Lecture 2 - History and Methodology
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Cognitive psych
Study of the human mind
Study of the structures and the processes of the mind and that brain that take it in, transform, and use the information
Problem with studying cogpsych
Mind is unobservable
“Black Box” problem:
Can see stimulus and response but not the PROCESS
Can observe manifestations of the mind
Behavior, physiology, …
Solutions to the Black Box problem (3)
Introspectionism
Behaviorism
Cognitivism
1) Introspectionism
Examining one’s own mind through thoughts and feelings - introspect one’s self
“Thinking about thinking” - think about / observe what you are doing / thinking about
Wundt and his student Titchener,
Structuralists
Titchener - counting sensations
1) PROBLEMS with Introspectionism
Difficult to verify others’ introspections
How can you independently verify (or replicate) Titchener’s sensations? YOU CAN’T!
Private events, not public
Only accessible to the subjects
End products, not process itself
We ourselves don’t have access to everything in are minds
Automatic processes, things we’re doing that we’re not aware of
Behaviorism
Psych = “Science of behavior”
Completely doesn’t consider mind observable at all - only looks at response/stimulus/what can be directly observed
Only looks at stimuli, responses, reinforcements/rewards, rats in mazes, etc
Ignore the mind (unobservable)
SR associations
Pavlov, Watson, and Skinner
Behaviorists (3)
Pavlov
Salivation with dogs
Watson
Argued that conscious doesn’t exist, conscious is automatic (extreme)
Skinner
Skinner / Operant Conditioning Boxes
Modify animals’ behaviors due to awards and punishments, make generalizations about humans
PROBLEMS with Behaviorism
