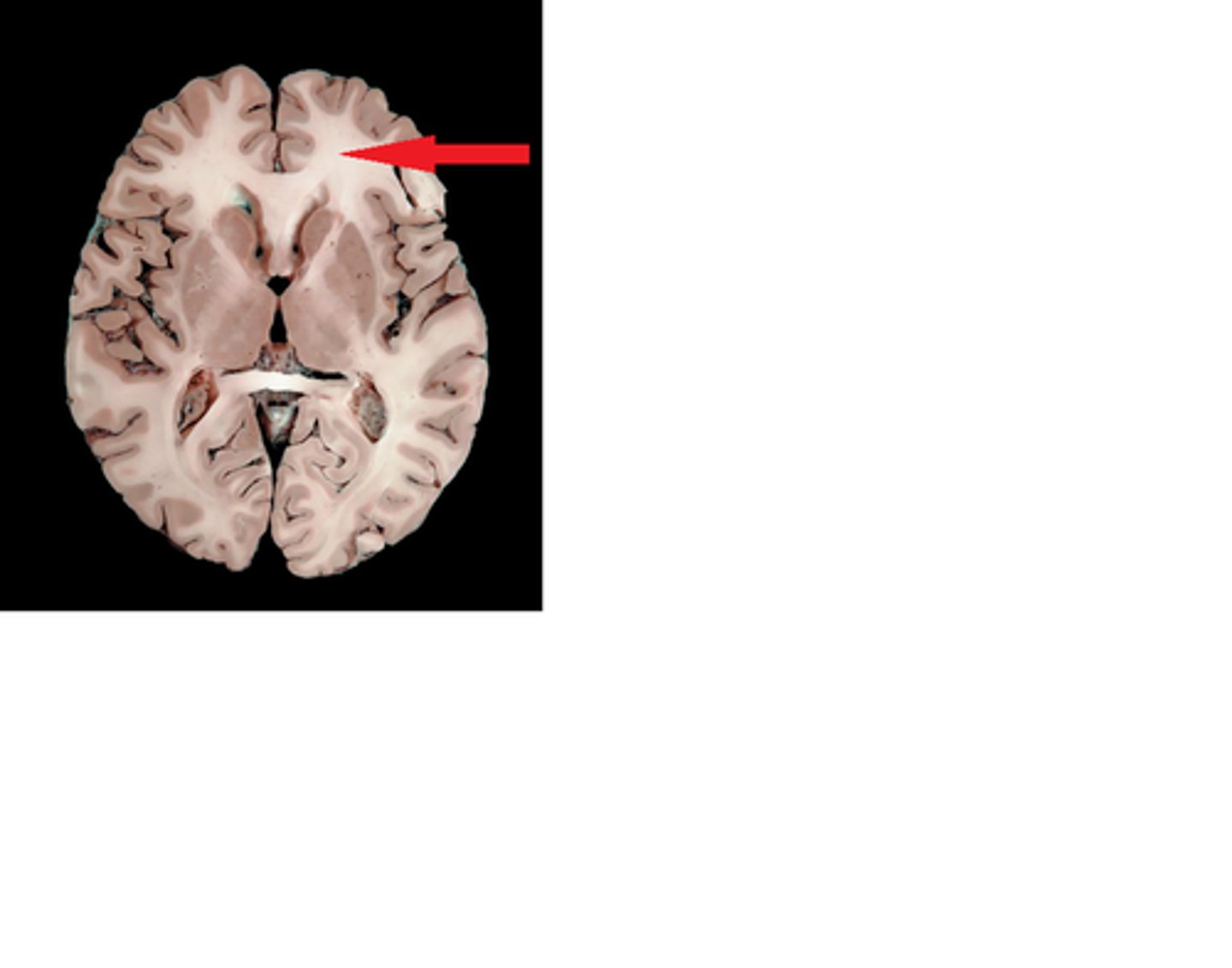
Decussation
The anatomical crossing over of neurons from left to right
______- as the fibers pass up or down the brainstem and spinal cord they cross over from the left to the right side and vise versa.
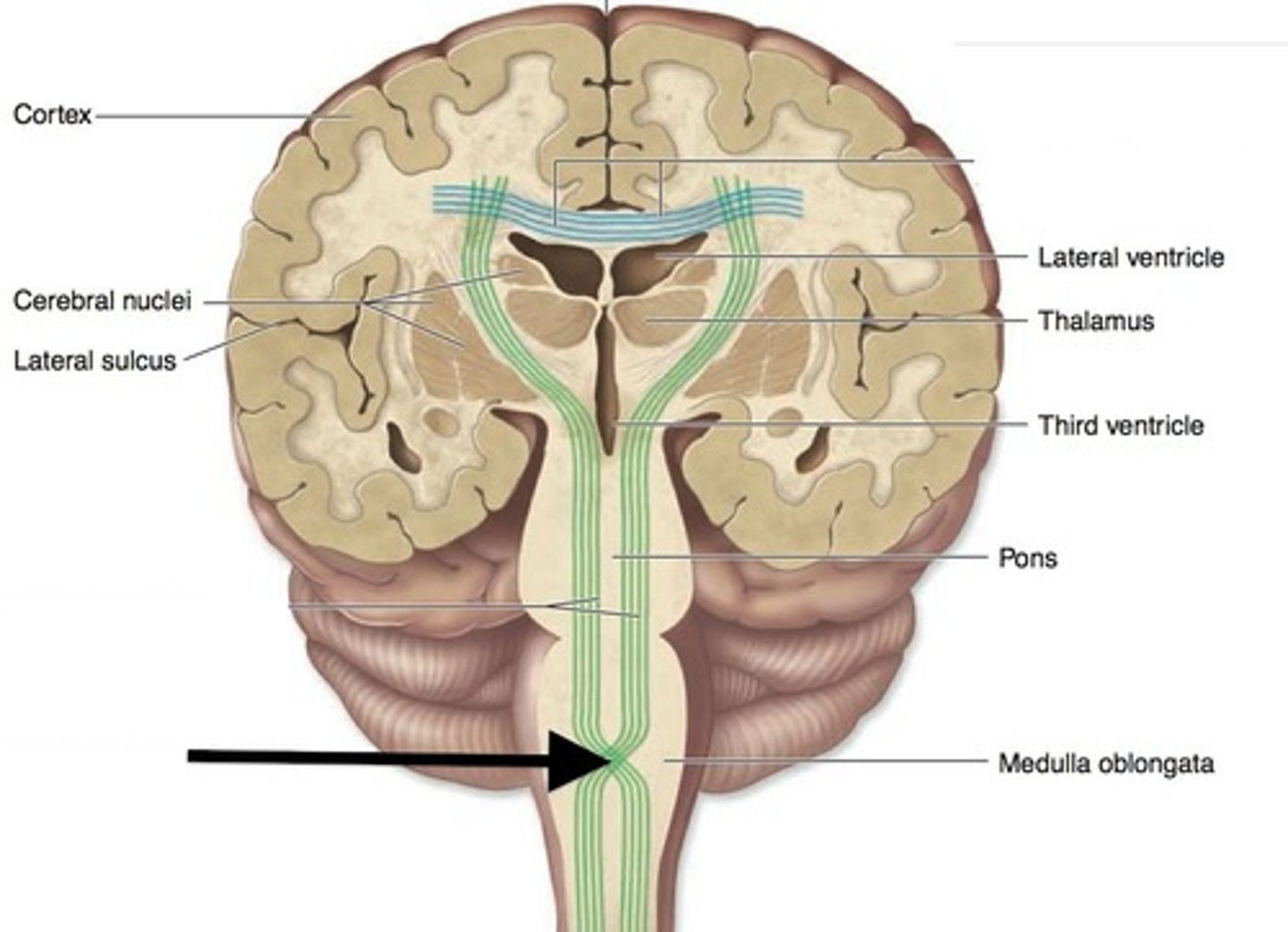
Vital functions
Functions of the body necessary for life
Commissures
Connections of neuron axons that allow the two hemispheres of the brain to communicate with one another
Hypoxia
Not enough oxygen in the blood, this can be dangerous for the brain because it kills neurons
Hypoglycemia
Abnormally low blood sugar (glucose) level can cause the brain to not function well because neurons can only use glucose for energy production
