Chapter 23: Intro to Organometallic Compounds
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Preparation of RLi
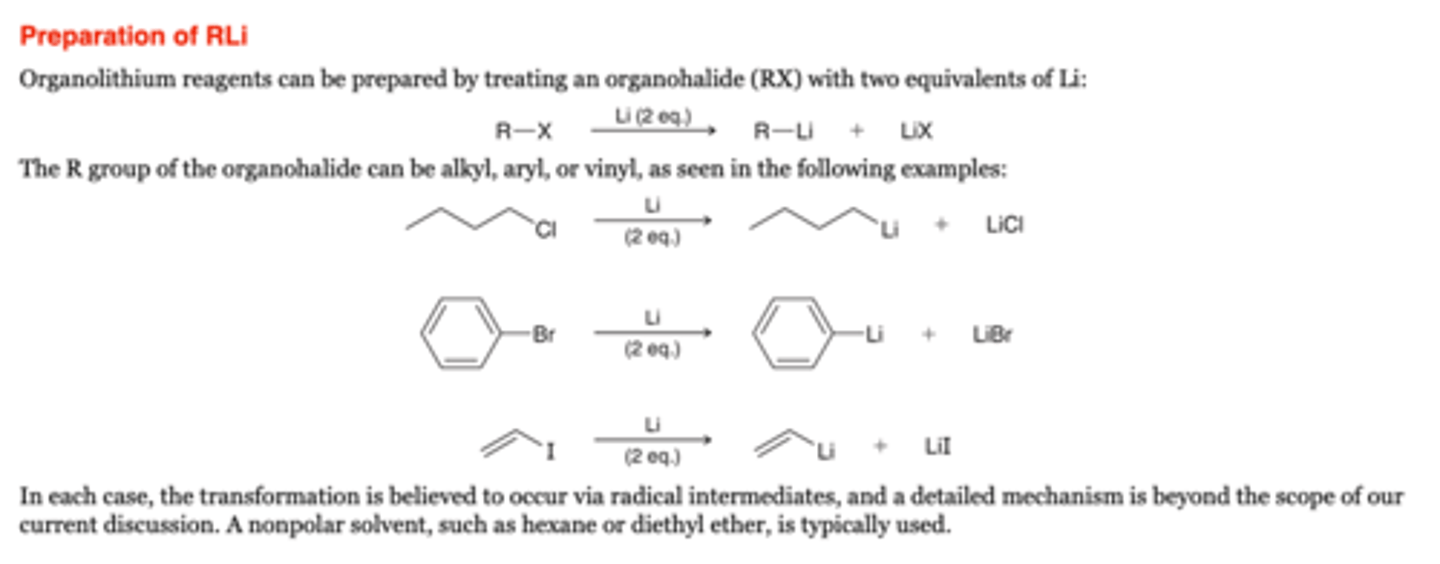
-Organolithium reagents can be prepared by treating an organohalide (RX) with two equivalents of Li
-The R group of the organohalide can be alkyl, aryl, or vinyl,
Reagents
-RX with Li (2 eq)
Preparation of RMgX
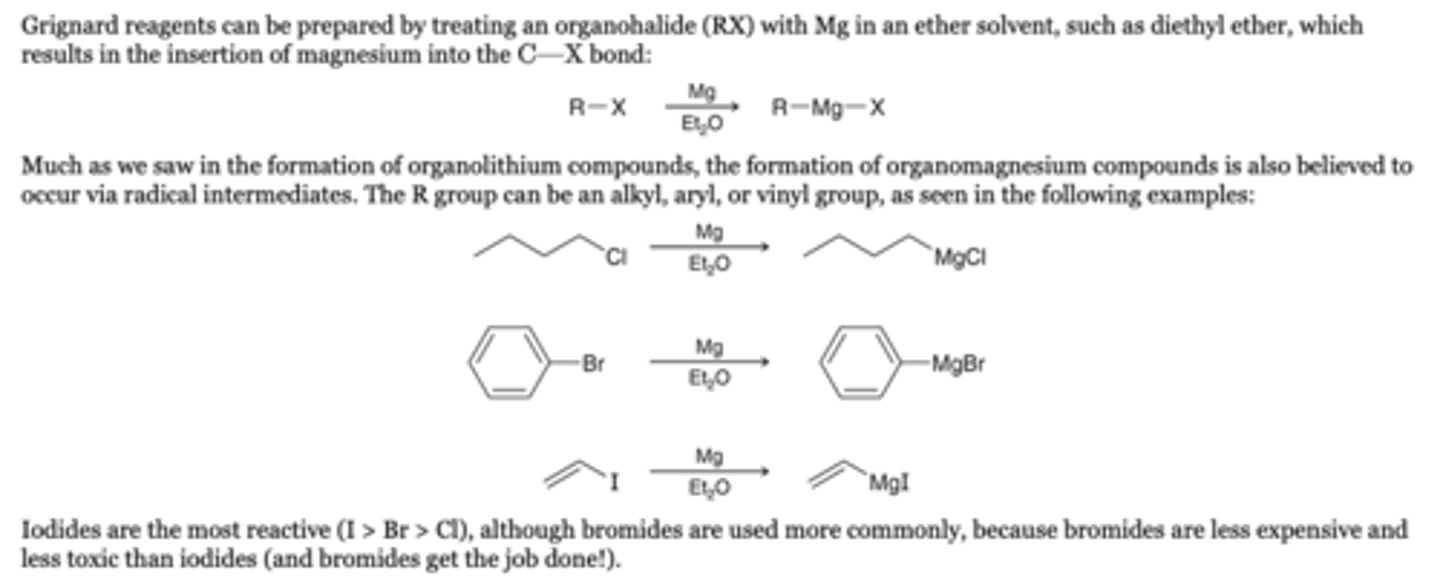
-Grignard reagents can be prepared by treating an organohalide (RX) with Mg in an ether solvent, such as diethyl ether, which results in the insertion of magnesium into the C-X bond
-The R group can be an alkyl, aryl, or vinyl group
-For less reactive halides, such as vinyl chlorides, tetrahydrofuran (THF) can be used in place of diethyl ether
Reagents
-Mg, Et2O
RLi and RMgX are strong bases
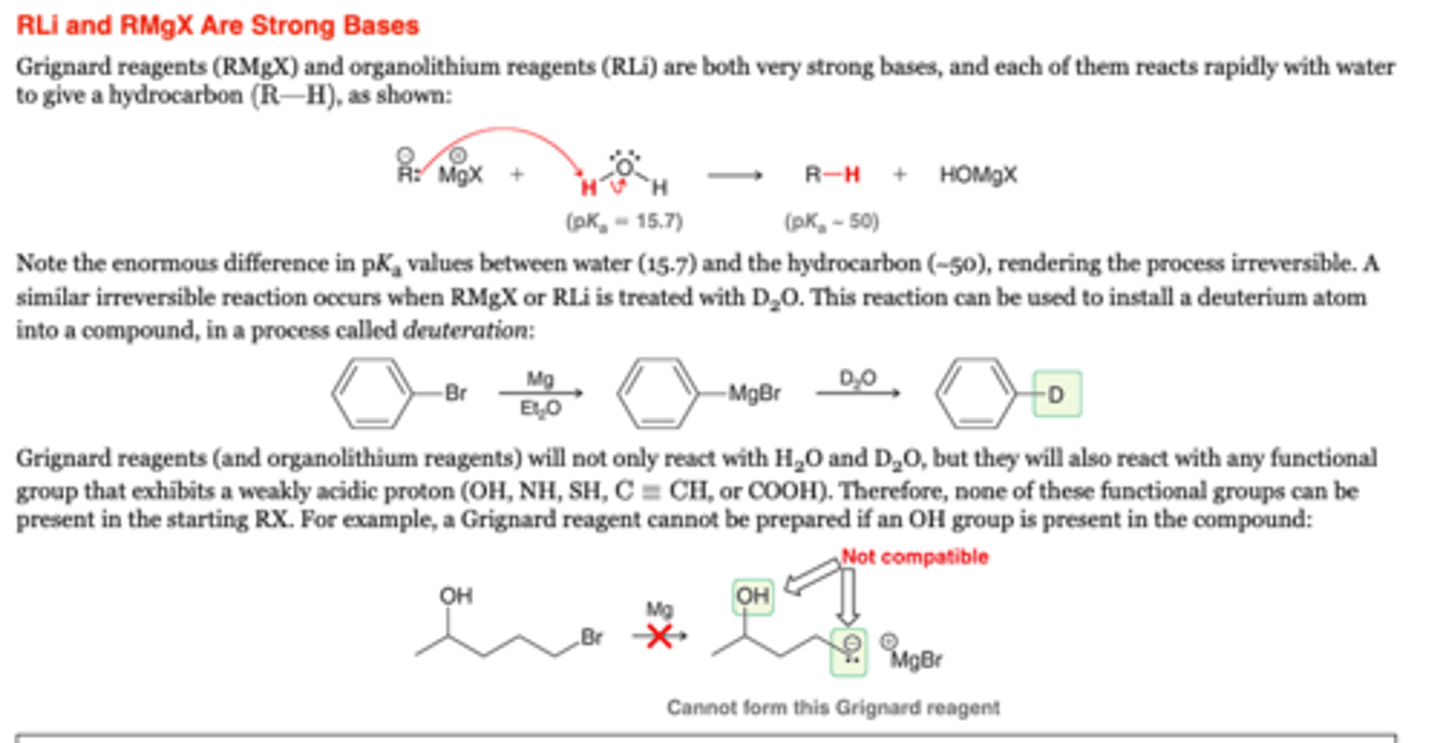
