4.3- Electricity
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
What is the circuit symbol for an open switch
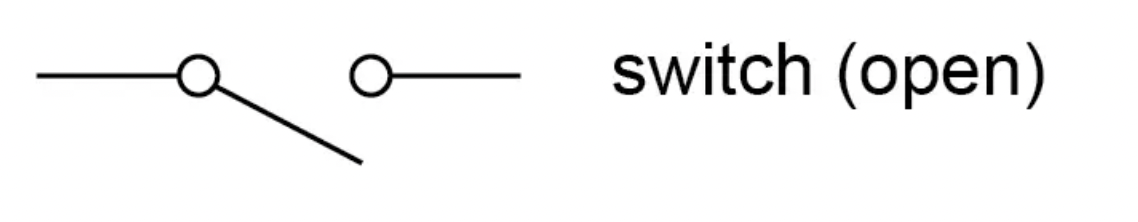
What is the circuit symbol for a closed switch
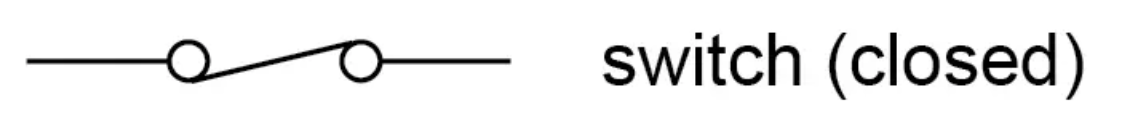
What is the circuit symbol for a cell
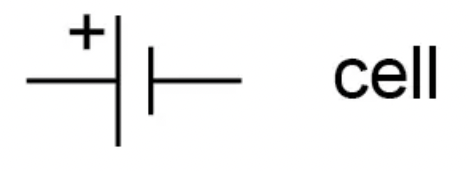
What is the circuit symbol for a battery
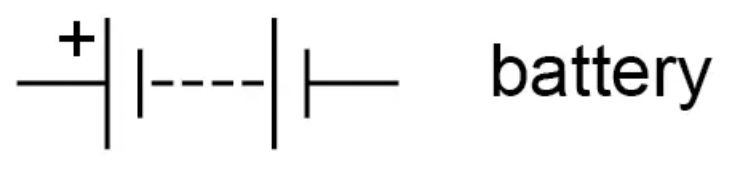
What is the circuit symbol for a diode
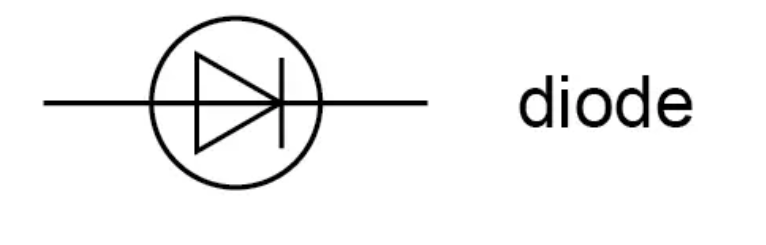
What is the circuit symbol for a resistor
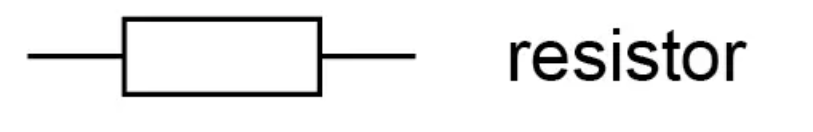