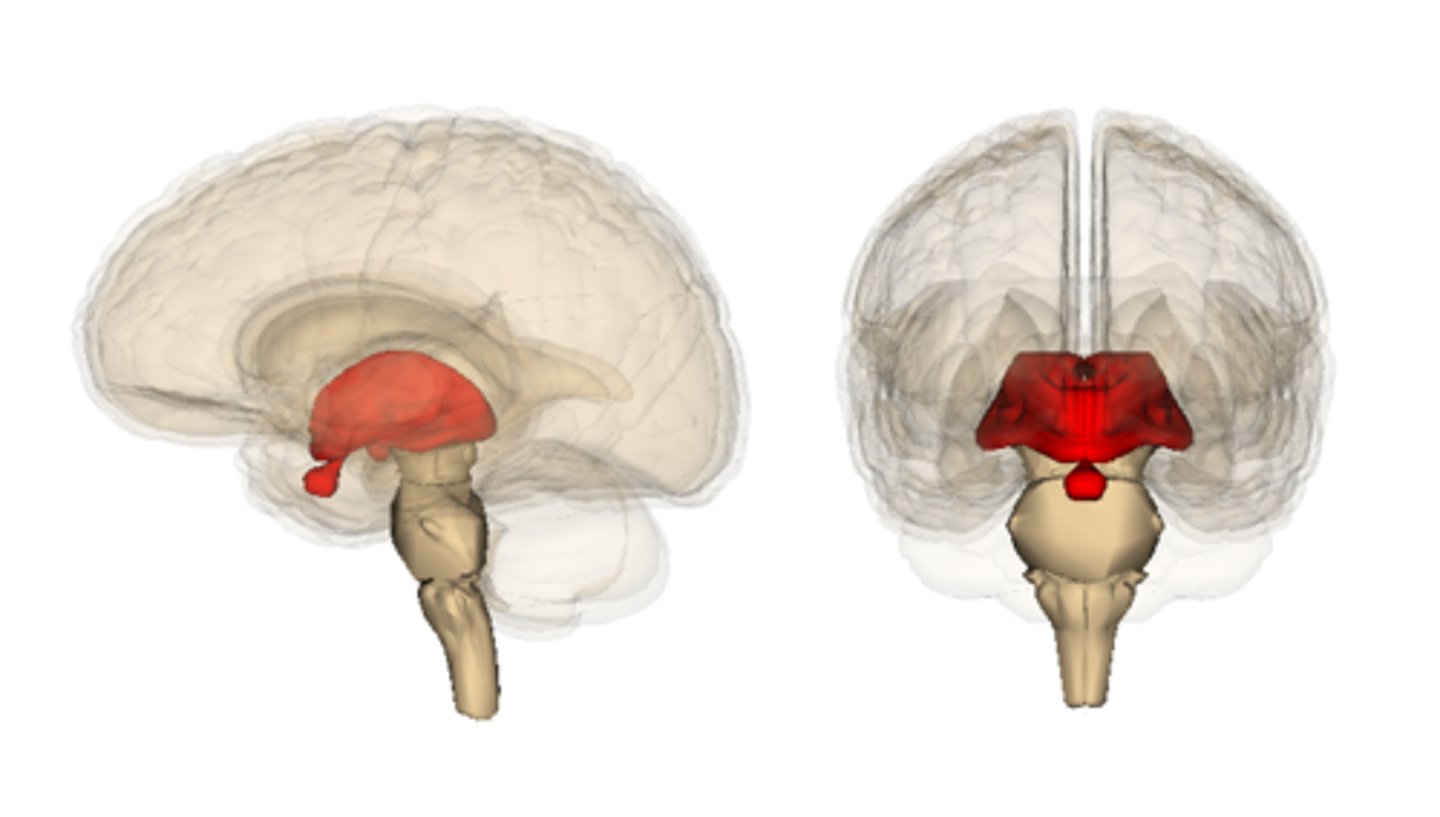
Brain stem structures
Midbrain, Pons, Medulla Oblongata
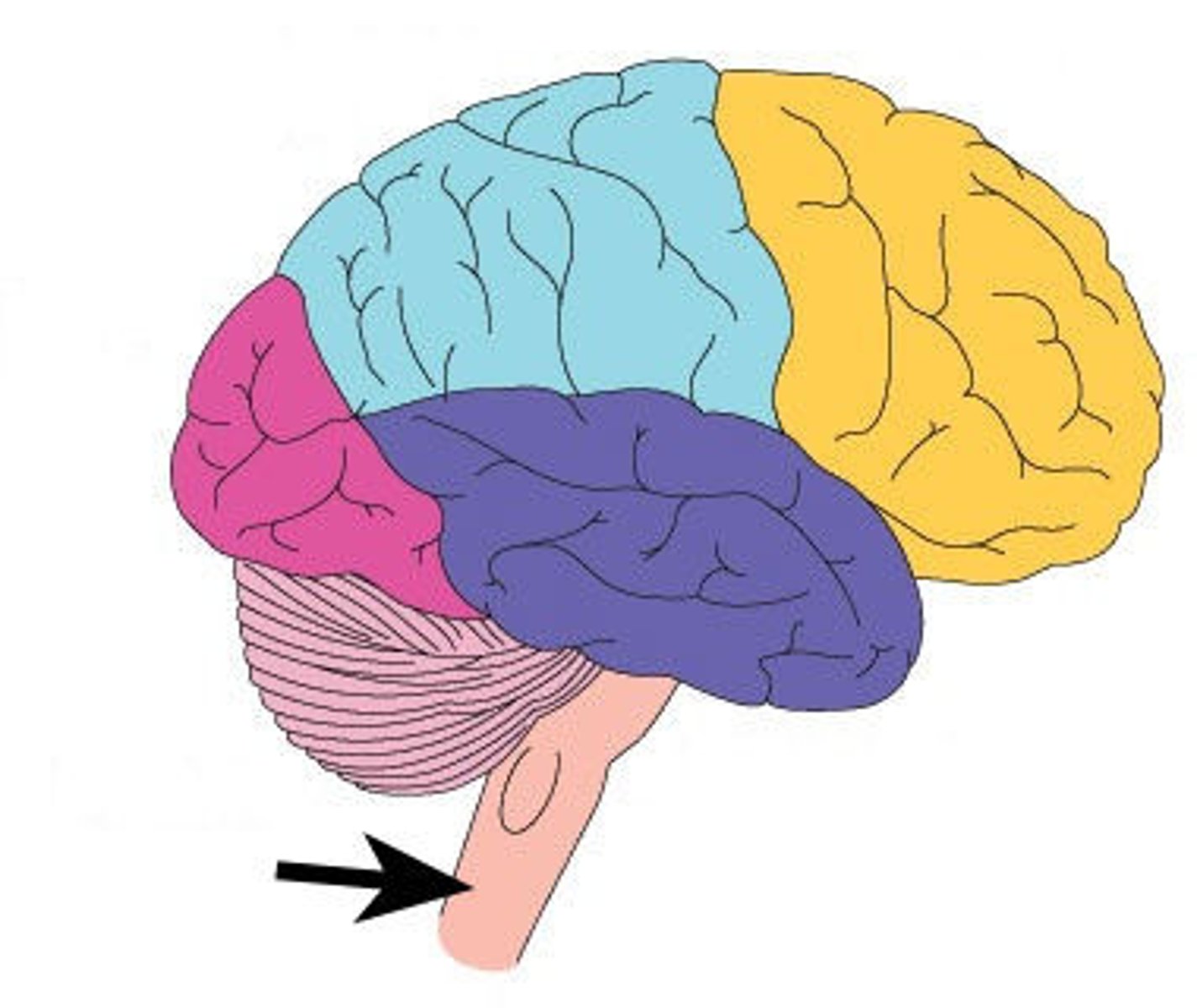
Diencephalon structures
A portion of the embryonic forebrain that includes the thalamus, hypothalamus,
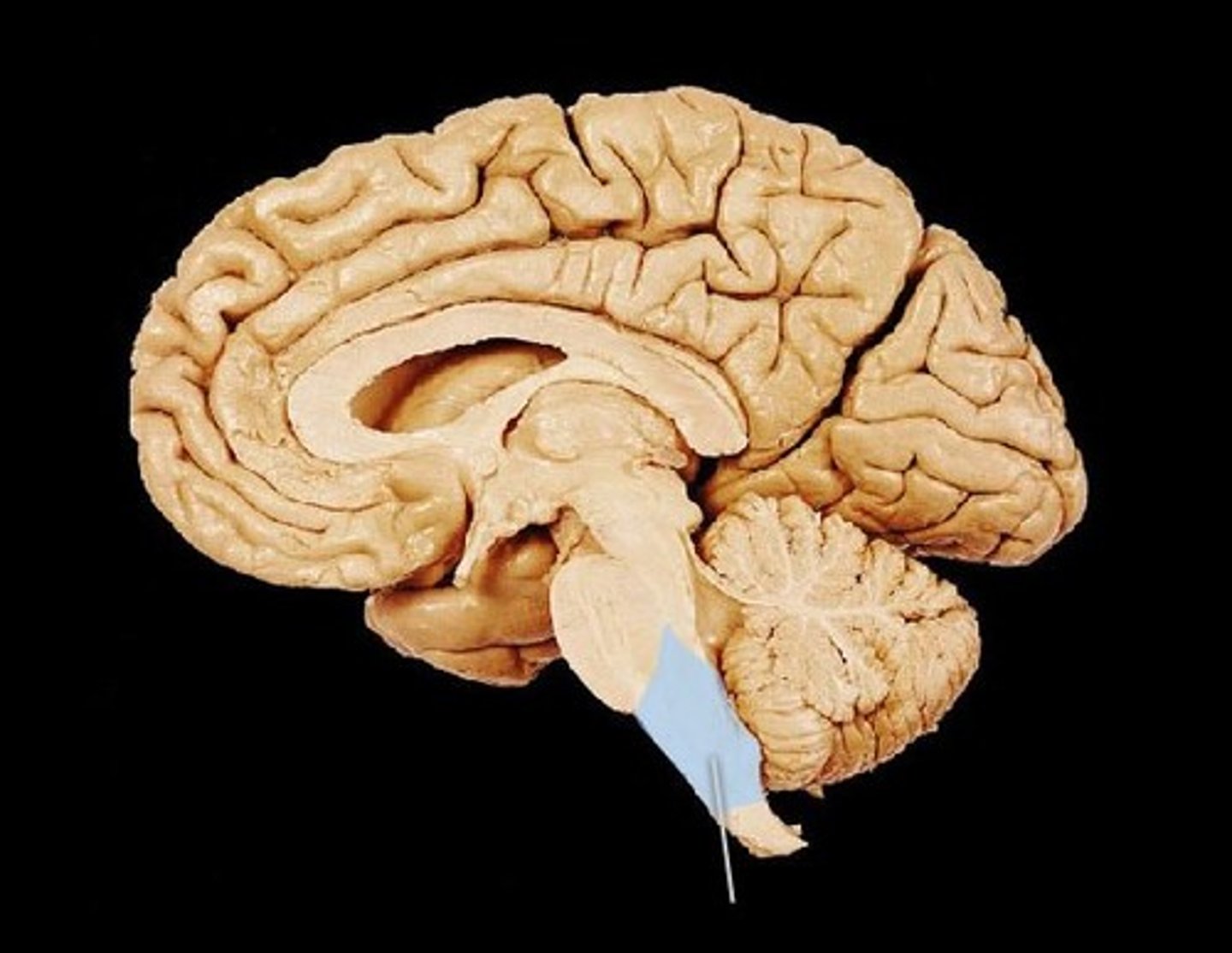
Medulla oblongata
- site of decussation
- contains nuclei which control many vital functions
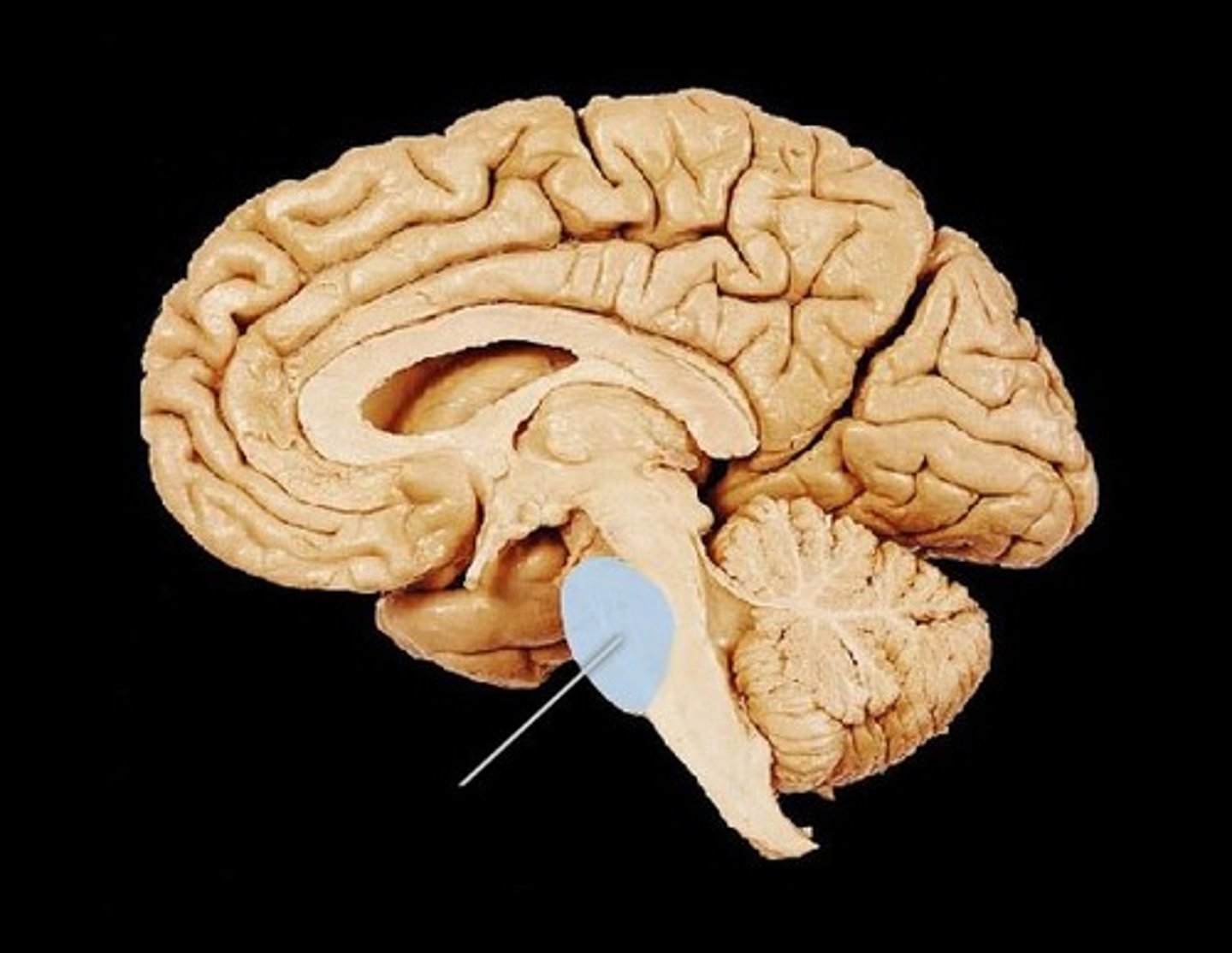
Pons
relays messages from the cerebrum to the cerebellum ("bridge")
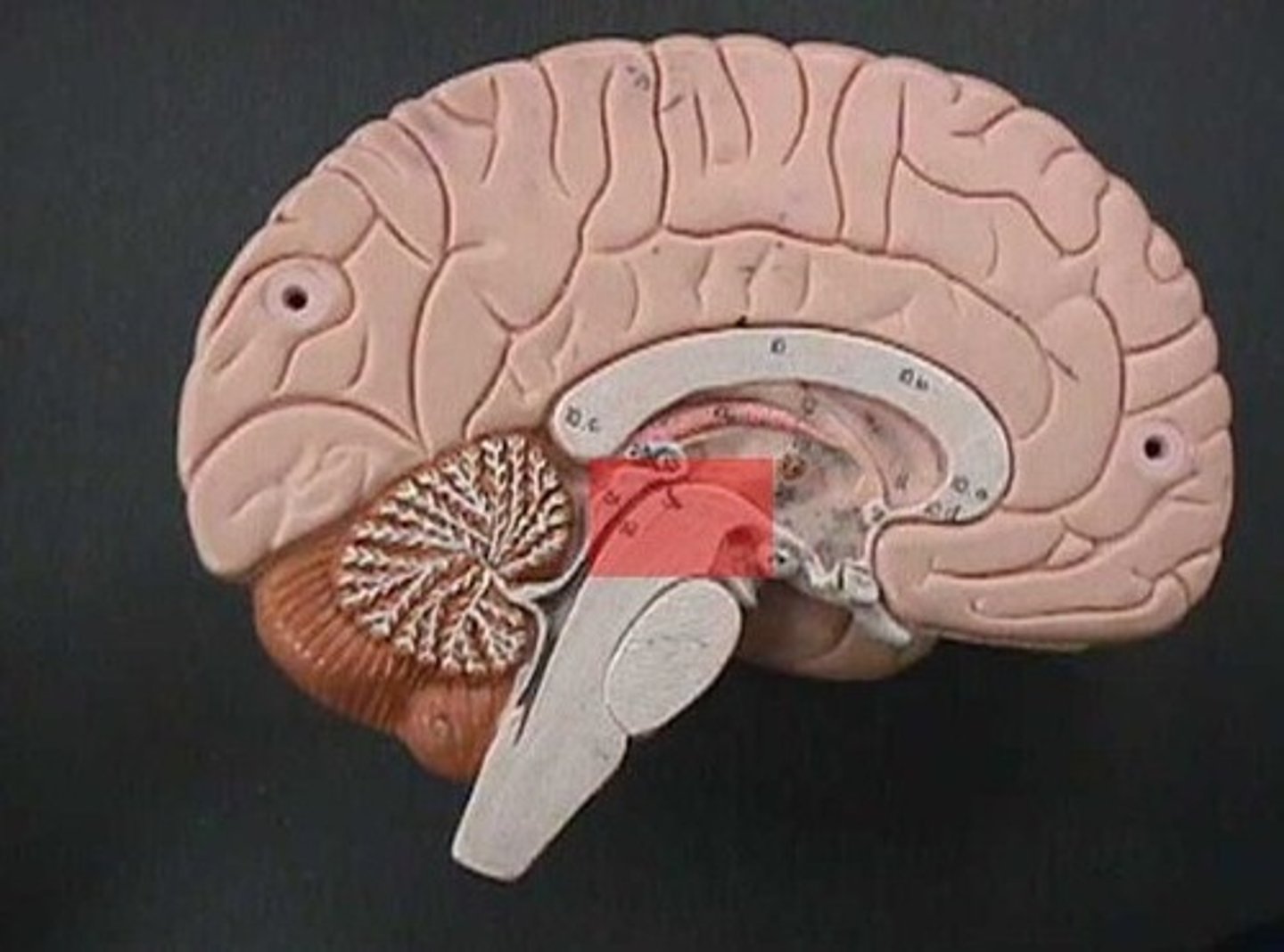
Midbrain
The portion of the brain responsible for visual and auditory startle reflexes.