-Grignard reagents (RMgX) and organolithium reagents (RLi) are both very strong bases, and each of them reacts rapidly with H2O to give a hydrocarbon (R-H)
-A similar irreversible reaction occurs when RMgX or RLi is treated with D2O. This reaction can be used to install a deuterium atom into a compound, in a process called deuteration
-Grignard reagents (and organolithium reagents) will not only react with H2O and D2O, but they will also react with any functional group that exhibits a weakly acidic proton (OH, NH, SH, , or COOH). Therefore, NONE of these functional groups can be present in the starting RX. For example, a Grignard reagent cannot be prepared if an OH group is present in the compound
Prep of Gilman Reagents
-These reagents can be prepared by treating an organohalide with lithium to give an organolithium, followed by treatment of the organolithium with CuX
-The R group can be alkyl, aryl, or vinyl,
Reagents
1. Li (2 eq)
2. CuX (0.5 eq)
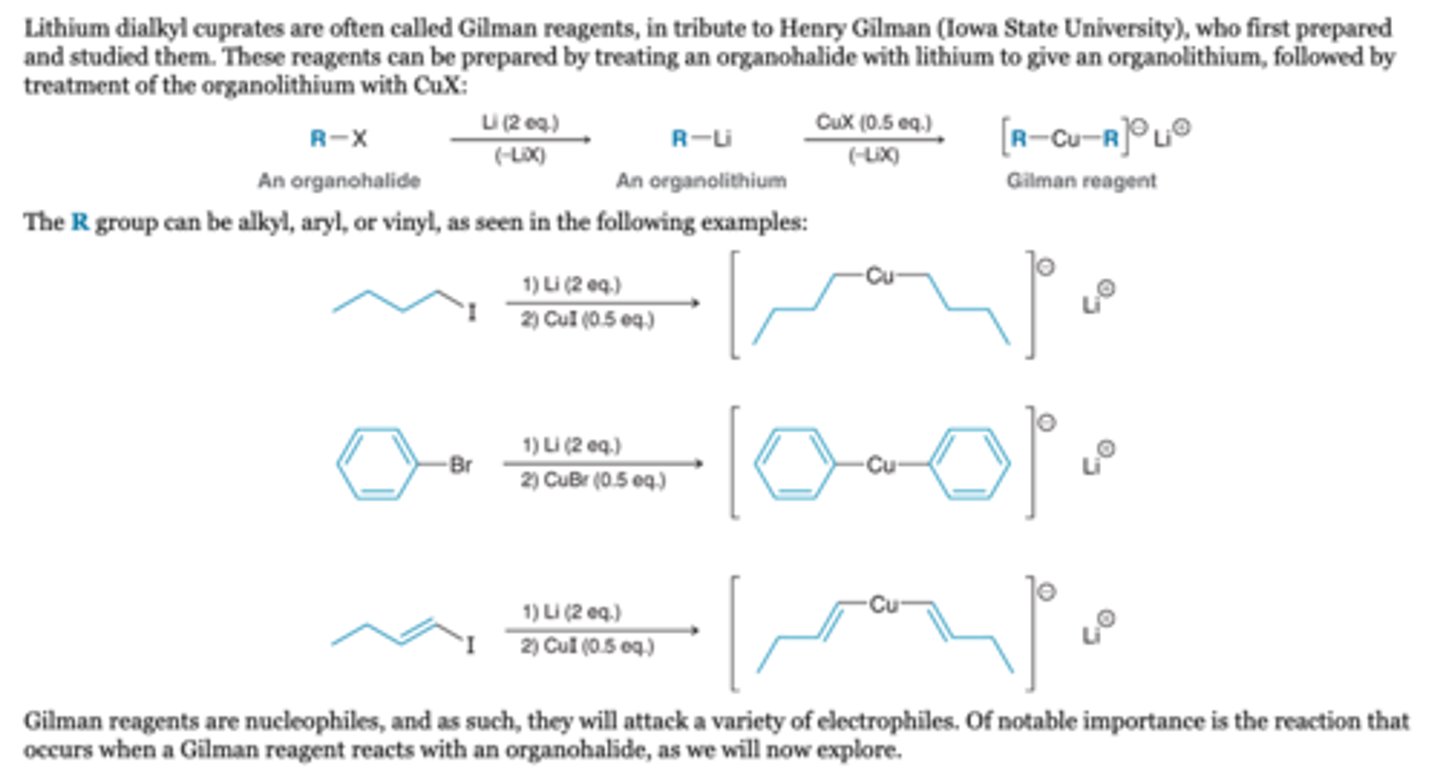
Reaction with RX (coupling)
-Gilman reagents (R2CuLi) react with organohalides (R′X) to give a product in which the R and R′ groups have been coupled together
RX
-The halogen can be I, Br, or Cl, with iodides being the most reactive and chlorides being the least reactive (I > Br > Cl). The R′ group of the organohalide (R′X) can be methyl, primary, vinyl, or aryl, as seen in the following general examples:
-R′X cannot be a tertiary alkyl halide or secondary, however, some secondary alkyl halides, such as cyclic halides, are observed to couple effectively with Gilman reagents
R2CuLi
-In each of the general reactions shown above, R (of R2CuLi) can be alkyl, aryl, or vinyl, giving rise to a wide variety of bonds that can be made with this process. During the process, only one of the two R groups (from R2CuLi) is coupled to R′ of the organohalide (R′X).
