Week 2: TCP/IP protocol architecture, sniffing and traffic analysis
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
What is a network protocol?
A set of rules or conventions that allow peer layers to communicate
What are the key features of network protocols?
Syntax - the format of the data block
Semantics - control information for coordination and error handling
Timing - speed matching and sequencing
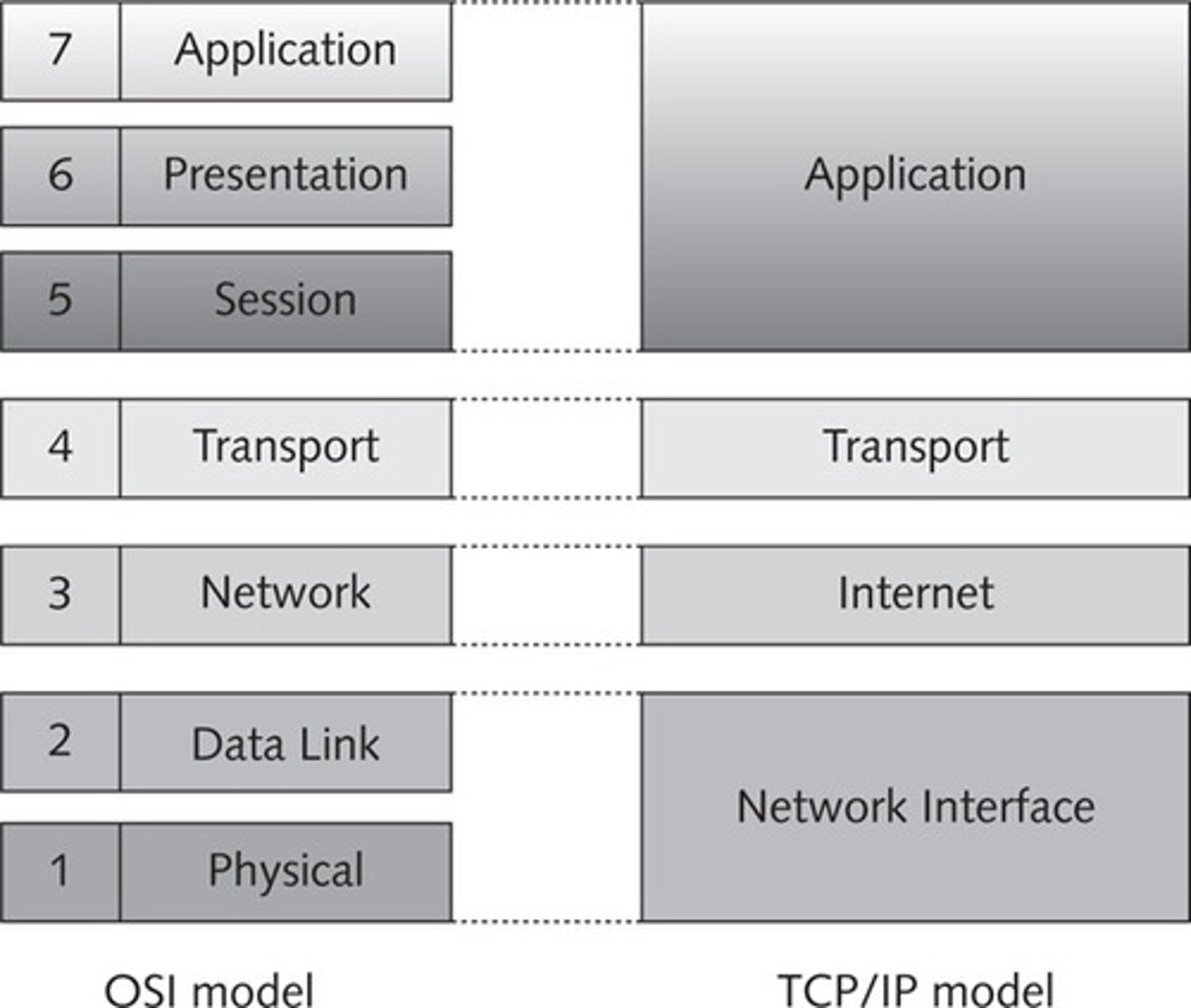
What is the TCP/IP Protocol Architecture?
