Parts of the Cell
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Centrosome
microtubule organizing center near nucleus
forms mitotic spindke during cell division
contains tubulins that build microtubules in non-dividing cells
centrioles
cylindrical structures, each composed of 9 clusters of microtubular triplets
chromatin
uncondensed DNA in interphase cells
cytoskeleton
determines cell shape and organizes cellular content
aids movement of organelles
microfilaments
thinnest; generate movement and provide mechanical support
microtubules
largest; determine shape and aid movement
mitotic spindle
separates chromosomes during cell division
asters
visible only when cells are in mitosis
cilia/cilium
contains microtubules; moves fluids along cell’s surface
flagella
moves an entire cell; hair-like
golgi complex
modifies, sorts, packages, and transports proteins received from the rough ER
forms secretory vesicles that discahrge processed proteins via exocytosis into extracellular fluid
microvilli
nonmotile, finger-like projections of the plasma membrane
inc. cell surface area
mitochondria
site for chemical reactions of aerobic cellular respiration that generate ATP
nucleus
contains cell’s genes (on chromosomes)
controls cellular structure
directs cellular activities
nuclear envolope
double membrane that separates the nucleus from cytoplasm
nuclear pores
protein-surrounded openings that extend through nuclear envelope
nucleolus
produces ribosomes and rRNA
plasma membrane
membrane made up of lipid bilayer separating the interior of a cell from the outside environment
facilitates exchange of subtances in and out the cell
ribosomes
function: protein synthesis
may be free in cytosol or attached to rough ER
rough endoplasmic reticulum
membranous network of flattened sacs/tubules covered by ribosomes
attached to nuclear envelope
synthesizes glycoproteins and phospholipids that are transferred to organelles, inserted into plasma mebrane, or secreted during exocytosis
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
membranous network of flattened sacs or tubules that lacks ribosomes
synthesizes fatty acids and steroids
inactivates/detoxifies drugs
stores and releases Ca+ ions in muscle cells

golgi complex
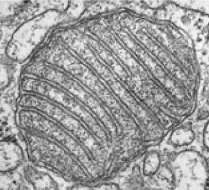
mitochondria
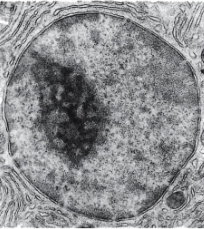
nucleus
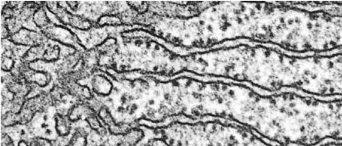
smooth ER (left) rough ER (right)