Anat I - Peripheral Nervous System
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
12, 31
The peripheral nervous system has:
__ pairs of cranial nerves
__ pairs of spinal nerves
C1-C8
In general, every spinal nerve is named after vertebra under which it emerges from vertebral canal
EXCEPT _____ (hint: spinal nerve count exception)
Visceral, somatic
The afferent sensory division is compromised of the (2) ___ nervous systems
Visceral, sympathetic, parasympathetic, somatic
The efferent motor division is compromised of the (4) ___ nervous systems
Multipolar motor neuron
Efferent neuron type, axon branching
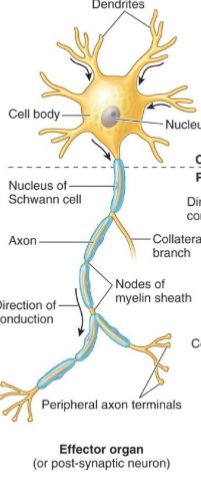
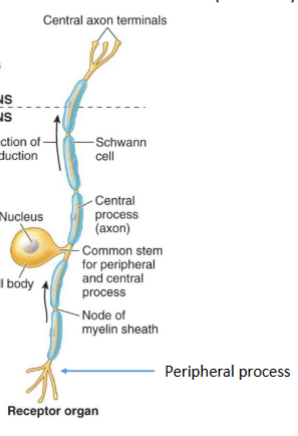
Pseudounipolar sensory neuron
Afferent neuron type, single branch
epi, dermis, superficial, deep, muscles, bones, glands, smooth
Body wall
Mostly somatic - conscious operating
__dermis, __ (skin), __ fascia, __ fascia, __ + __ (MSK)
Somewhat visceral - unconscious, involuntary
__ (endocrine component)
__ muscle
Visceral
The body cavity is all ___ (somatic/visceral)
General Somatic Afferent (GSA)
System that carries sensory information from somatic structure
General Visceral Afferent (GVA)
System that carries sensory information from visceral structure
General Somatic Efferent (GSE)
System that carries motor information to a somatic structure
General Visceral Efferent (GVE)
System that carries motor information to a visceral structure
Vertebral, Late, puberty, shorter, cervical
Spinal cord
Spinal cord sits inside the __ column
Spinal cord growth is complete in __ fetal development, however vertebral column continues to lengthen thru __
Spinal cord is much __ (larger/shorter) than the vertebral column
Although same # of segments, exception is +1 __ (spinal region) nerve
8, 12, 5, 5
Cervical* nerves = _
Thoracic nerves = _
Lumbar nerves = _
Sacral nerves = _
Conus medullaris, cauda equina
Spinal nerve roots
A = __ __ around L1-L2
B = __ __
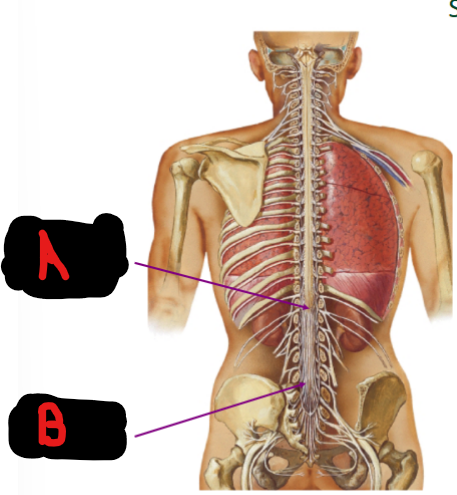
Superior, L1-L2, shorter
Spinal Cord Length