Can’t account for human behavior
Language
Not likely that simple stimulus-response associations of rewarding past experiences could account for language
Speaking new sentences - if we haven’t heard of / said it before, no past reinforcement
Too Complex
Limiting science to the observable is a bad idea
Some things in other fields we cannot see, but we know they exist, so we can’t just ignore
Cognitive Approach
Consider the stimulus and response and use them to infer how the mind is working
Study mental processes - memory, perception, decision making
Infer internal processes by observing how inputs lead to outputs
Computational view of the mind - the mind is somehow like a computer program
Independent vs Dependent variable
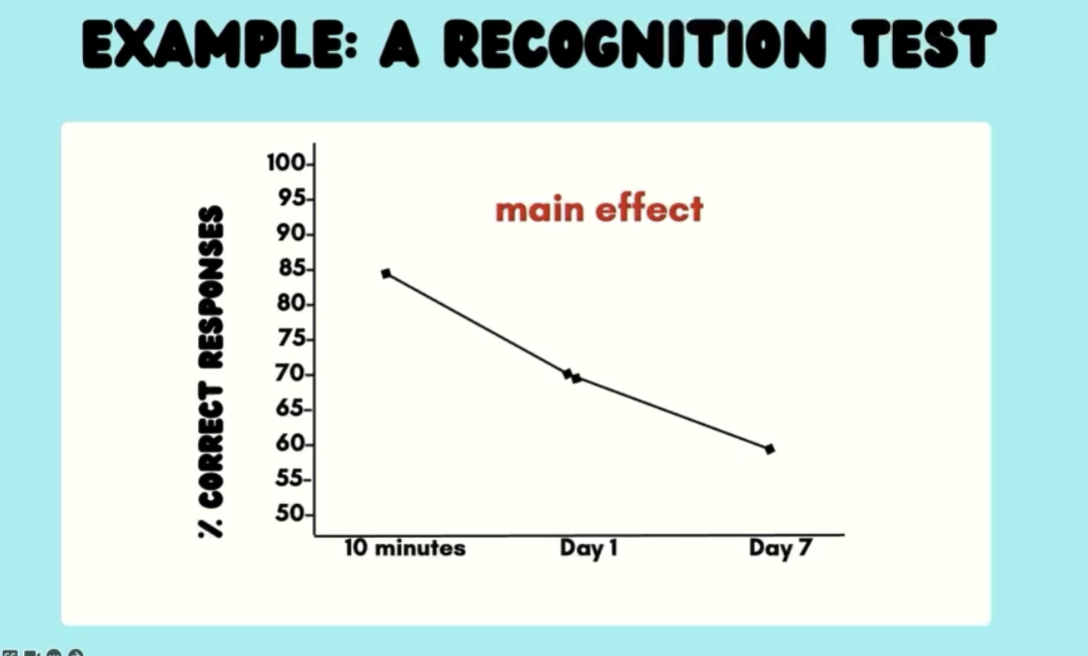
Main effect
Changing the IV has an effect on the DV
Ex: changing the delay (IV) affects the performance (DV)
