Psychology 100 Exam 2 (Electric Boogaloo)
1/152
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
153 Terms
consists of the brain and spinal cord and processes sensory information and sends messages to muscles, glands, and internal organs
Central Nervous System
Consists of all portions of the nervous system outside of the brain and spinal cord and sends sensory information to the central nervous system
Peripheral Nervous System
Consists of nerves connected to sensory receptors and skeletal muscles (voluntary action)
Somatic Nervous System
Regulates functioning of blood vessels, glands, and internal organs (involuntary action)
Autonomic Nervous System
Mobilizes body resources and increases energy output during emotion and stress (excitatory; an accelerator)
Sympathetic Nervous System
Operates during relaxed states and conserves energy output (inhibitory; a brake)
Parasympathetic Nervous System
Nerve cells; transmits electrochemical messages to and from the central nervous system
Neurons
Cells that support, nurture, and insulate neurons; make up about 90% of the brain's cells
Glial Cells
Branches from a neuron that receive information from other neurons and transmits data to the cell body
Dendrites
Part of the neuron that keeps it alive and determines whether or not it will fire a message
Soma / Cell Body
Fiber that transmits electrical signals from the cell body
Axon
A fatty substance that insulates some axons
Myelin Sheath
Small knobs at the end of an axon that hold pockets of chemicals (neurotransmitters)
Synaptic Bulbs
Neuron that releases chemicals into the synapse
Presynaptic Neuron
Neuron that receives chemicals from the synapse
Postsynaptic Neuron
Small gap between the synaptic bulbs of one neuron and the dendrites of another neuron; site where the message of one neuron is sent to another neuron
The Synaptic Cleft
Occurs within the neuron
Electrical Component
Occurs between neurons
Chemical Component
The neuron is inactive, with a negative charge inside the cell and a positive charge outside the cell
The Resting Potential
A brief change in the neurons electrical charge that occurs when channels open, allowing + ions to rush into the cell
The Action Potential
A neuron will either fire or not
All-Or-None Law
