Chapter 10 Bushong
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
5 Interactions with Matter
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
5 Interactions with Matter
classical/coherent/thompson
compton scatter
photoelectric
pair production
photodisintegration
Two Interactions Associated with Radiology
compton
photoelectric
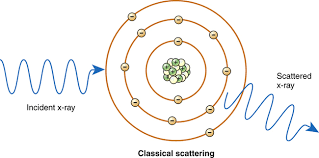
Classical Scattering
incoming x-ray interacts with target atom itself
becomes excited
produces scattered x rays
no energy is transmitted or loss
no ionization occurs
kVp Range -
10 keV or lower
at 70% kVp, 5% undergo classical scattering
Contribution to image-
image fog/noise
Interaction-
between low energy x rays and atoms
x ray loses no energy, but changes direction slightly
wavelength of incident x ray = wavelength of scattered x ray
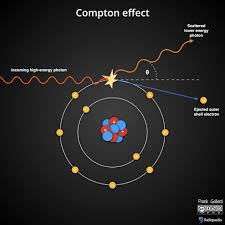
Compton Scattering
incoming x ray interacts with loose outer shell electron
ejects it
becomes a compton electron
ionizes the atom
kVp Range-
moderate diagnostic range
40-120 keV
Interaction
occurs between moderate level energy x rays and outer shell electrons
results in ionization of the target atom
changes x ray direction
reduces x ray energy
wavelength of scattered x ray is greater than incident x ray
Extra info
associated with backscatter radiation- x rays that have interacted with an object and are deflected back
probability is determined by energy of xrays, not atomic number
higher the energy, less chance of compton
probability decreases with increasing x ray energy
source of most occupational radiation (common in fluoroscopy)
contributes to image fog/noise
Photoelectric Absorption
incoming x ray interacts with inner k-shell electron
incident photon is totally absorbed and disappears
knocks out k-shell electron
becomes photoelectron
ionization occurs
Energy Range
30-120 keV
Interaction
occurs when an incident x ray is totally absorbed during ionization of an inner shell electron
the incident photon disappears and the k-shell electron that is now called a photoelectron, is ejected from the atom
Extra Info
sometimes produces characteristic x rays (secondary radiation)
probability
you need high kV and something with a high atomic # in order for photoelectric to occur
depends on atomic number of material
important to radiology: this is where we get our diagnostic info that we see on the radiograph
has a greater chance occurring in bone due to higher atomic number than soft tissue
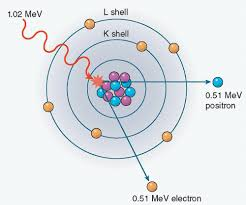
Pair Production
incoming high energy x ray interacts with nucleus of atom
incident x ray disappears
results in formation of two electrons
Energy Requirement-
1.02 meV
Interaction
occurs in x rays that have 1.02 meV or higher energies
the x ray interacts with the nuclear force field
2 electrons that have opposite charges are created
Extra Info
occurs in PET scans
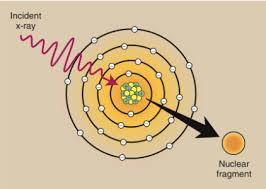
Photodisintegration
high energy x rays are totally absorbed by the nucleus
become excited
instantly emits a nucleon or nuclear fragment
Energy Requirement
10 meV
Interaction
occurs between high energy x rays and the nucleus
the x ray is absorbed by the nucleus and a nuclear fragment is emitted
Extra Info
occurs in nuclear reactors, never diagnostic imaging
Differential Absorption
different degrees of absorption in different tissues results in image contrast and formation of the x ray image
increases as the kVp is reduced
downside of this is that reducing the kVp to increase differential absorption, increases patient dose
Differential absorption occurs because of?
compton scattering
photoelectric scattering
x rays transmitted throught the patient
Differential absorption depends on what 3 factors?
atomic number of tissue
mass density of the tissue
energy of kVp
What does differential absorption look like for the three factors?
• Compton scatter
provide no useful information, only noise.
• Photoelectric
provide diagnostic information to the image (show radiopaque anatomic structures w/ high absorption characteristics.
• Transmitted x-rays
produce the dark areas on images
(show radiolucent anatomical structures)
Attenuation
defined- reduction in the # of x-rays left in an x-ray beam after it goes through tissue
• Attenuation is the product of absorption and scattering
Which two compounds help demonstrate internal organs in x rays? What type of compounds are they?
barium (atomic #56)
iodine (atomic #53)
positive compounds
Air
is also a contrast medium that is a negative contrast and is used along with barium (double-contrast examination)