18 - Cytologic Samples
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Biopsy
What is the term for a sample of body tissue taken for further investigation? It can be unknown cutaneous masses, lymph nodes, or fluids. Sample quality will be of the utmost significance.
Cytomorphology
What characteristic of the nucleated cell population is what is observed in microscopic examination of a biopsy?
No
Does diagnostic cytology replace histopathology?
Touch Imprint
What procedure, also called an impression smear, is obtained from an excision biopsy, is performed before tissue is dropped in formalin, and is done by cutting the tissue in half to expose intra-lesion cells and facilitate penetration of tissue by formalin?

Formalin
In tough imprints from excision biopsies they are cut in half in order to allow what preservative to penetrate the tissue?
Negatives
Will false positives or negatives occur in a touch imprint if ulcerated surface lesions are used?
22-25
What gauge range of needles are commonly called fine needles?
Fine
Which needles are used in aspirates to do cell harvesting instead of a core biopsy, reduce contamination with blood, eliminate superficial contamination? When doing an internal organ they are US-guided and the specimen is smeared and rapidly air-dried.
Cutaneous
What types of lumps, as well as lymph nodes, are the most common FNAs samples as the masses are easily recognized by owners and are easily palpable and aspirated by clinicians?
Capillary Sampling
What procedure uses fine needles without syringes, is not an aspirate, and is recommended for vascular tissues like liver, spleen, kidney, and thyroid? The needle is redirected peripherally to increase representation of the lesion.
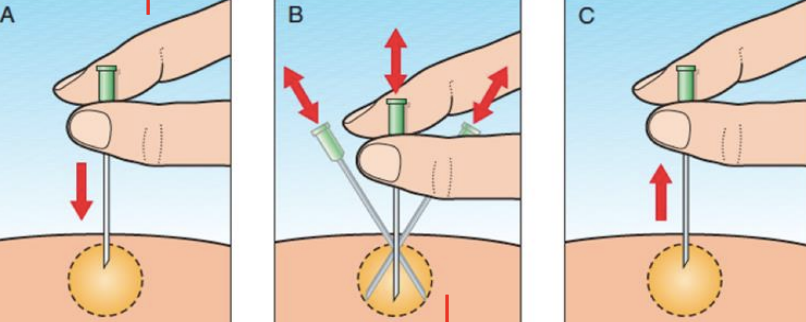
1-1.5
What length in inches is the needle used for a skin biopsy?
2.5-3.5
What length in inches is the needle used for internal organ biopsy?
5-20
About how many mLs (range) is the syringe used for fine needle aspiration biopsy? For soft masses it will be smaller.
Effusions
Fine needle aspiration biopsy is done following unsuccessful non-aspiration attempts, for collection of joint and bone marrow samples, and for the collection of what sampes?
Yes
When putting a cytology sample on a slide should you spread the sample around to show the cytomorphology?
Swab
What cytology collection technique is done on vaginal, fecal, oral, and nasal samples?
Scrapping
Which cytology collection technique is done on skin and parasitology samples?
Clean Specimen
What type of staining station is done for blood smears, effusions, and lymph nodes?
Blood smear, effusion, lymph node
What three things are done at clean specimen staining stations?
Dirty Specimen
What type of staining station is done for skin scrapings, fecal, ear, intestinal, and suspected abscess samples?
Romanowsky
What stains are used in cytology but give poor nuclear detail?
Non-diagnostic
If the cytology sample submitted is not adequate to be studies, the lab will return it as what? The presence of artifacts or a lack of cells for whatever reason are common causes of this.
Fridge
What type of artifact is shown?

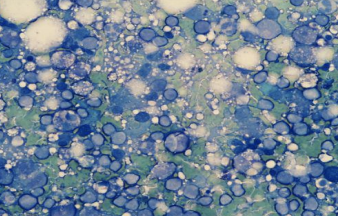
Ultrasound gel
What artifact is shown?
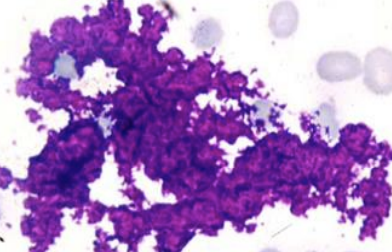
Formalin
The sample shown turned blue because it was placed too close to what preservative?
Inexpensive, Safe
Diagnostic cytology is advantageous over histopathology in some cases for what two reasons?
Inflammation, Neoplasia
One limitation of diagnostic cytology is that diagnosis is limited to one of which two results?
Positives
Reactive mesothelial cells and dysplasia can cause false what in cytology?
Negatives
Superficial touch imprints of ulcerated lesions and necrosis can cause false what in cytology?