Bh cycle and entropy test
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
enthalpy change
heat energy transferres in a reaction at constant pressure
bohn hager example for solution
enthalpy change symbol
ΔH
units of enthalpy change
kJ mol^-1
enthalpy change of atomisation of an element
enthalpy change when 1 mole of gaseous atms is formed from an element under standard conditions
enthalpy change of atomisation symbol
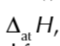
enthalpy change of atomisation of cl
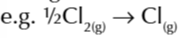
enthalpy change of atomisation of a compound
enthalpy change when 1 mole of a compound is converted to gaseous atoms under standard conditions
enthalpy change of atomisation of NaCl
second ionisation energy
energy needed to change 1 mole of gaseous 1+ ions atoms into 1 mole of gaseous 2+ ions
first electron affinity
energy needed to change 1 mole of gaseous atoms into 1 mole of gaseous 1- ions
second electron affinity
energy needed to change 1 mole of gaseous 1- into 1 mole of gaseous 2- ions
lattice enthalpy
enthalpy change when 1 mole of a solid ionic compound is formed from its gaseous ions under standard conditions
lattice enthalpy symbol
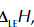
lattice enthalpy of NaCl
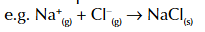
enthalpy change of hydration
enthalpy change when 1 mole of gaseous ions is dissolved in water under standard conditions
enthalpy change of hydration symbol
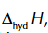
enthalpy change of hydration of Na
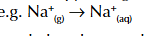
enthalpy change of solution
enthalpy change when 1 mole of solute is dissolved in a solvent such as water under standard conditions
enthalpy change of solution symbol
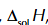
enthalpy change of solution of NaCl
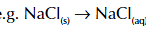
what is lattice enthalpy a measure of
ionic bond strength
Factors affecting lattice enthalpy
ionic charge
ionic radius
how does ionic charge affect lattice enthalpy
the higher the charge on the ions
the stronger the electrostatic attraction between the ions
so the more energy is released when an ionic lattice forms.
more energy released meand lattice enthalpy will be more negative
so lattice enthalpy for compounds with 2+ or 2- iions are more negative than 1+ or 1- ions
how does ionic radius affect lattice enthalpy
the smaller the ionic radii of the ions involved the higher the charge density of the ion this means the electrostatic attraction between the ions is greater so the lattice enthalpy is mor exothermic
born haber cycle example
what happens if there is 2 of a molecle in bohn haber cycle
times enthalpy change of atomisation for element by 2 and either is ionisation energy or electron affinity by 2
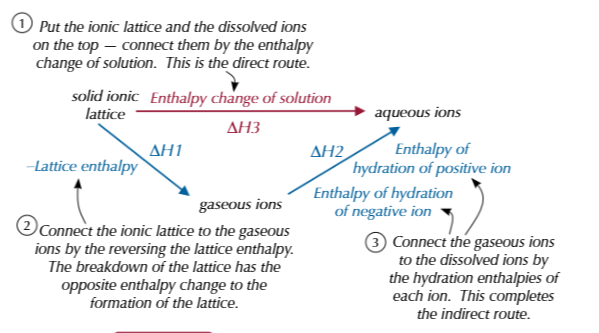
what happens when a solid ionic lattice dissolves in water
bonds between ions break to give gaseous ions which is endothermic,enthalpy change is opposite of lattice enthalpy
bonds between ions and water and made-exothermic,enthalpy change of hydration
enthalpy change of solution equation
enthalpy of hydration-lattice enthalpy
enthalpy change of solution enthalpy cycle
factors affecting enthalpy of hydration
ionic charge
ionic radius
how does ionic charge affect enthalpy of hydration
ions with a greater charge have a greater enthalpy of hydration
because ions with a higher charge are better at attracting water molecules than those with lower charges
more energy is released when the bonds are made giving them a more exothermic enthalpy of hydration
how does ionic radius affect enthalpy of hydration
smaller ions have greater enthalpy of hydration
as smaller ions have a higher charge density than bigger ions
they attract water molecules better and have more exothermic enthalpy of hydration
is lattice enthalpy endo or exothermic
exothermic
bond enthaly
The enthalpy change when 1 mole of a particular covalent bond in the gaseous state is broken.