If no main effect (changing delay doesn’t matter) — 0 slope / horizontal line
Anything other than a flat line is a main effect
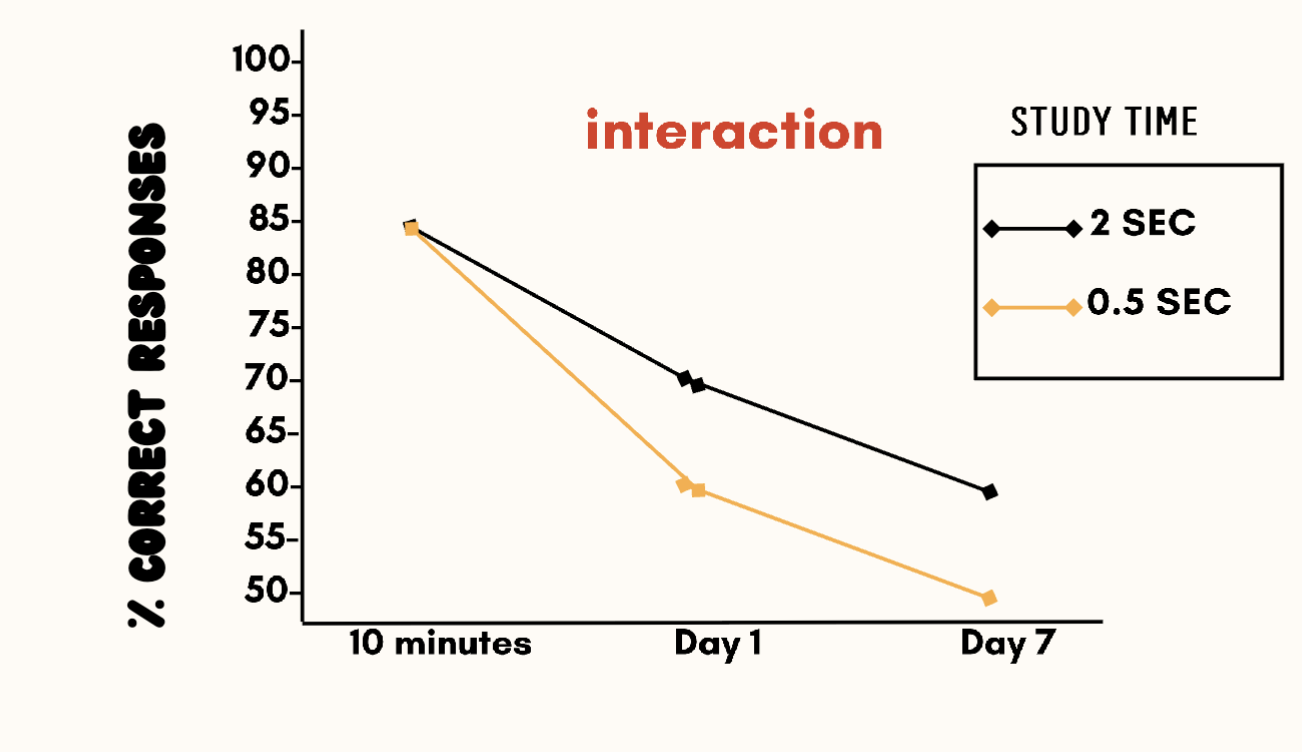
2 Main effects
Time delay and Study time = IV
Both affect DV
No interaction*
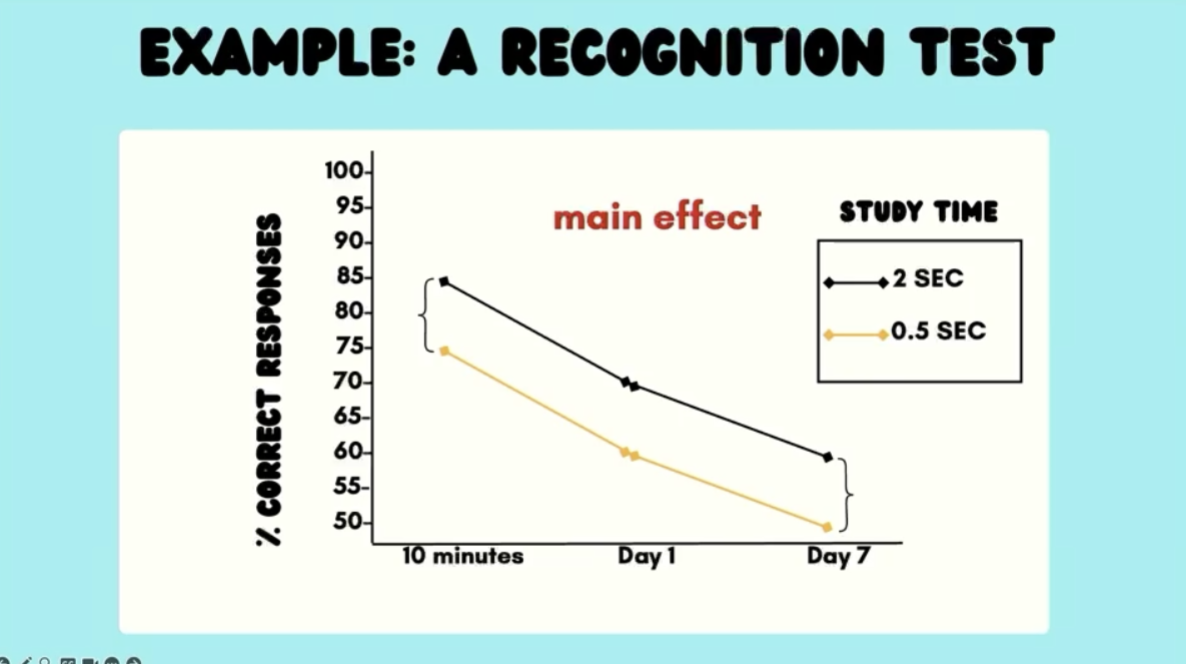
Interactions between lines
There is still a main effect here of Study time (IV 1), but affect of the Study time DEPENDS on the Delay (IV 2)
One IV DEPENDS on / affects the other IV
Mental Chronometry
Donders
Study of the time course of mental processes
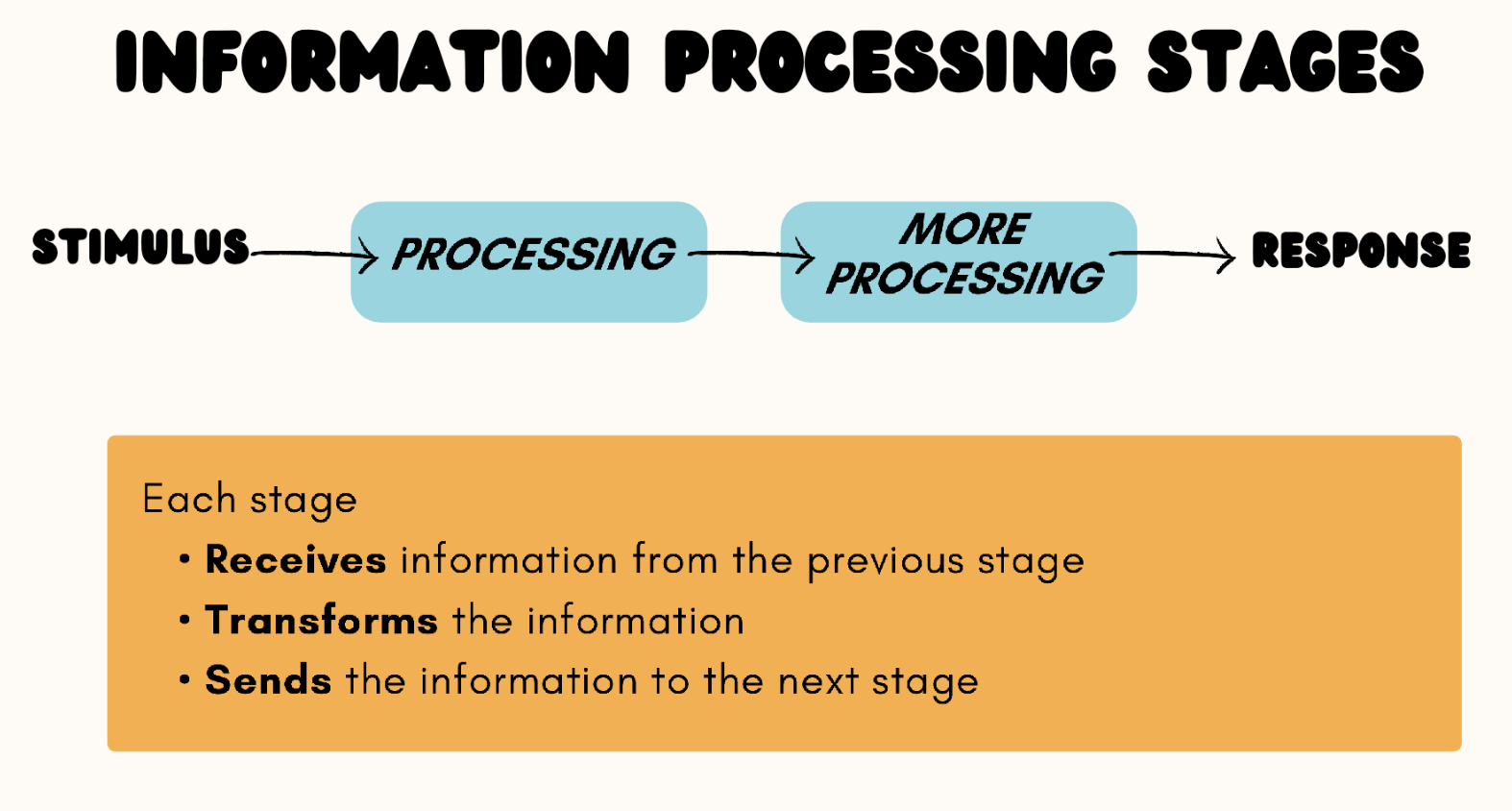
Information processing Stages
Stimulus
Processing
More Processing
Response
Each stage receives info from previous stage
Transforms info
Sends info to next stage
Multiple can occur at once ; one starts at a time that doesn’t necessarily have to be the end at the previous stage - it could still be going!
