Musculoskeletal Trauma & Orthopedic Surgery: Repetitive Strain Injury, ACL Injury, Buritis, Fractures, and Osteomyelitis
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
What is repetitive strain injury?
it is when someone strains a body part several times over a period of time
What is an example of repetitive strain injury?
carpal tunnel syndrome
What are some signs and symptoms of repetitive strain injury?
pain in affected area
weakening in affected area
numbness of extremity
What are the types of ACL injuries?
partial tear
complete tear
avulsion
What are some signs and symptoms of ACL injuries?
pt. states they heard a loud pop
knee pain
What is the diagnostic test for ACL injury?
MRI
What is a surgical intervention for ACL injury?
ACL reconstruction
What are some nursing actions and interventions for ACL injury?
keep pt.’s leg elevated
administer NSAIDs when ordered
What are some teachings for patients with ACL injury?
tell pt. they do not need to have surgery right away
tell pt. to elevate their affected knee
tell pt. to ambulate on leg as tolerable
tell pt. they can take NSAIDs for pain
What is buritis?
it is inflammation of the bursae from repeated or excessive trauma, friction, gout, RA, or infection
What are buritis most commonly found?
hands
elbows
shoulders
knees
hips
What are some signs and symptoms of buritis?
warmth on affected area
pain on affected area
limited range of motion of the affected area
What is the surgical intervention for buritis?
bursectomy
What are some nursing actions and interventions for buritis?
elevate the extremity
keep the affected extremity immobilized and at rest
administer NSAIDs when ordered
What are some teachings for patients with buritis?
tell pt. to rest extremity with immobilization
tell pt. to ice affected area
tell pt. to take NAIDs when prescribed
What are fractures?
they are a break in the continuity of the bone caused by trauma, twisting as result of muscle spasm or indirect loss of leverage or bone decalcification and disease that results in osteopenia
What are some signs and symptoms of fractures?
pain/tenderness over involved area
decreased or loss of muscular strength or function
obvious deformity of affected area
crepitation and erythema
edema and bruising around affected area
muscle spasm and neurovascular impairment
What are the complications for fractures?
compartment syndrome
fat embolism
What are some signs and symptoms of compartment syndrome due to a fracture?
unrelieved or increased pain in limb
distal area of cast becomes pale, dusty, or edematous
What are some signs and symptoms of fat embolism due to a fracture?
restless
increased anxiety
dyspnea
chest pain
develop a cough
decreased stats
lung crackles
confusion
What are some surgical interventions for fractures?
fasciotomy- for compartment syndrome
amputation- for avascular necrosis
What are some nursing actions and interventions for fractures?
if suspected Compartment Syndrome: notify HPC immediately and loosen tight dressings or viable restrictive cast
if suspected fat embolism: give supplemental oxygen, make sure pt. has IV for medication, monitor vitals, monitor respiratory stats
What are some patient teachings for patients with fracture?
tell pt. to keep cast dry
tell pt. to report pain, swelling, or discoloration to distal extremity to cast
teach pt. R.I.C.E.
tell pt. to report sores or foul odor under cast
tell pt. they can dry cast with hair dryer on low, cool setting if cast gets wet
What is osteomyelitis?
it is severe infection of the bone, bone marrow and surrounding soft tissue
What are some labs and diagnostic tests for osteomyelitis?
blood & wound cultures
WBC
MRI
x-ray
CT
What is a surgical intervention for osteomyelitis?
debridement of infected bone
What are some teachings for patients with osteomyelitis?
tell pt. they may go home with a PICC Line and IV antibiotics for 4-6 weeks
tell pt. they may have to have a hyperbaric oxygen chamber at home
tell pt. they may have long term myelitis
What does a strain involve?
muscles and tendons
What does a sprain involve?
ligaments
Which picture depicts subluxation of the hip?