How can we discriminate between different intensities of a stimulus?
The number of neurons that fire
Brief period of time after an action potential during which the neuron cannot fire
The Absolute Refractory Period
Chemical substances used to communicate messages from one neuron to another
Neurotransmitters
Neurotransmitter associated with sleep and appetite
Seratonin
Neurotransmitter associated with voluntary movement
Dopamine
Neurotransmitter associated with memory and emotion
Acetylcholine
Neurotransmitter associated with increasing heart rate and dreaming
Norepinephrine
Neurotransmitter that acts as a general inhibitory
GABA
Neurotransmitter that acts as a general excitatory
Glutamate
Dendrites of one neuron receive neurotransmitters from the synaptic cleft (step ____)
1
Message from incoming neurotransmitters is sent to the soma - decision is made to fire or not (step ____)
2
If firing, neuron becomes less negative, and an electrical message is sent from the stoma down the axon (step ____)
3
Neurotransmitters stored in the synaptic bulbs are released into the synaptic cleft (step ____)
4
A post-synaptic neuron receives the neurotransmitters and the process begins again (step ____)
5
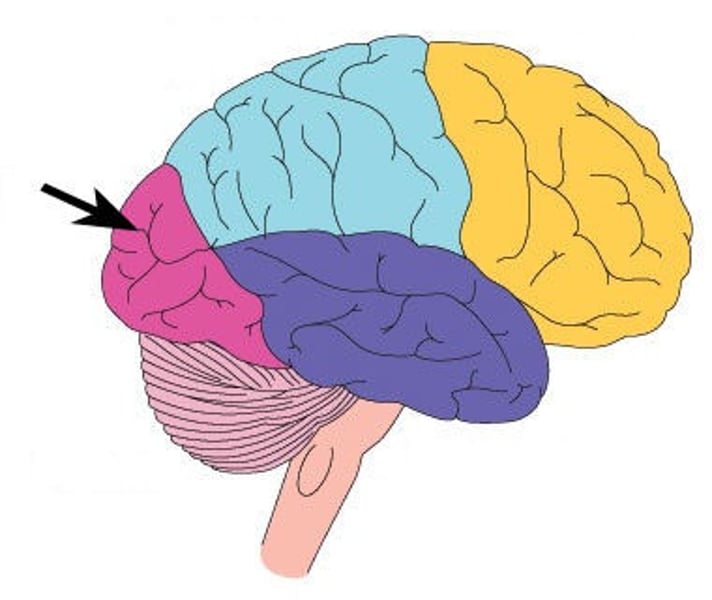
Contain areas involved in short-term memory, emotion, thinking creatively, speech production (Broca's area), and motor movements
Frontal Lobes
Controls voluntary muscle movements
Motor cortex
The most forward part of the frontal lobe involved in social judgement
Prefrontal Cortex
Contains areas involved in attention, touch, pressure, pain, and temperature
Parietal Lobe
Receives information for the touch sense
Somatosensory Cortex
Contains the visual cortex, which processes visual information
Occipital Lobe
Contains the auditory cortex, which processes sound and is involved in language comprehension, memory, perception, and emotion
Temporal Lobe
Involved in controlling involuntary processes, such as breathing and heart rate
Medulla
Involved in regulating sleeping, waking, and dreaming
Pons
Involved in regulating movement and balance and plays a role in some higher cognitive processes, such as problem solving
Cerebellum
Regulates emotion, hunger, thirst, and reproduction (drives to survive)