Dunder’s stages for doing a task (Subtractive Method)
Detection task
Decision task
Detection task
Red light green light, press button
Stimulus, detection, response
About 197 MS
Decision task
Red light green light, left or right hand up
Stimulus detected, decision - typically takes longer
About 88 MS decision stage
Subtractive method: Problems
Problem of Pure insertion
All stages remain the same when the new one is added
PROBLEM : Adding the decision stage may influence another stage, like detection
Assumption at Additivity
Durations of stages added together to yield reaction time
PROBLEM : Stages may operate in parallel
Assumes you already know what the stages are
YOU MAY NOT
Modern Cog Psych
Confirming evidence is weak, so try to eliminate alternative explanations
Hypothesis about how the mind works —> prediction —> experiment, prediction confirmed, BUT….
Doesn’t PROVE hypothesis is right since there could be other hypotheses that confirm the prediction
Can only support hypothesis
Easier to disprove a hypothesis
Huppert and Piercy exp 1
Amnesiacs vs Controls - want to see what memory impairments the amnesiacs had
Possible impairments: encoding, storage, retrieval
Encoding - learning, issue with “putting gas into the tank”
Storage - memory degrades quicker
Retrieval
STRAT for exp 2: See if improving encoding helps
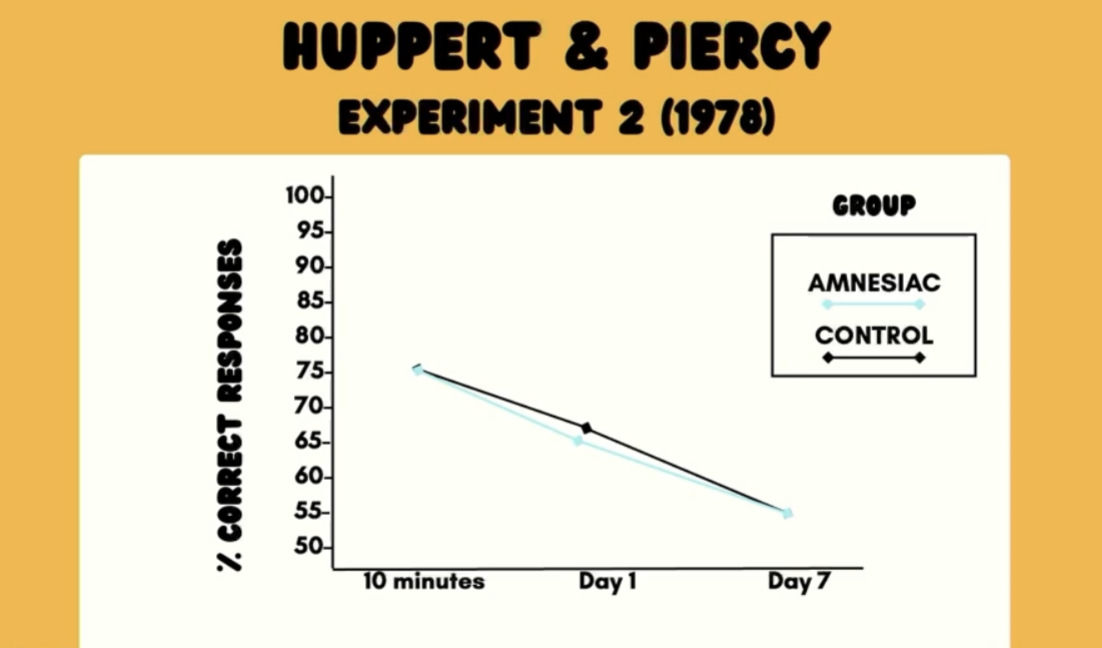
Huppert and Piercy exp 2
Allowed Controls and Amnesiacs to study for as long as they need until they get 80% correct, tested at different delays
Day 1 - same accuracy
Day 7 - same accurage
NOT A STORAGE DEFICIT!
If info was being degraded faster in the Amnesiacs, they would have lower performance
Possibly encoding or retrieval issue
MAIN EFFECT?
YES, ME of delay since lines are straight, and also…
NO, ME of group = no ; Lines are on top of each other, groups didn’t perform differently
IV: Time Delay and Group
DV: Accuracy on test