Anat-Phys of Domestic animals Exam 2
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
What makes up the cardiovascular system?
The heart, blood, and blood vessels
Cardiac muscle makes up..
the bulk of the heart (provides force to pump heart)
What is the protective layer of the heart called?
the pericardial sac
What is the outermost layer of the pericardium?
fibrous pericardium
What is the innermost layer of the pericardium? (double-layered membrane)
Serous pericardium
What is the outermost layer of the heart?
Epicardium
The pericardial cavity separates…
the epicardium and serous pericardium
The middle muscular layer is called?
Myocardium
What is the layer that lines that heart?
Endocardium
The upper chambers of the heart are called?
the left and right atria (atrium)
The lower chambers of the heart are called?
the right and left ventricles
What separates the chambers internally?
The septum
How are the chambers separated externally?
by the coronary sulcus and interventricular sulci
The systemic system consists of..(in order)
Left ventricle > aortic semilunar valve > aortic arch > descending aorta > arteries > arterioles > Capillary bed (O2 and CO2 exchange) > venules > veins > cranial/inferior vena cava (repeat)
The pulmonary system consists of..(in order)
Right atrium > right AV valve > right ventricle > pul. SL valve > pul. artery > lungs > lobar arteries > arterioles > capillaries > Alveoli (CO2 and O2 exchanged) > capillaries > lobar vein > pul. vein > left atrium > left AV valve > left ventricle
The superior vena cava receives
deoxygenated blood from upper body (diaphragm-up)
The inferior vena cava receives
deoxygenated blood from lower body (lower limbs and abdominopelvic region)
The coronary sinus collects
deoxygenated blood from heart muscle and delivers to right atrium
The pulmonary trunk (right and left artery) carries..
deoxygenated blood to the lungs
The pulmonary veins (4) return..
oxygenated blood to the heart
The ascending aorta brings
oxygenated blood out to the body (systemic system starts)
The tricuspid valve is between
the right atrium and right ventricle
The bicuspid valve is between
the left atrium and the left ventricle
The thread-like bands of fibrous tissue that attach to ventricles are called?
Chordae tendineae
The atrioventricular valve consists of..?
the bicuspid and tricuspid valves
The semilunar valve consists of..?
the pulmonary and aortic valve
The pulmonary valve is between
right ventricle and pulmonary trunk that exits the heart
The aortic valve is between
left ventricle and the ascending aorta that leaves the heart
when two atria contract
ventricles relax
Deoxygenated blood returns from body to
right atrium
Left ventricle sends blood to the body via
the ascending aorta
Sinoatrial node is the
pacemaker that initiates impulse
Atrioventricular node sends
impulse to the AV bundle
Bundle of His sends
impulse to both sides of system (rythmic)
Purkinje’s fiber sends
impulse to myocardial cells
One cycle (one heartbeat) consists of
Atria contract/ventricles relax; ventricles contract/atria relax
systole is what phase?
contraction phase
Diastole is what phase?
relaxation phase
Systemic circulation is when..?
all blood leaves left ventricle (oxygenated) and all blood returns to right atrium (deoxygenated)
Coronary circulation is..?
circulation through the heart
The pulmonary blood circulation route is when blood..?
flows to lungs for gas exchange
Cerebral route is the route to..?
The brain
The fetal blood circulation route is the route between..?
the developing fetus and mother (through the placenta)
What is the innermost layer of arteries/veins called?
Tunica intima (elastic fibers)
What is the middle layer of arteries/veins called?
Tunica media (collagen fibers)
What is the outer layer of arteries/veins called?
Tunica adventitia
What are the blood vessel cavities called?
Lumen
What is the junction of blood vessels called
Anastomosis
What artery does not carry oxygenated blood? (exception)
Pulmonary artery
What vein carries oxygenated blood? (exception)
pulmonary vein
What are capillaries?
Site of gas, nutrient, and waste exchange
Venules carry what substance?
CO2
Right and left coronary arteries branch off and supply..?
oxygenated blood to the heart
The first branch of the aortic arch consists of?
right common carotid artery and right subclavian artery
The second branch of the aortic arch consists of?
Left common carotid artery, left internal carotid, and left external carotid artery
The third branch of the aortic arch consists of?