Hypothalamus
Directs sensory information to other areas of the brain
Thalamus
Involved in regulating our response to sensory stimuli and highly involved with our memory system
Hippocampus
Involved in the arousal and regulation of emotions
Amygdala
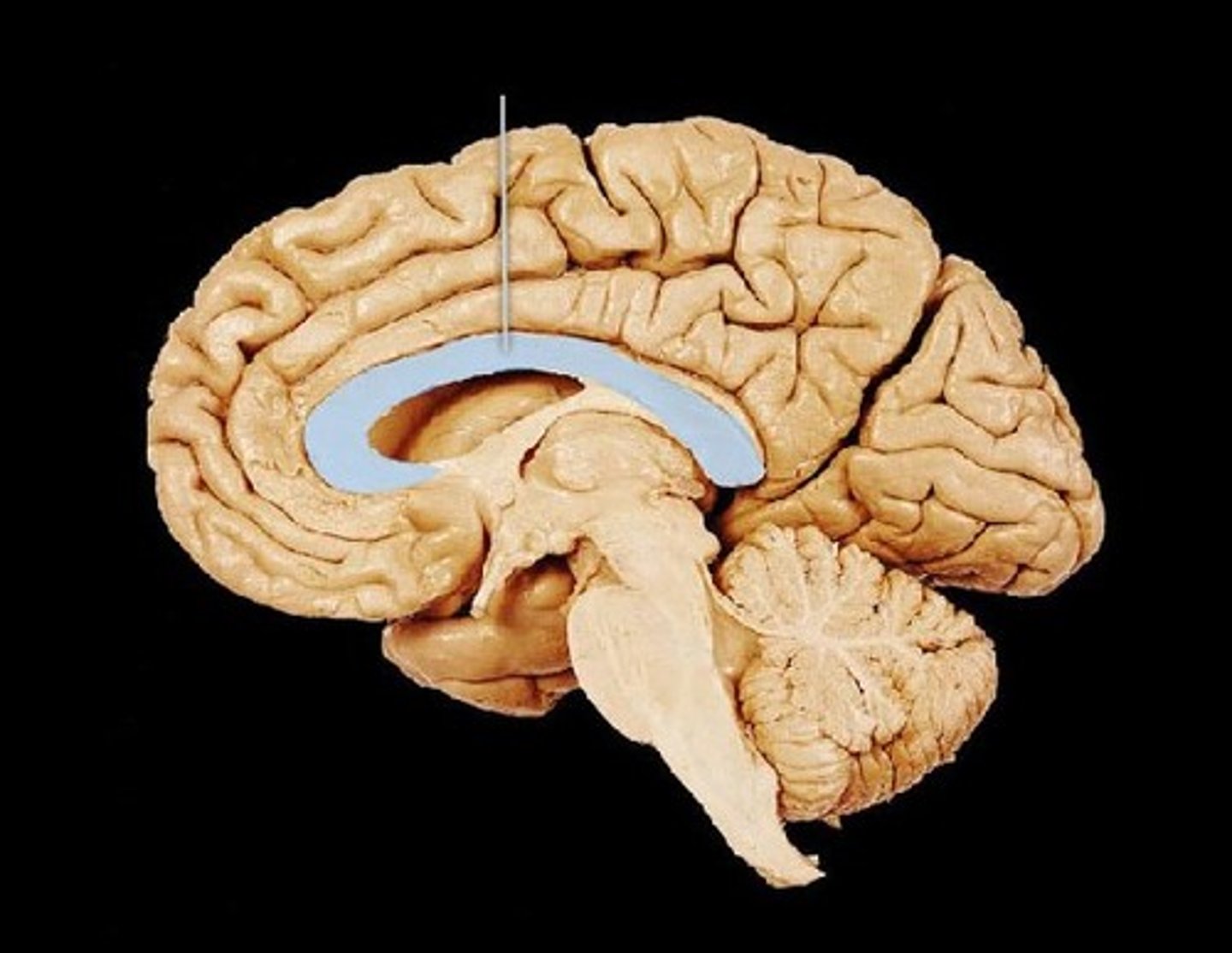
The bundle of fibers that connect the left and right brain hemispheres
Corpus Callosum
According to Sperry's findings, the left hemisphere of the brain responsible for ____
language
According to Sperry's findings, the right hemisphere of the brain could recognize a word but not ____ it
articulate
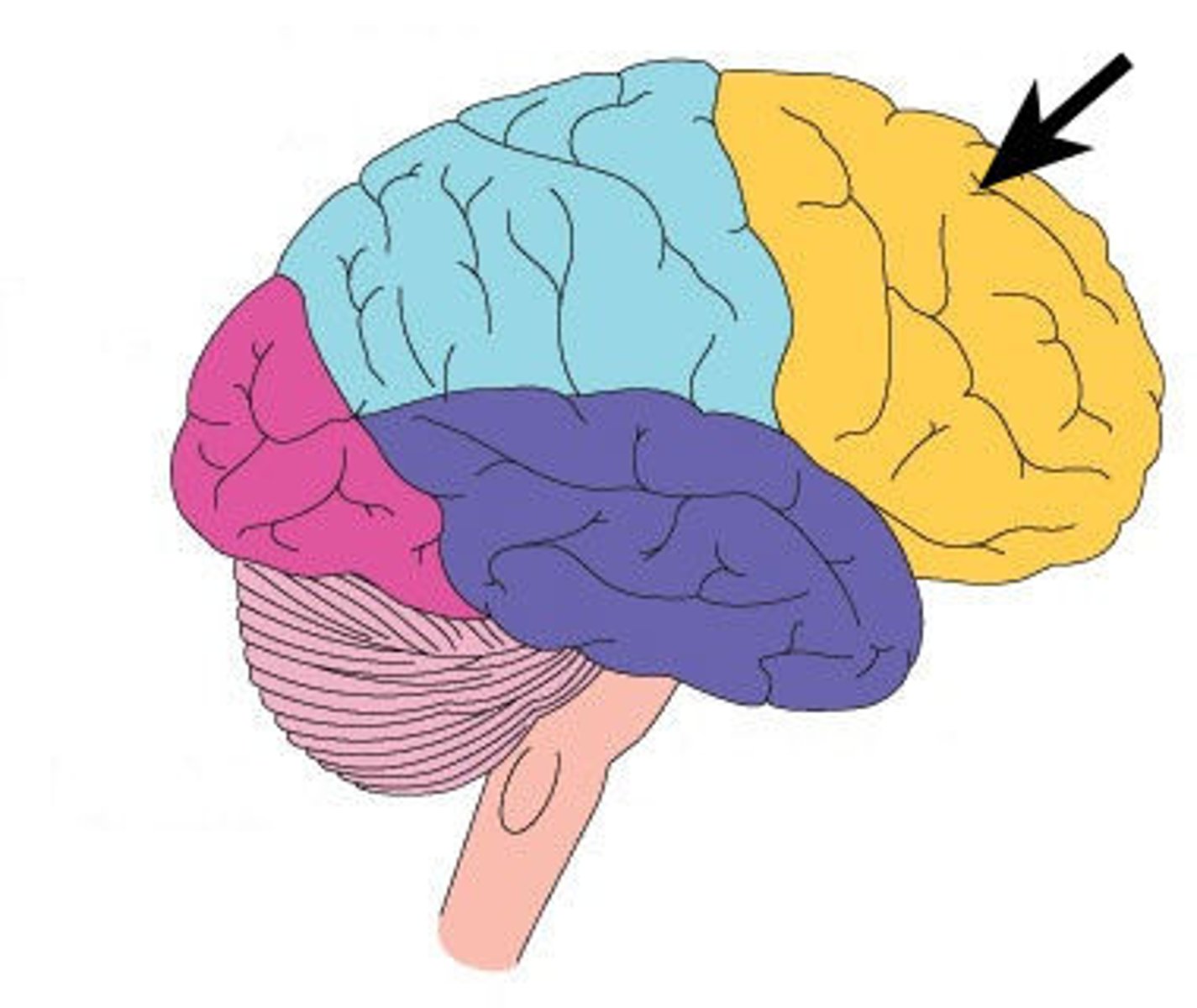
Frontal Lobe
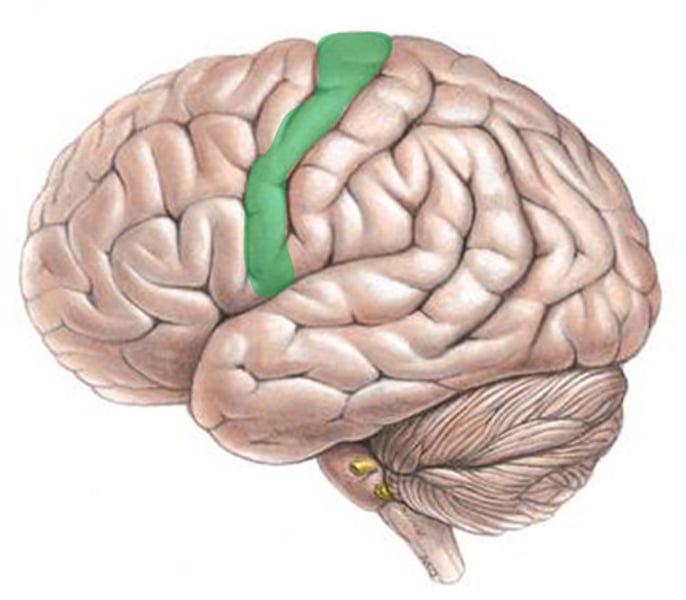
Motor Complex
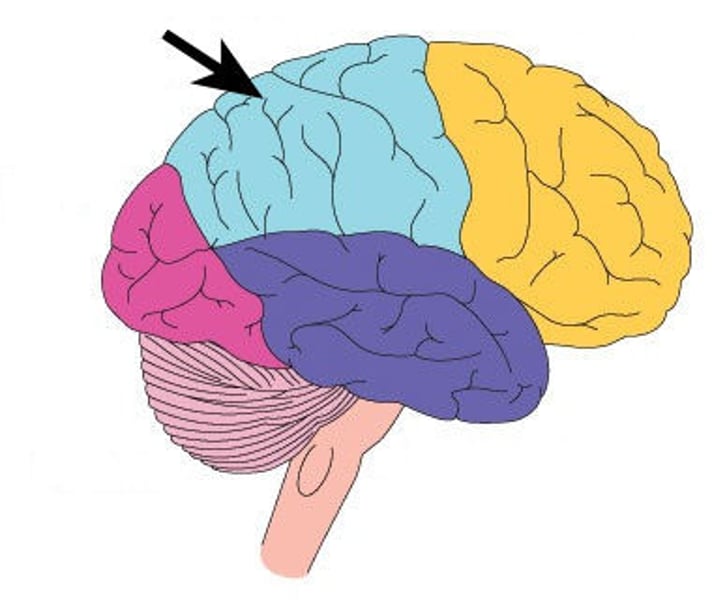
Parietal Lobe
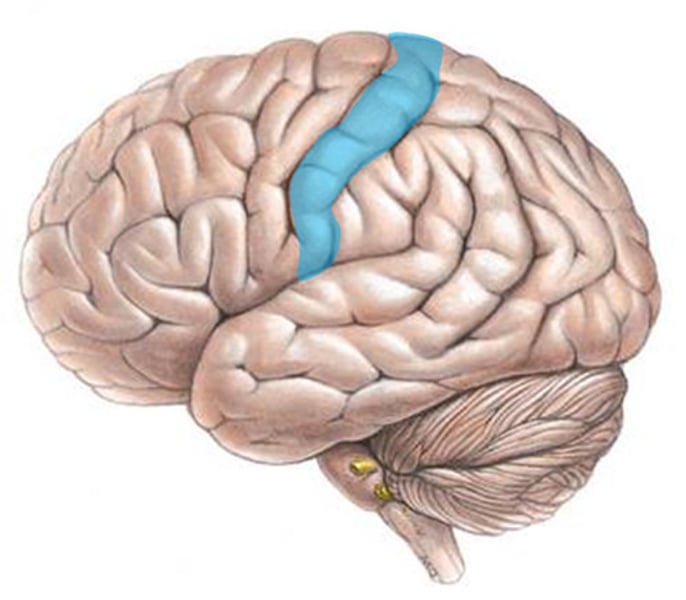
Somatosensory Cortex
Occipital Lobe
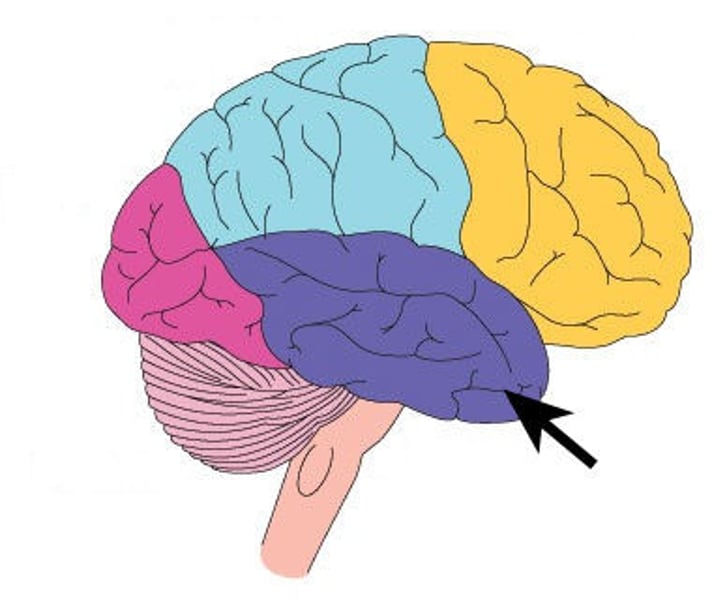
Temporal Lobe
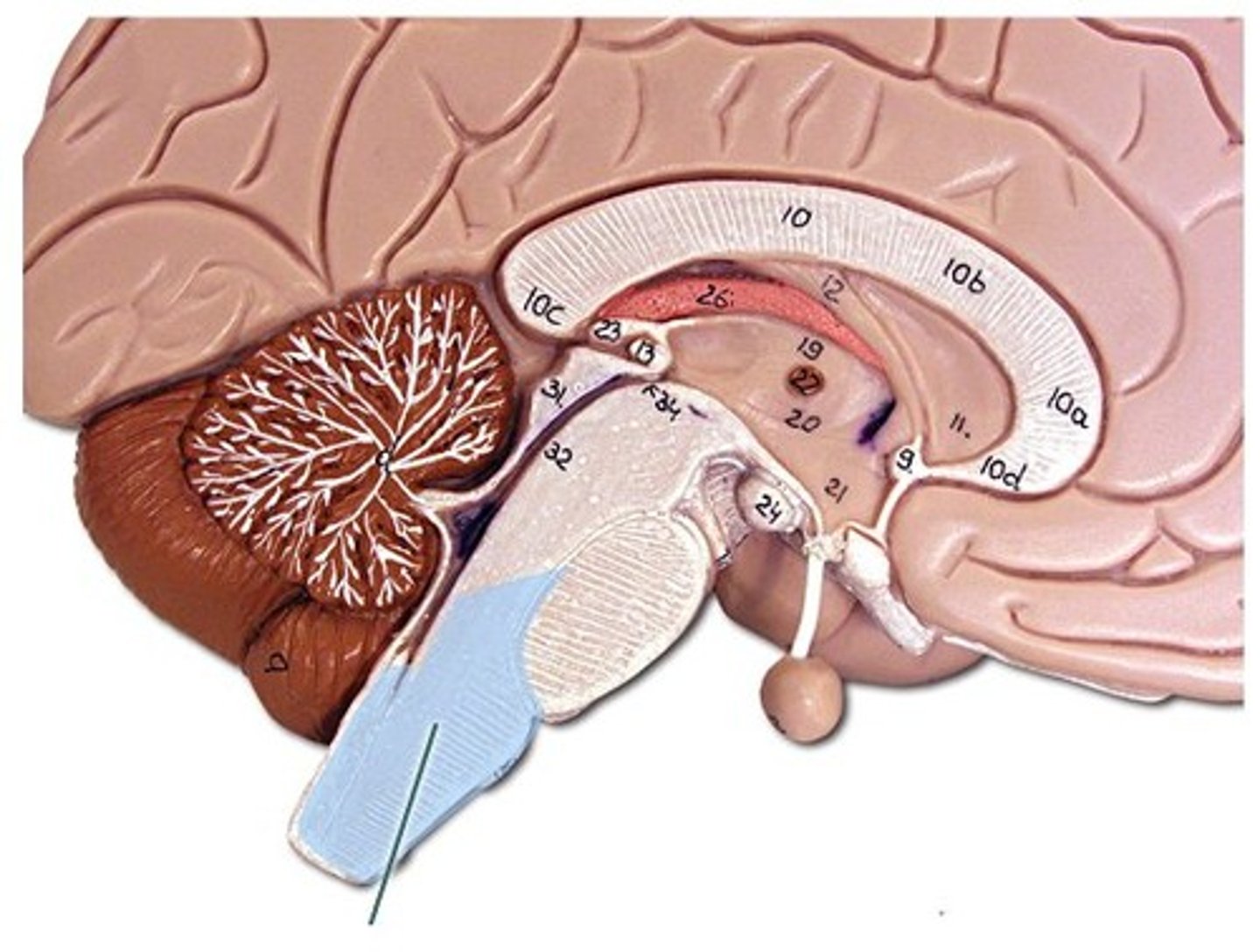
Medulla
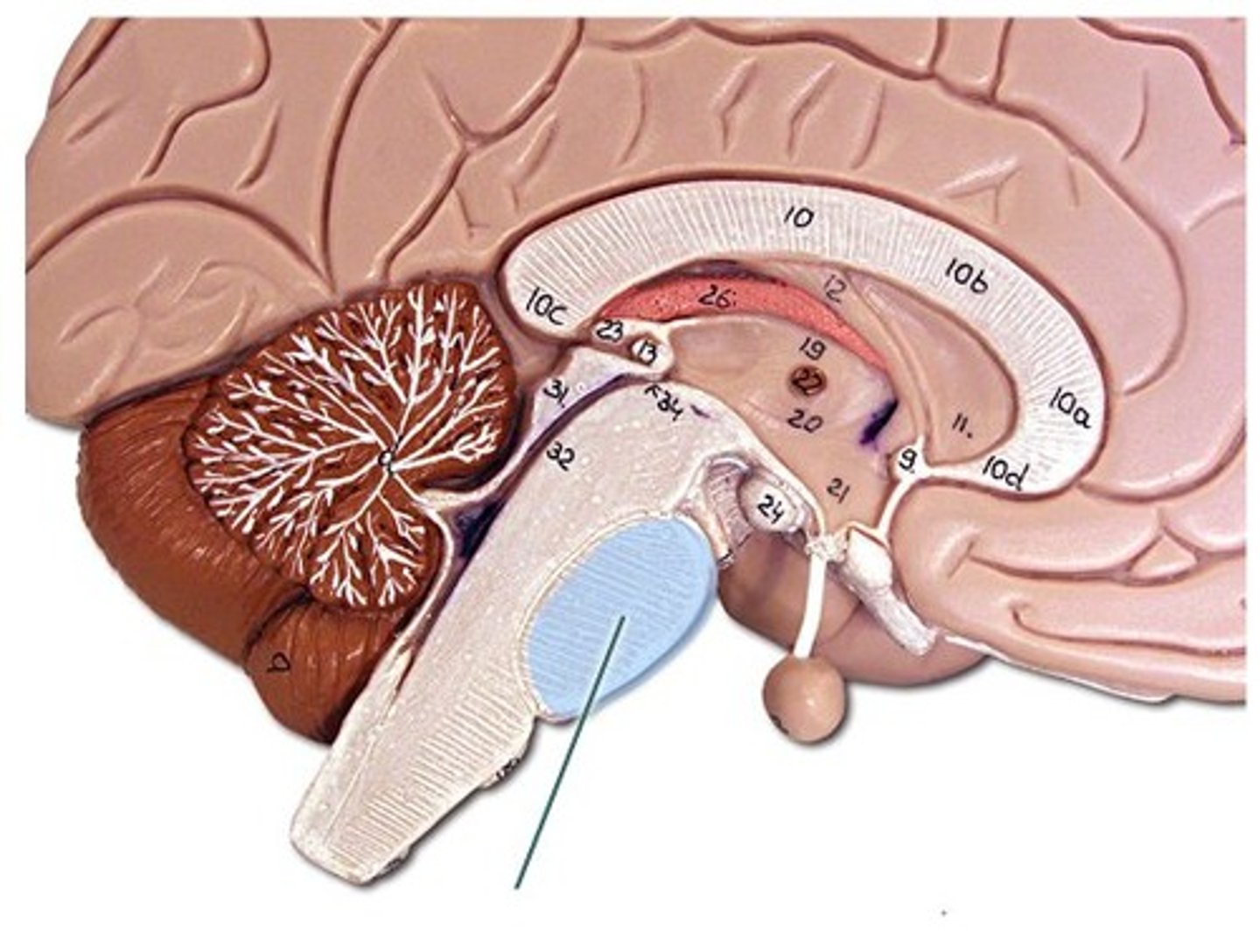
Pons
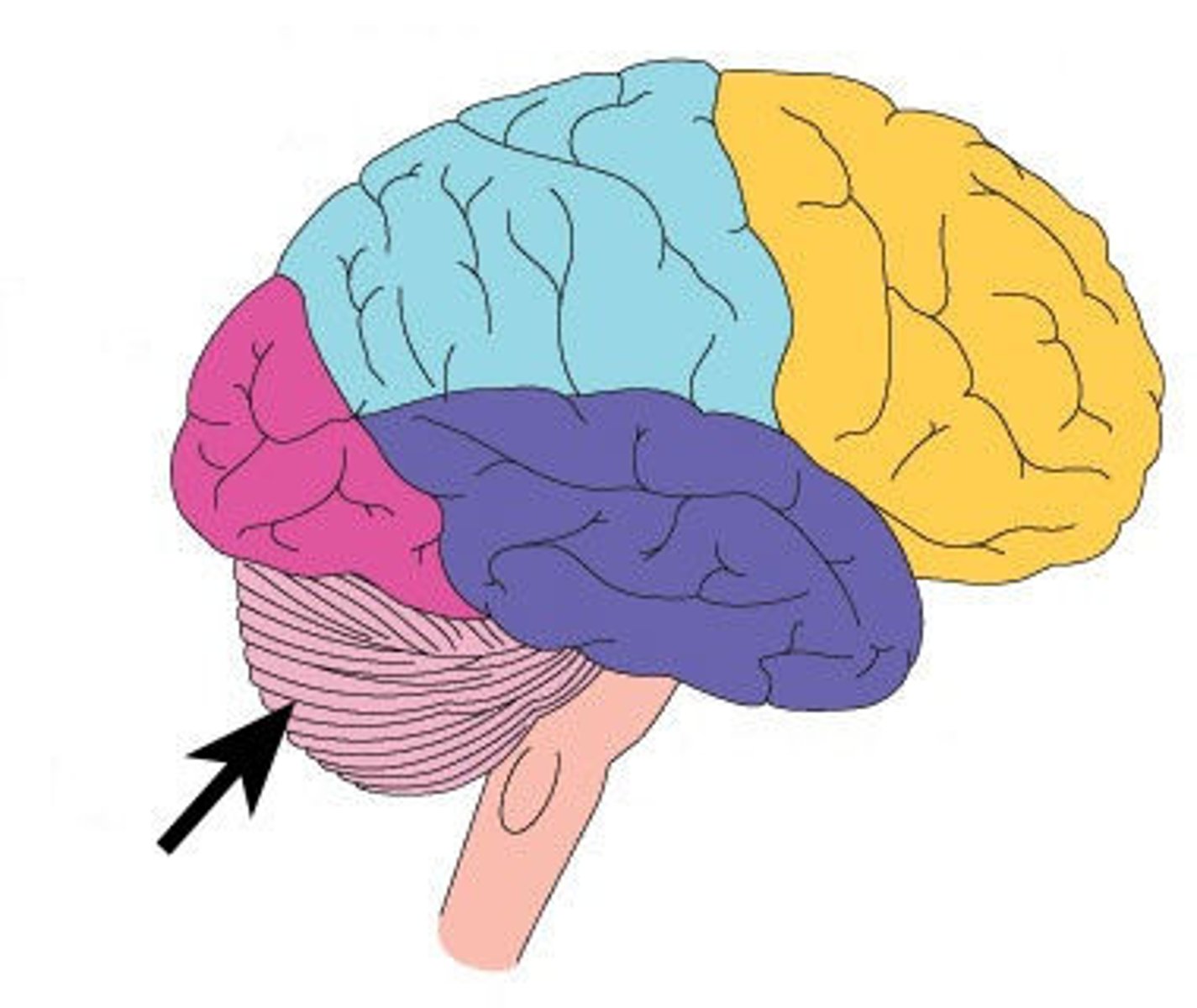
Cerebellum
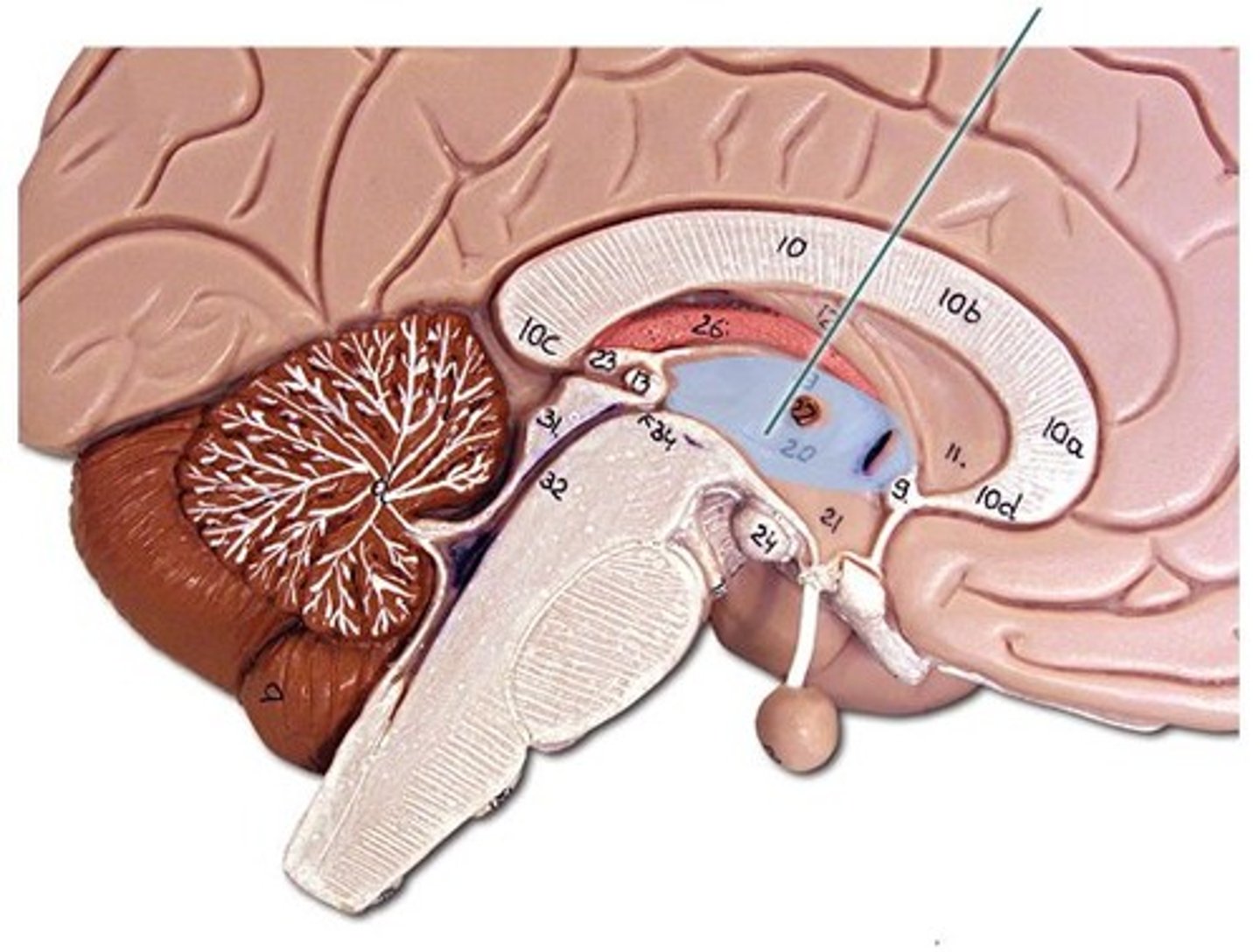
Thalamus
Hypothalamus
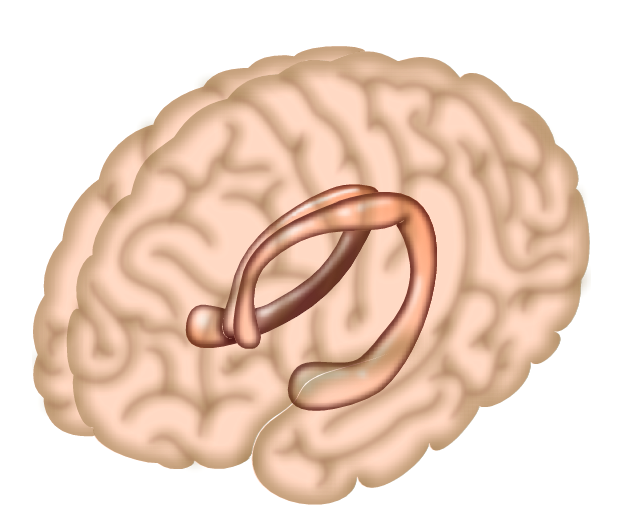