What is the circuit symbol for a variable resistor
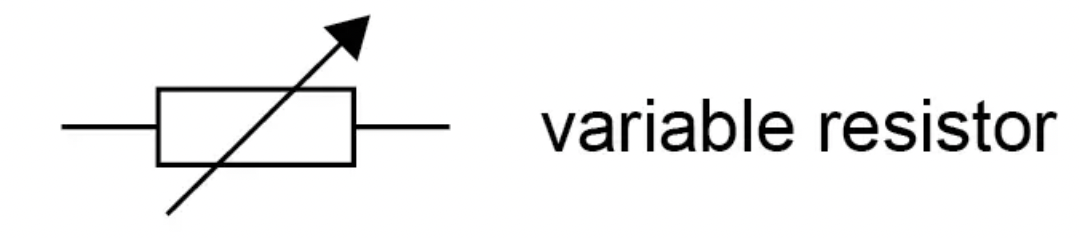
What is the circuit symbol for an LED
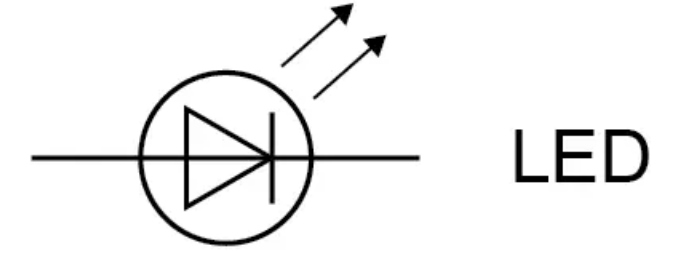
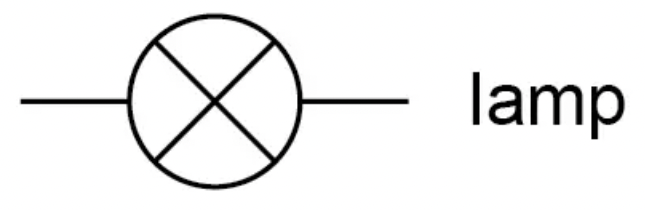
What is the circuit symbol for a lamp
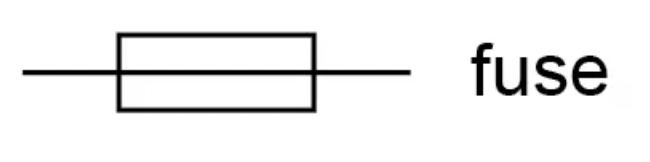
What is the circuit symbol for a fuse
What is the circuit symbol for a voltmeter
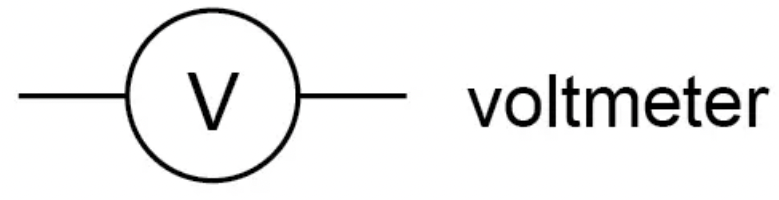
What is the circuit symbol for an ammeter
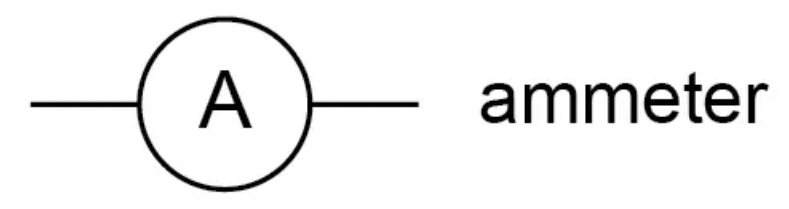
What is the circuit symbol for a thermistor