Superior to inferior look of spinal segments sees more acute angle of spinal nerve exit
End of spinal cord shifts __ (superior/inferior) in development to __ (spinal vertebrae region)
Explains why spinal cord is much __ (shorter/larger) than vertebral column
Dura mater, arachnoid mater, pia mater, denticulate
Meninges
A =
B =
C =
D = __ ligaments
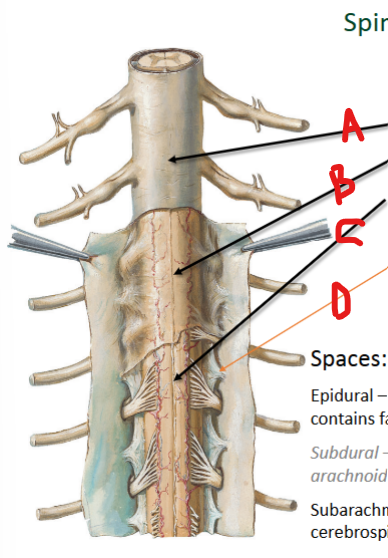
Epidural, fat, vessels
The __ space is between dura m and vertebral canal
containing __ and blood __
Subdural Space
Potential space between dura m and arachnoid m; no contents inside
Subarachnoid, CSF
The __ space is between the pia m and arachnoid m
containing ___
Subarachnoid, conus medullaris, 3-4, 4-5
To sample CSF or administer anesthesia
This is done within the __ space
Inferior to the __ __ (spine anatomical region)
Between L_ - L_ OR L_ - L_
Dorsal, lateral, ventral
A =
B =
C =
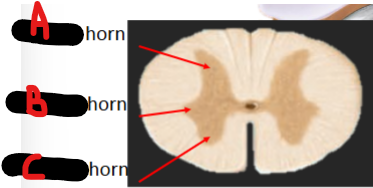
Gray matter
Transmits information laterally to and from spinal nerves
(Grey vs white matter)
White matter
Transmits information up and down spinal cord
(Grey vs white matter)
ventral root, ventral ramus, spinal nerve, dorsal root, dorsal root ganglion, dorsal ramus
A =
B =
C =
D =
E =
F =
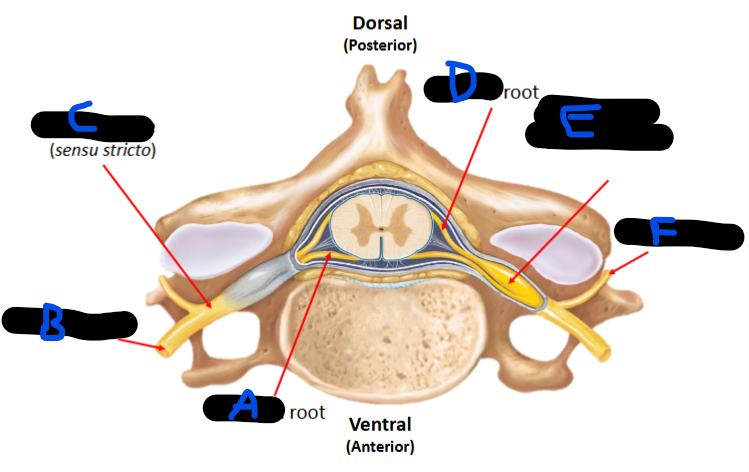
Afferent sensory, sensory
The dorsal root only uses __ (efferent/afferent) __ neurons
DRG are cell bodies of __ neurons
Efferent motor
The ventral root only uses __ (afferent/efferent) __ neurons
afferent, efferent, back, neck, body, larger
Dorsal ramus + ventral ramus
Uses both __ (sensory) and __ (motor) fibers
Dorsal R - Primarily innervates the skin and intrinsic muscles of the __ and __
Ventral R - Innervates rest of the __, is slightly __ (smaller/larger) in size than dorsal ramus
Cervical, neck
__ plexus relates to C1-C5 ; and the __
Brachial, upper
__ plexus relates to C5-T1 ; and the __ limb
Intercostal, thorax
__ plexus relates to T1-T12 ; and the __
Lumbar + sacral, pelvis, perineum, lower
The __+__ plexus relates to L1-S4 ; __, __, and the __ limb