A layered model that defines how data is transmitted over the internet
What are the layers of the TCP/IP architecture?
Application, Transport, Internet, Network Access, and Physical layers
What is the Application layer in TCP/IP?
The top layer of the TCP/IP model, providing network services to end-user applications (e.g., HTTP, SMTP, DNS)
What is the Data Processing Unit of the Application layer?
The application byte stream
What is the Transport layer in TCP/IP?
The layer in the TCP/IP model responsible for end-to-end data transfer, providing services like connection establishment, reliability, and flow control (e.g., TCP, UDP)
What is the TCP protocol?
A reliable protocol that establishes an end-to-end connection between two hosts, as if they were connected by a physical circuit
How is TCP reliable?
It ensures ordered delivery of packets using sequence numbers
It ensures error-free transmission by using ACKs and retransmitting lost or corrupted packets
What is the UDP protocol?
It is a faster connectionless protocol relying on datagrams but there is no verification of connection between the sender and receiver
When would we use UDP?
When an application sends small amounts of data and when an application prioritises speed over reliability of the service
What is the Data Processing Unit of the Transport layer?
TCP segment/UDP datagram which is provided irrespective of distance and network locality
What is the Internet layer in TCP/IP?
The layer in the TCP/IP model responsible for routing and forwarding packets across networks (e.g., IPv4, IPv6)
How many bits are in IPv4?
32 bits
How many bits are in IPv6?
128 bits
What is a router?
A processor that connects two networks, relaying data from one to the other
What are the different routing protocols?
OSPF - open shortest path first
BGP - border gateway protocol
RIP - routing information protocol
What is the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)?
