11.2 The light-dependent reaction
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
The light dependent reaction of photosynthesis involved the capture of light whose energy is used for two purposes:

Oxidation and reduction

The making of ATP:

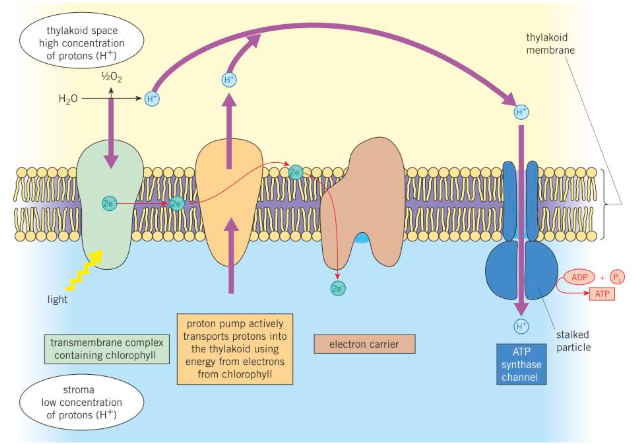
The precise mechanism by which ATP is produced can be explained by the chemiosmotic theory:
Each thylakoid is an enclosed chamber into which protons are pumped from the stroma using protein carriers in the thylakoid membrane called proton pumps.
The energy to drive this process comes from electrons released when water molecules are split by light —photolysis of water
The photolysis of water also produces protons which further increases their concentration inside the thylakoid space.
Overall this creates and maintains a concentration gradient of protons across the thylakoid membrane With a high concentration inside the thylakoid space and a low concentration in the stroma.
The protons can only cross the thylakoid membrane through ATP synthase channel proteins — the rest of the membrane is impermeable to protons. These channels form small granules on the membrane surface and so are also known as stalked granules.
As the protons pass through these ATP synthase channels they cause changes to the structure of the enzyme which then catalyses' the combination of ADP with inorganic phosphate to form ATP
Photolysis of water: 1

Photolysis of water 2:
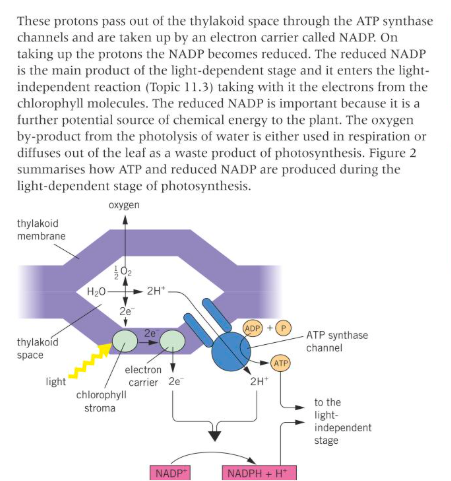
Site of the light-dependent reaction

Chloroplasts are structurally adapted to their function of capturing sunlight and carrying out the light-dependent reaction of photosynthesis in the following ways:
