AQA A level Chemistry 3.2.3 Group 7
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
What is the trend in electronegativity in Group 7 elements? (2)
Electronegativity decreases down the group
Why does electronegativity decrease down Group 7? (3)
1. The size of the atom increases.
2. The number of principal energy levels increases
3. There is weaker attraction between the nucleus and electrons in a covalent bond
What is the trend in boiling points in Group 7 elements? (1)
Increase down the group
Why do boiling points increase down Group 7? (2)
- The size of the atom increases
- There are more Van der Waals forces between the molecules that need to be broken
What is the appearance of fluorine (F₂) at room temperature? (1)
Pale yellow gas
What is the appearance of chlorine (Cl₂) at room temperature? (1)
Pale green gas
What is the appearance of bromine (Br₂) at room temperature? (1)
Dark red/orange liquid
What is the appearance of iodine (I₂) at room temperature? (1)
Dark purple/black solid
What is an oxidising agent? (1)
Electron acceptor
What is the trend in the oxidising power of halogen atoms down the group? (1)
The oxidising power decreases down the group from fluorine (strongest) to iodine (weakest)
Why does the oxidising power of halogen atoms decrease down the group? (3)
- The size of the atom increases.
- The effect of the nuclear charge is reduced due to shielding.
- The halogen gains electrons less readily.
What is the observation when chlorine (Cl2) is added to a solution of potassium chloride (KCl)? (1)
No visible change
What is the observation when bromine (Br2) or iodine (I2) is added to a solution of potassium chloride (KCl)? (1)
No visible change
Write the ionic equation when chlorine (Cl2) reacts with potassium bromide (KBr). (2)
Cl2 + 2Br- → Br2 + 2Cl-
What is the observation when chlorine (Cl2) reacts with potassium bromide (KBr)? (1)
A yellow solution of bromine (Br2) is formed
What is the observation when bromine (Br2) or iodine (I2) is added to potassium bromide (KBr)? (1)
No visible change
Write the ionic equation when chlorine (Cl2) reacts with potassium iodide (KI). (2)
Cl2 + 2I- → I2 + 2Cl-
Write the ionic equation when bromine (Br2) reacts with potassium iodide (KI). (2)
Br2 + 2I- → I2 + 2Br-
What is the observation when chlorine (Cl2) reacts with potassium iodide (KI)? (1)
A brown solution of iodine (I2) is formed
What is the observation when bromine (Br2) reacts with potassium iodide (KI)? (1)
A brown solution of iodine (I2) is formed
What is the observation when iodine (I2) is added to potassium iodide (KI)? (1)
No visible change
Draw a displacement summary diagram for halogens (6)
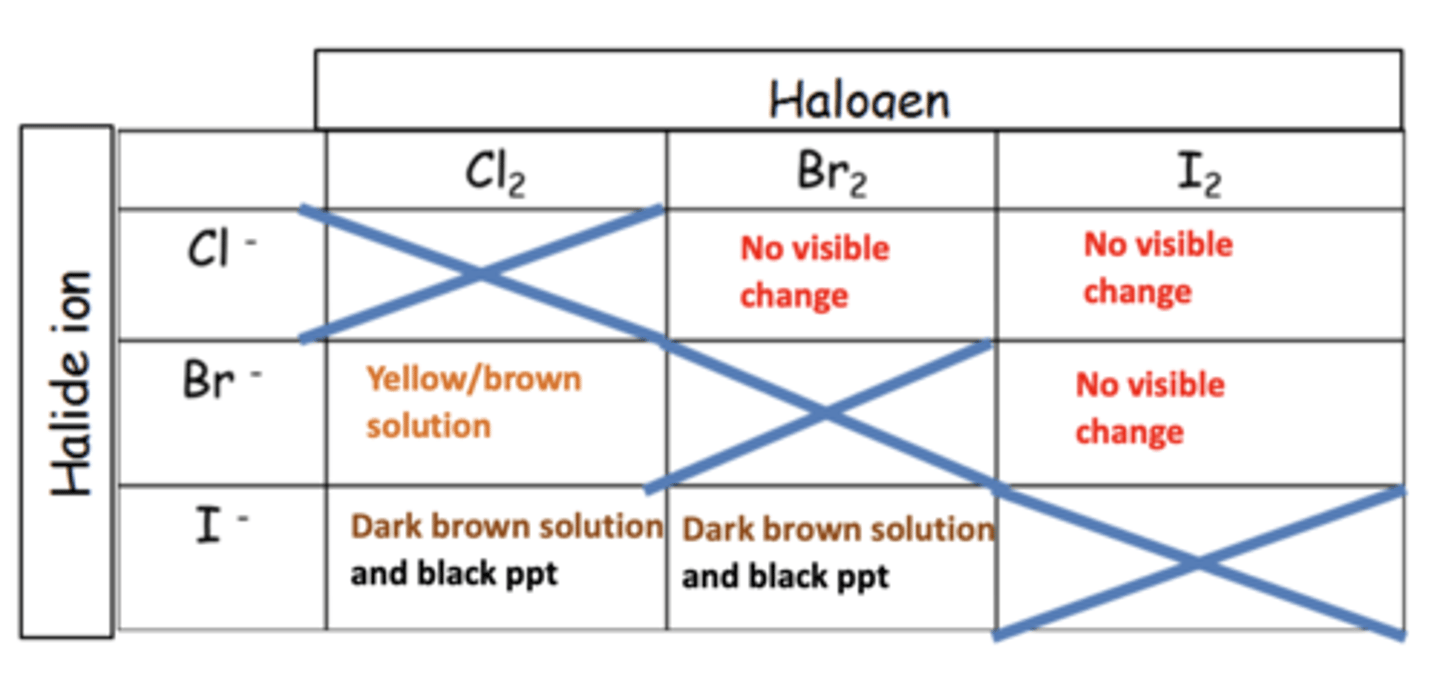
What is a reducing agent? (1)
Electron donor
What is the trend in reducing power of halide ions down the group? (1)
The reducing power increases from fluoride (weakest) to iodide (strongest)
Why does the reducing power of halide ions increase down the group? (3)
- The size of the ion increases.
