HSC Chemistry Module 6
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/46
Last updated 11:13 PM on 1/28/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
1
New cards
indicator
a compound that can reversibly change color depending on pH,
2
New cards
neutralisation
the reaction between an acid and a base producing a salt and water
3
New cards
Arrhenius' theory
this theory states that acids ionise in water to give H+ ions and bases ionise to produce OH- ions, when an acid is neutralized a salt & water is produced
4
New cards
Lewis theory
an acid accepts electron pairs and a base donates electron pairs
5
New cards
Bronsted-Lowry theory
defines an acid as a proton donor, and a base as a proton acceptor
6
New cards
amphiprotic
a species that can either accept or donate a proton
7
New cards
pH
a measure of the power of hydrogen in a system
8
New cards
weak acid
an acid that only undergoes partial ionisation in water
9
New cards
weak base
a base that only undergoes partial ionisation in water
10
New cards
strong acid
an acid that fully ionises in water
11
New cards
strong base
a base that fully ionises in water
12
New cards
solubility rules
a set of rules used to predict whether an ionic compound will be soluble or insoluble in water
13
New cards
alkali
a soluble base
14
New cards
acid dissociation constant
Ka, the ratio of the concentrations of the dissociated and undissociated acid parts
15
New cards
base dissociation constant
Kb, the ratio of the concentrations of the dissociated and undissociated base parts
16
New cards
ionisation constant of water
Kw, the ionic ratio between H3O and OH in water
17
New cards
buffer solution
a solution made from a weak acid and its conjugate base that neutralizes small amounts of acids or bases added to it
18
New cards
buffer capacity
the amount of acid or base a buffer solution can absorb without a significant change in pH, the greatest buffer capacity with a high concentration and equal concentration of weak acid & conjugate base.
19
New cards
amphoteric
A substance that can act as both an acid and a base, (Ex. water dissociation of acid to form hydronium ion/ dissociation of base to form hydroxide)
20
New cards
acidic solution
a solution in which \[H3O+\] > \[OH-\]
21
New cards
titration
a measured amount of a solution of unknown concentration is added to a known volume of a second solution until the reaction between them is just complete
22
New cards
equivalence point
the point in a titration where the amount of titrant added is enough to completely neutralise the analyte solution and number of moles of acid and base completely react

23
New cards
end point
the point in a titration at which an indicator changes color
24
New cards
primary standard
a standard solution that has a known concentration and is prepared by the chemist
25
New cards
secondary standard
A solution that has been prepared in a laboratory and has been titrated against a primary standard solution
26
New cards
hygroscopicity
the ability to absorb water from the atmosphere
27
New cards
analyte
the unknown concentration but known volume of the substance being analysed
28
New cards
titrant
the standard being titrated against
29
New cards
titre
the volumes of the titrant measured in the burette
30
New cards
conductometry
a measurement of electrolytic conductivity to monitor a progress of chemical reaction
31
New cards
buffer
compound that is able to resist a change in pH when small amounts of acid or base are added.
32
New cards
acidic buffer
a buffer solution with a pH less than 7, made from a weak acid and it's conjugate base.
33
New cards
basic buffer
a buffer solution with a pH greater than 7, made from a weak base and it's conjugate acid.
34
New cards
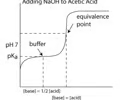
buffer region
The portion of a titration curve in which the concentration of an acid is approximately equal to that of its conjugate base; pH remains relatively constant through this region
35
New cards
conjugate pair
two substances related to each other by the donating or accepting of a single proton
36
New cards
making primary standard
1. weigh solid on electronic balance in clean beaker
2. dissolve solid in distilled water, pour into clean volumetric flask, rinsing to ensure all dissolved solid is in flask
3. add sufficient distilled water so meniscus is on calibration line
37
New cards
monoprotic
an acid that can donate only one proton (H+ ion) per molecule (e.g., HCl)
38
New cards
diprotic
acid that can donate two protons (H⁺ ions) per molecule (e.g., H2SO4)
39
New cards
differentiating strong & weak acids
* pH probe
* electrical conductivity conductometer
* titration with a strong base (weak base will have higher equivalence point)
* magnesium strip (strong acid will have more fizzing)
* electrical conductivity conductometer
* titration with a strong base (weak base will have higher equivalence point)
* magnesium strip (strong acid will have more fizzing)
40
New cards
enthalpy of neutralisation
enthalpy change when one mole of water is formed in a reaction between an acid and an alkali under standard conditions
41
New cards
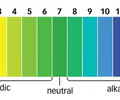
universal indicator
a mixture of indicators which show different colours in solutions of different pHs
**pH range:** 1-14
**pH range:** 1-14
42
New cards
phenolphthalein
indicator with **pH range:** 8.3-10
**colour change:** clear to pink/purple
**colour change:** clear to pink/purple
43
New cards
bromothymol blue
indicator with **pH range:** 6-7.6
**colour change:** yellow to blue
**colour change:** yellow to blue
44
New cards
litmus
indicator with **pH range:** 4.5-8.3
**colour change:** red to blue
**colour change:** red to blue
45
New cards
methyl orange
indicator with **pH range:** 3.1-4.4
**colour change:** red to yellow
**colour change:** red to yellow
46
New cards
conjugate base
acid - proton(H+)
47
New cards
conjugate acid
base + proton (H+)