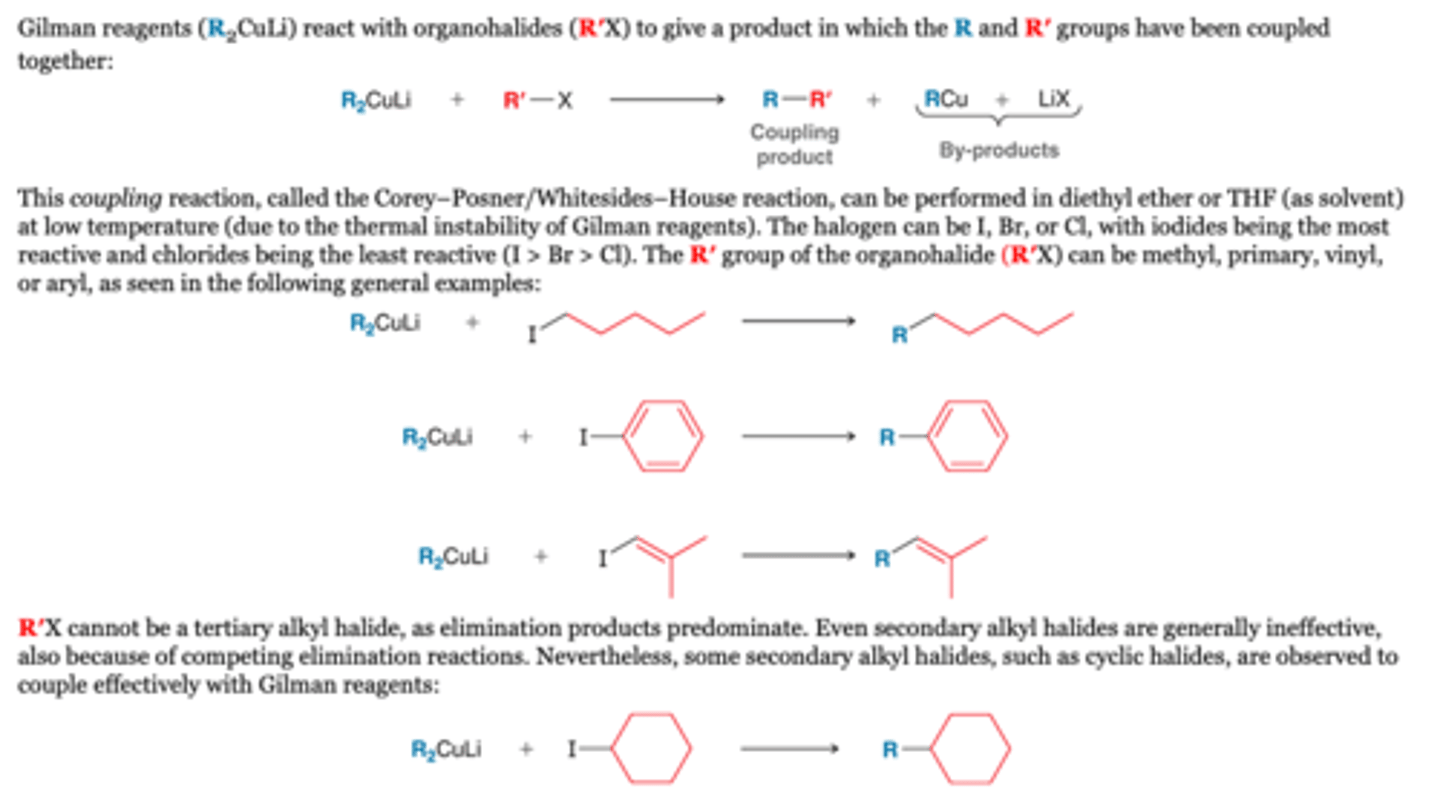
Reaction with RX (coupling): Functional Groups
-The coupling process can occur in the presence of a variety of functional groups, including keto, ester, or amide groups. For example, consider the following transformation, in which the presence of the ester group does not interfere with the reaction
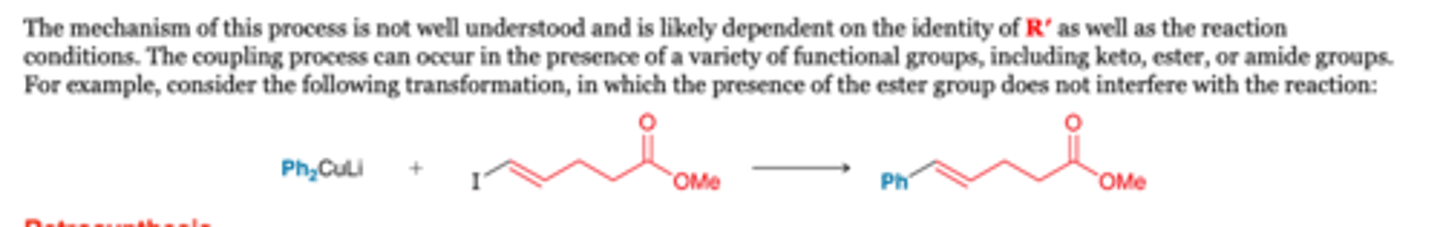
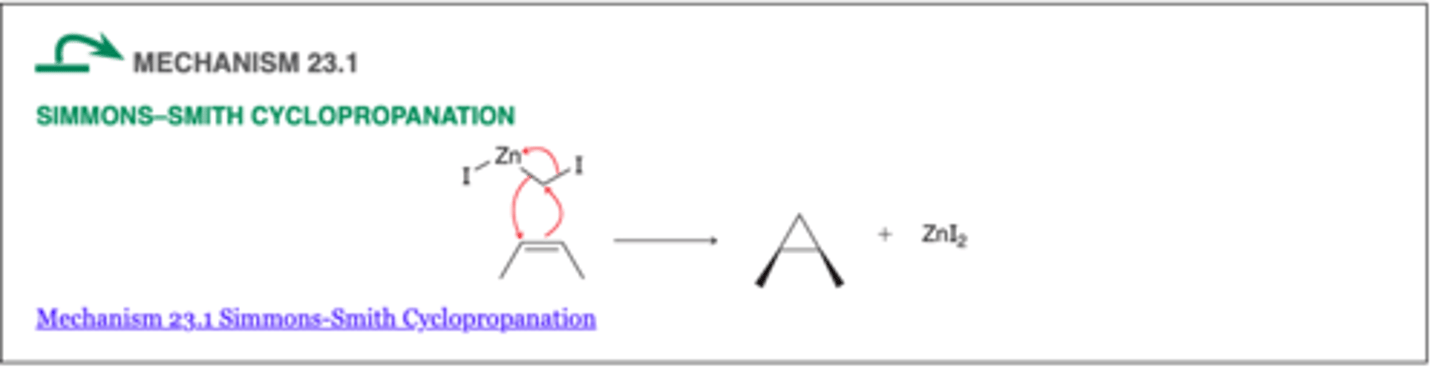
The Simmons–Smith Reaction and Carbenoids: Iodomethyl zinc iodide (ICH2ZnI)
-Simmons and Smith demonstrated that alkenes react with ICH2ZnI to form a three-membered ring. This process is called cyclopropanation
-Notice that one methylene (CH2) group is added across the π bond, thereby converting the alkene into a cyclopropane derivative
Reagents
CH2I2, Zn-Cu, Et2O
The Simmons–Smith Reaction and Carbenoids: Carbenes