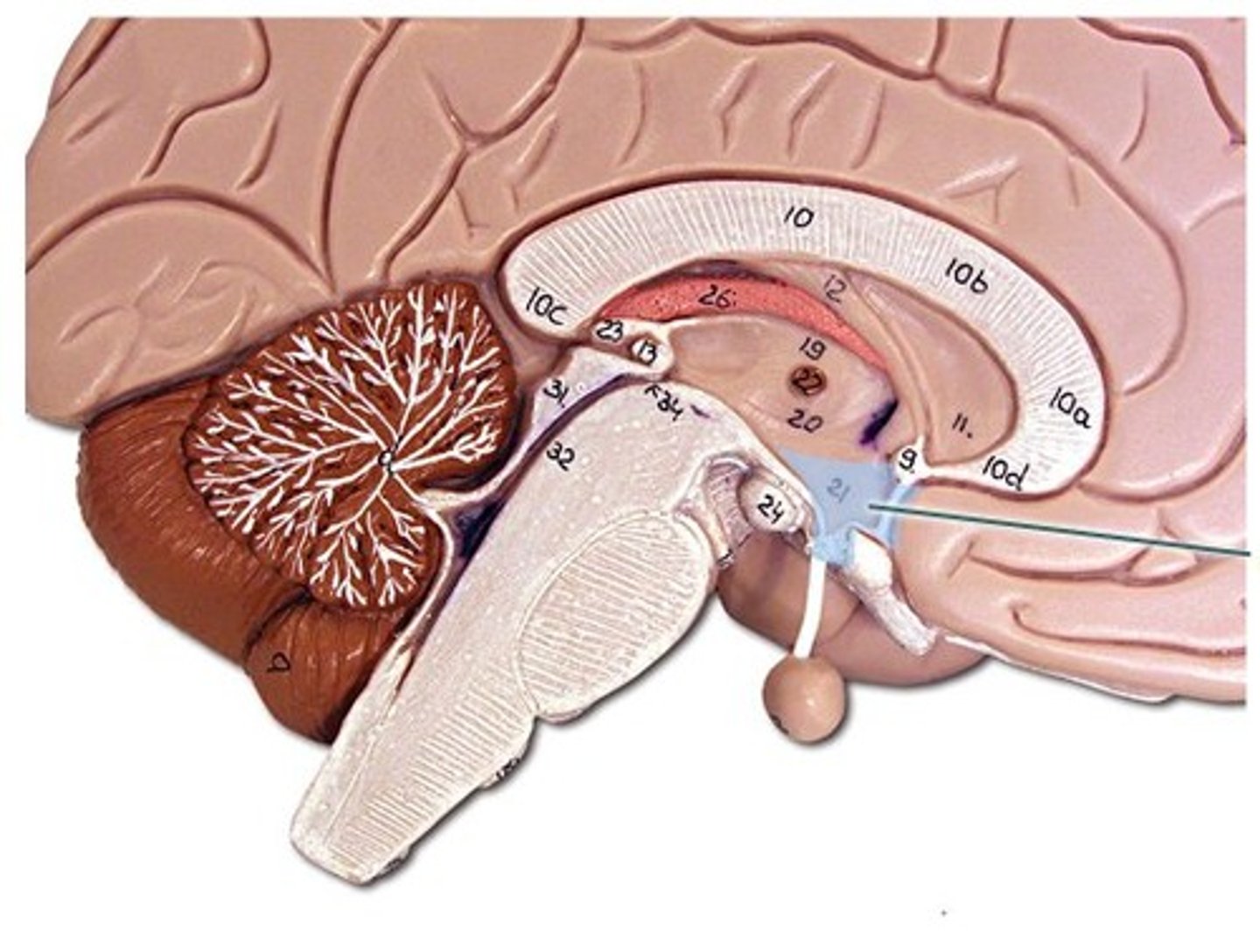
Hippocampus
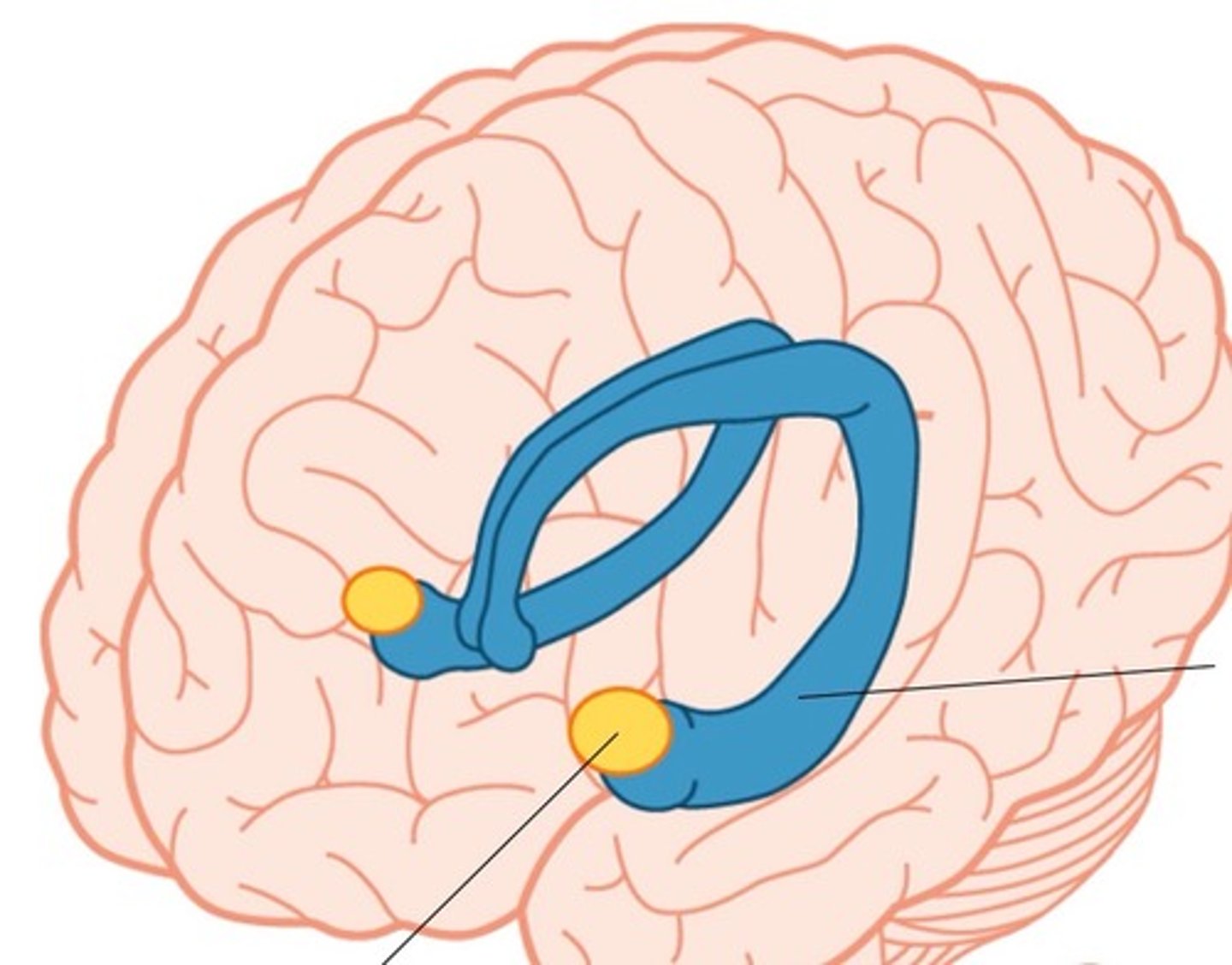
Amygdala
Corpus Callosum
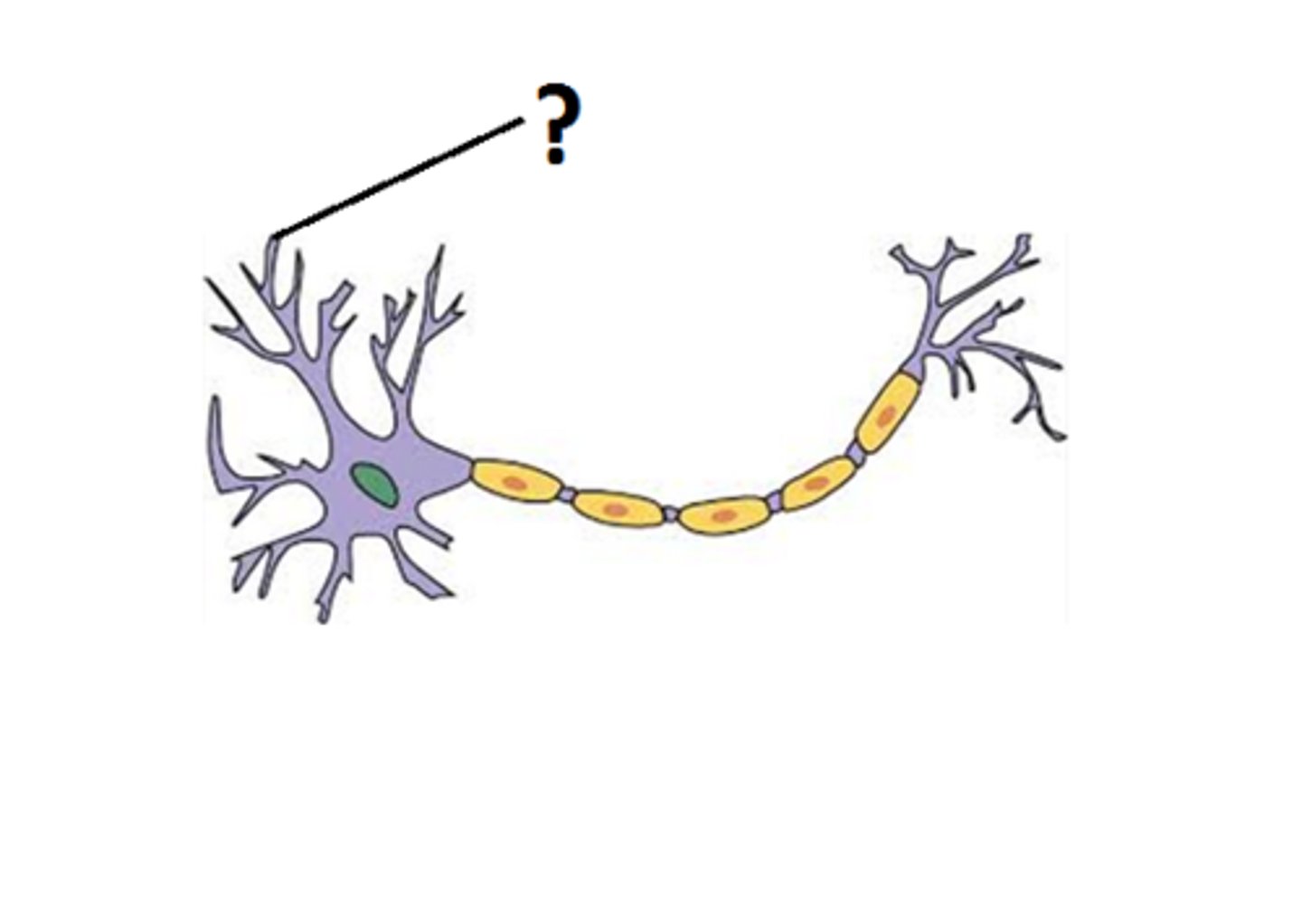
Dendrites
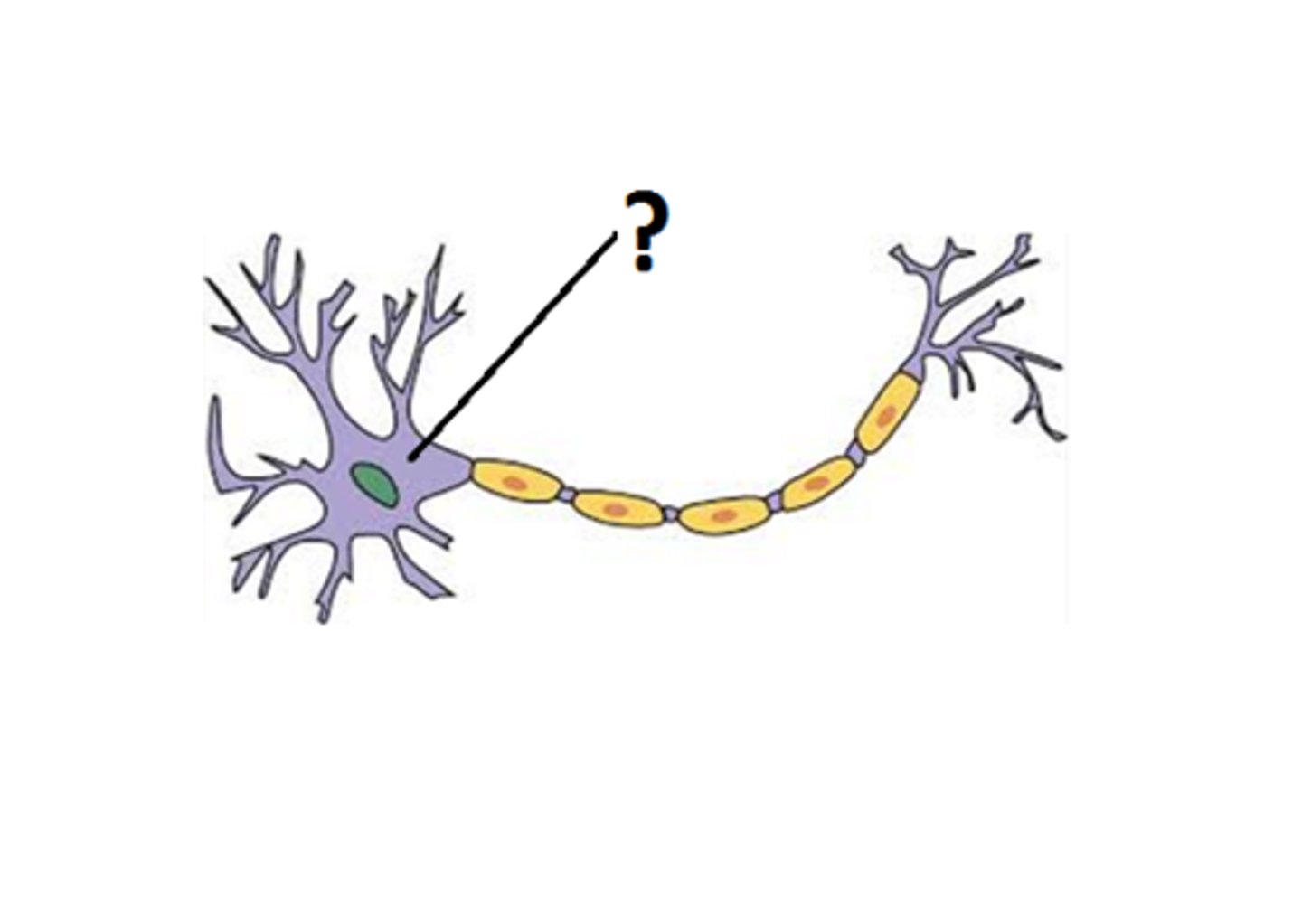
Cell Body/ Soma
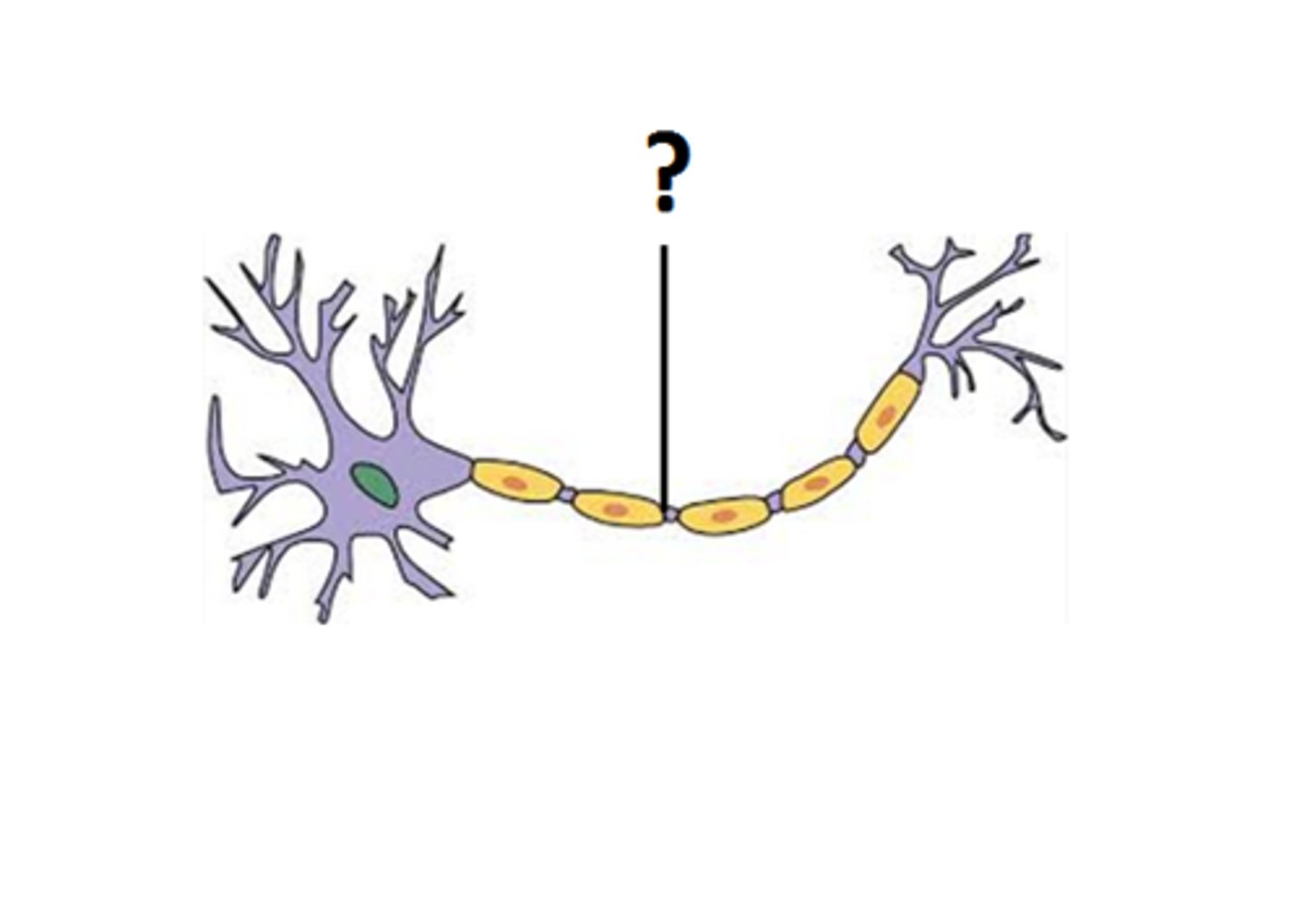
Axon
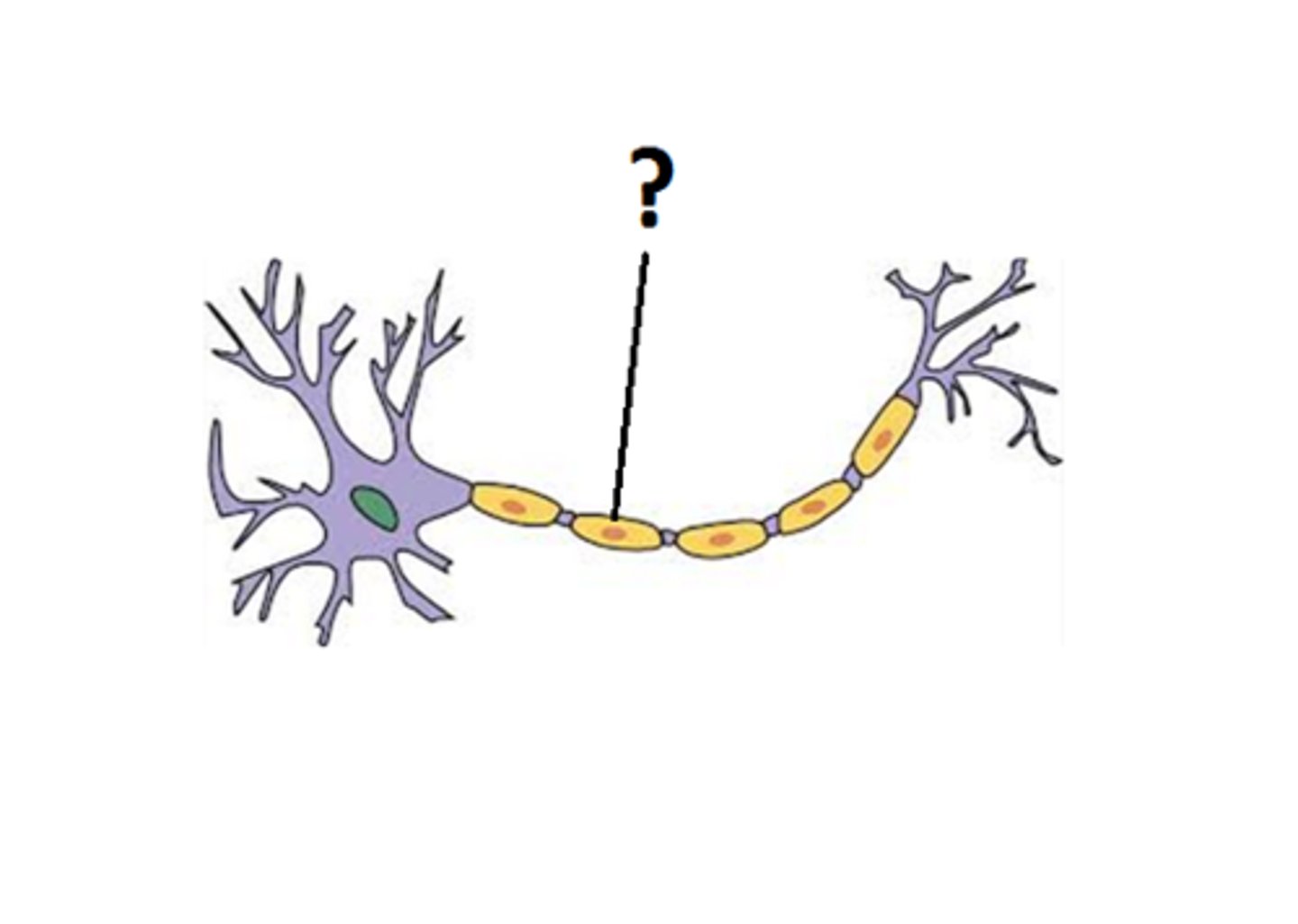
Myelin Sheath
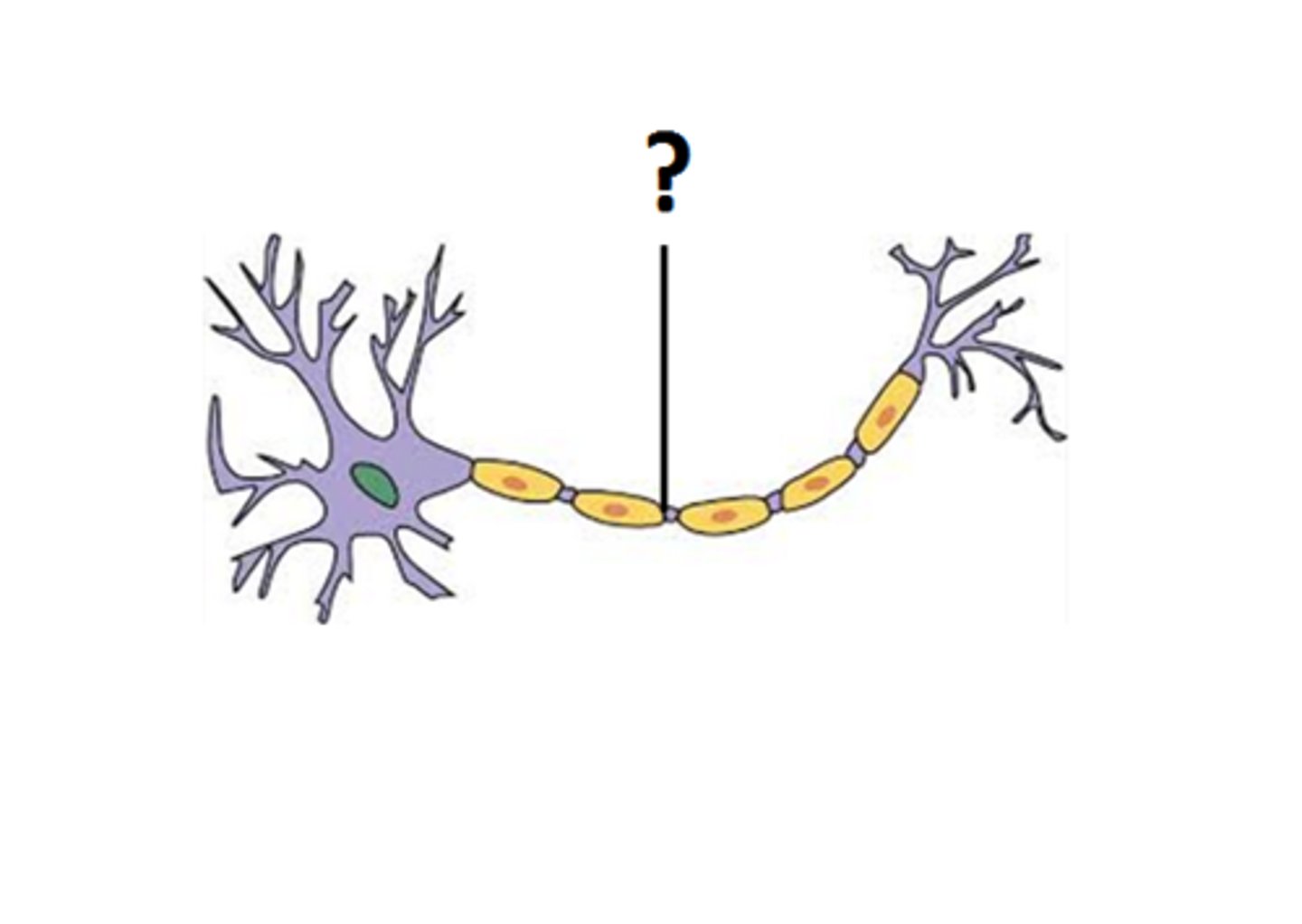
Node
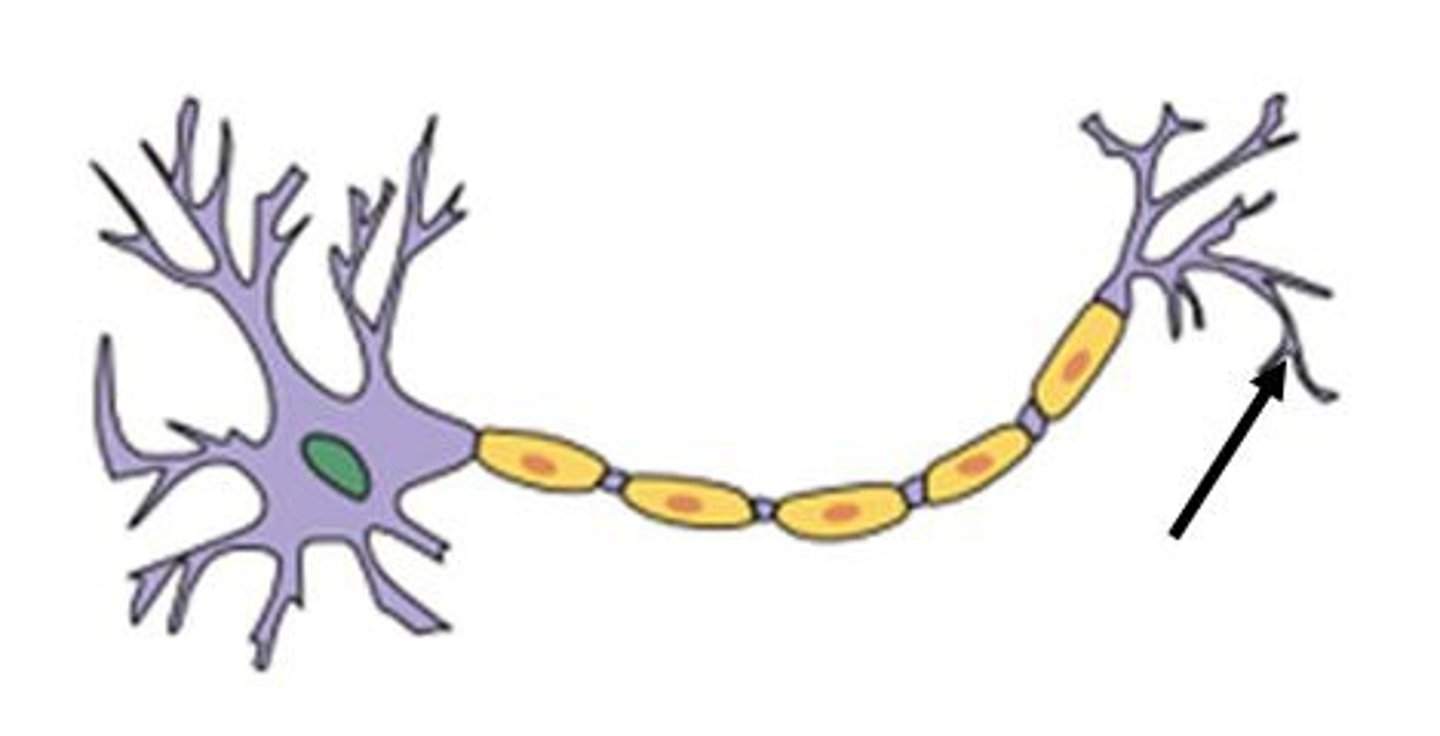
Axon Terminals
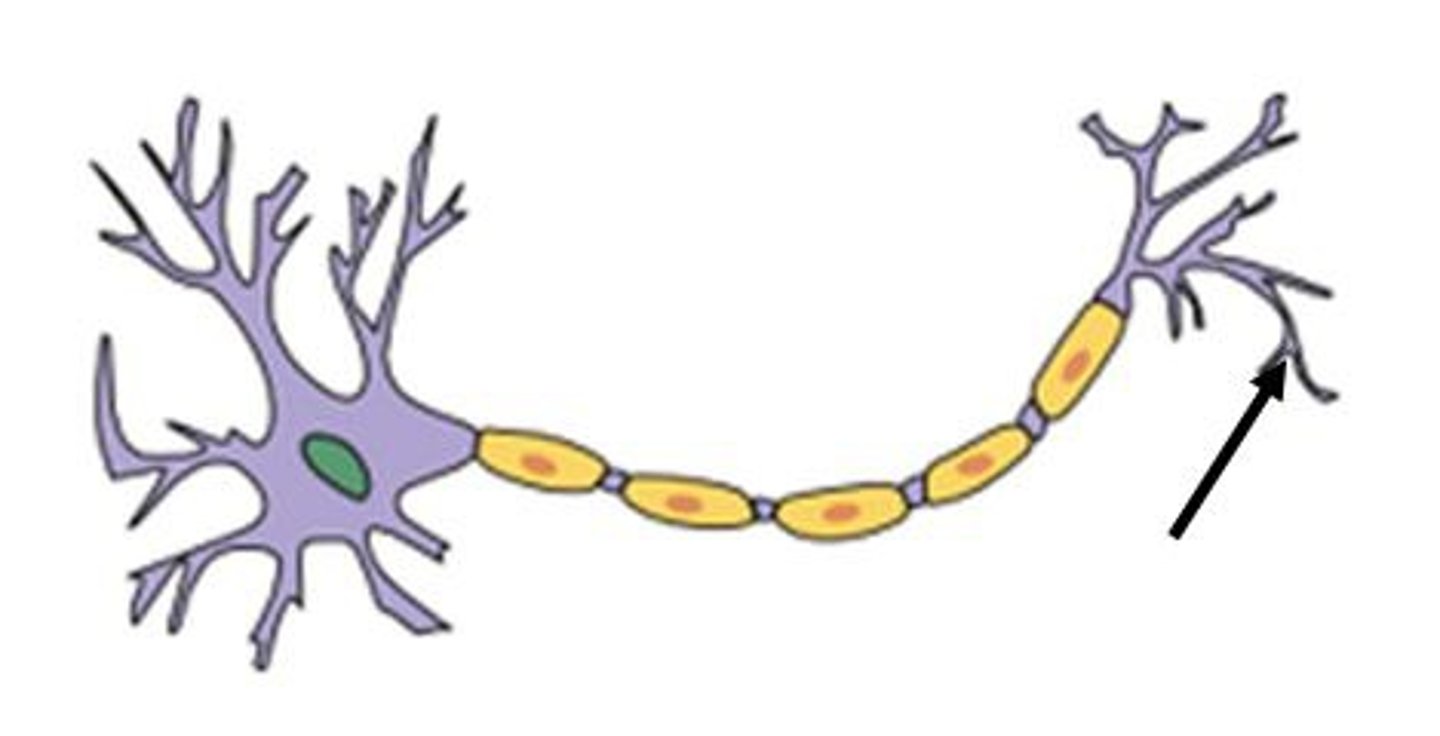
Synaptic End Bulbs
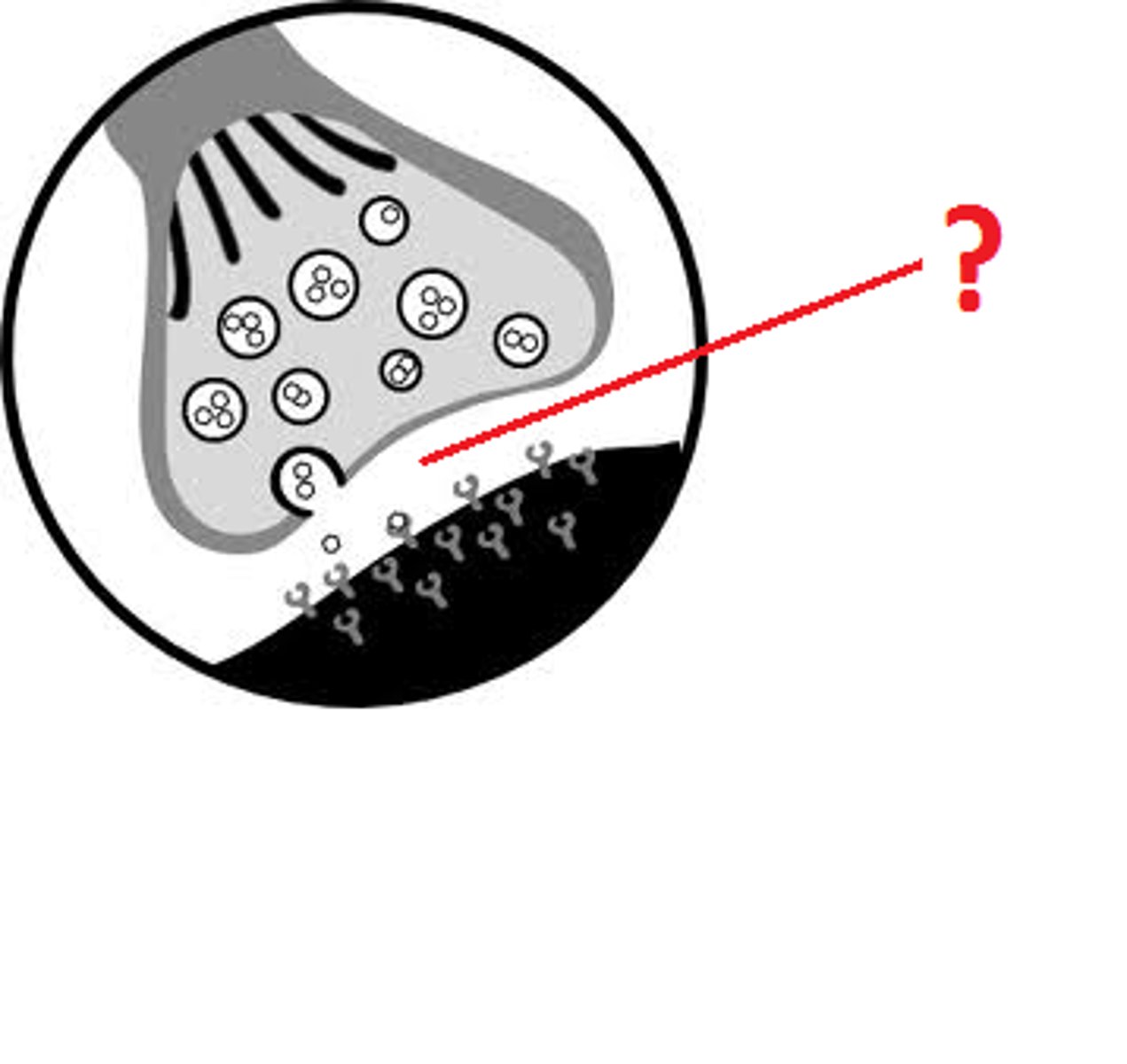
Synapse
Periodic, more or less regular fluctuations in a biological system (typically in tune with external time cues)
Biological Rhythms
Generated from within the body and still cycle absence of external time cues
Endogenous
A biological rhythm with a period of about 24 hours
Circadian Rhythms
Small cluster of cells contained within the hypothalamus that controls messages related to circadian rhythms
Suprachiasmatic Nucleus
A state in which biological rhythms are not in phase with one another
Internal Desynchronization (Definition answer)
Appears to be responsible for whether you are a "morning or night person"