A network protocol used to determine the MAC address of the next router or device on the path
Why do we need ARP?
For a host to communicate with another host, it must know the MAC address of the destination host (if they are on the same network) or next-hop router.
What is the Data Processing Unit of the Internet layer?
IP packets where the destination of the packet is filled in at the source and vice versa
What is the Network Access/Link layer in TCP/IP?
The layer in the TCP/IP model that provides the logical interface to the physical network hardware and handles medium access control (e.g., Ethernet, Wi-Fi)
What does the Network Access/Link layer concern?
Devices on the same local network
What is a network switch?
A device at the link layer that knows the specific MAC addresses to send a MAC layer frame to
What is the Data Processing Unit of the Network Access/Link layer?
MAC frames which are read by the network switches of the sender and receiver devices
What is the Physical layer in TCP/IP?
The layer in the TCP/IP model that covers the physical interface between the computer and the network
What is a network hub?
A device connecting multiple ethernet devices as a segment and broadcasts messages it receives from any port to all the other ports of the hub
What are peer layers?
The corresponding layers between two communicating entities in the TCP/IP protocol architecture, with no knowledge of the underlying layers
What is the Data Processing Unit of the Physical layer?
Physical bit stream
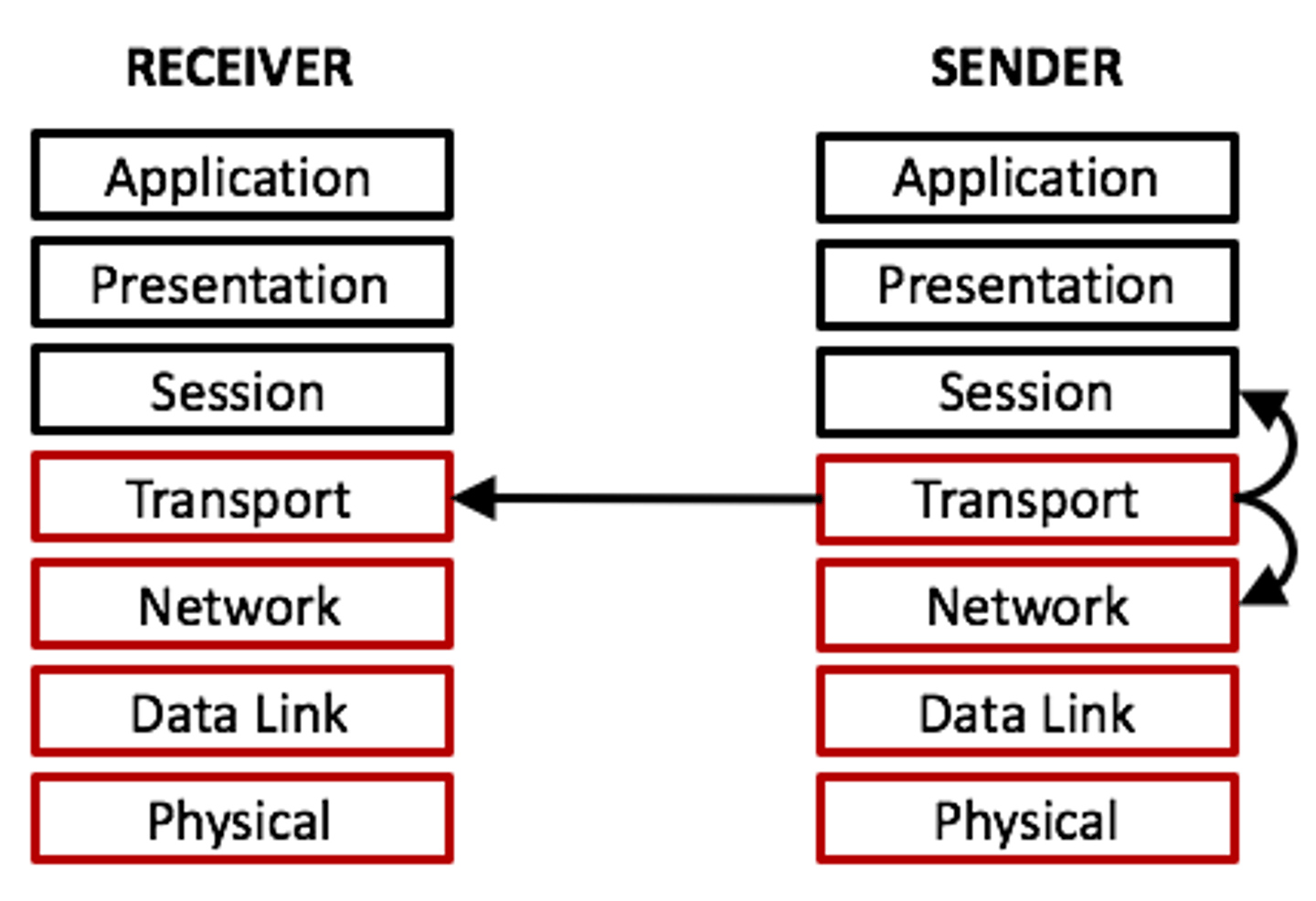
What is encapsulation?
The process of adding protocol headers (and sometimes trailers) to data as it moves down the TCP/IP stack on a sending host, preparing it for transmission over the network
What is decapsulation?
The process of removing protocol headers as data moves up the TCP/IP stack on a receiving host, revealing the original data at the Application layer
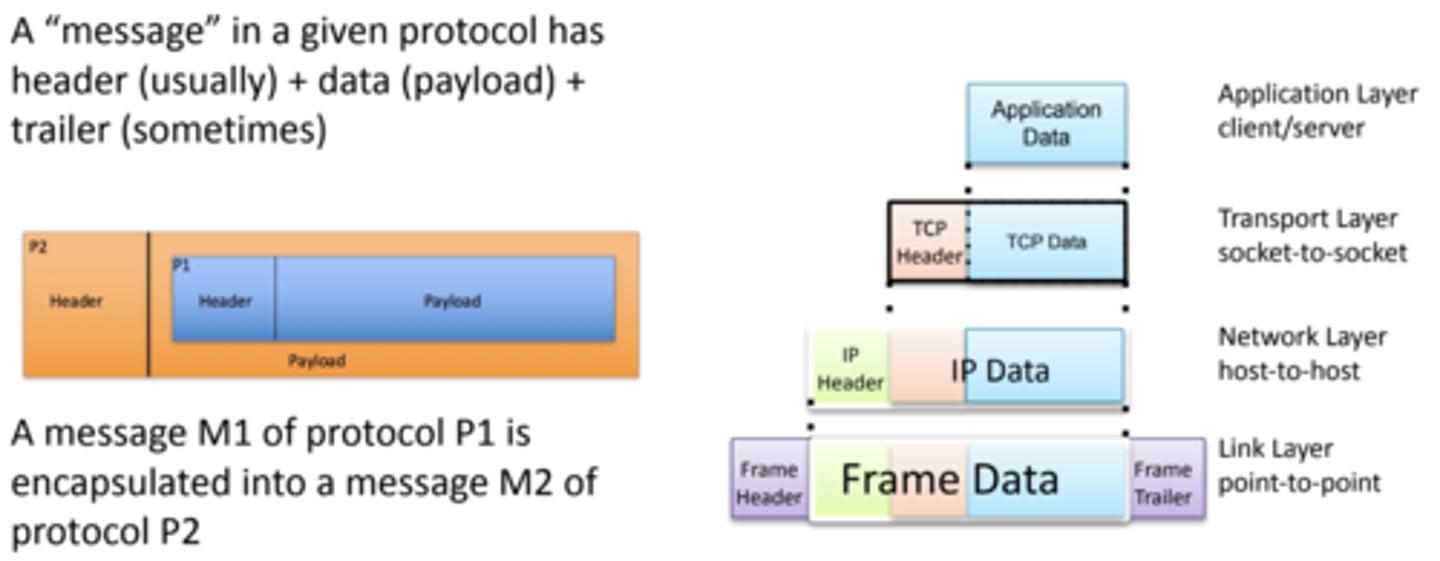
How does encapsulation work?