-When dichlorocarbene is prepared in the presence of an alkene, the carbene reacts with the alkene to give a cyclopropane ring,
Reagents
t-BuOK, CHCl3

SIMMONS-SMITH CYCLOPROPANATION
Suzuki Coupling
-For a Suzuki coupling, the coupling partners are an organoboron compound (RBY2) and an organic electrophile (R′X), giving (R-R) as the coupling product
Reagents
Pd(PPH3)4, NaOEt

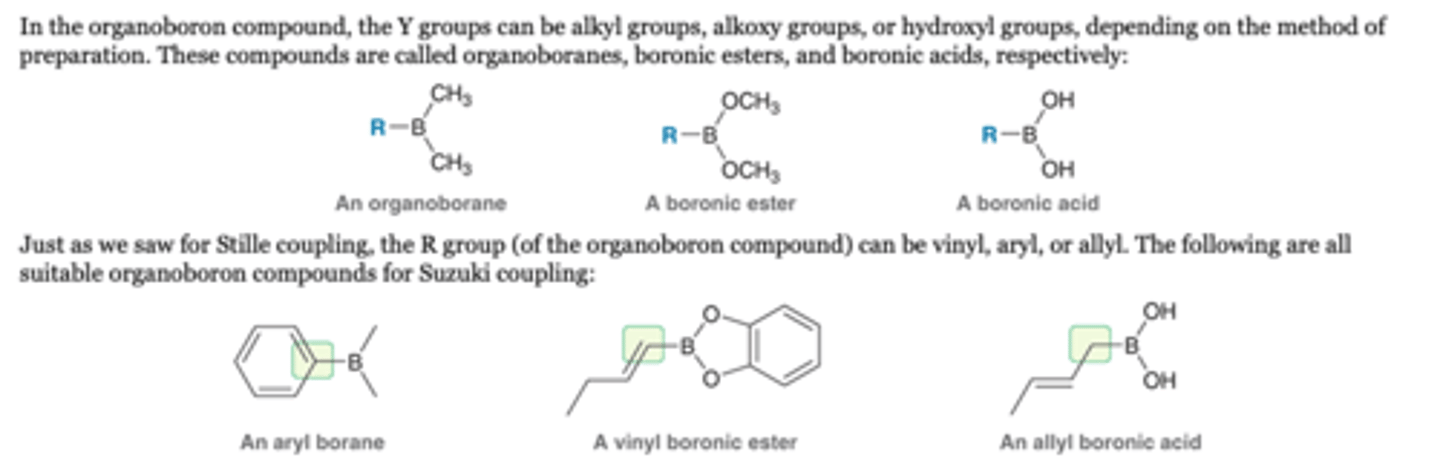
Suzuki Coupling: organoboron
Y groups
In the organoboron compound, the Y groups can be alkyl groups, alkoxy groups, or hydroxyl groups
R Group
the R group (of the organoboron compound) can be vinyl, aryl, or allyl
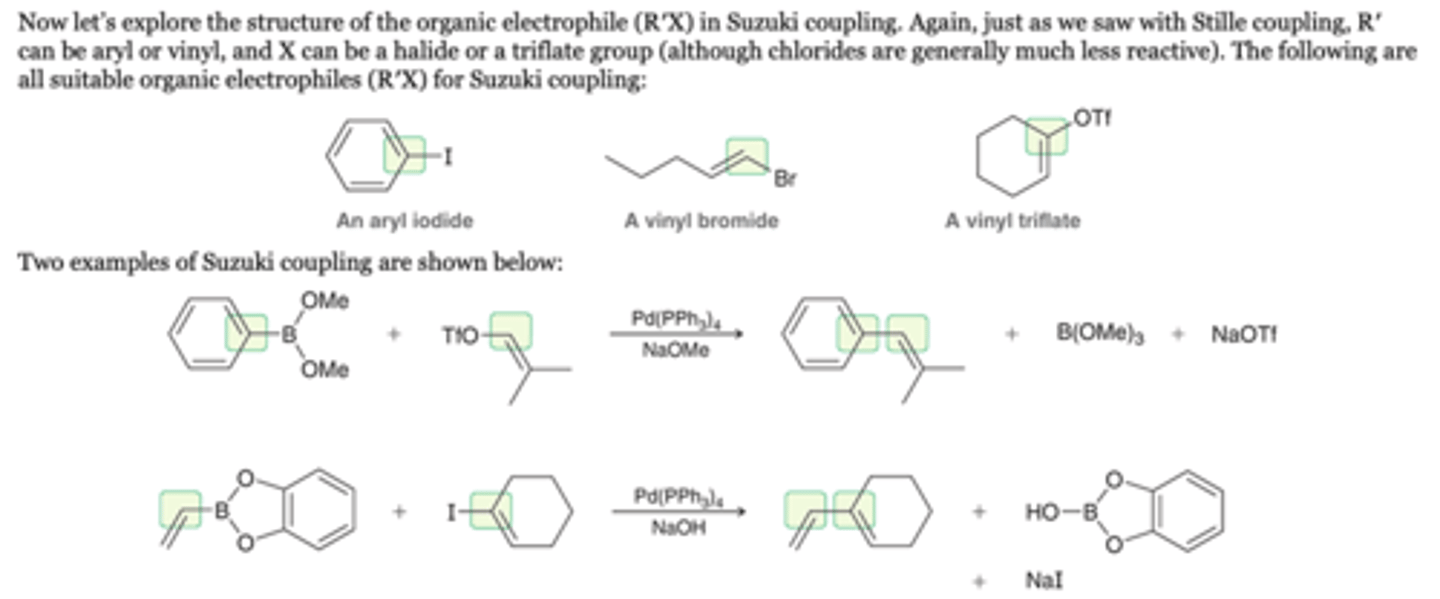
Suzuki Coupling: RX
R′ can be aryl or vinyl, and X can be a halide or a triflate group (although chlorides are generally much less reactive).