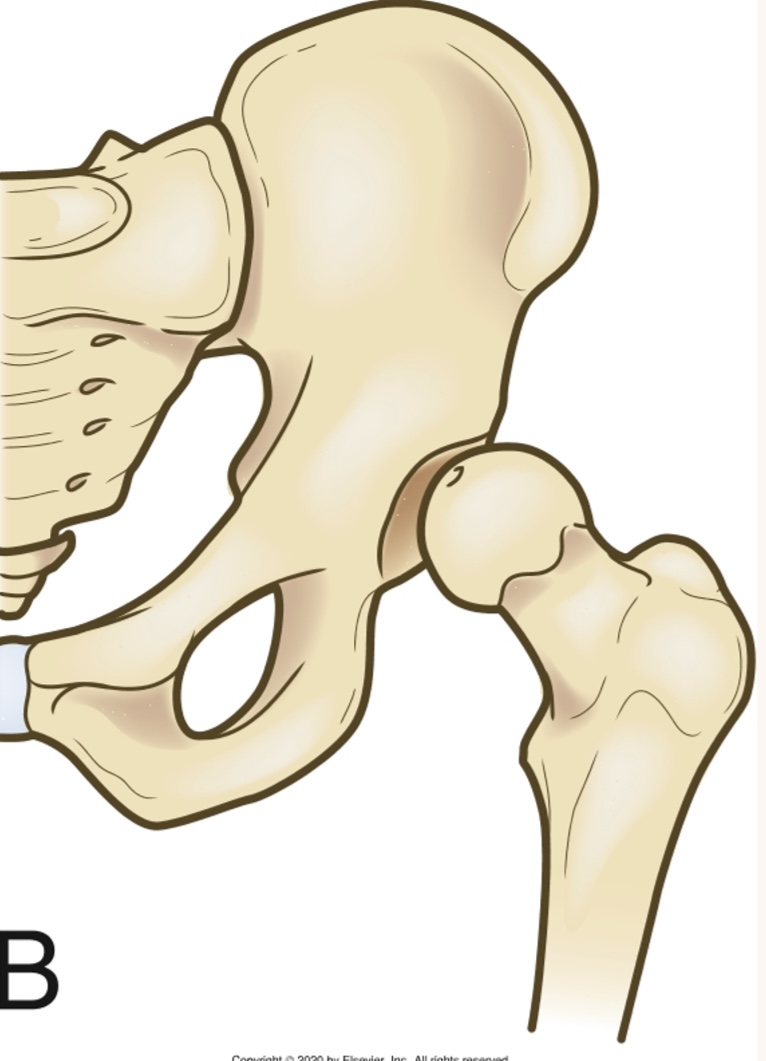
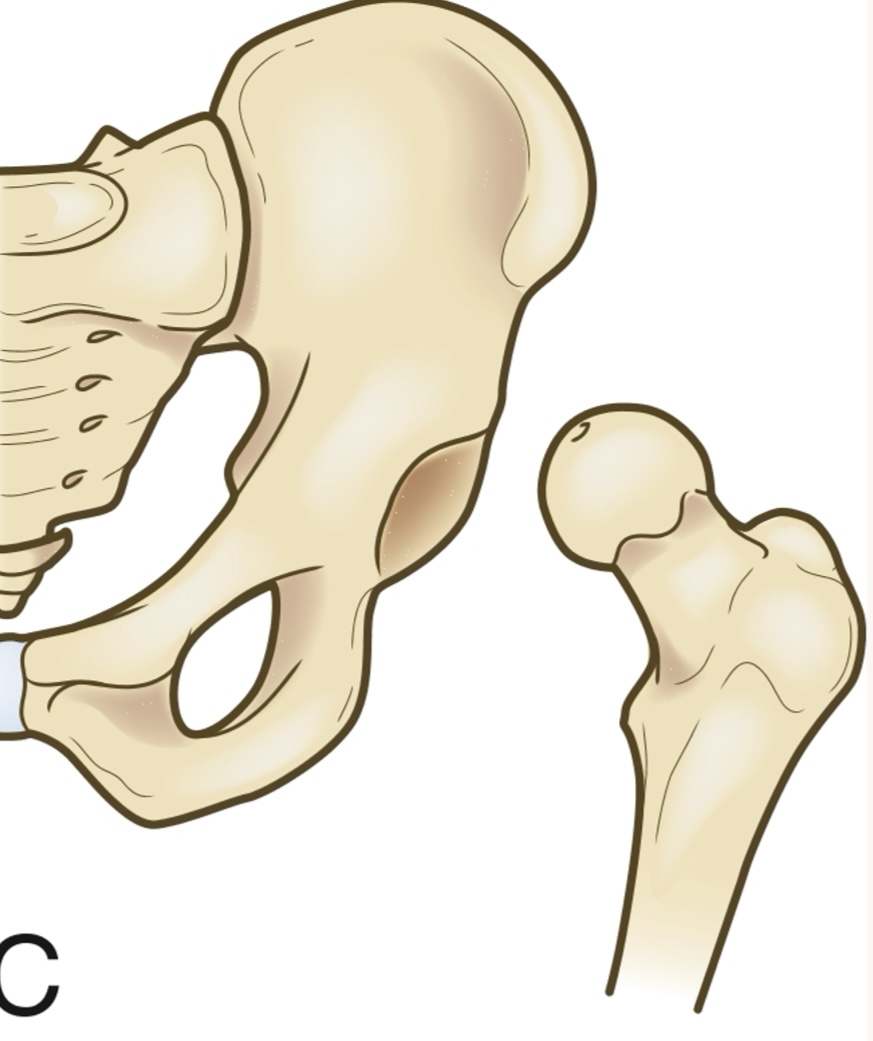
What picture depicts dislocation of the hip?
What is some patient teaching postop for Arthroscopic surgery for a torn rotator cuff?
tell pt. their arm will be immobilized for 6 weeks
tell pt. to take anti-inflammatory medications
tell pt. they can have steroid injections in shoulder
What is a complication of Arthroscopic surgery for a torn rotator cuff?
“frozen shoulder” is a complications