why is the second and third electron affinities endothermic
incoming electron is added to an already negative ion so energy is required to overcome the repulsive forces between the incoming electron and negative ion
what is entropy
measure of dispersal of energy in a system
what does the greater the entropy mean
the more disordered the system
symbol for entropy
S
symbol for entropy change
ΔS
what happens to entropy as you go solid to liwuid to gas
becomes more disordered
what happens to entropy as you dissolve a solid
increases its entropy
what happens to entropy as there are more gaseous particles
increases
units of entropy change
JK^-1mol^-1
when will chemical reactons only take place with entropy change
when overall entropy change is positive
entropy change of system equation
ΣSproducts - ΣSreactants
entropy change of surroundings equation
-enthalpy change/temperature
what is units of enthalpy change in entropy change of surroundings equation
Joules
what is units of temperature in entropy change of surroundings equation
K
total entropy change
entropy change of system + entropy change of surroundings
what happens to entropy as temperature increases
entropy increases
what is free energy change
measure used to predict whether a reaction is feasible
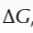
feasible reaction
reaction that once started will carry on to completion without any energy being supplied to it
when is a reaction feasbile
if free energy change is negative or zero
gibbs / free energy change equation
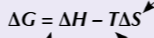
units of free energy change
Jmol^-1
units of enthalpy change in gibbs equation
Jmol^-1
why might a reaction not take place even if △G is negative
high activation energy,slow rate of reaction
equation to work out temperature at which reaction is feasible
△H/△S
id a reaction is exothermic and has a positive entropy change what will △G always be
negative
id a reaction is endothermic and has a negative entropy change what will △G always be
positive
if a reaction is exothermic and has negative entropy change when will it be feasible
low temperature
if a reaction is endothermic and has positive entropy change when will it be feasible
high ttemperatres
gibbs equation in y=mx + c form
△G=-△s T + △H
what is the gradient of straigt line gibbs
-△S
what is the y intercept of straight lien gibbs
△H
enthaly change
is the heat energy transferred in a reaction at constant ressure ∆H
standard conditions for enthaly changes
100kPa
298K
ΔH°
standard states
hysical states of reactants under standard conditions
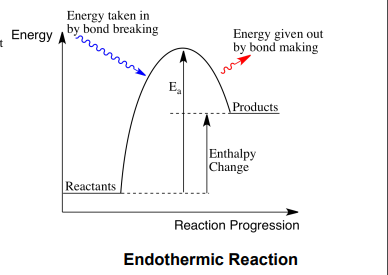
endthermic reaction
when energy is taken in from the surroundings so roducts have more energy than reactants heat taken in
endothermic enthaly change
ositive
exothermic reaction
when energy is released to surroundings roducts have less energy than reactants heat is given out
enthaly change of exothermic reaction
negative
overall enthaly change equation
energy needed to break bonds(reactants - energy released making bonds (roducts
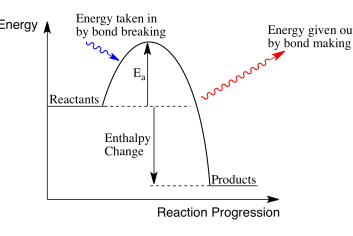
activation energy
minimimum amiunt of energy for a chemical reaction to tak lave
activation energy on enthaly rofile diagrm
difference btween reactants and to of hum
exothermic enthaly rofile diagram
endothermic enthaly rofile diagram
standard enthaly change of reaction
∆r H
enthaly change when a reaction occurs in the molar quantities shown in the chemical equation under standard conditions with all reactants and roducts in their standard states
standard enthaly change of fromation
∆f H
enthaly change when 1 mole of a comound is formed from its elements in their standard states under standard conditions
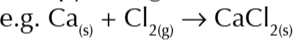
standard enthaly change of combustion
∆c H
enthaly change when 1 mole of a substance is comletely burned in oxygen under standard conditions with all reactants and roducts in their standard syayes
standard enthaly change of neutralisation
∆neutH
enthaly change when solutions of an acid and alkali react together to form 1 mole of water under standard conditions
calorimetry
exerimetnak method for finding enthaly change by measuring temerature chnage over time
how to measure enthlay changes in lab
neutralisation,dislacement stick thermometer into solution in olysteren beaker
combustion - copper calorimeter containing known mass of water burn and measure temerature change
equation for enthaly change
q=mc∆T
q=energy change(j
m=mass g
c= secific heat caacity jg^1K^1
∆t temerature chnage K
secific heat caacity
energy required to raise 1g of subsatance by 1K without change of state
how to calculate nergy change er mole
qx10^-3/moles or kj/g x mr
errors with enthaly change exepriments
calorimetry not comleteyly accurate
heat loss can occurbut can insulate
use secific heat cacity of water not solution
average bond enthaly
energy required to break one mole of the stated bond in a gaseoys state under standard conditions
hess law
total enthalychanges of reaction is alwys the ame no matter which route is taken
enthaloy change of formation hess law
arrows oint up
-Hf of reactanta + hf of roducts
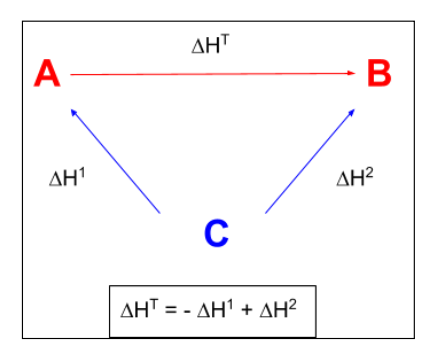
enthaly change of cobustion hess law
oint down
H2O and CO2
reactants - products
bohn haver solution