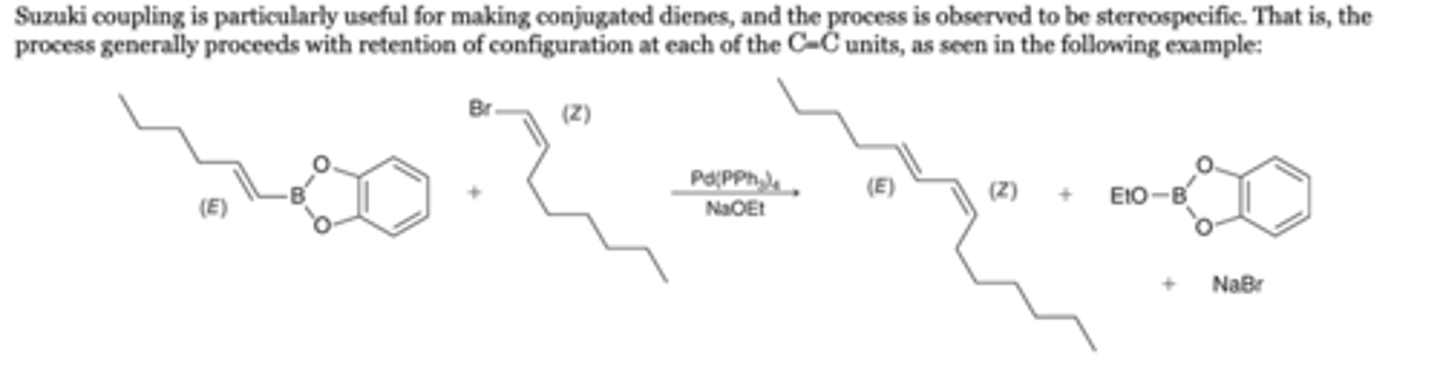
Suzuki Coupling Advantages
Suzuki coupling is particularly useful for making conjugated dienes, and the process is observed to be stereospecific. That is, the process generally proceeds with retention of configuration at each of the C=C units, as seen in the following example:
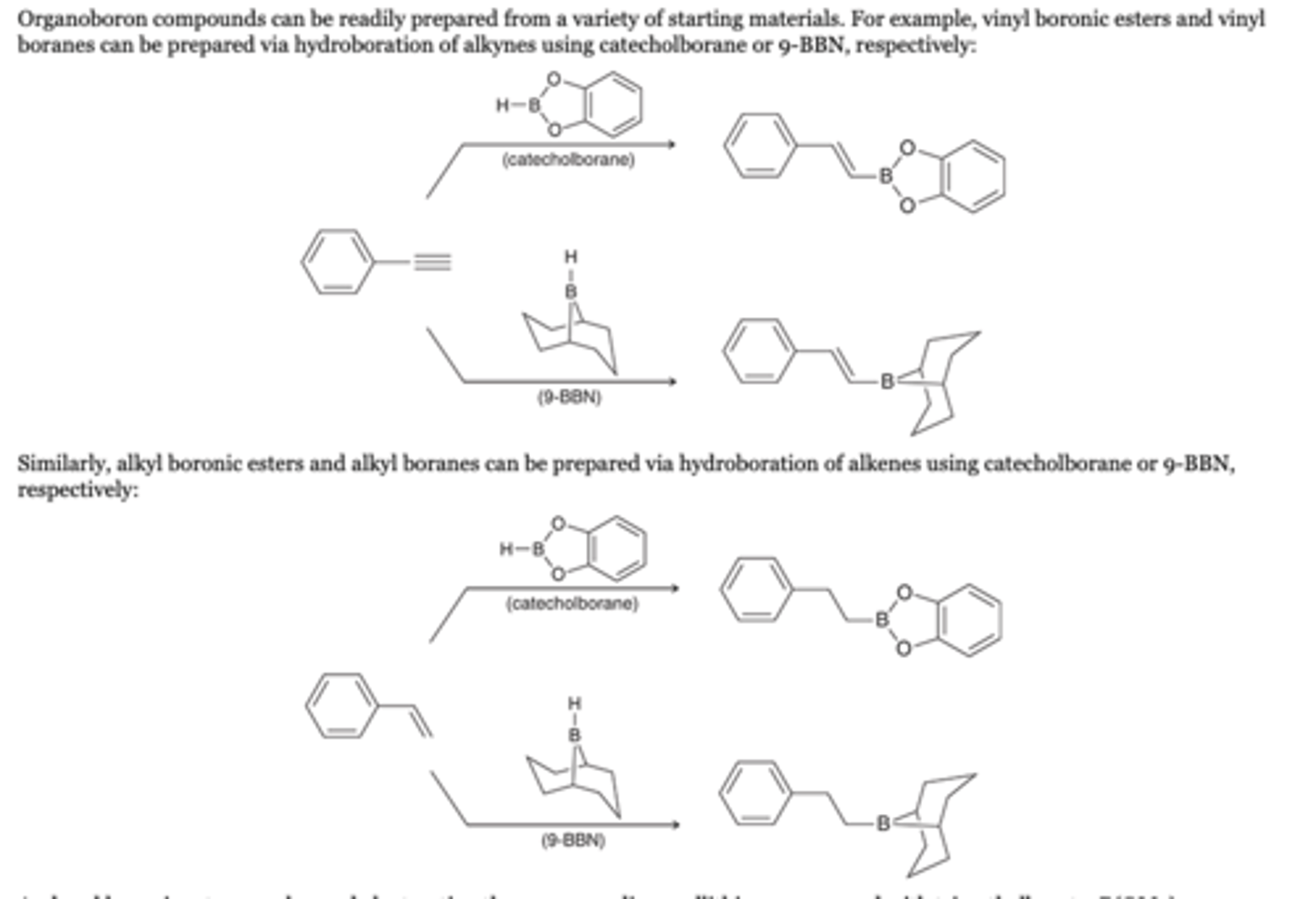
Preparation of Organoboron Compounds
Alkyne
Organoboron compounds can be readily prepared from a variety of starting materials. For example, vinyl boronic esters and vinyl boranes can be prepared via hydroboration of alkynes using catecholborane or 9-BBN, respectively