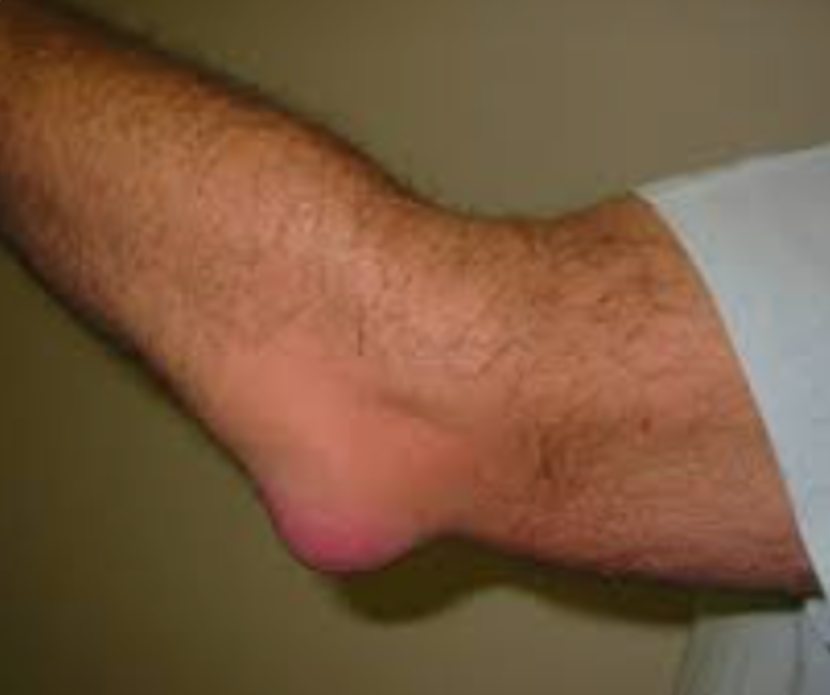
What picture depicts bursitis?
What is buck’s traction?
it is a traction that is used to treat fractures, realign broken bones, correct contractures or deformities, and for knee immobilization
What are some nursing assessments for a patient with buck’s traction?
assess for muscle spams
assess skin
monitor affected extremities for sensation
assess for proper body alignment
When is ischemia irreversible with compartment syndrome?
it is irreversible in 4-6 hours after onset