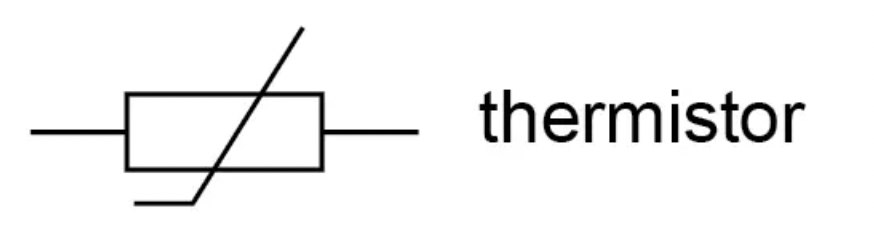
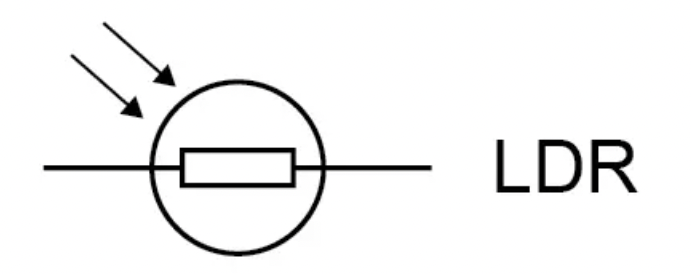
What is the circuit symbol for an LDR
What is needed for a charge to flow in a circuit
A source of potential difference
What is current
Electric current is a flow of electrical charge. The size of the electric current is the rate of flow of electrical charge
Equation for charge

Equation for potential difference

Define Potential Difference
The differences in charge that drive the movement of charge around (V)
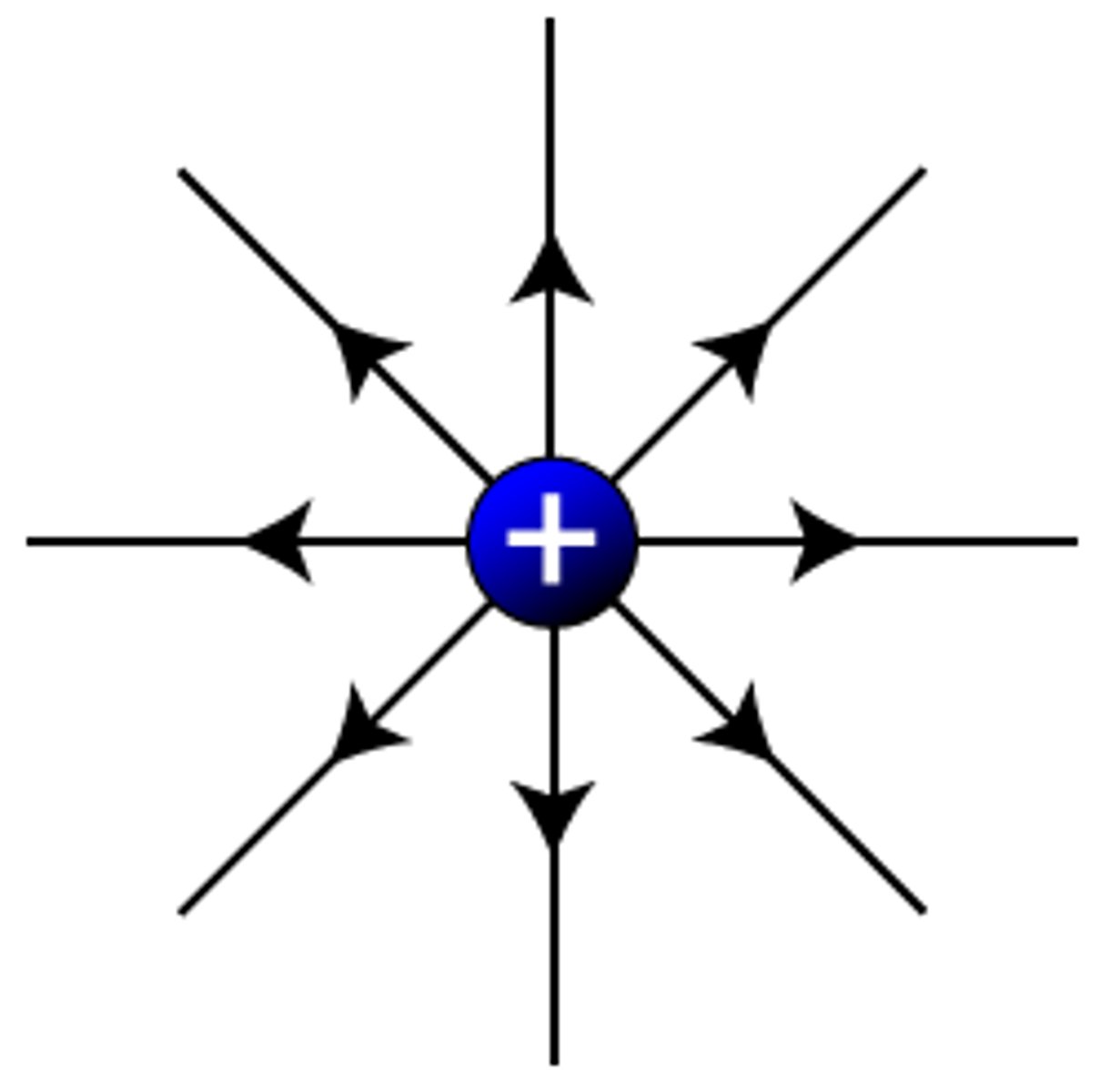