Alkenes
Similarly, alkyl boronic esters and alkyl boranes can be prepared via hydroboration of alkenes using catecholborane or 9-BBN, respectively
Reagents
catecholborane
And aryl boronic esters can be made by treating the corresponding aryllithium compound with trimethylborate, B(OMe)3
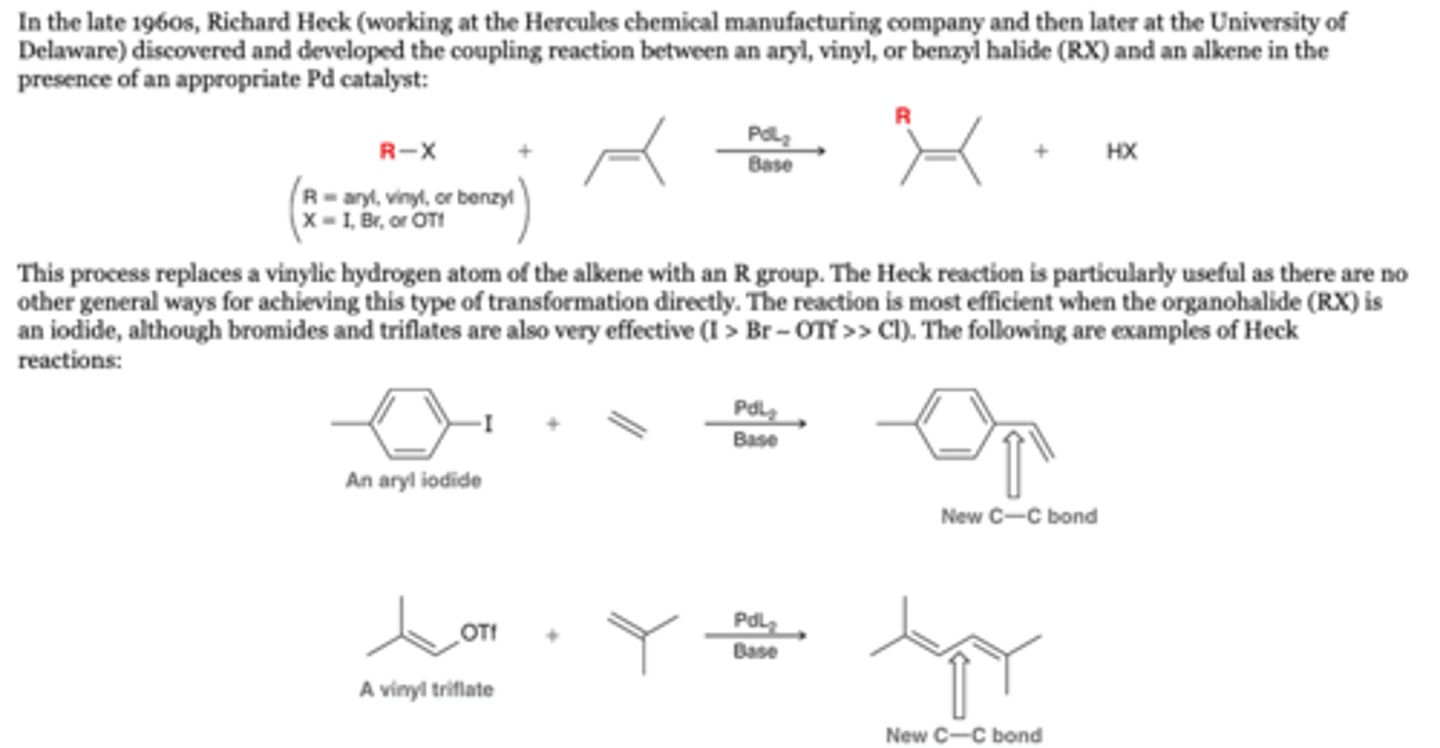
The Heck Reaction: General Reaction
-the coupling reaction between an aryl, vinyl, or benzyl halide (RX) and an alkene in the presence of an appropriate Pd catalyst:. This process replaces a vinylic hydrogen atom of the alkene with an R group.