Vertebral artery, axillary artery, brachial artery, and radial/ulnar arteries
splenic artery supplies blood to
spleen
coronary artery supplies blood to
heart
bronchial arteries supplies blood to
Non-respiratory tissue
Carotid Artery supplies blood to
the face
The circle of willis supplies blood to
the brain
Hepatic Artery supplies blood to
the liver
Illiac Artery supplies blood to
the Legs
Renal Artery supplies blood to
the kidneys
Gonadal Artery supplies blood to
testes/ovaries
Lumbar Artery supplies blood to
the lower back
Vertebral Artery supplies blood to
the spinal cord
Phrenic Artery supplies blood to
the Diaphragm
Ulnar artery supplies blood to
Wrist and hands
Gastric artery supplies blood to
Stomach
Esophageal artery supplies blood to
Esophagus
Mesenteric artery supplies blood to
Small/large intestine
What is the first wave called
P-wave
The QRS wave allows the spread of
Electrical current to cause ventricle systole
The T-wave repolarizes ventricles and
Marks end of ventricle systole
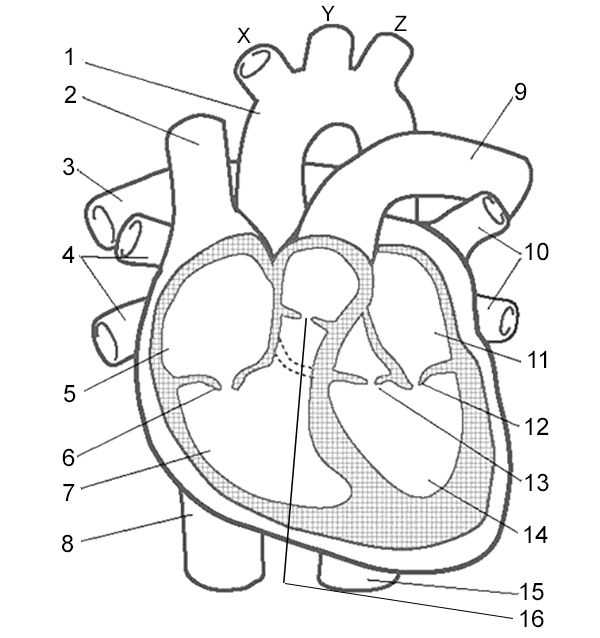
Aorta
What is number 2?
Cranial vena cava
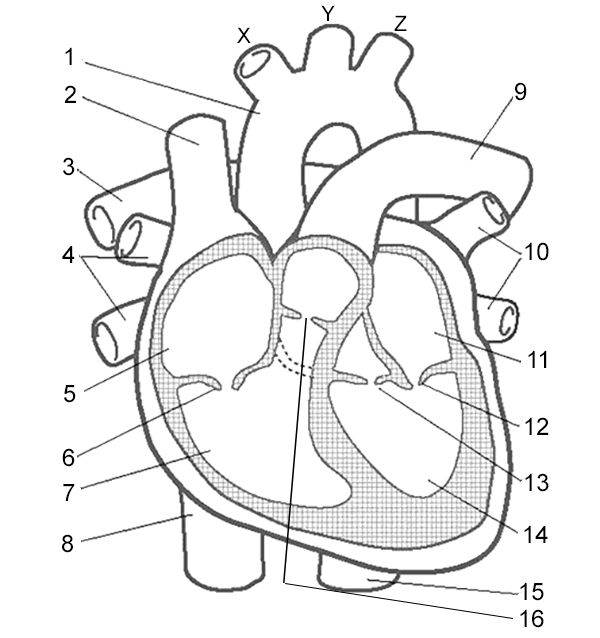
Wha is number 3?
Pulmonary artery
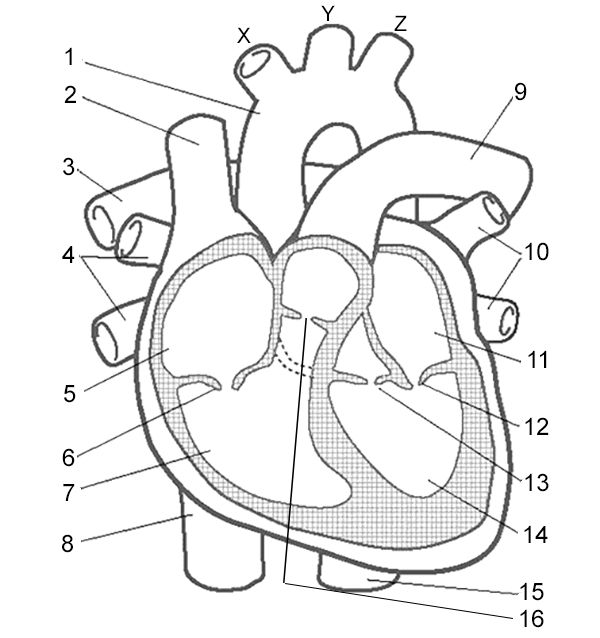
What is number 5 and 7?
Right atrium and right ventricle
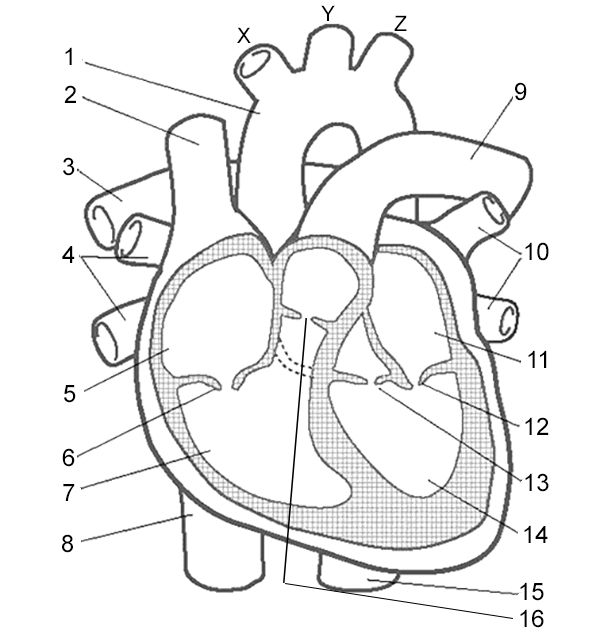
What is number 11 and 14?
Left atrium and left ventricle
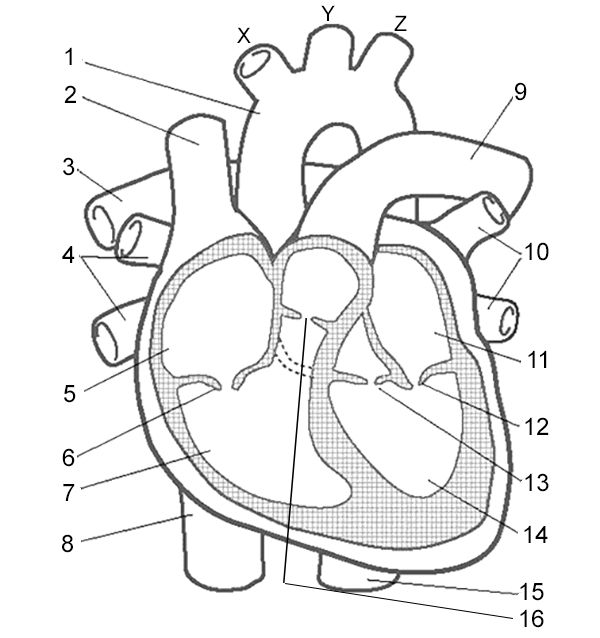
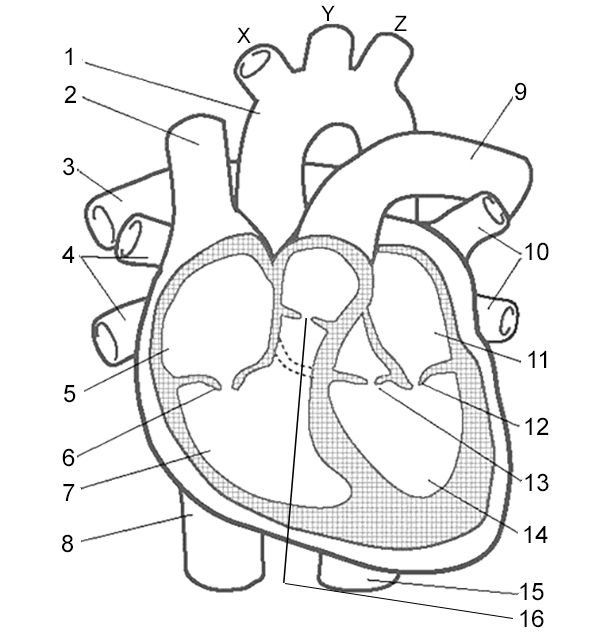
What is number 10?
Pulmonary veins
Excess build-up of bilirubin in circulatory system (eyes and mouth become yellow)
Jaundice
Hemoglobin in blood plasma and excreted through the urine
Red water
Clumping of RBC transfusing of blood of the wrong type
Hemagglutination
Due to decrease in functional RBC and decrease in quantity of Hb
Anemia
Over production of RBC
Polycythemia