Draw the field lines of a positively charged object
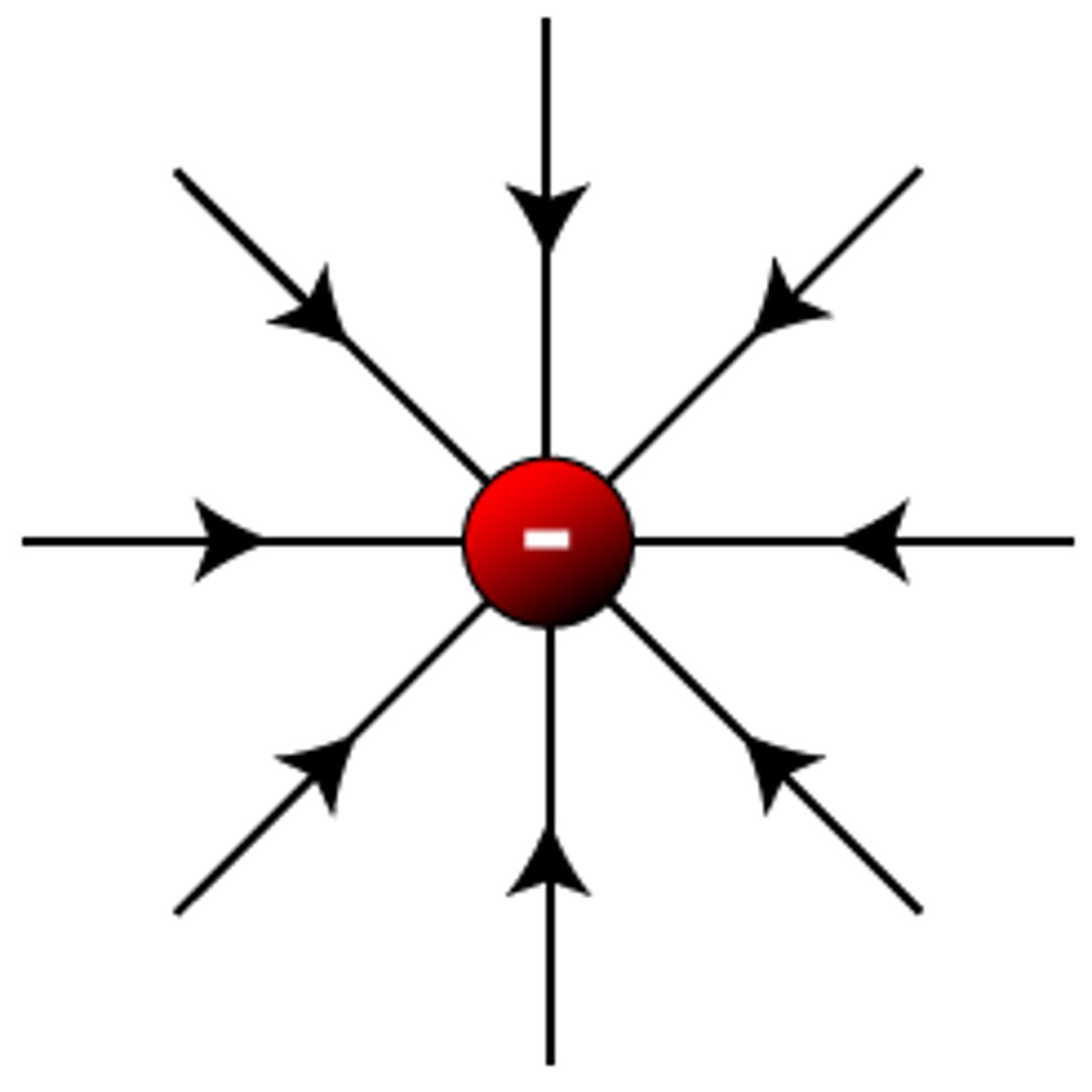
Draw the field lines of a negatively charged object
What do closer field lines mean
The electric field is stronger
What is an electric field and how do they interact
A charged object creates an electric field around itself.
The electric field is strongest close to the charged object.
The further away from the charged object, the weaker the field.
A second charged object placed in the field experiences a force.
The force gets stronger as the distance between the objects decreases.