-The reaction is most efficient when the organohalide (RX) is an iodide, although bromides and triflates are also very effective (I > Br ∼ OTf >> Cl). The following are examples of Heck reactions:
Reagents
1. PdL2, base
The Heck Reaction: The Catalyst
-Like Stille coupling and Suzuki coupling, the Heck reaction can be achieved with a catalyst such as Pd(PPh3)4, in which the palladium atom has an oxidation state of 0. Alternatively, Pd(II) complexes can be used, such as Pd(OAc)2.
-A commonly used base is triethylamine (Et3N), although other bases are often used, including NaOAc, KOAc, and NaHCO3.
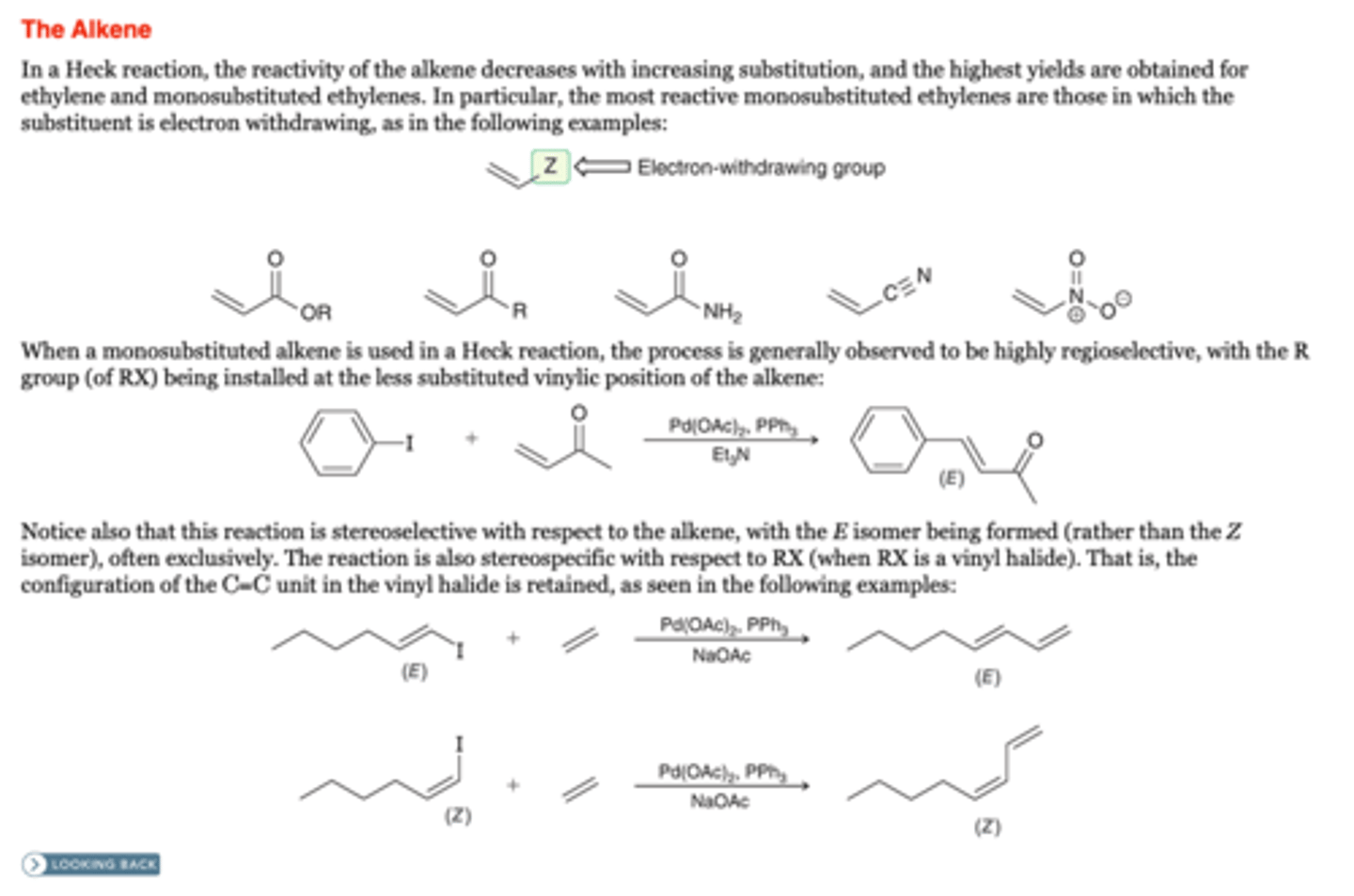
The Heck Reaction: The Alkene
-the reactivity of the alkene decreases with increasing substitution, and the highest yields are obtained for ethylene and monosubstituted ethylenes. In particular, the most reactive monosubstituted ethylenes are those in which the substituent is electron withdrawing,
-When a monosubstituted alkene is used in a Heck reaction, the process is generally observed to be highly regioselective, with the R group (of RX) being installed at the less substituted vinylic position of the alkene: