BIOL 200 Lecture 9: DNA Repair and Genome Integrity
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
skeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeet
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
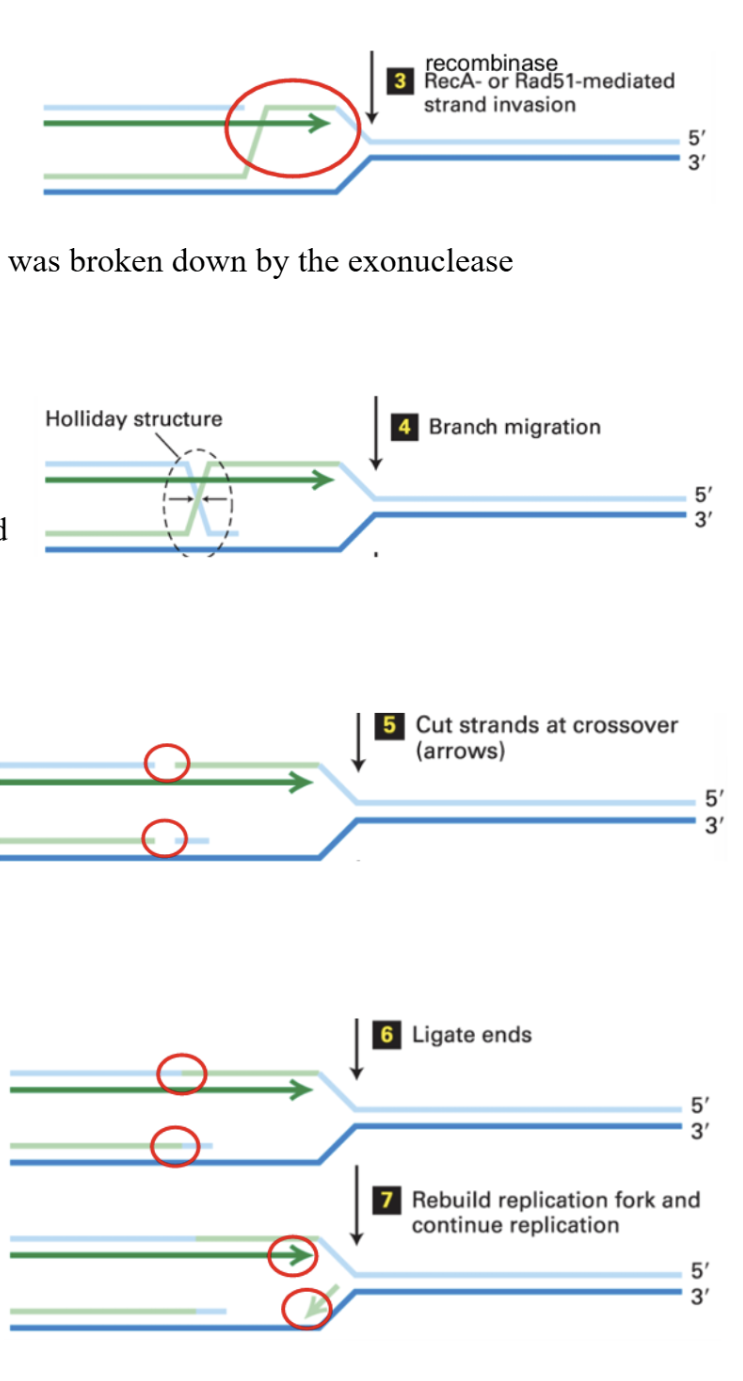
Homologous Recombination to repair single strand breaks
break generated through DNA replication, so DNA is going through a single strand discontinuity
Exonuclease will recognize 5’ end at the single strand break and remove nucleotides from it.
Newly synthesized 5’ end strand on other double strand will be ligated to parental 5’ end strand, repairing that break.
Recombinase (Rec A or Rad51) will act on the ligated 5’ end and move it up along the 5’ end strand that was broken by the exonuclease.