Variation in a single gene
The cluster of physical and emotional symptoms presumed to occur in the days preceding mensuration
Premenstrual Syndrome
Reporting PMS symptoms varies by ____
culture
Many women ____ have physical symptoms, but emotional symptoms are ____.
do, rare
There is ____ difference between men and women in symptoms related to PMS
no
Women's moods fluctuate based more on ____ ____ ____ ____
day of the week
Women who tracked their daily symptoms, ____ reported PMS symptoms
retroactively
More attention is paid to emotional and physical symptoms around ____.
mensuration
Women may attribute symptoms to menstruation just before, and to a situation at ____ ____.
other times
A controversial disorder in which a person experiences depression during winter, when there is less light, and an improvement of mood in the spring, typically treated with light therapy
Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD)
A high percentage of studies on light therapy are ____
flawed
An assessment of 20 acceptable studies found reduced symptoms following exposure to ____ ____ for a brief period after waking or to a light that slowly became brighter
bright light
Many researchers believe that SAD is a result of chronic ____ ____ or an abnormality in how the body produces or responds to the hormone melatonin
Internal Desynchronization
Brain waves become small and irregular and you begin to drift off
Stage 1
brain waves begin to show rapid, high-peaking waves called sleep spindles
Stage 2
In addition to sleep spindles, the brain begins to show delta waves, which are very slow waves with high peaks; breathing begins to slow and a person is difficult to wake
Stage 3
Brain waves are mostly delta waves and person is in very deep sleep; almost impossible to wake person, but this is likely when sleep talking and walking occur
Stage 4
Sleep periods characterized by eye movement, loss of muscle tone, and dreaming
REM Sleep
Typical length of a sleep cycle
90 minutes
The process by which a memory becomes durable and stable and is believed to be highly related to sleep
Consolidation
Freud argued that our dreams are unconscious wishes and thoughts being expressed symbolically
Unconscious Wishes