- There is increased shielding.
- It is easier to lose an electron
What is the reaction type of sodium fluoride (NaF) with concentrated sulfuric acid?
What is the reaction type of sodium fluoride (NaF) with concentrated sulfuric acid? (1)
Acid-base reaction
Write the equation for the reaction of sodium fluoride (NaF) with concentrated sulfuric acid. (2)
2NaF + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + 2HF
What observation is made when sodium fluoride (NaF) reacts with concentrated sulfuric acid? (1)
Misty fumes of HF are produced
What is the reaction type of sodium chloride (NaCl) with concentrated sulfuric acid? (1)
Acid-base reaction
What observation is made when sodium chloride (NaCl) reacts with concentrated sulfuric acid? (1)
Misty fumes of HCl are produced
What are the reaction types observed when sodium bromide (NaBr) reacts with concentrated sulfuric acid? (2)
- Acid-base reaction.
- Redox reaction
Write the acid-base reaction equation for sodium bromide (NaBr) with concentrated sulfuric acid. (2)
2NaBr + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + 2HBr
What is observed during the acid-base reaction of sodium bromide (NaBr) with concentrated sulfuric acid? (1)
Misty fumes of HBr are produced
Write the redox reaction equation for sodium bromide (NaBr) with concentrated sulfuric acid. (2)
2H+ + H2SO4 + 2Br⁻ → Br2 + SO2 + 2H2O
What are the observations for the redox reaction of sodium bromide (NaBr) with concentrated sulfuric acid? (2)
- Choking gas (SO2) is produced
- Brown gas (Br2) is produced
What are the reaction types observed when sodium iodide (NaI) reacts with concentrated sulfuric acid? (2)
- Acid-base reaction.
- Multiple redox reactions.
Write the acid-base reaction equation for sodium iodide (NaI) with concentrated sulfuric acid. (2)
2NaI + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + 2HI
What is observed during the acid-base reaction of sodium iodide (NaI) with concentrated sulfuric acid? (1)
Misty fumes of HI are produced
Write one redox reaction equation for sodium iodide (NaI) with concentrated sulfuric acid, producing iodine and sulfur dioxide. (2)
2H+ + H2SO4 + 2I⁻ → I2 + SO2 + 2H2O
What are the observations for the redox reaction of sodium iodide (NaI) producing iodine and sulfur dioxide? (2)
- Choking gas (SO2) is produced.
- Black solid or purple fumes (I2) are produced
Write one redox reaction equation for sodium iodide (NaI) with concentrated sulfuric acid, producing sulfur. (2)
6H+ + H2SO4 + 6I⁻ → S + 4H2O + 3I2
What are the observations for the redox reaction of sodium iodide (NaI) producing sulfur? (2)
- Yellow solid (S) is produced.
- Black solid or purple fumes (I2) are produced
Write one redox reaction equation for sodium iodide (NaI) with concentrated sulfuric acid, producing hydrogen sulfide. (2)
8H+ + H2SO4 + 8I⁻ → H2S + 4H2O + 4I2
What are the observations for the redox reaction of sodium iodide (NaI) producing hydrogen sulfide? (2)
- Smell of rotten eggs (H2S) is produced.