1. Application layer - application data
2. Transport layer - TCP segment/UDP datagram = TCP/UDP header + application data
3. Internet layer - IP packet = IP header + TCP segment/UDP datagram
4. Network access/link layer - MAC layer frame = MAC header + IP packet
5. Physical layer - encodes this as a bit stream to send to the switch
At the Application layer, how does encapsulation occur?
It passes down the application data as the payload to the transport layer
At the Transport layer, how does encapsulation occur?
The data is segmented by the protocol and appends a TCP/UDP header with source port and destination port
Encapsulated form: TCP segment/UDP datagram = TCP/UDP header + application data
At the Internet layer, how does encapsulation occur?
The IP header is appended with the source IP and destination IP, along with their subnet masks
Resulting form: IP Packet = IP Header + TCP Segment/UDP Datagram
How does the device decide if the destination is local or remote?
It uses the destination IP and subnet mask. If outside its subnet, it sends the packet to the default gateway
At the Network Access/Link layer, how does encapsulation occur?
It creates a MAC frame by adding a MAC header with the source MAC and destination MAC, which is known through ARP
How is the encapsulated data sent to the receiver in the Physical layer?
The MAC frame is turned into a bit stream (0s and 1s) and transmitted over the medium (e.g., twisted pair cable) - we use the Ethernet CSMA/CD protocols to access the medium
What is the difference between forwarding and routing packets?
Forwarding is the local decision to send a packet to the next hop
Routing is the global process of building the path using routing protocols (e.g., RIP, BGP)
What is a default gateway?
The router that allows you to communicate outside of your local subnet
How does the first part of decapsulation work?
1. The bitstream arrives at the router, recovers the MAC layer frame
2. At the link layer, the header of the MAC frame is read - if the CRC checksum at the end of the frame has no error, then the router checks the MAC destination address
3. The payload of the MAC frame (IP packet) is passed up to the Internet layer
What happens if the destination MAC address is the same as the router's MAC address?
The link layer removes the MAC header and CRC checksum, passing it up to the Internet layer
What is a routing table?
A list of all destinations on the network, and where their next hop is
What happens when the decapsulated IP packet reaches the Internet layer through a network interface?
The router checks the routing table and uses a packet forwarding algorithm to determine the correct interface to forward it to
What is the packet forwarding algorithm?
The algorithm that determines what outgoing network interface to forward an IP packet towards, using the packet's destination IP address, subnet mask and routing table
Do the source and destination IP addresses change at each router hop?
The IP addresses stay the same - only the MAC addresses change per hop
What does the router do after choosing the outgoing interface?
The router re-encapsulates the IP packet with a new MAC header and sends it out via the Physical layer
What are the new MAC addresses in the MAC frame after routing hops?
The source is the router's MAC address, the destination is the next hop's interface MAC
What happens during decapsulation when the data finally reaches an interface connected to the same subnet as the receiver?
The router forwards the packet to the interface, where it will be decapsulated and validated to be processed
What is sniffing?
The act of listening to network conversations that are not intended for the listener, often involving capturing and logging network traffic
Where does sniffing occur?