Resistance
Anything that slows down charge flow (Ω)
What does current depend on
Resistance of component- more resistance=less current
Potential difference across the circuit- More PD= more current (for fixed resistance)
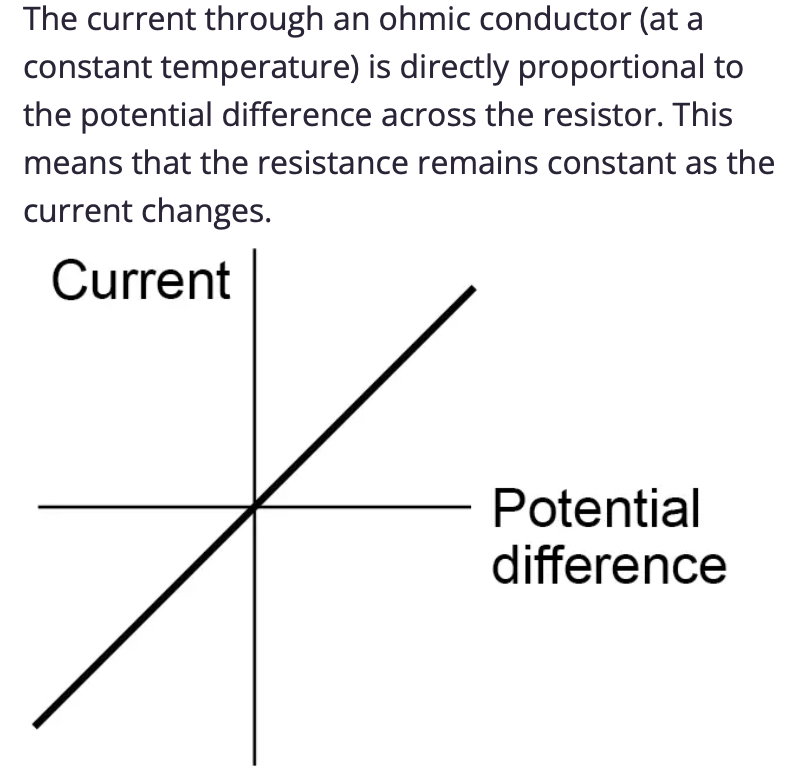
Draw the IV graph for a ohmic/fixed resistor
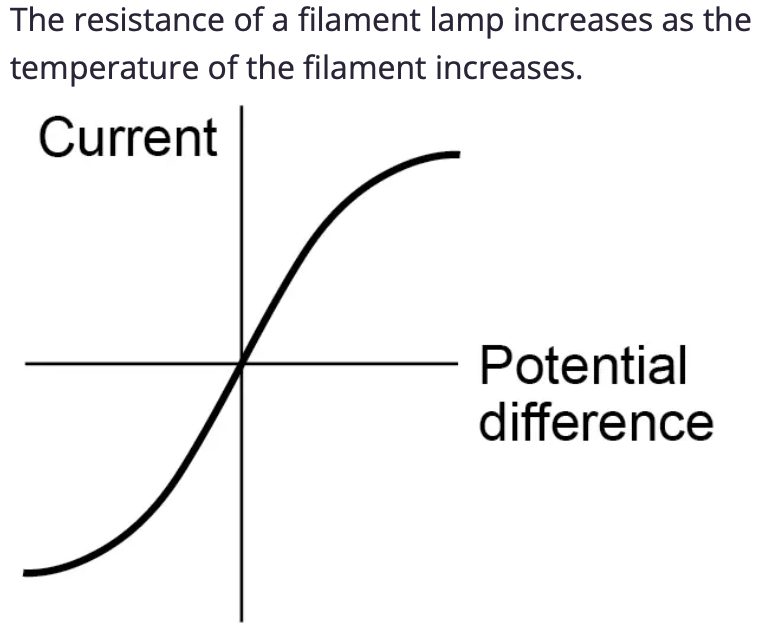
Draw the IV graph for a filament lamp
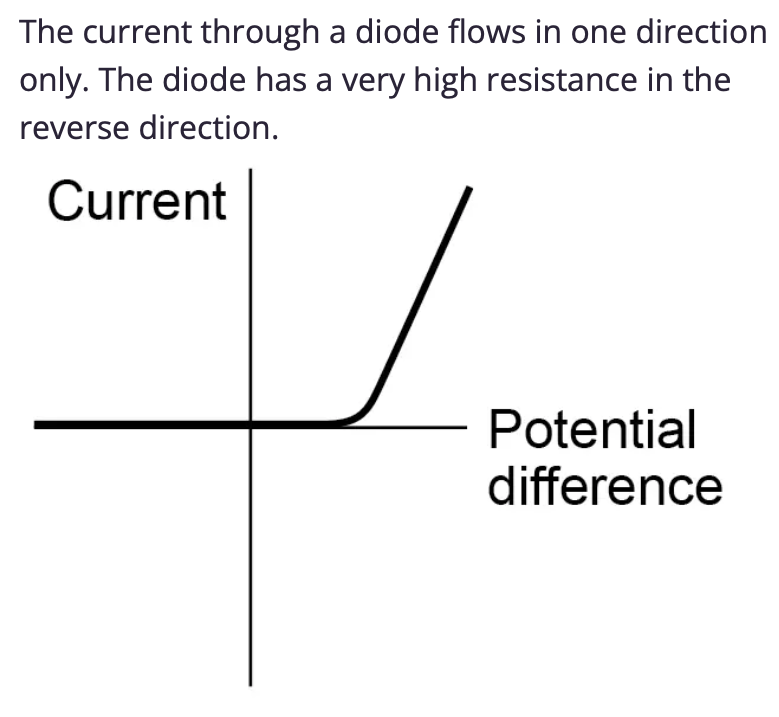
Draw the IV graph for a diode
How do LDRs work
Resistance depends on light intensity
Lower resistance in higher light intensity (BIRD)
Used in automatic night lights (eg switching lights on when it gets dark)
How do thermistors work
Resistance depends on temperature
Lower resistance in higher temperatures (TURD)
Used in thermostats
What are the rules for a series circuit
For components connected in series:
there is the same current through each component
the total potential difference of the power supply is shared between the components
the total resistance of two components is the sum of the resistance of each component.
Rtotal=R1+R2+…
What are the rules for parallel circuits
For components connected in parallel:
the potential difference across each component is the same
the total current through the whole circuit is the sum of the currents through the separate components