- Black solid or purple fumes (I2) are produced
What is used to identify halide ions in solution? (1)
Acidified silver nitrate solution
What is the simplest ionic equation for the reaction of silver nitrate with halide ions? (1)
Ag⁺ + X⁻ → AgX
What is the observation when fluoride ions (F⁻) react with acidified silver nitrate solution? (1)
No visible change as AgF is soluble
What is the observation when chloride ions (Cl⁻) react with acidified silver nitrate solution? (1)
White precipitate (AgCl)
What is the observation when bromide ions (Br⁻) react with acidified silver nitrate solution? (1)
Cream precipitate (AgBr)
What is the observation when iodide ions (I⁻) react with acidified silver nitrate solution? (1)
Yellow precipitate (AgI)
Why must hydroxide and carbonate ions be removed before testing for halide ions with silver nitrate? (1)
Hydroxide and carbonate ions will form a precipitate with silver ions, interfering with the test
Which acid is used to acidify the solution before testing for halide ions with silver nitrate? (1)
Nitric acid (HNO3)
Why should hydrochloric acid (HCl) not be used to acidify the solution when testing for halide ions? (1)
HCl contains Cl⁻ ions, which would form a white precipitate, interfering with the test
Write the equation for the reaction between nitric acid (HNO3) and sodium carbonate (Na2CO3). (2)
2HNO3 + Na2CO3 → 2NaNO3 + CO2 + H2O
Which silver halide is soluble in dilute ammonia? (1)
AgCl
Which silver halide is partially soluble in dilute ammonia and soluble in concentrated ammonia? (1)
AgBr
Which silver halide is insoluble in both dilute and concentrated ammonia? (1)
AgI
Write the equation showing the solubility of silver chloride (AgCl) in ammonia. (2)
AgCl(s) + 2NH3(aq) → Ag(NH3)2⁺(aq) + Cl⁻(aq)
Write the equation showing the solubility of silver bromide (AgBr) in ammonia. (2)
AgBr(s) + 2NH3(aq) → Ag(NH3)2⁺(aq) + Br⁻(aq)
What is the trend in solubility of silver halides in ammonia? (2)
- Decreases
- Most soluble: AgF
- Least soluble: AgI
What is the equation for the reaction of sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) with nitric acid (HNO3)? (2)
2HNO3 + Na2CO3 → 2NaNO3 + H2O + CO2.
What is the ionic equation for the reaction of carbonate ions (CO3²⁻) with hydrogen ions (H⁺)? (2)
2H⁺ + CO3²⁻ → H2O + CO2
What observation is made when carbonate ions react with an acid? (1)
Effervescence (fizzing) is observed due to the release of CO2 gas.
What is the test for an acid using sodium carbonate? (1)
Add sodium carbonate; effervescence (fizzing) is observed
What is the equation for the reaction of sodium sulfate (Na2SO4) with barium nitrate solution (Ba(NO3)2)? (2)
Na2SO4(aq) + Ba(NO3)2(aq) → BaSO4(s) + 2NaNO3(aq)
What is the ionic equation for the reaction of sulfate ions (SO4²⁻) with barium ions (Ba²⁺)? (2)
Ba²⁺(aq) + SO4²⁻(aq) → BaSO4(s)
What observation is made when sulfate ions react with barium ions? (1)
A white precipitate (BaSO4) is formed.
What is the test for barium ions? (1)
Add sodium sulfate (Na2SO4); a white precipitate forms
Write the ionic equation for the reaction between silver ions and chloride ions. (1)
Ag⁺(aq) + Cl⁻(aq) → AgCl(s)
Write the ionic equation for the reaction between silver ions and bromide ions. (1)
Ag⁺(aq) + Br⁻(aq) → AgBr(s).
Write the ionic equation for the reaction between silver ions and iodide ions. (1)
Ag⁺(aq) + I⁻(aq) → AgI(s)
Write the equilibrium equation for chlorine water. (2)
Cl₂(g) + H₂O(l) ⇌ HCl(aq) + HClO(aq)
What type of redox reaction occurs when chlorine reacts with water and why? (2)
- Disproportionation reaction
- Chlorine is both oxidised (to +1 in HClO) and reduced (to -1 in HCl) in the same reaction
What happens when universal indicator paper is added to chlorine water? (2)
- Initially turns red due to the formation of acidic products (HCl and HClO).
- The red colour disappears, and the indicator turns white as HClO acts as a bleach
Write the equation for the reaction of chlorine with water in the presence of bright sunlight. (2)
2Cl₂ + 2H₂O → 4HCl + O₂
What are the colours of chlorine and its products in bright sunlight? (2)
- Chlorine: Pale green.
- Products (HCl and O₂): Colourless.
What happens to the green colour of chlorine water under bright sunlight? (1)
The green colour fades
What type of reaction occurs when chlorine reacts with water in bright sunlight? (1)
Chlorine oxidises water to oxygen and is reduced to chloride ions.
What is the primary use of chlorine and its compounds in water treatment? (1)
To sterilise drinking water and the water in swimming baths
Why must chlorine be used in very small amounts in water treatment? (1)
Because chlorine is toxic
Why is the concentration of chlorine in swimming pools carefully monitored? (2)
- To ensure it is sufficient to kill bacteria.
- To prevent it from being toxic.
What compound is now being used to replace chlorine in swimming pools and why? (2)
- Calcium chlorate(I).
- Because it is less hazardous
Write the equation for the reaction of chlorine with cold dilute sodium hydroxide. (2)
Cl2 + 2NaOH → H2O + NaCl + NaClO
Write the ionic equation for the reaction of chlorine with cold dilute sodium hydroxide. (2)
Cl2 + 2OH⁻ → H2O + Cl⁻ + ClO⁻
Why is the reaction of chlorine with cold dilute sodium hydroxide of great commercial importance? (1)
Because sodium chlorate(I) (NaClO) is the active ingredient in household bleach