Hypothalamus
controls the pituitary gland
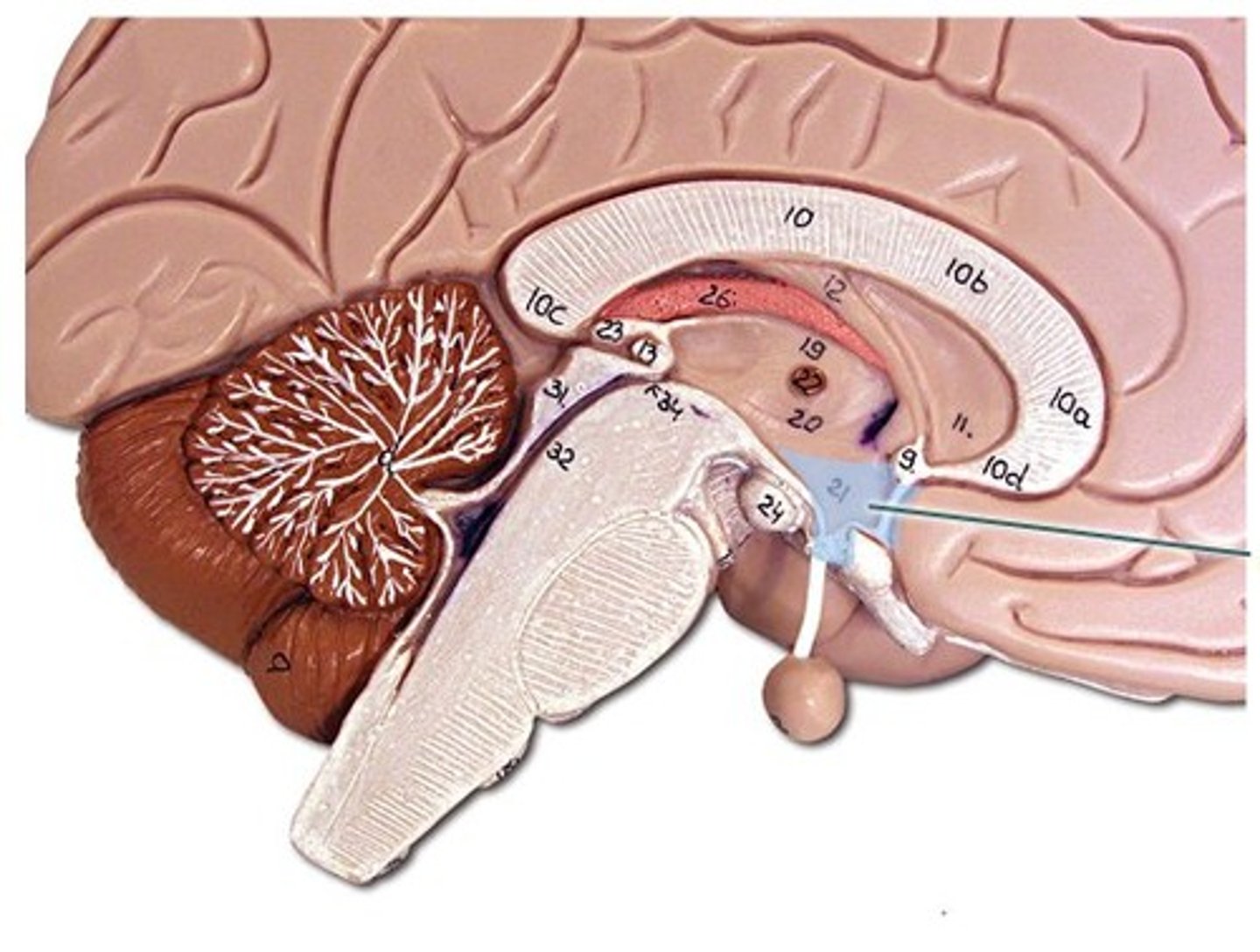
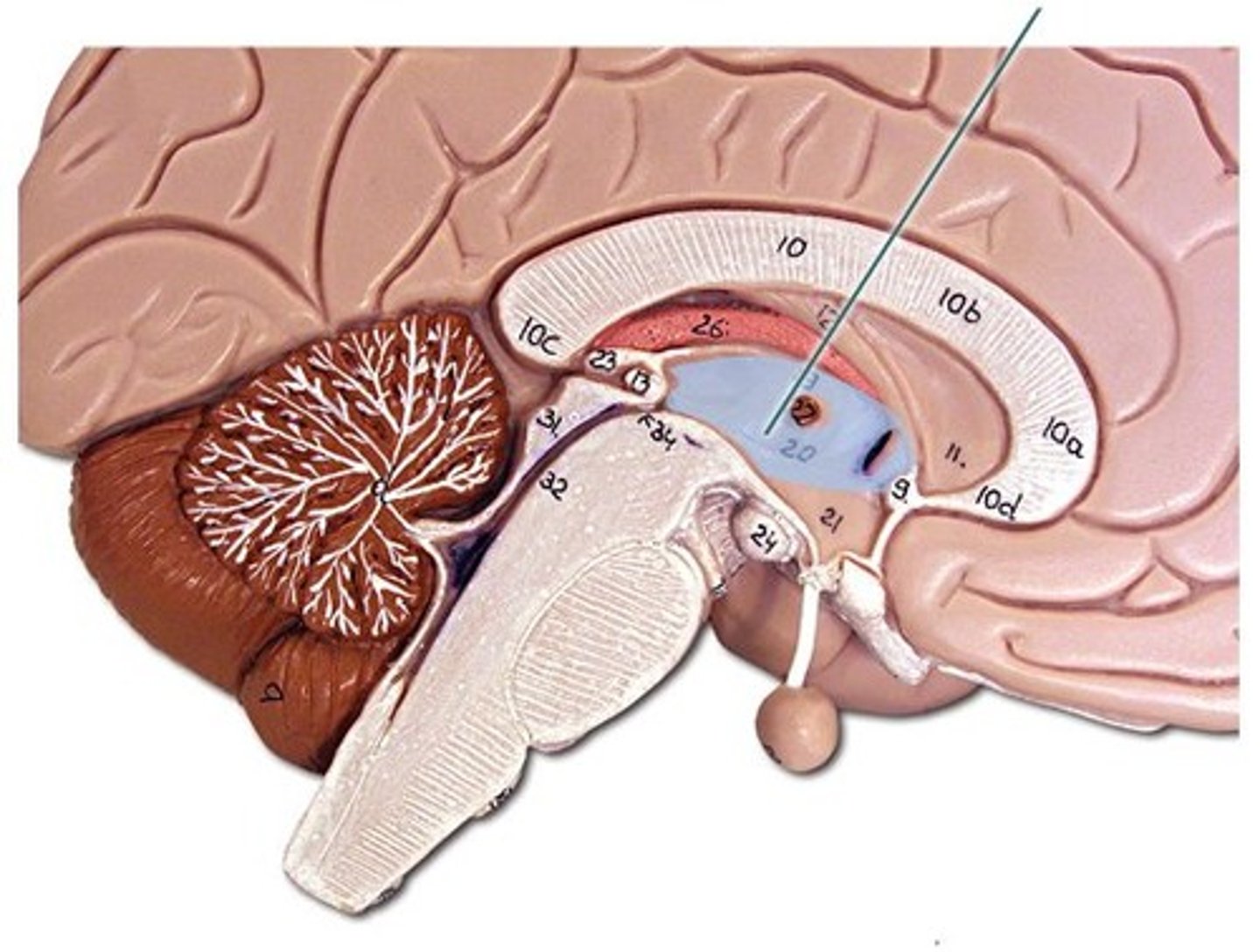
Thalamus
Performs a crude interpretation of the sensory information and then relays that information to the cerebrum
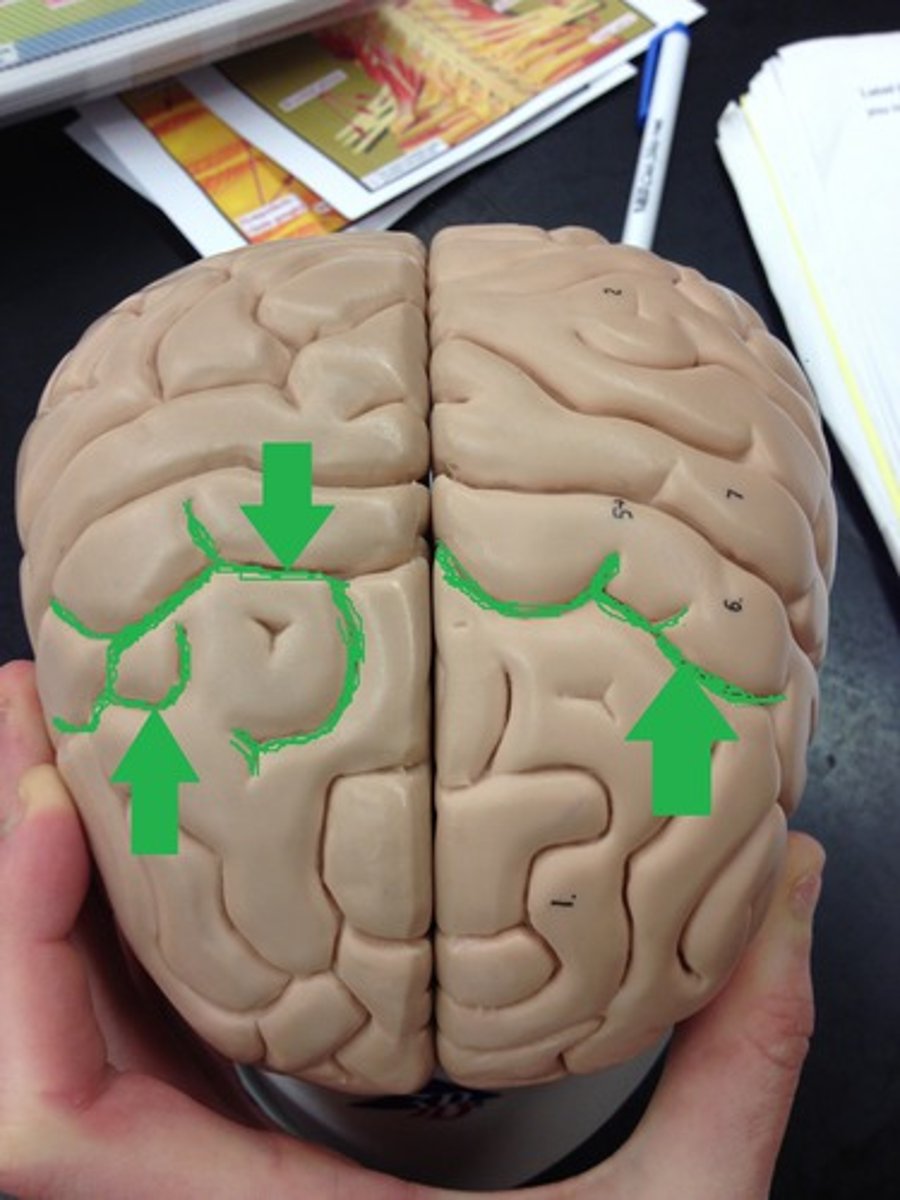
Gyri
Elevated portions of the cerebral cortex ("hills")
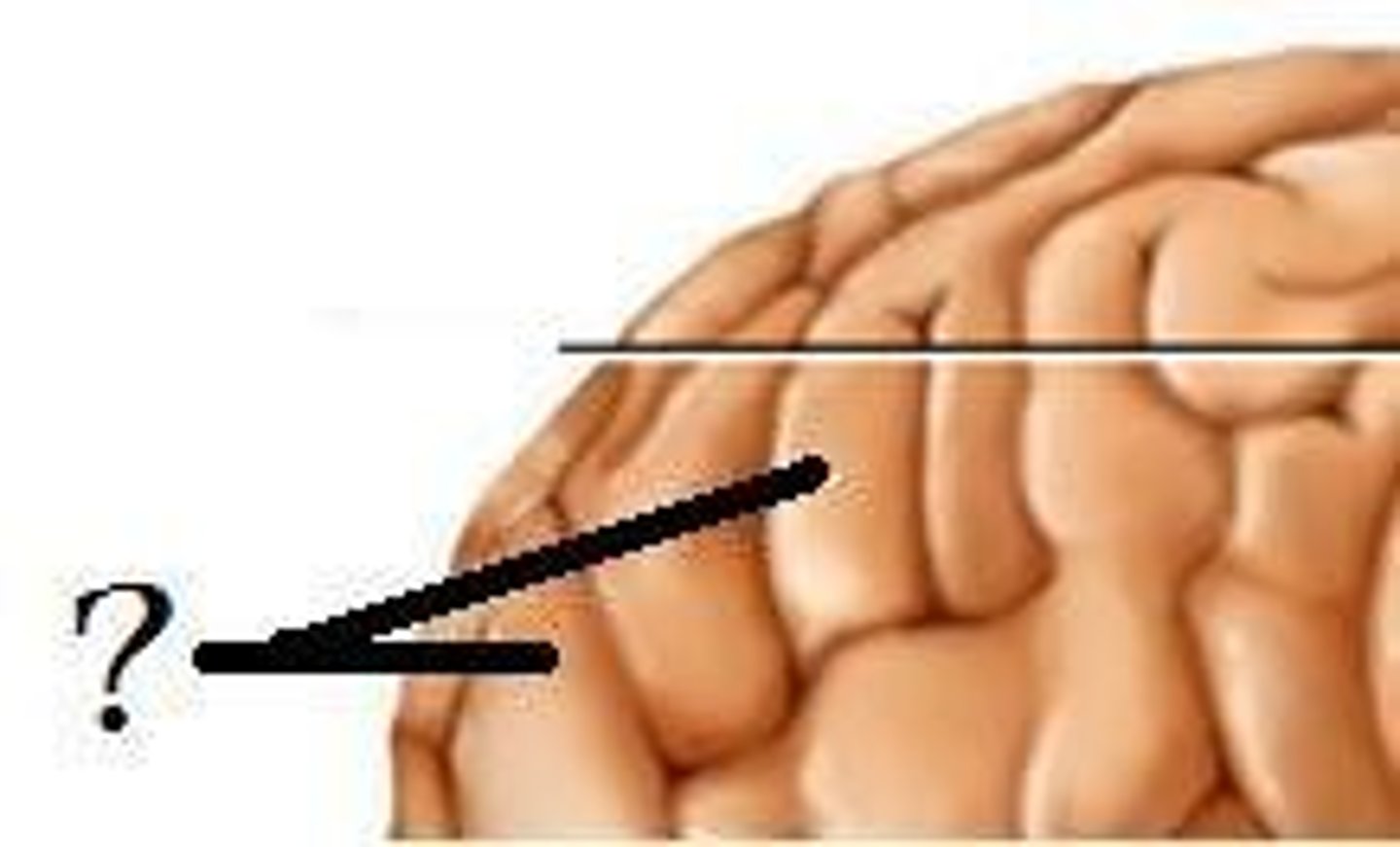
Sulci
Shallow grooves or furrows in the cerebral hemispheres ("valleys")
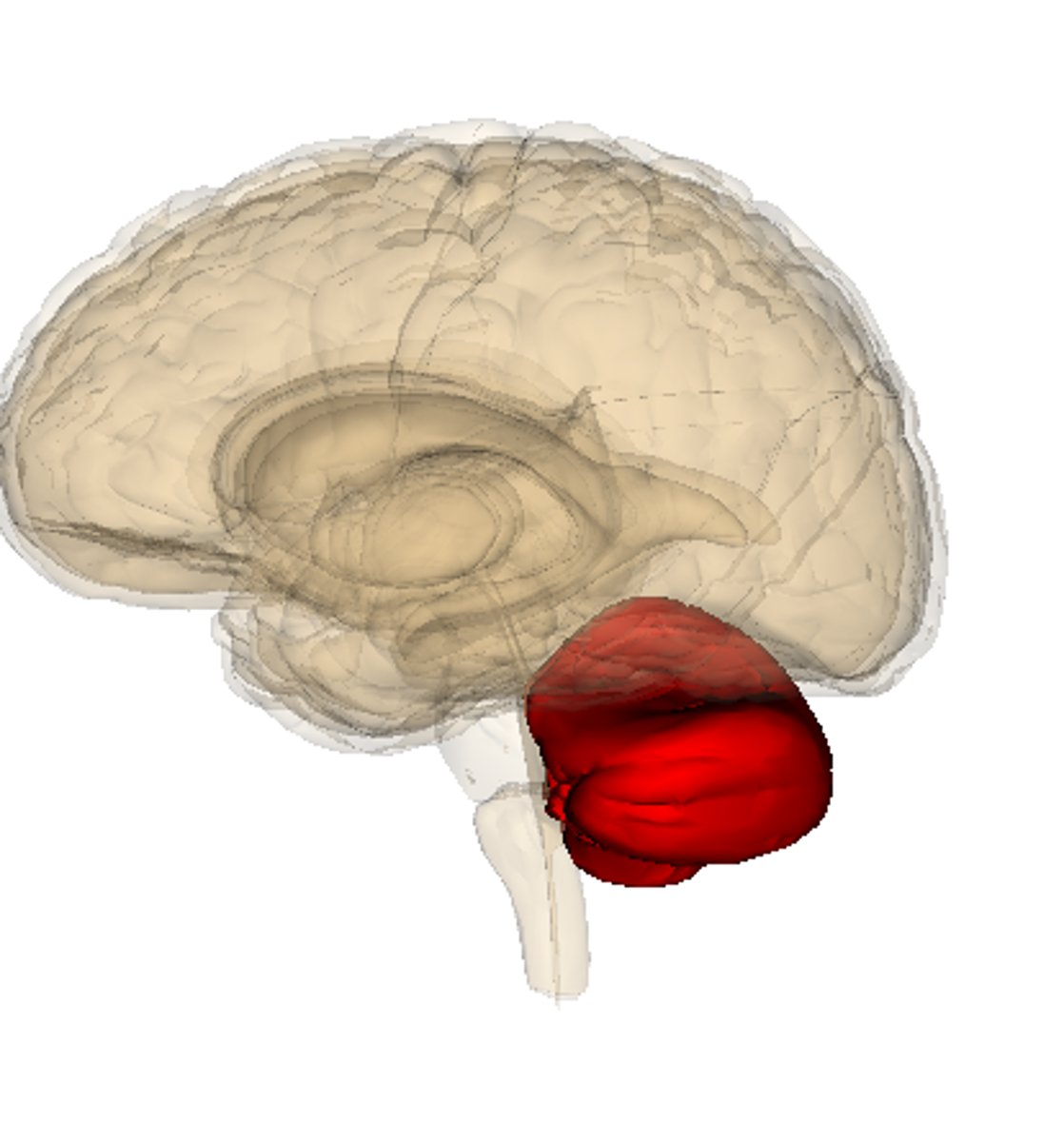
Cerebellum
Major structure of the brain which is considered the control center for subconscious motor functions
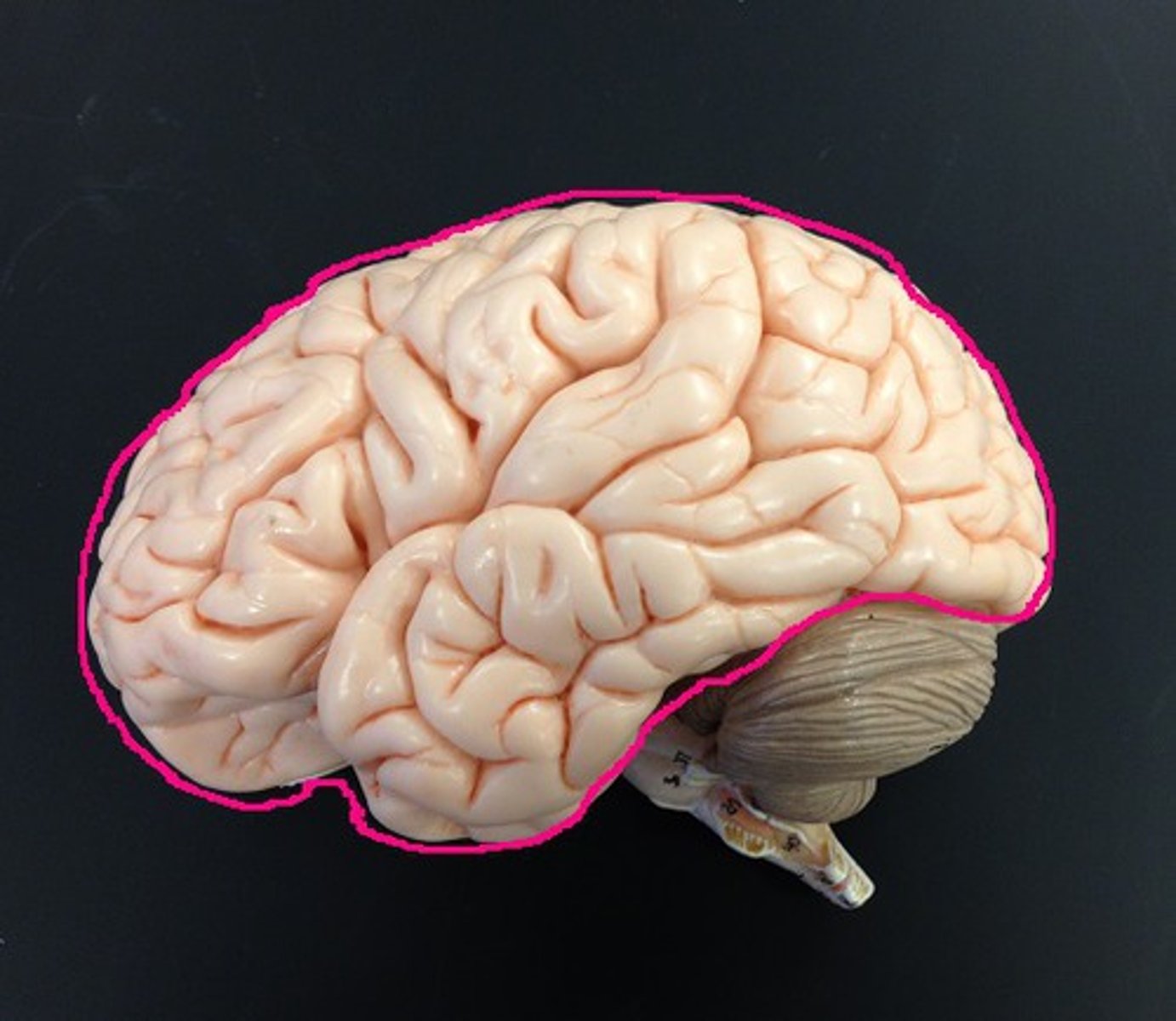
Cerebrum
Area of the brain responsible for all voluntary activities of the body, the largest part of the brain that contains the cerebral cortex, limbic system, and basal ganglia.
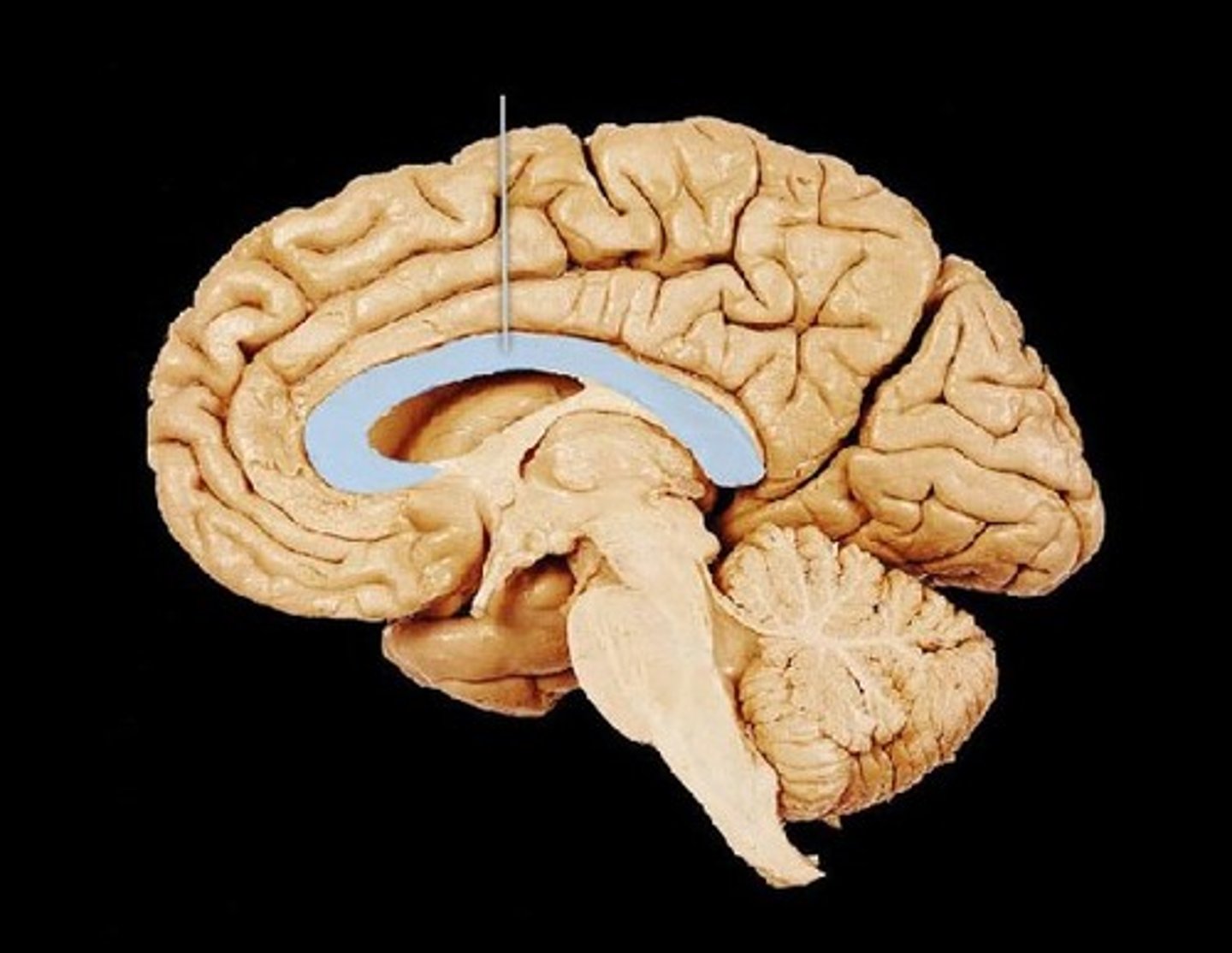
Corpus callosum
Nerves that enable communication between the right and left cerebral hemispheres.
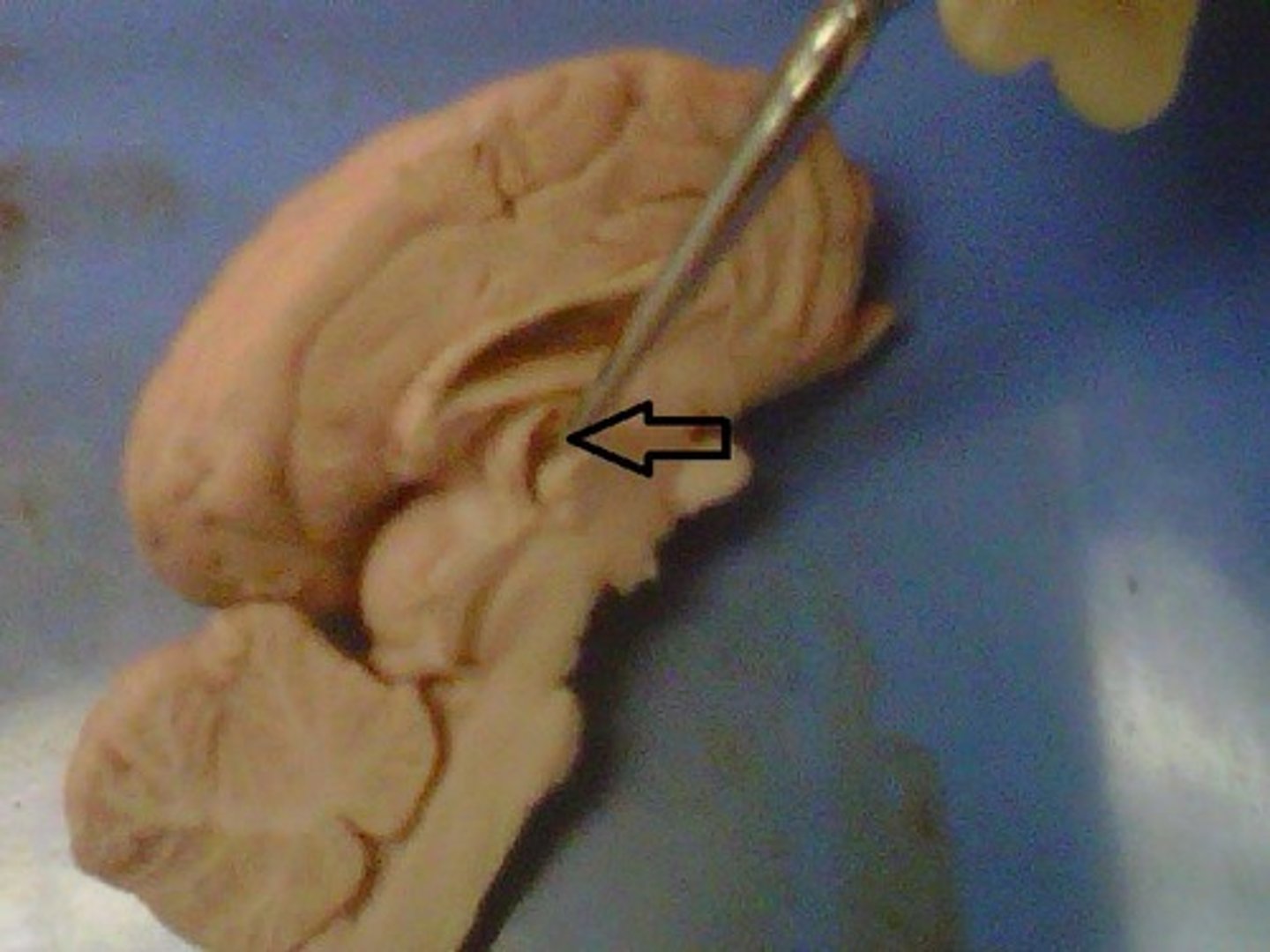
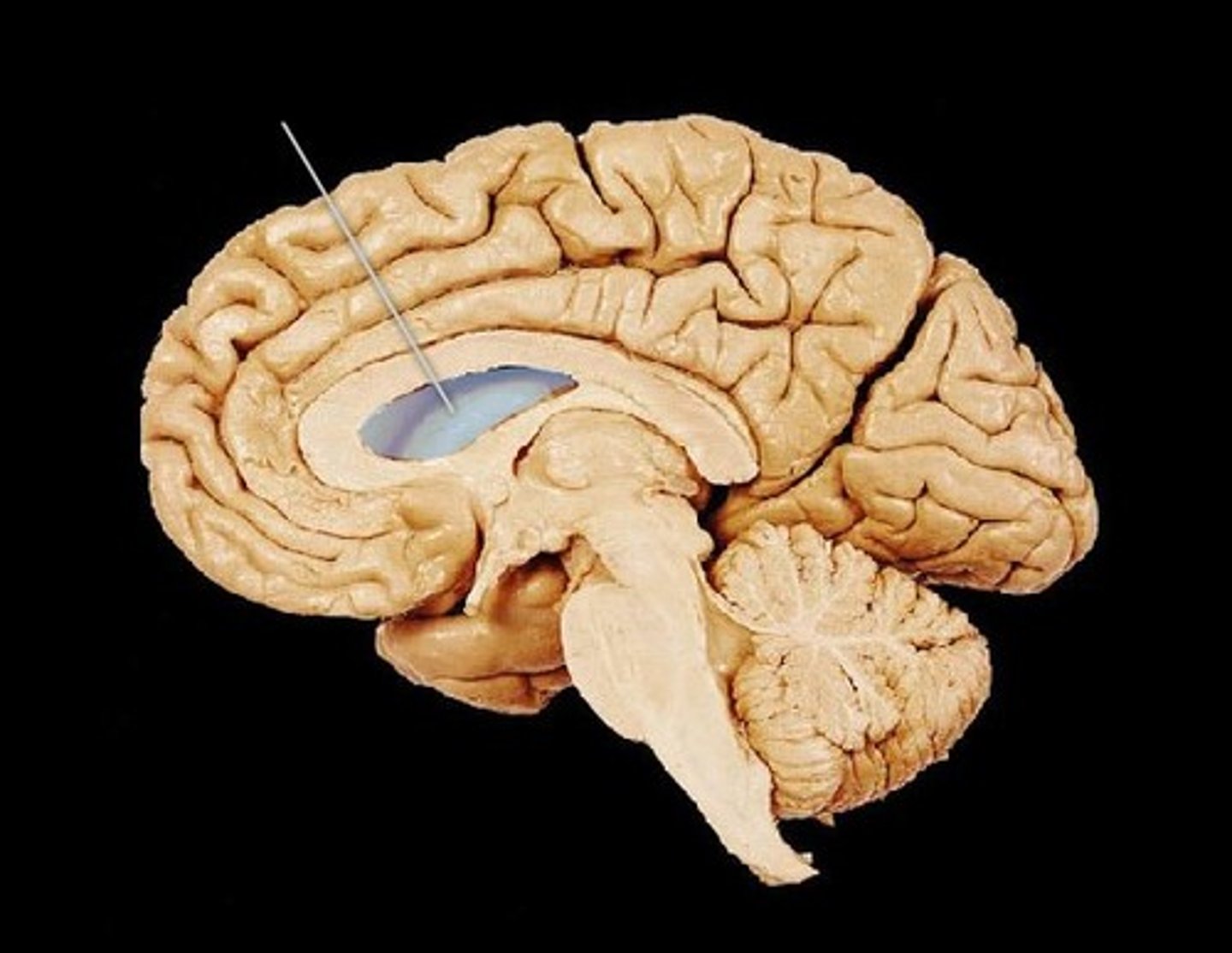
Ventricles of the brain
Canals in the interior of the brain that are filled with CSF or cerebral spinal fluid which cushions and protects the brain.
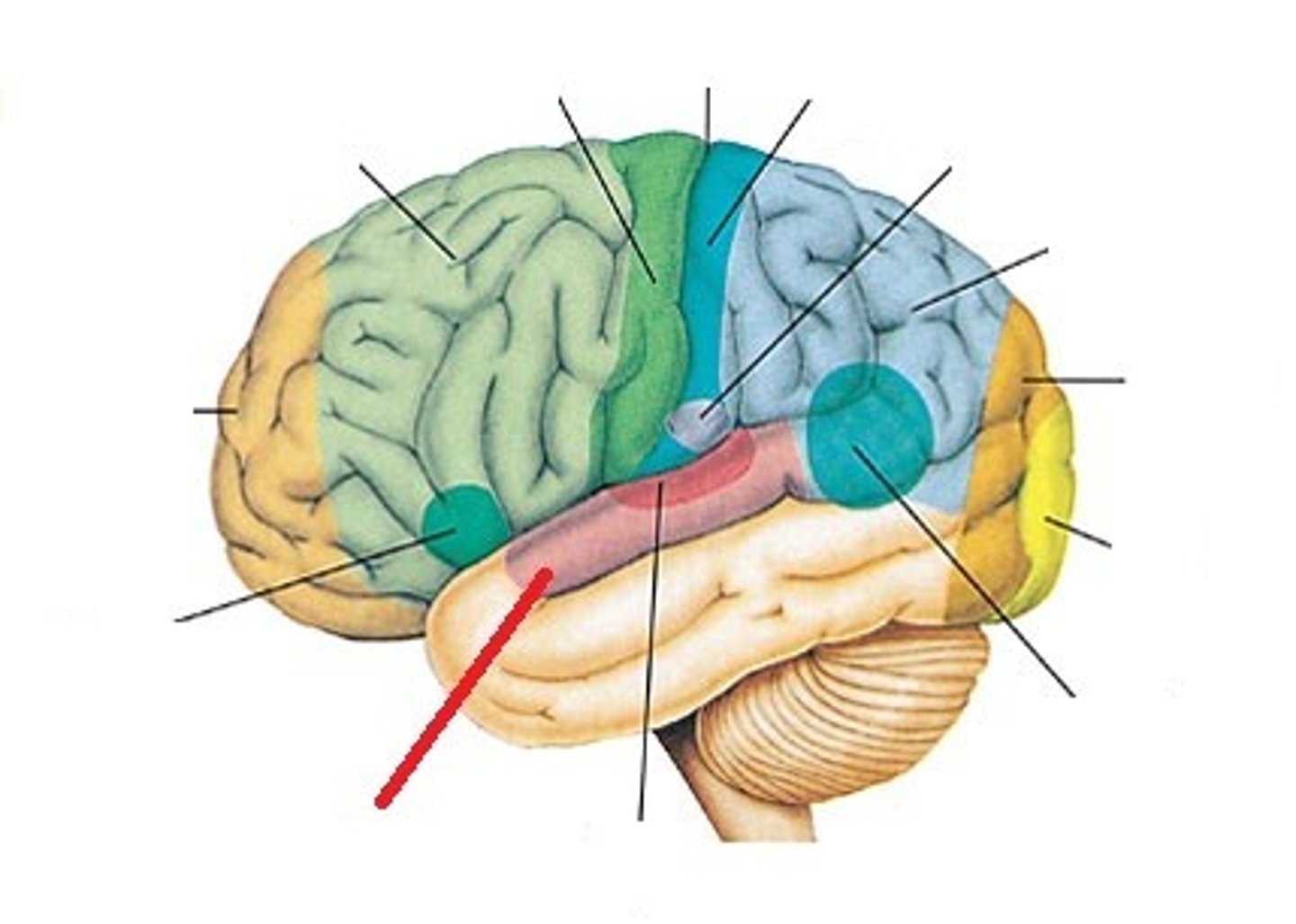
Primary somatic sensory area
receives and localizes sensations from the entire body
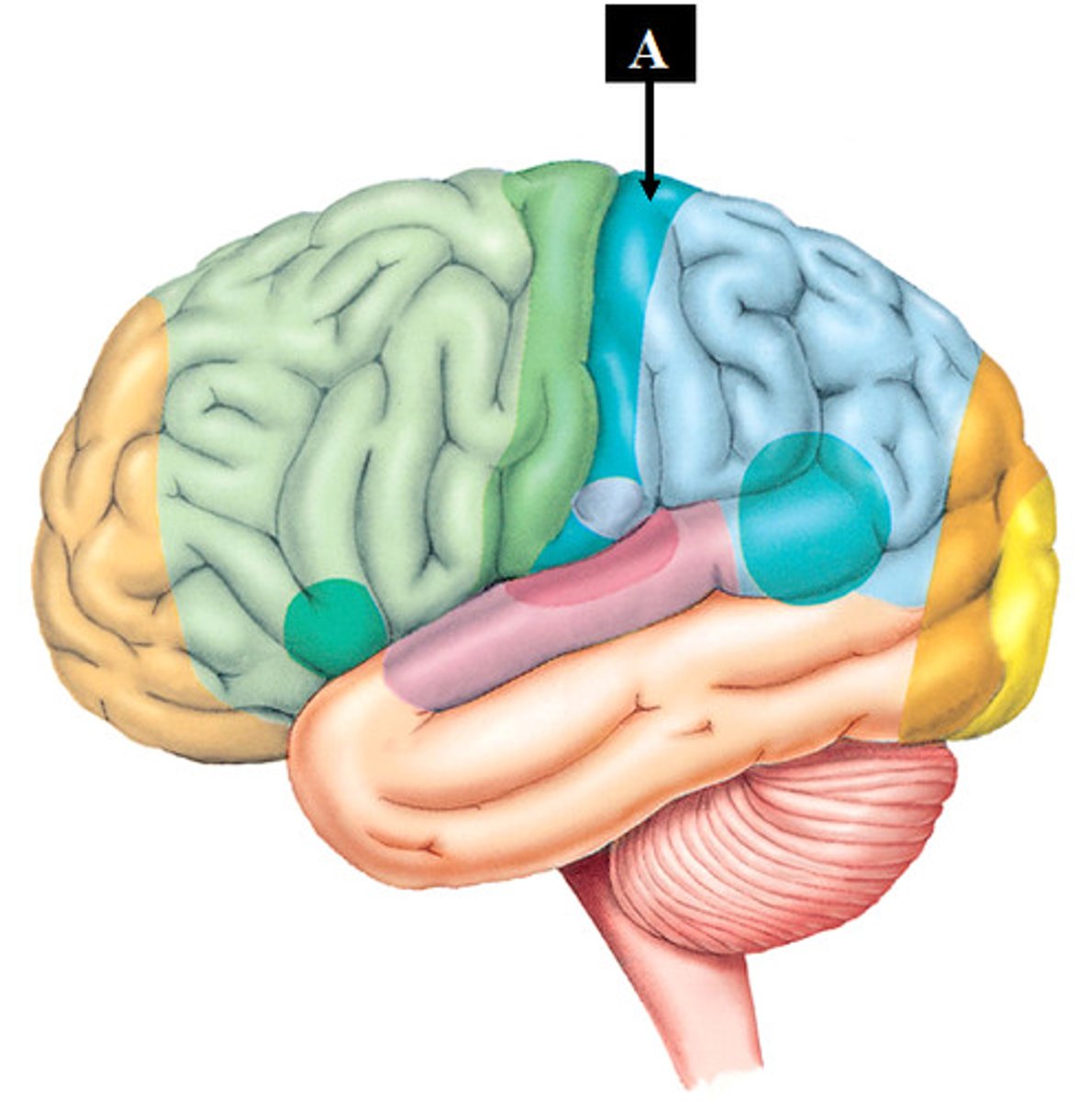
Somatic sensory association area
interprets the sensory information and puts it into context with past experiences
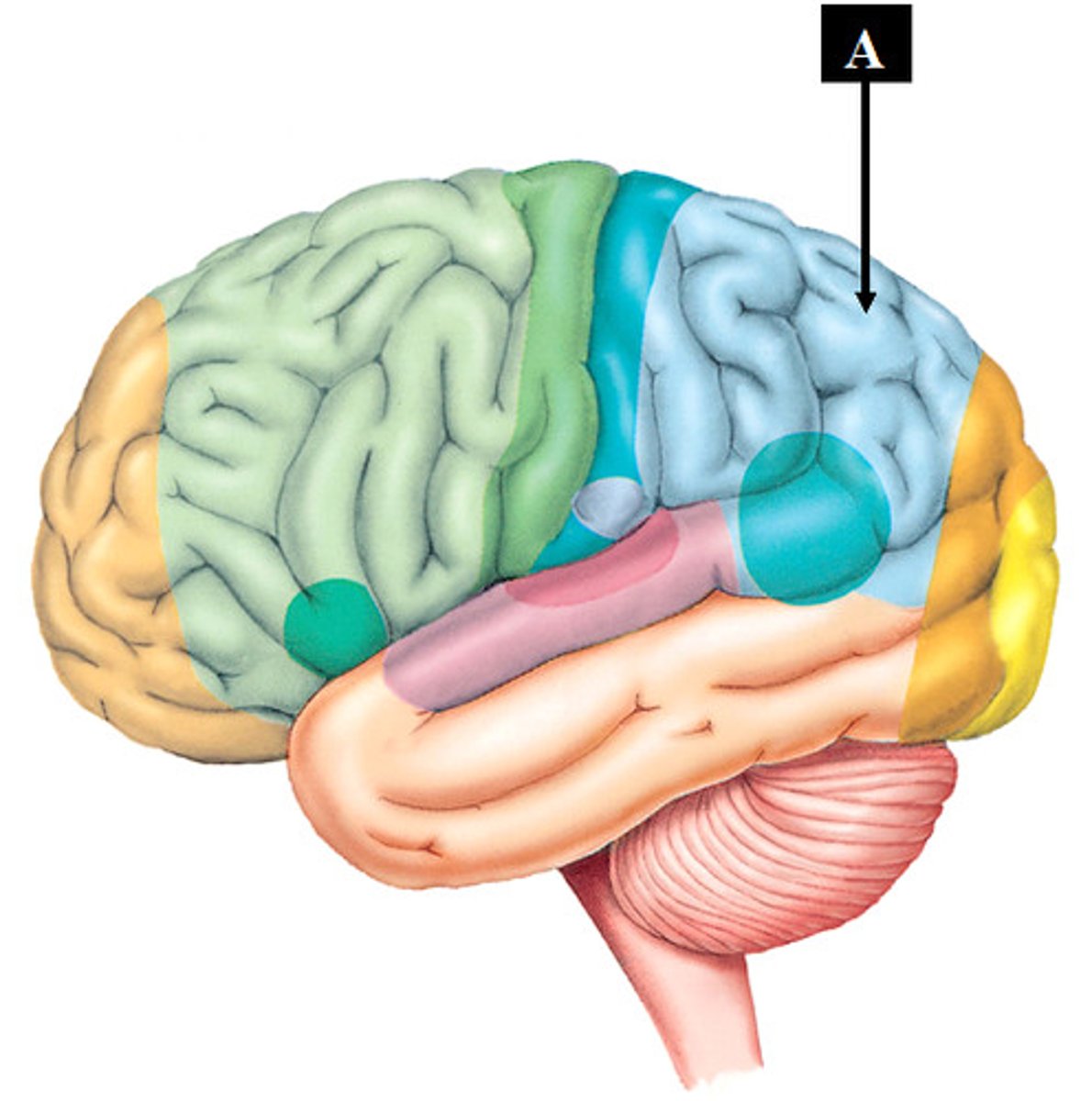
Visual association area
recognizes the meaning of visual information by putting it into context with past experiences
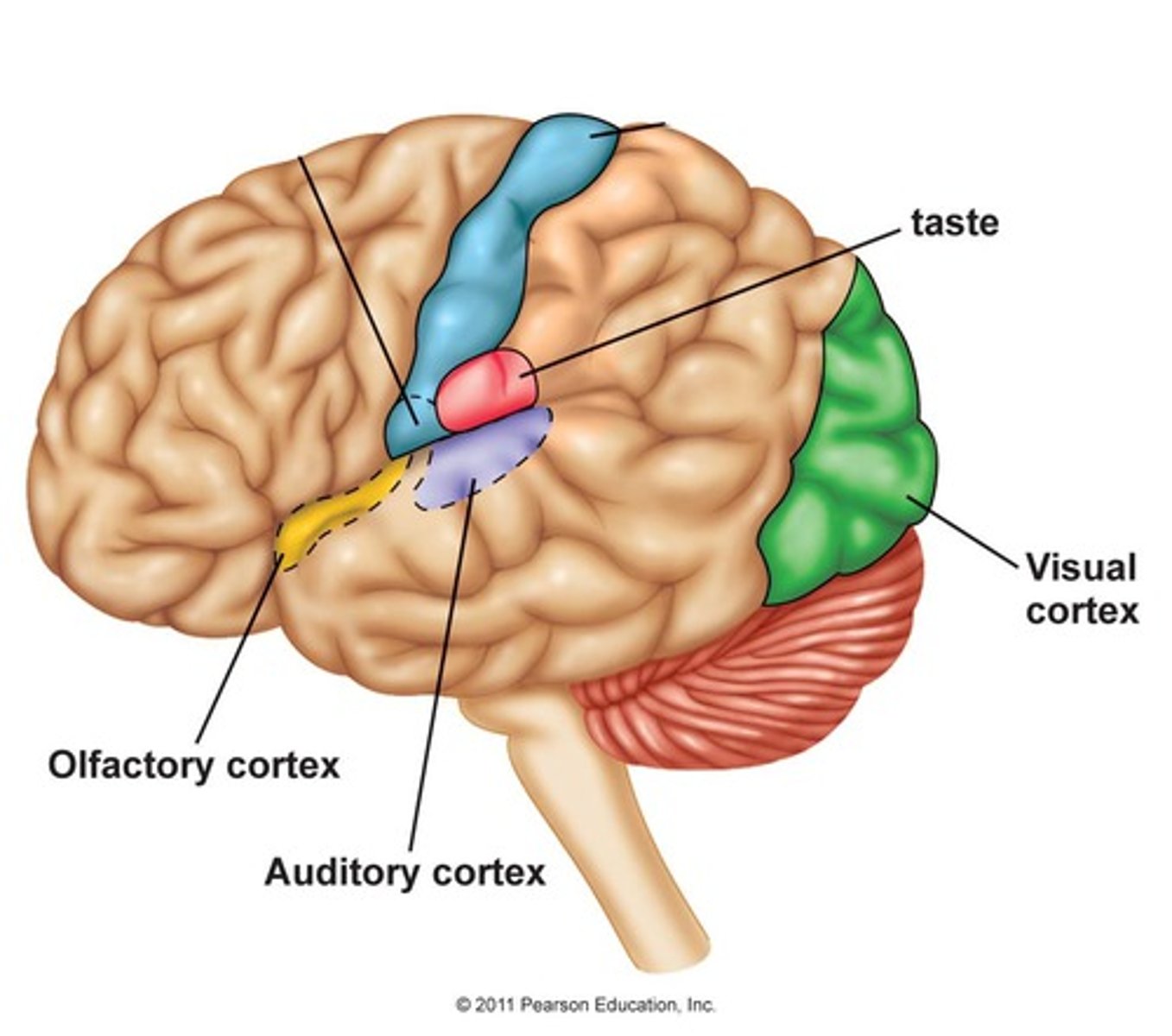
Visual cortex
interprets basic visual information like color, shape and size
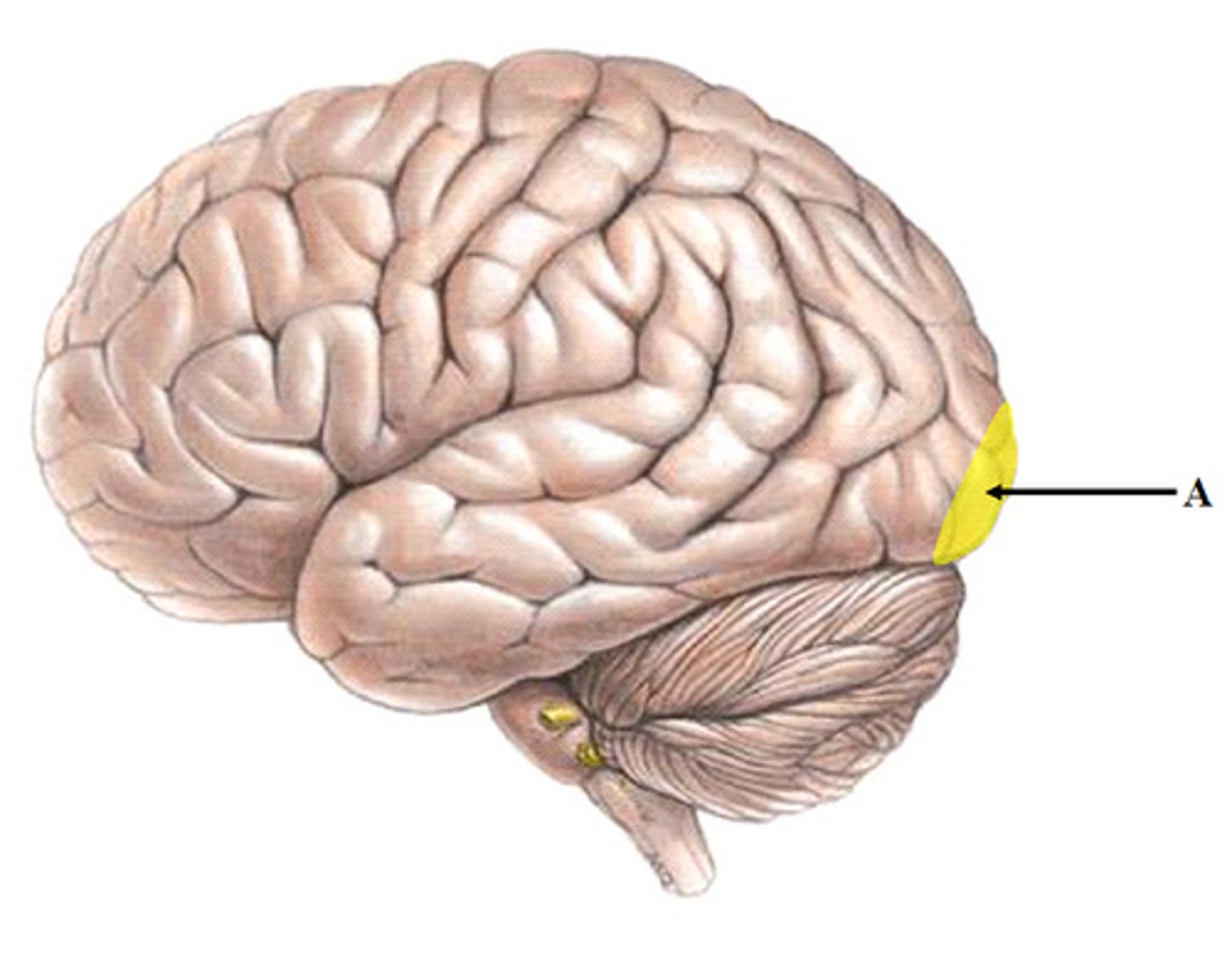
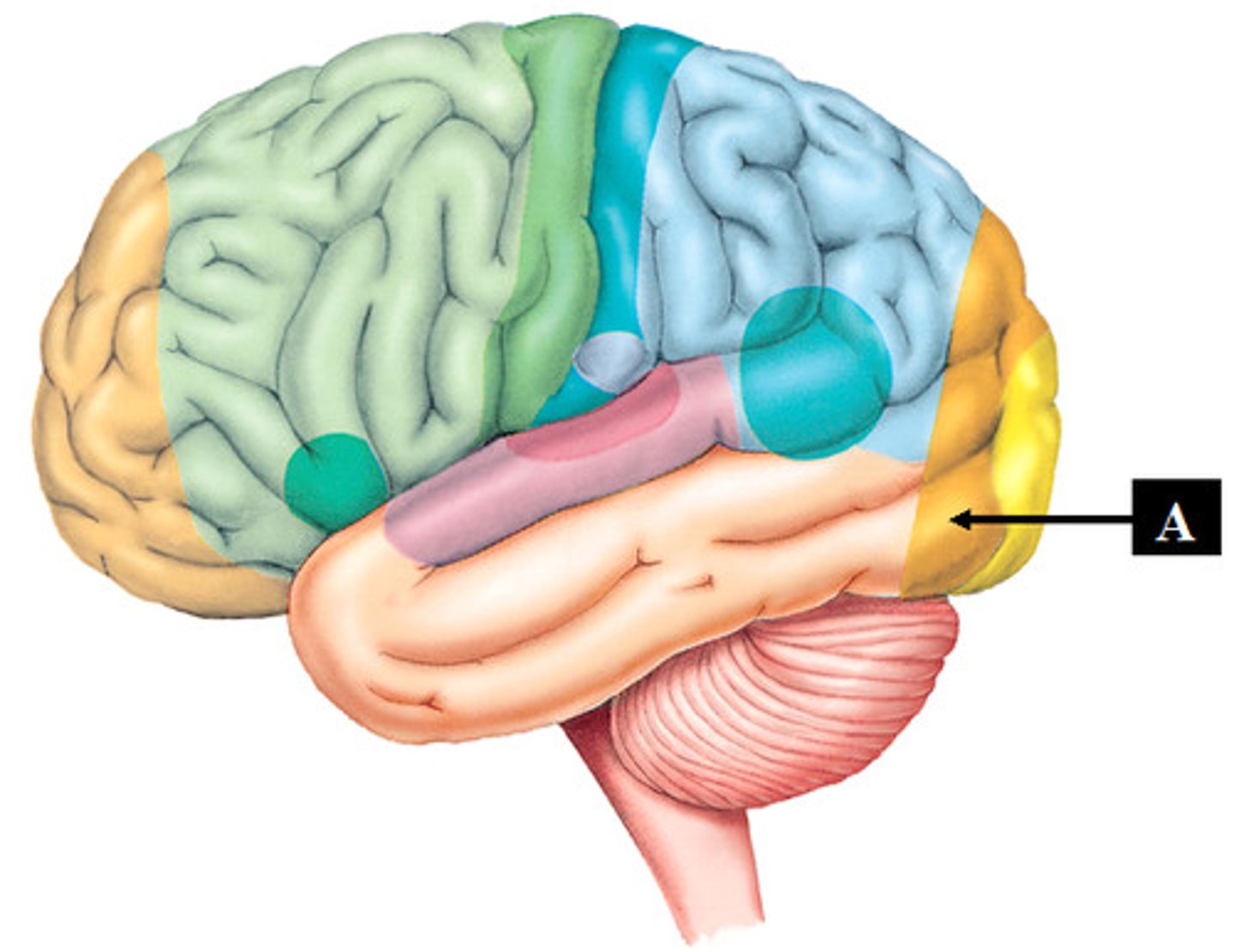
Wernicke's area
comprehension of speech
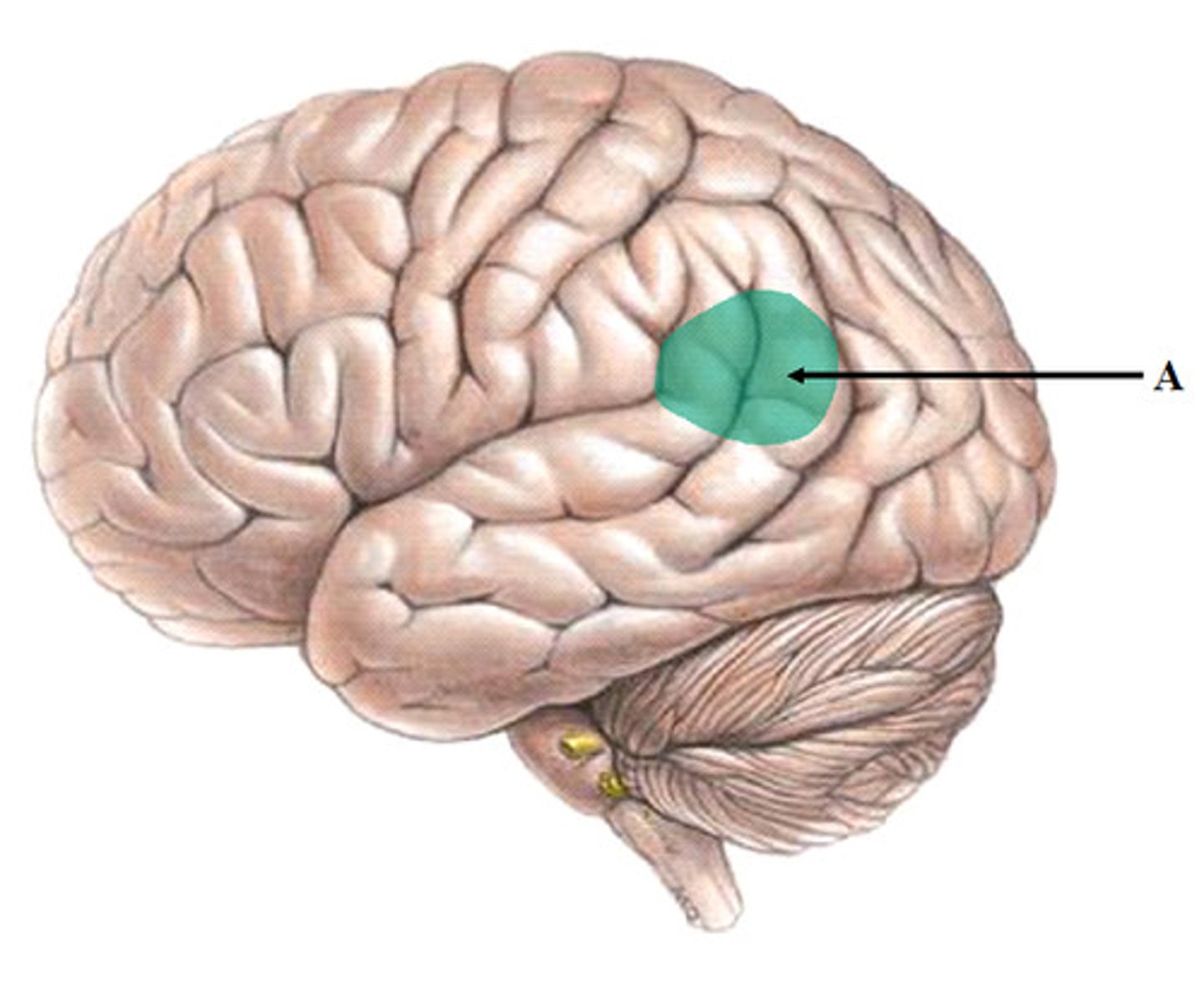
Auditory association area
interprets meaning of sound by placing it into context with past experiences
Primary auditory area
interprets basics of sound such as pitch and volume
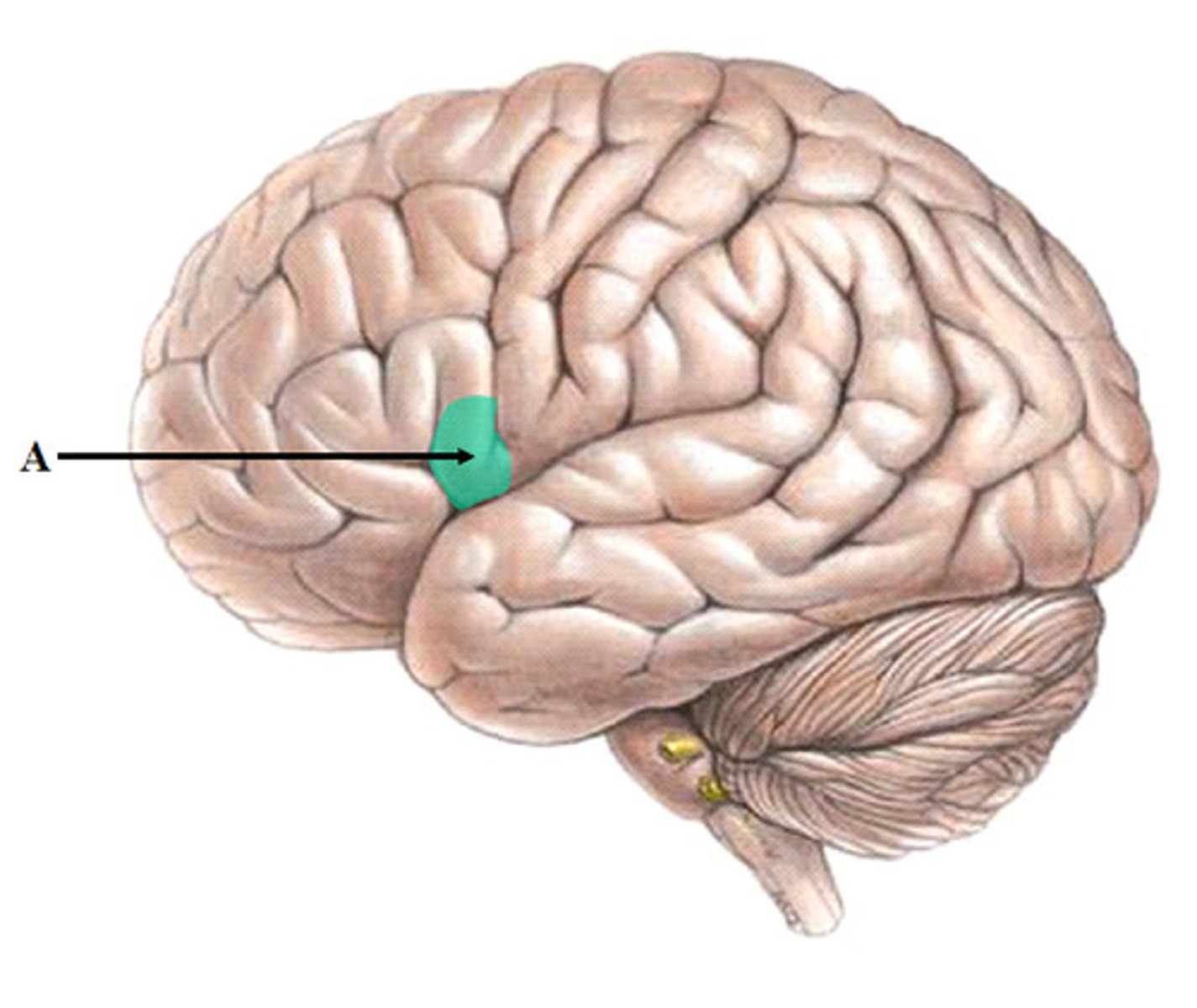
Broca's area
initiates muscle movement for speech
Taste area
interprets taste
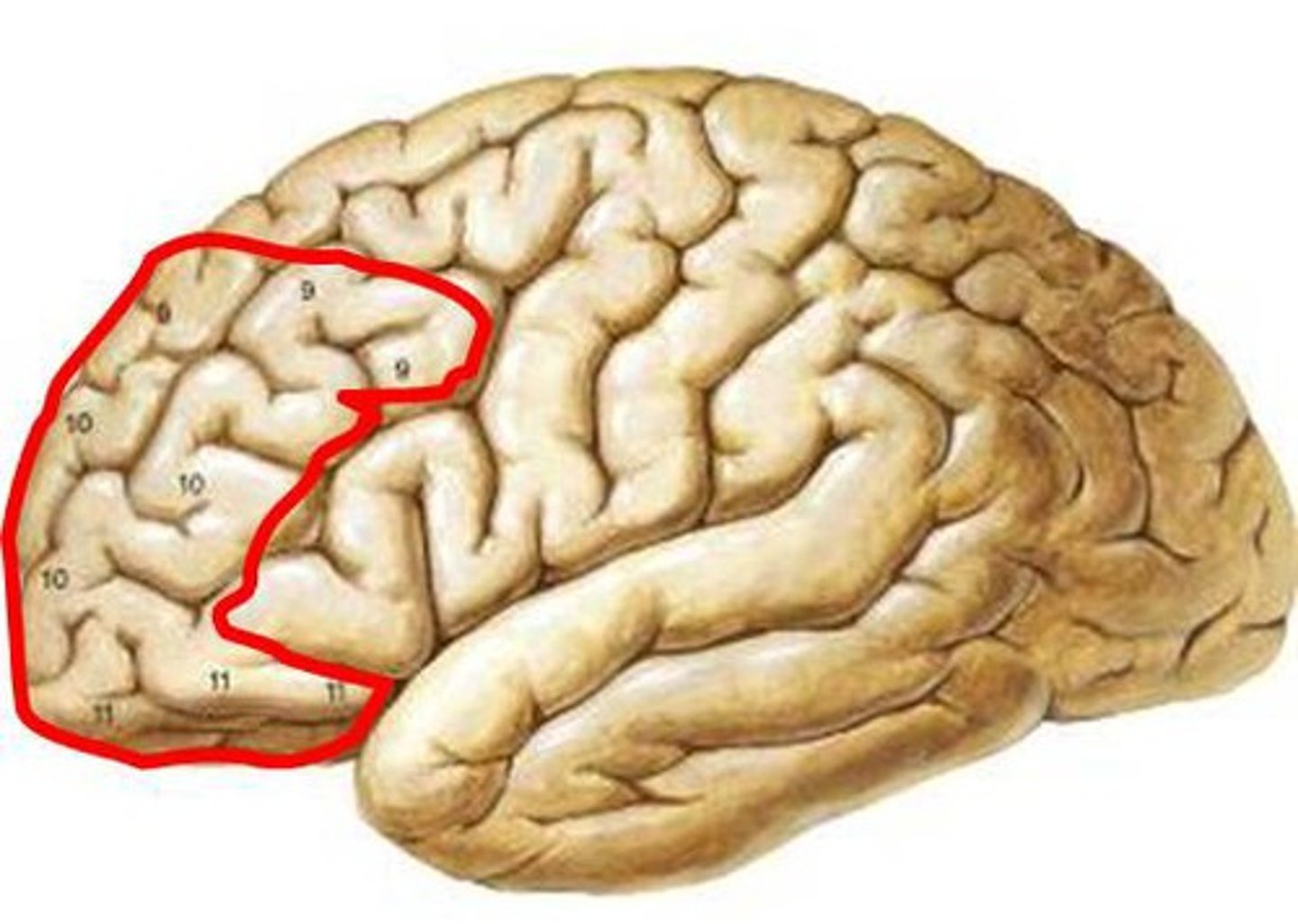
Prefrontal area
Motivation and insight / regulates mood and emotion / inhibits impulsive behavior
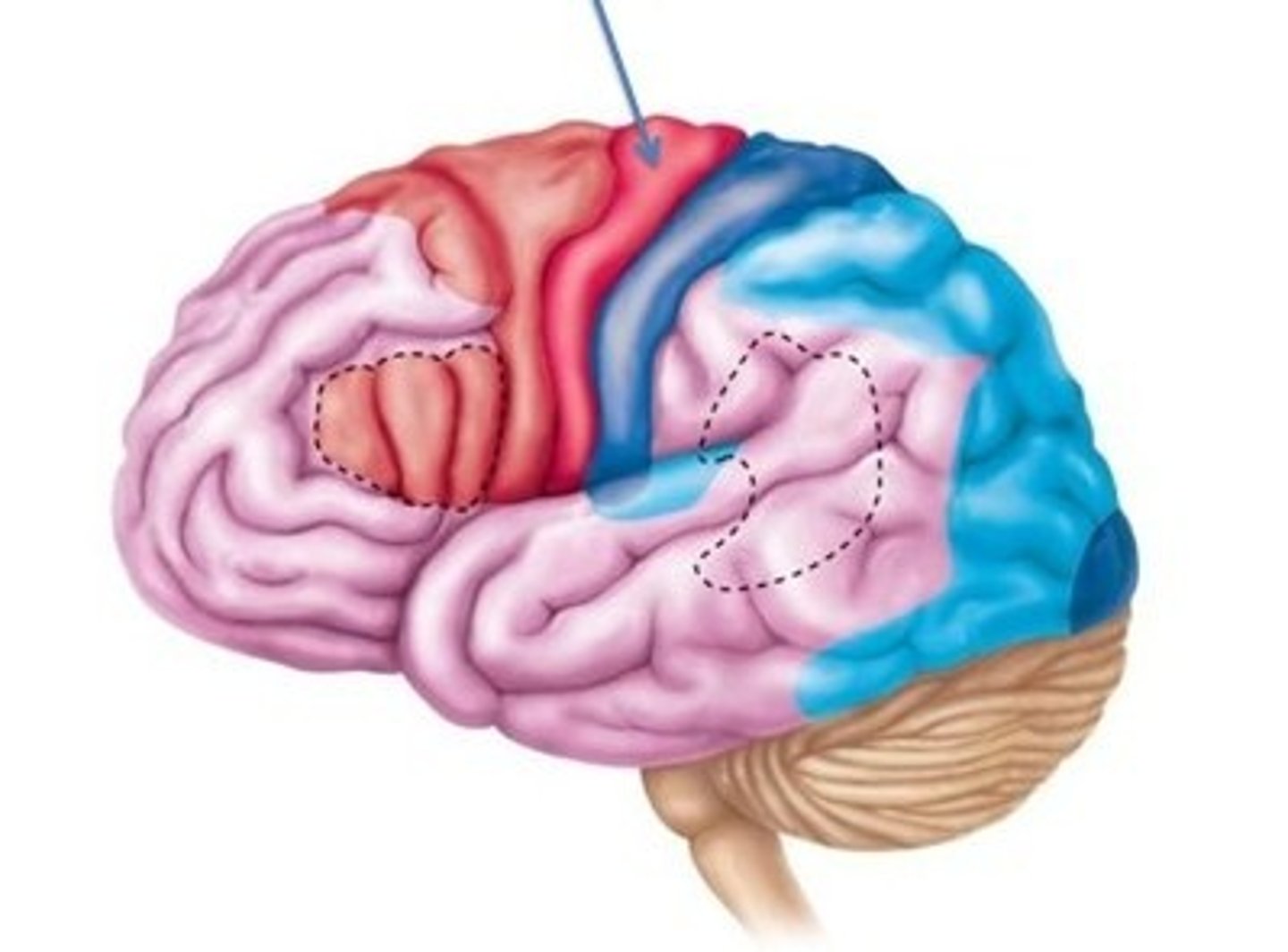
Premotor area