the total resistance of two resistors is less than the resistance of the smallest individual resistor.
Why does adding another resistor in parallel decrease the total resistance
The total potential resistance is the same across each resistor
So adding an extra resistor in parallel increases the total current entering the combination
Total resistance is equal to the battery potential difference / total current entering the combination
So the total resistance is less than before
Equations for energy

Equations for power

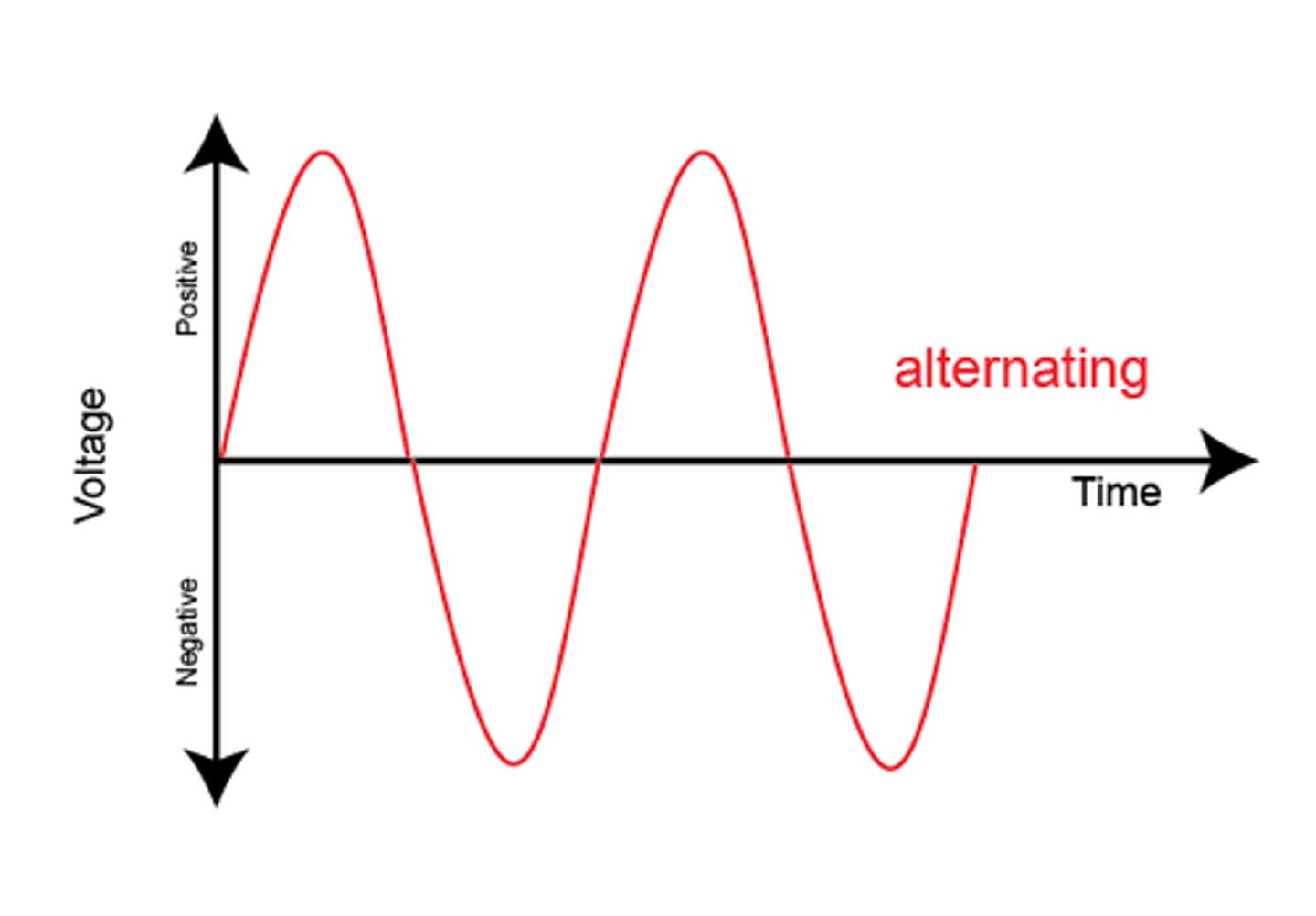
What is AC
Alternating current- current that constantly changes direction or polarity and is produced by an alternating voltage. Used in mains supply
Alternating potential difference means voltage changes direction and changes polarity
What is DC
Direct Current- Current that always flows in the same direction or polarity and is produced by a direct voltage.
Supplied by batteries
Direct potential difference means the voltage stays in the same direction, and keeps the same polarity
Frequency of uk mains supply
50Hz
Potential difference of uk mains supply
230V
Is the uk mains supply AC or DC
AC
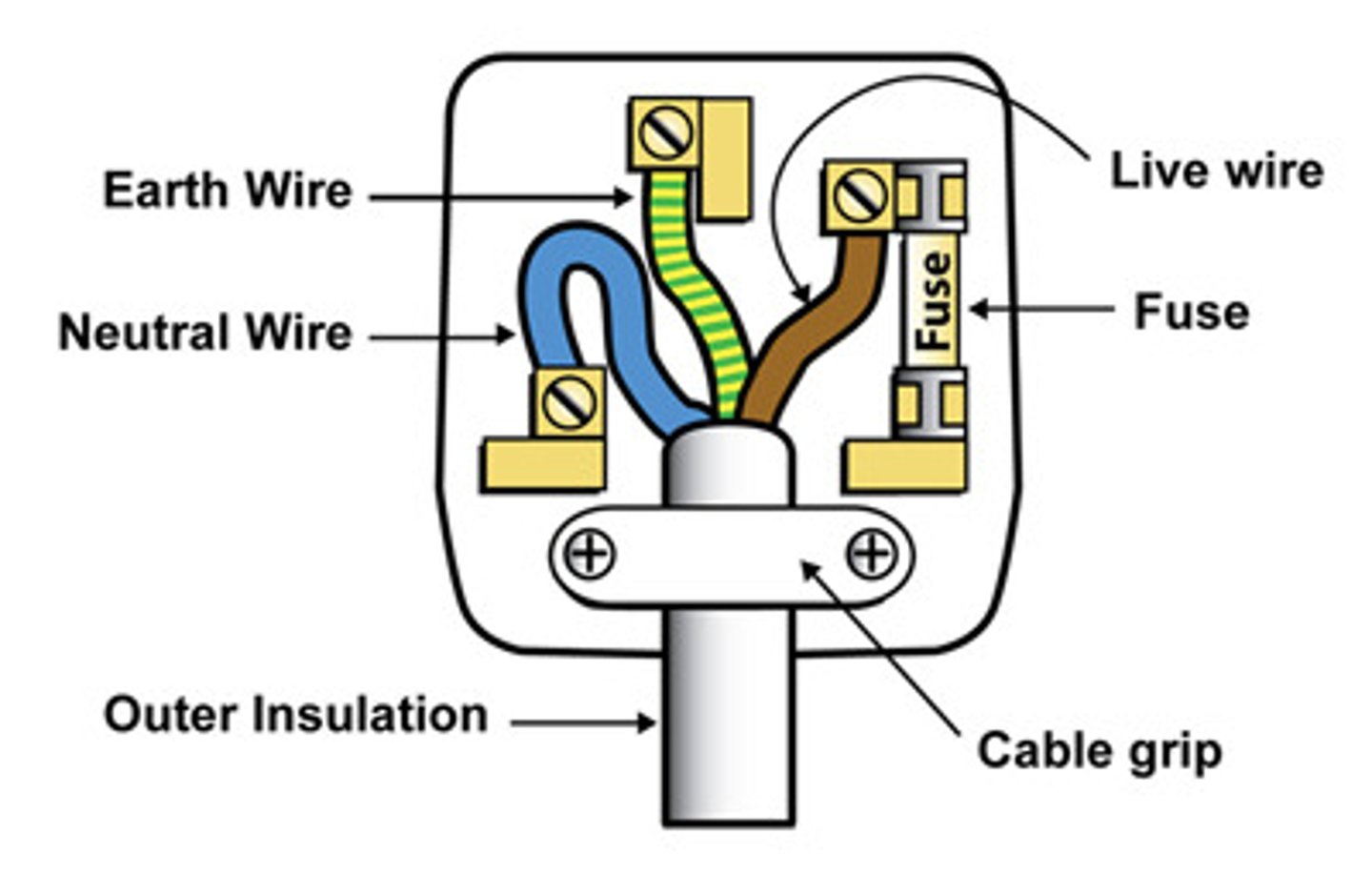
Why are the wires in a plug colour labelled
The insulation covering each wire is colour coded for easy identification