The upper 5’ strand is displaced downward onto the parental 3’ strand, forming an X structure.
To cut this holiday structure, specific endonucleases recognize the rare error and cut them.
Cuts are ligated
DNA replication continues
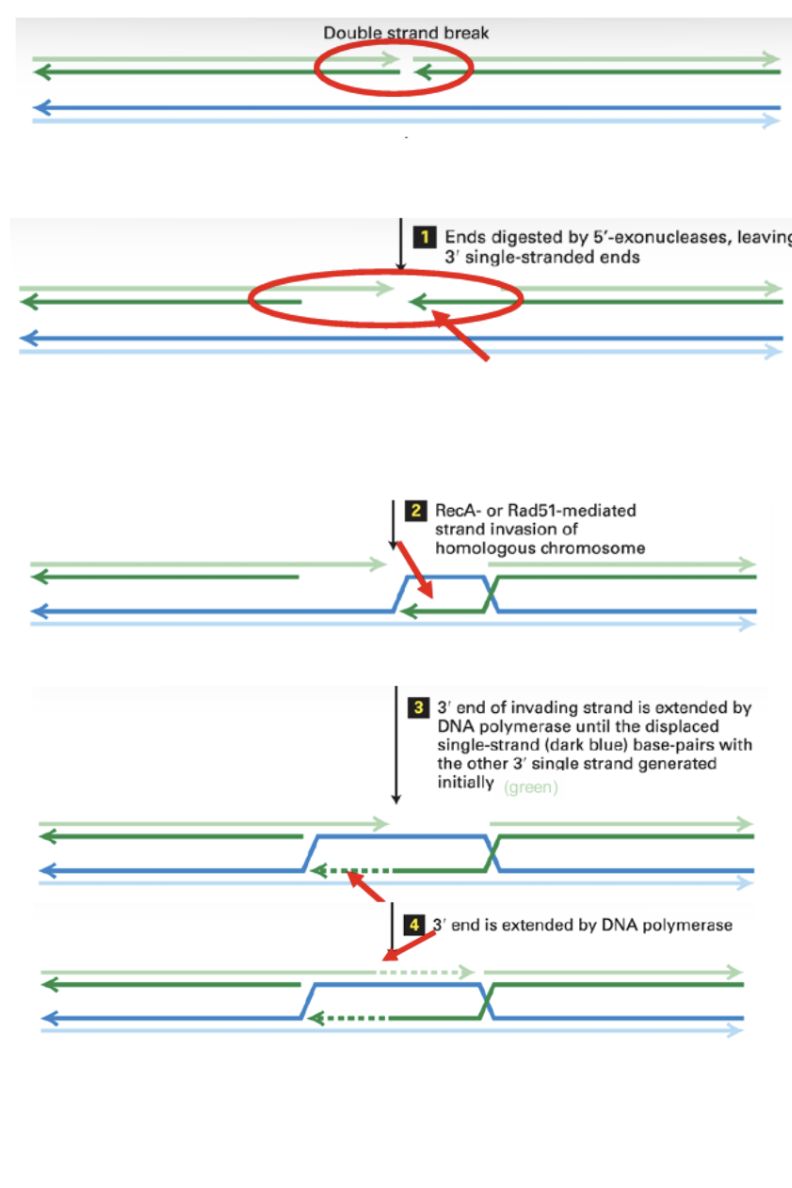
Homologous recombination to repair a double stranded break.
5’ enxonuclease breaks down nucleotides on 5’ end of both strands, leaving 3’ ends exposed.
Rec A or Rad 51 invade complementary strands, forcing 3’ end to migrate to other double strand.
This pushes one strand of non broken double strand upwards
DNA polymerase adds new nucleotides to both 3’ ends until they reach other end of strand
Both strands are ligated to form holiday structures.
Endonuclease cuts both holiday structures
Structures are resolved and now have 2 repaired double strands.