Works out sequence of neural signals needed for learned complex motion
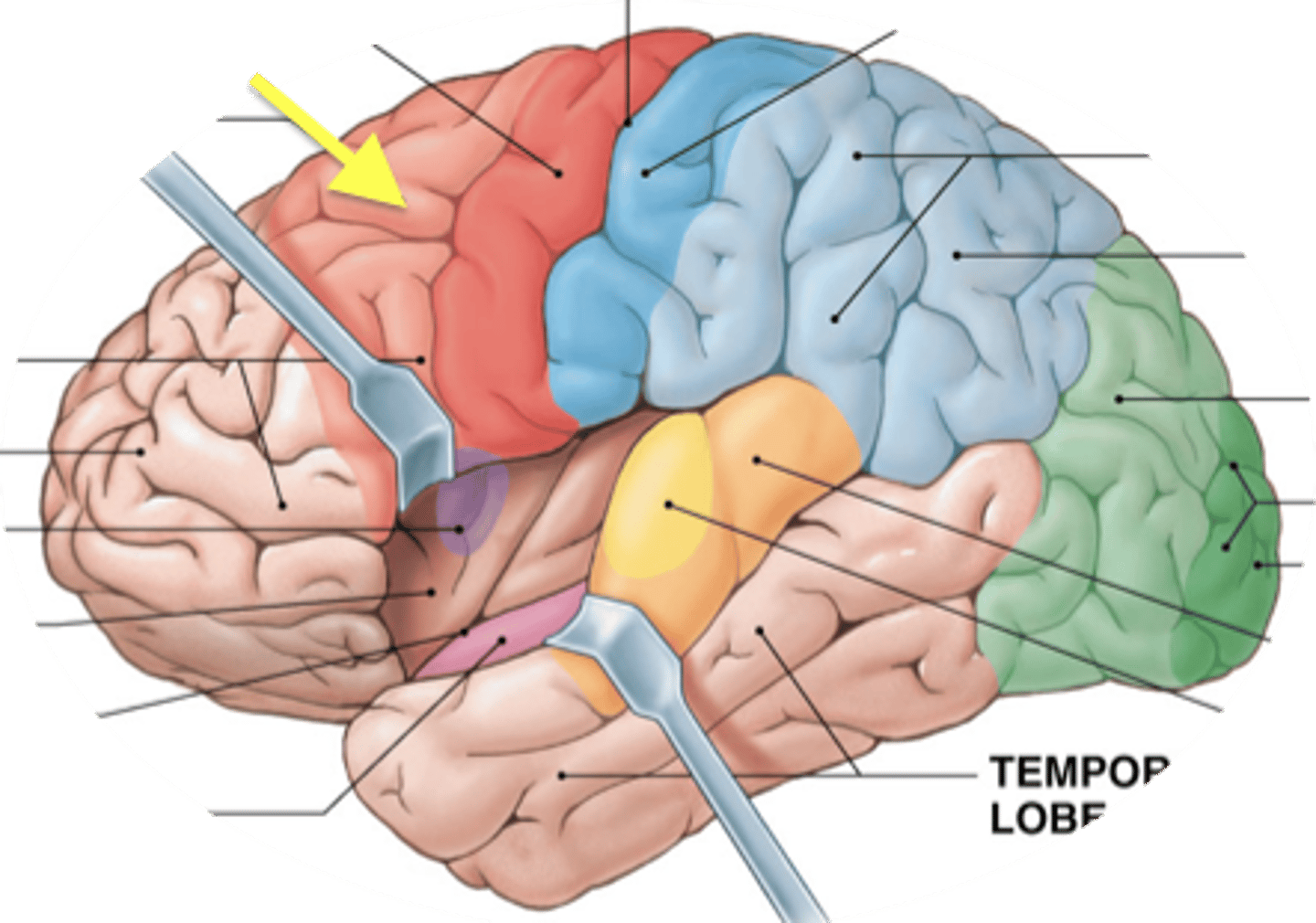
Primary motor cortex
initiates basic skeletal muscle movements
Lateral ventricles
produces most of the cerebrospinal fluid
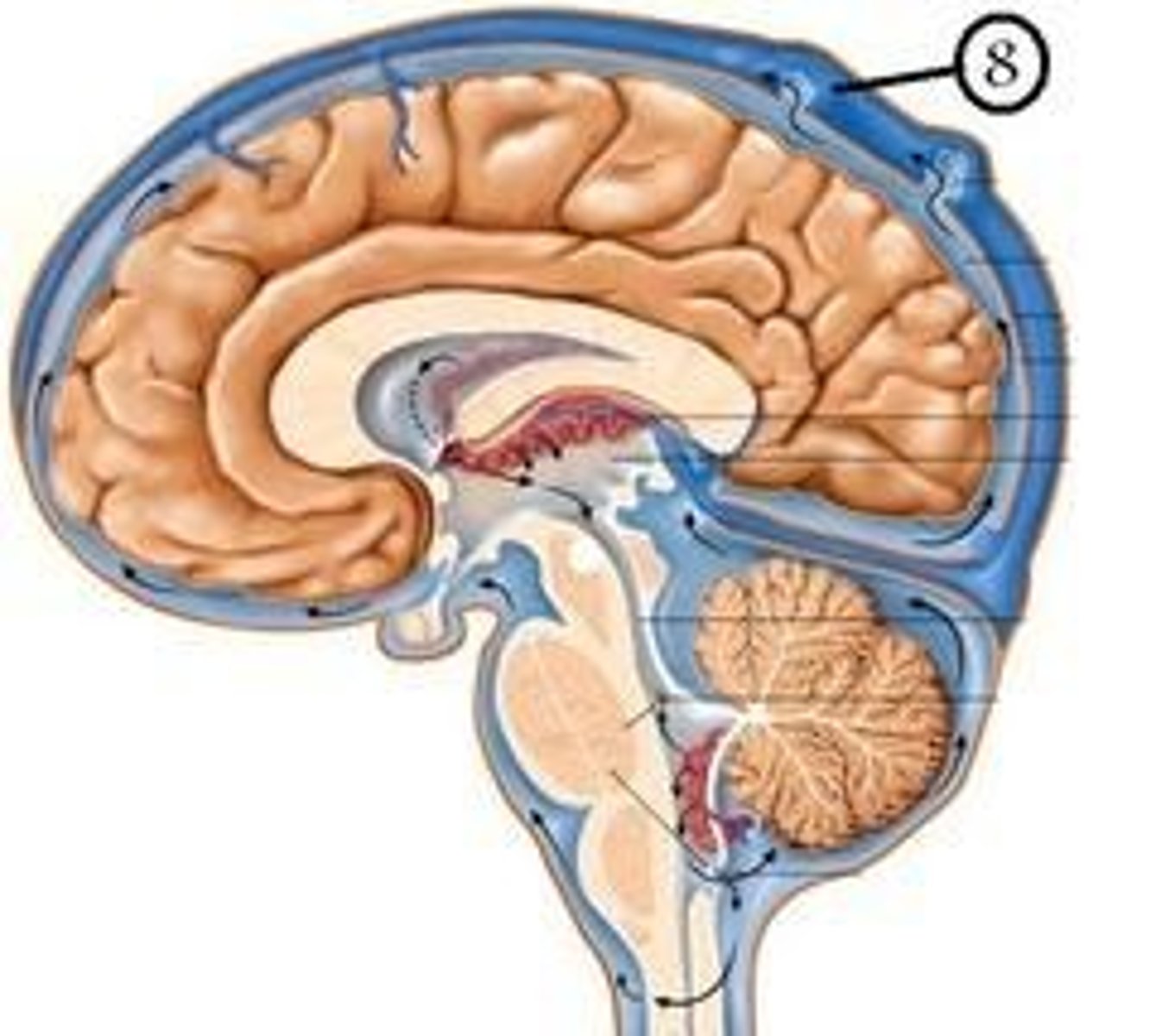
Meninges
the three membranes (the dura mater, arachnoid, and pia mater) that line the skull and vertebral canal and enclose the brain and spinal cord.
Arachnoid granulation
Small projections of the arachnoid membrane through the dura mater into the superior sagittal sinus; CSF flows through them to be reabsorbed into the blood supply.