At the physical layer
What is the non-promiscuous mode of an NIC?
The NIC drops all traffic that was unintended for the device
What is the promiscuous mode of an NIC?
The NIC receives all packets from the network regardless of initial destination
What cases does passive traffic interception work in?
For networks with a broadcasting medium (like network hubs, WiFi networks)
Why does passive interception not work for networks using a network switch?
Because a switch uses a MAC address table to forward traffic only to the specific port associated with the destination device. This means unicast traffic is not broadcasted to all devices, so a device in promiscuous mode can't see other devices' traffic unless it's the intended recipient.
What is active interception?
Occurs when a computer is placed between the sender and receiver and is able to capture or modify the traffic between them
What are types of active interception?
Port mirroring, network tapping, WarXing, Rogue Access Point
What is SPAN (Switch Port Analyzer) / port mirroring?
A feature on network switches that allows a copy of network traffic from one or more ports (or VLANs) to be sent to a designated monitoring port.
How can port mirroring be used for a good purpose?
It can be used for network diagnostics and intrusion detection
What is network TAPping?
A Layer 1 hardware device inserted at a specific point in a network, where data can be accessed for testing/troubleshooting
What does TAP stand for?
Traffic Access Point/Test Access Point
What are the components of the network TAP?
Ports to connect the two hosts A and B to, and two TAPs: TAP A and TAP B which are connected to a packet sniffer
What traffic does TAP A capture?
Traffic from Host A to Host B
What traffic does TAP B capture?
Traffic from Host B to Host A
What pins are used by TAP A and TAP B to capture traffic?
TAP A uses pins 3 and 6 to connect to pins 1 and 2 of Host A and B
TAP B uses pins 3 and 6 to connect to pins 3 and 6 of Host A and B
How can bidirectional traffic be monitored by the network TAP?
By connecting TAP A and TAP B's ports to a monitoring device (+ by a hub) to receive both streams simultaneously
What is a bypass TAP?
An inline TAP on a critical link that continues to forward traffic even if the monitoring tool is offline
What is a vampire TAP?
A tool piercing the copper wire shielding to access network signals, and is used in telecoms
What is WarXing?
An umbrella term of doing an action X to search for a WiFi network to connect to, e.g. wardriving is for an attacker driving a car to find a WiFi network
What is a Rogue Access Point?
An unauthorised wireless access point that allows an attacker to bypass network security configurations
How does a Rogue Access Point work?
It mimics the same behaviour as a legit access point for users to unknowingly send traffic to
What are the types of Rogue Access Points?
Using a wireless router
Using a computer/laptop with a virtual router
What is data acquisition?
The process of understanding the meaning of captured traffic
What is PCAP?
A C API for capturing live network traffic
What were the inefficiencies of traditional packet capturing?
All packet filter modules sit on top of the module, so all packets are copied to a buffer and then filtered regardless of relevance - this wastes lots of CPU cycles
How were the inefficiencies of traditional packet capturing solved?
Use Berkeley packet filter (BPF) which uses a user-defined filter to filter the packets beforehand and then buffer the required parts
What are the components of the BPF?
Network tap to connect copies of packets from device drivers and deliver to listening apps
Packet filter to decide accepted packets and the contents to be buffered
What are the steps of filtering packets with BPF?
1. the link level device driver calls BPF and feeds the packet through each participant process' filter
2. the filter decides whether the packet is accepted and how many bytes of the packet should be saved
3. the BPF copies the requested amount of data to the buffer
What is the BPF filter model?
A directed acyclic control flow graph to demonstrate the BPF filter function
What are the components of the BPF filter model?
Ovals are the condition to filter on, left branch represents not meeting the condition and right branch represents meeting the condition
How do sniffers use libpcap?
- packets are sent to network card
- network card driver usually sends packets to protocol stack but then also sends to packet filter
- This sent to sniffers and network monitor
What is protocol analysis?
A type of traffic analysis focused on dissecting and interpreting the specific protocols within a network packet to understand the data being transmitted
What is packet analysis?
The process of examining the protocols and contents of individual network packets or a set of packets to understand network behaviour or identify security issues
What is flow analysis?
The examination of related groups of network packets, often belonging to the same communication session, to identify patterns, suspicious activity, or reconstruct higher-layer data