Rec A
Exonuclease found in bacteria. It wraps around single strand DNA and extends the strand. It is not understood how it searches across the genome to find the correct complementary sequence to invade.
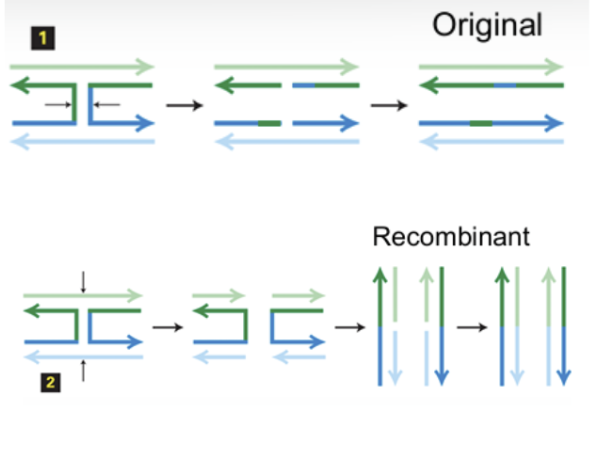
Two ways of cutting holiday structures
Horizontally, resulting in almost identical new strands to the originals as they both return to their original places.
Vertically, and after straightening, 2 DNA molecules that are mixes of both chromosomes are formed, called “recombinants”.
When and why does homologous recombination occur?
It occurs during meiosis to mix genetic material from both parents, creating variable offspring.
Non-Homologous Ends Joining general requirements
needs blunt ends to occur (equally cut double strands)
Simpler than homologous recombination
Not directed by sequence
Non-Homologous Ends Joining Process
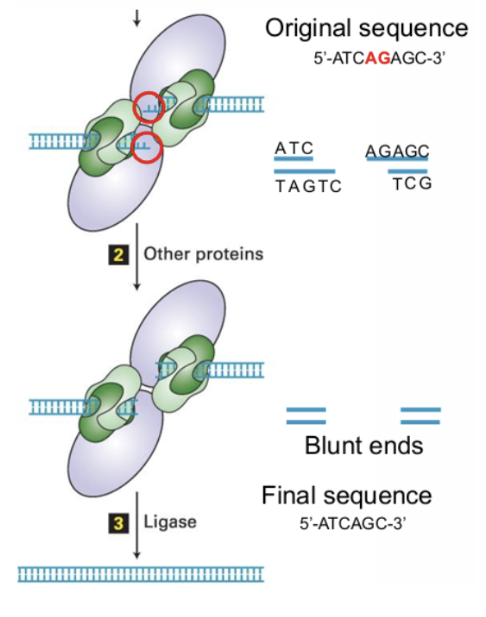
Double stranded break is recognized by protein kinase (DNA-PK) and Ku80/Ku70 heterodimer
Proteins will bind to ends of the break and bring other proteins that make the ends blunt.
As a result, the ends will either be slightly broken by exonuclease or slightly rebuilt by polymerase to make them blunt (all nucleotides paired with complementary strands)
May result in a loss of information by the removal or addition of nucleotides.
Why is Non Homologous Ends Joining Error-prone?
cuts nucleotides out of sequence to create blunt ends
can cause chromosomal translocations (rearranging between nonhomologous chromosomes)
Not driven by sequence similarities
When in the cell cycle is homologous recombination used?
since it requires a pair of chromosomes, it can occur after DNA replication has occured
S phase, G2 phase, or mitosis
When in the cell cycle is Non-Homologous Ends Joining used?
G1 (between cell division and replication) since cells only have one copy of their genome
Used in mismatch repair and translesion synthesis
What effects does chemotherapy have on DNA?
Generates different types of lesions
Causes single and double strand breaks
modifies bases
Adds bulky additions to bases repaired by nucleotide excision.
sticks proteins covalently to DNA.
OVERALL: it targets tumour cells by causing errors in their rapid DNA replication, eventually making them die.
Are humans good at repairing DNA?
No, they cannot withstand high ionizing radiation (discovered after chernobyl).