Colour, PD and purpose of live wire
- Brown
- 230V
- Provides alternating potential difference from mains supply
Colour, PD, and purpose of neutral wire
- Blue
- About 0V
- Completes the circuit- carries electrons back to the power source
Colour, PD, and purpose of earth wire
Yellow and green striped
0V
Stops appliance casing becoming live; Current only flows through the earth wire when there's a fault
Draw a diagram of a plug from the back
What is the purpose of electrical appliances
Everyday electrical appliances are designed to bring about energy transfers.
The amount of energy an appliance transfers depends on how long the appliance is switched on for and the power of the appliance.
Describe how electric shocks work
Your body has a potential difference of 0V, the wire has a PD of 230V
There is potential difference between the body and the wire
Your body provides a route to the earth
This causes current to flow through your body- can cause injury or even death
What is the national grid
The National Grid is a system of cables and transformers linking power stations to consumers.
Describe the stages in the national grid
- Power station produces electricity by burning fuel to heat water, which produces steam, which spins a turbine, and runs a generator, which converts kinetic energy to electrical energy
- A step up transformer increases the potential difference, and therefore decreases current
- This is because P lost=I2R, so less current= less power lost=more efficient; more current would heat up the wire, which would lose energy through thermal energy dissipation
- At this point, PD is about 400,000V in the power lines and pylons
- When it reaches houses, a step-down transformer decreases the PD to 230V for domestic use
How are static charges created
When certain insulating materials are rubbed against each other they become electrically charged.
Negatively charged electrons are rubbed off one material and on to the other.
The material that gains electrons becomes negatively charged.
The material that loses electrons is left with an equal positive charge.
This causes equal opposite charges between the objects
There is attraction between the objects
What is an electric spark
The passage of electrons across a gap between a charged object and the earth, or an earthed conductor.
This usually happens when the gap is small
What are the steps to an electric spark
Electric charge builds on an object
Potential difference between object and earth (at 0V) increases
When the potential difference is large enough there is a spark
The charge has been earthed