The three neurons in a reflex arc
- afferent neuron
- association neuron
- efferent neuron
efferent neuron
nerve cell that send messages from brain and spinal cord to other parts of body; also called motor neurons
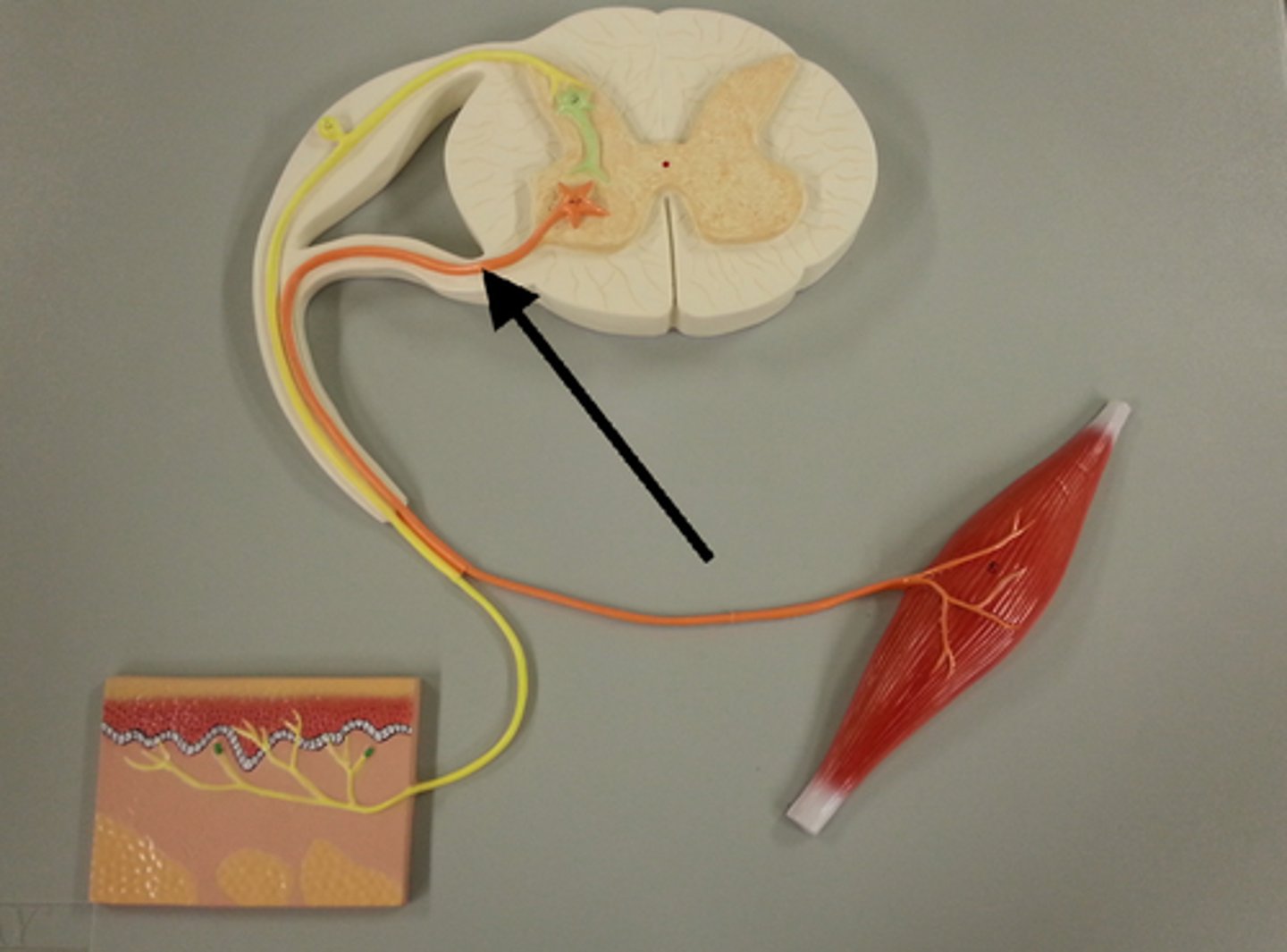
afferent neuron
nerve cell that sends messages to brain or spinal cord from other parts of the body; also called sensory neurons
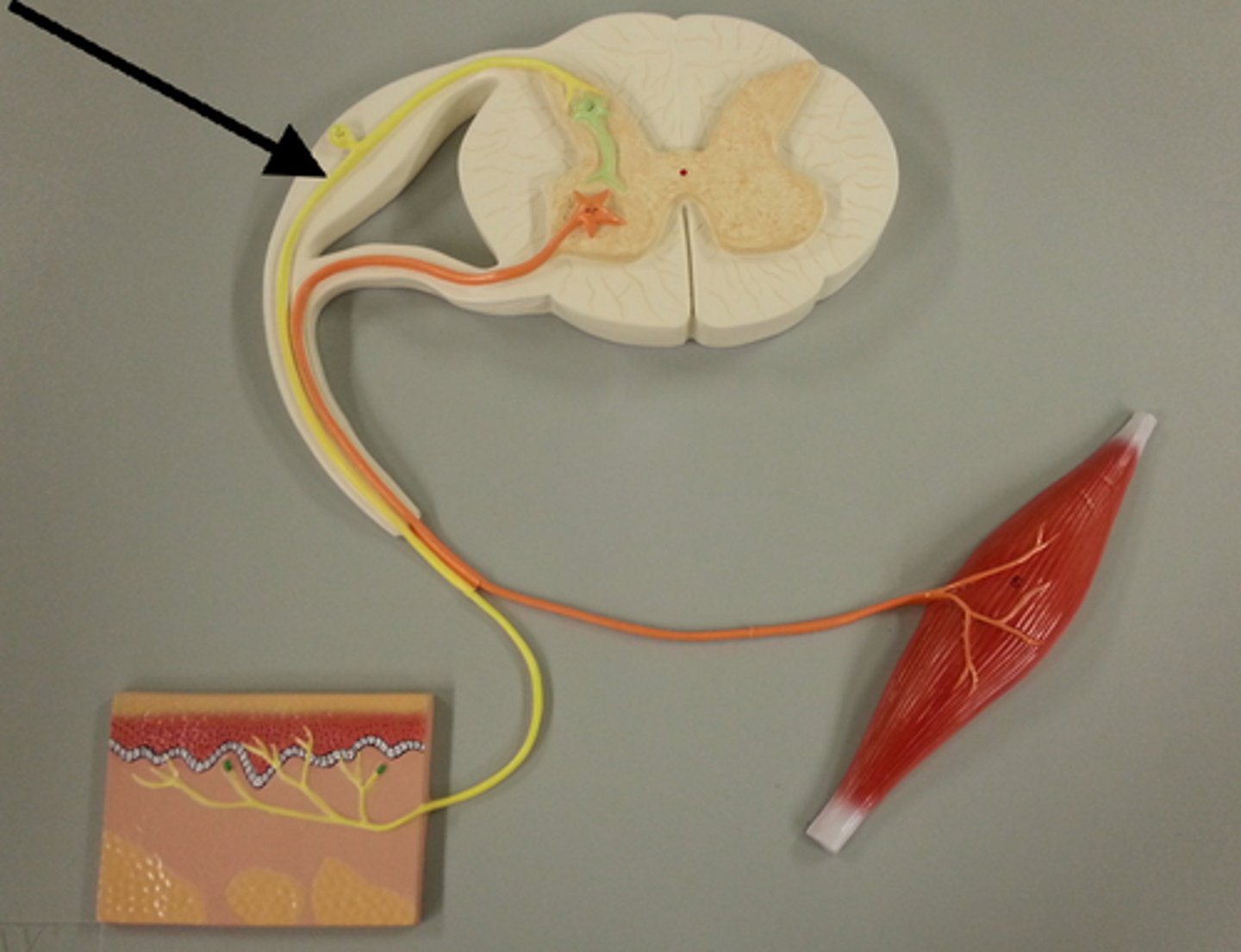
association neuron
A neuron that has as its primary function the job of connecting other neurons is called a(n) ________.
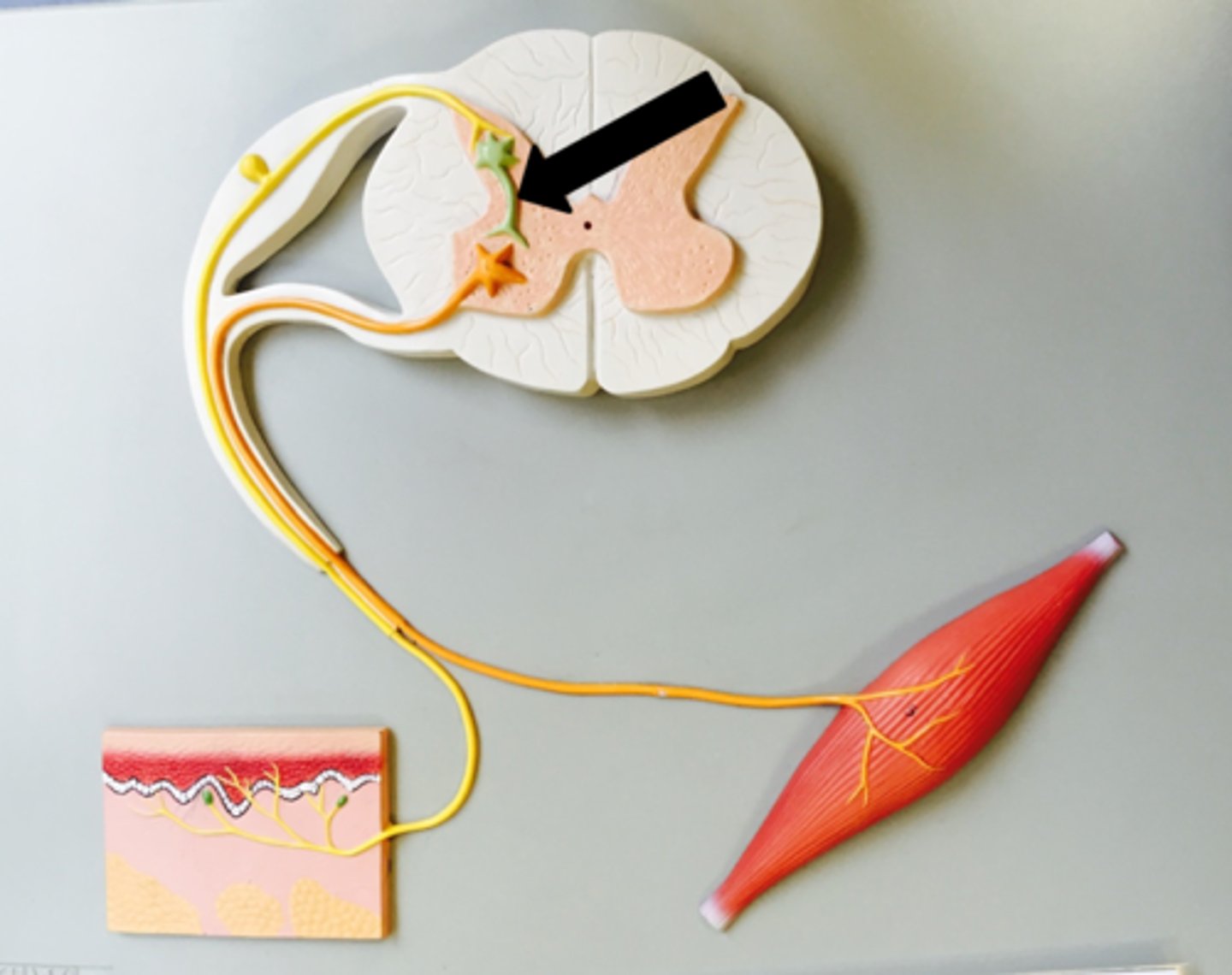

reflex arch
allows for a pre-programmed muscle response without a need for a neural message traveling to and from the brain. The neuronal circuit that coordinates a spinal cord reflex response
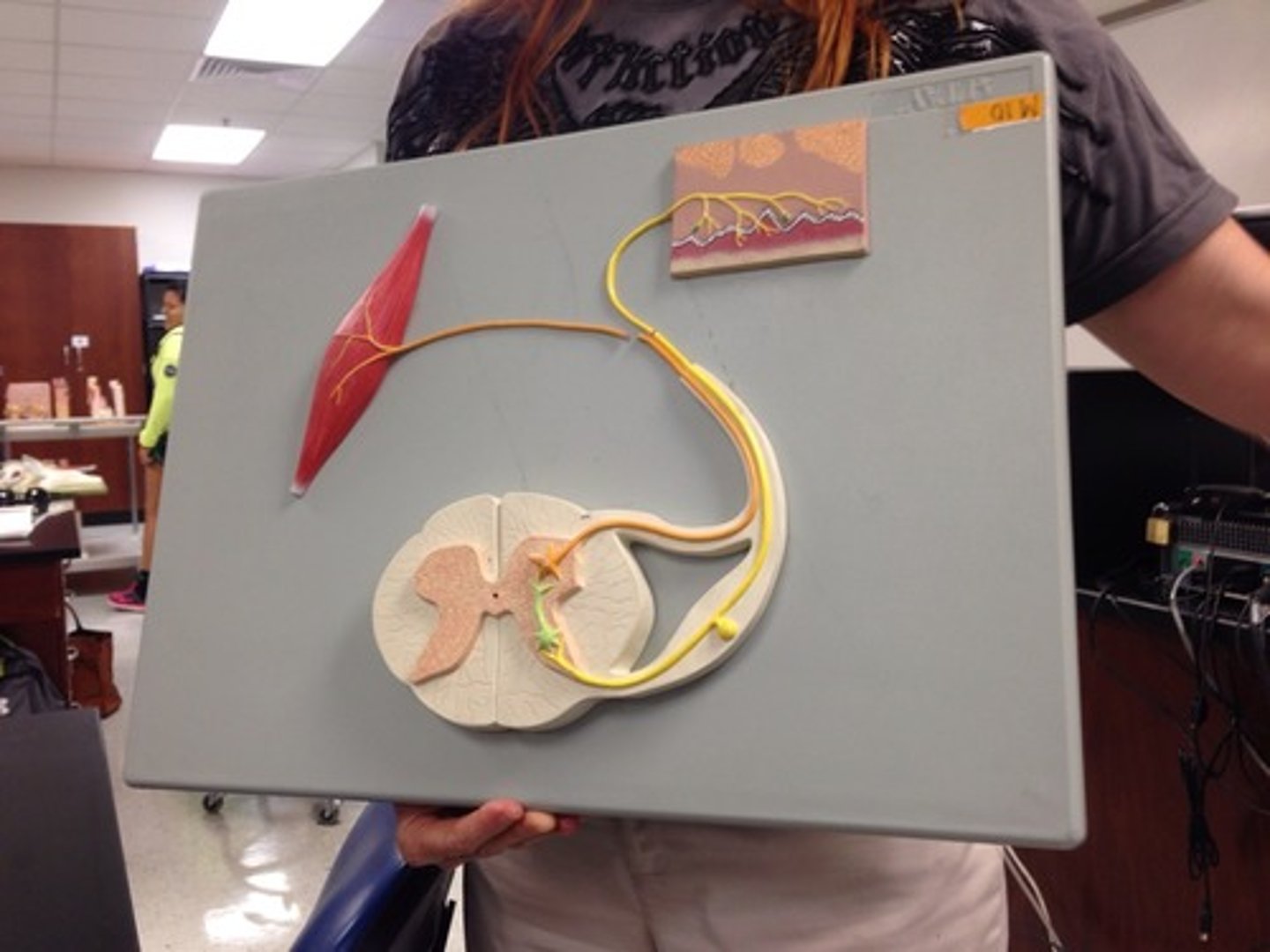
Converging circuit
allows the effector to be controlled by both the reflex arc and the brain, this allows the signals from the brain and reflex to act as one since the two neurons both synapse with the same effector neuron
Diverging circuit
in the spinal cord, the signal divides which it allows the afferent signal to both initiate the reflex to the muscle and initiate a signal to the brain
Cerebrospinal fluid
Cushions, protects and provides nutrients to the brain