EXAM 4-BIO
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/130
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
131 Terms
1
New cards
DNA is semi-conservative
hat each of the two strands in double-stranded DNA acts as a template to produce two new strands
2
New cards
Replication relies on complementary base pairing,
that is the principle explained by Chargaff's rules: adenine (A) always bonds with thymine (T) and cytosine (C) always bonds with guanine (G).
3
New cards
sketch a replication bubble label on it the 5’ and 3’ ends, the origin of replication,
replication forks, as well as the direction of the leading and lagging strands
replication forks, as well as the direction of the leading and lagging strands
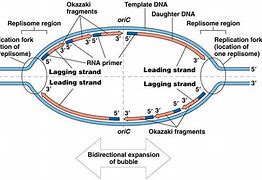
4
New cards
helicase function
An enzyme that breaks hydrogen bonds between nucleotides of DNA, "unzipping" a double-stranded DNA molecule.
5
New cards
DNA replication is described as bidirectional
because DNA replication proceeds outward from two replication forks.
6
New cards
During what process are parental DNA strands used as templates for the synthesis of new DNA strands?
replication
7
New cards
Why do eukaryotic cells have multiple origins of replication?
To ensure timely replication of multiple, relatively large chromosomes
8
New cards
DNA Ligase
an enzyme that joins pieces of DNA by catalyzing the formation of a phosphodiester bond between the pieces.
9
New cards
DNA polymerase
Any enzyme that catalyzes synthesis of DNA from deoxyribonucleotides.
10
New cards
double helix
The secondary structure of DNA, consisting of two antiparallel DNA strands wound around each other.
11
New cards
lagging strand
In DNA replication, the new strand of DNA that is synthesized discontinuously.
12
New cards
leading strand
In DNA replication, the new strand of DNA that is synthesized in one continuous piece .
13
New cards
Okazaki fragments
Short segments of DNA produced during replication of the lagging strand.
14
New cards
origin of replication
The site on a chromosome at which DNA replication begins.
15
New cards
primer
A short, single-stranded RNA molecule that base-pairs with a DNA template strand and is used as a starting point for DNA synthesis by DNA polymerase.
16
New cards
replication fork
The Y-shaped site at which a double-stranded molecule of DNA is separated into two single strands for replication.
17
New cards
Daughter DNA
he new DNA strand that grows continuously in the 5' to 3' direction.
18
New cards
Primase is in charge of
synthesizing a RNA primer and provide a 3' end
19
New cards
Topoisomerase is in charge of
relieving torque stress
20
New cards
Ligase is charge of
closing the gap between Okazaki fragments
21
New cards
DNA polymerase III is in charge of
synthesizing the daughter strand
22
New cards
DNA is a semiconservative process meaning
each parental strand serves as a template strand for a daughter
23
New cards
DNA helicase is in charge of
untwisting the double helix
24
New cards
7 different proteins and enzymes
DNA helicase, single-stranded binding proteins, Topoisomerase, primase, DNA polymerase III, ligase
25
New cards
DNA polymerase I
replacing an RNA primer with DNA nucleotides
26
New cards
single strand binding proteins
Keep DNA strands from repairing
27
New cards
leading strand
made continuously, made in segments, the daughter strand elongates away the replication fork, only one primer needed, synthesized 5-3
28
New cards
lagging strand
daughter strand elongates towards from the replication fork, synthesized 5-3, multiple primers needed
29
New cards
order of events of synthesizing Okazaki fragments
1. DNA polymerase 3 binds to three end of primer B
2. DNA polymerase 3 moves 5-3 elongating the fragment B
3.DNA polymerase 1 replaces primer A with DNA
4.DNA ligase OKASAKI FRAGMENTS a &b
2. DNA polymerase 3 moves 5-3 elongating the fragment B
3.DNA polymerase 1 replaces primer A with DNA
4.DNA ligase OKASAKI FRAGMENTS a &b
30
New cards
life cycle
shows the role of mitosis and meiosis in the life of an individual
31
New cards
zygote
2n, diploid, 1 cell
32
New cards
How is a zygote created
fertilization
33
New cards
fertilization
fusion of sperm and egg
34
New cards
Meiosis
-type of nuclear division
-produces gametes/haploid cells
- reduces the# of genetic material in half
-produces gametes/haploid cells
- reduces the# of genetic material in half
35
New cards
gametes
sperm and egg
36
New cards
M phase
The phase of cell division in which replicated chromosomes are pulled apart.
37
New cards
Interphase
The phase of the cell cycle in which a cell spends most of its life.
38
New cards
S phase
The phase of the cell cycle in which DNA is replicated.
39
New cards
G2 phase
Phase of the cell cycle where the cell synthesizes the proteins necessary for chromosome sorting and cell division.
40
New cards
G1 phase
A period when a cell may become committed to divide based on the environmental conditions and the presence of signaling molecules.
41
New cards
sex chromosomes
Chromosomes that determine the sex of an individual.
42
New cards
Interphase starts with
G1
43
New cards
order of phases
-prophase
-prometaphase
-metaphase
-anaphase
-telophase
-cytokenisis
-prometaphase
-metaphase
-anaphase
-telophase
-cytokenisis
44
New cards
allele
A particular version of a gene.
45
New cards
autosome
Any chromosome other than a sex chromosome.
46
New cards
dominant
Referring to an allele that determines the same phenotype when it is present in heterozygous form.
47
New cards
48
New cards
gene
The hereditary determinant of a trait or a section of DNA that codes for a protein.
The hereditary determinant of a trait or a section of DNA that codes for a protein.
The hereditary determinant of a trait or a section of DNA that codes for a protein.
49
New cards
genotype
All the alleles of a gene or genes present in a given individual.
50
New cards
heterozygous
Having two different alleles of a gene
51
New cards
homozygous
Having two identical alleles of a gene.
52
New cards
phenotype
The detectable traits of an individual.
53
New cards
recessive
Referring to an allele whose phenotypic effect is observed only in homozygous individuals
54
New cards
sex chromosomes
Chromosomes that differ in shape or in number in males and female.
55
New cards
true breeding line
a variety of a species that exhibits the same trait after several generations of self-fertilization
56
New cards
P (parental) generation
true breeding parents in Mendel's experiments
57
New cards
F1 generation
offspring of the P generation
58
New cards
F2 generation
offspring of the F1 generation
59
New cards
Aneuploidy
An alteration in the number of a particular chromosome, so the total number of chromosomes is not an exact multiple of a set.
60
New cards
crossing over
The exchange of corresponding segments of non-sister chromatids between a pair of homologous chromosomes during meiosis I.
61
New cards
diploid
Having two sets of chromosomes, one inherited from the mother and the other set inherited from the father.
62
New cards
fertilization
Fusion of the nuclei of two gametes (haploid cells) to form a zygote (diploid cell).
63
New cards
gametes
A haploid reproductive cell.
64
New cards
haploid
Having one set of chromosomes.
65
New cards
homologous chromosome pair
In diploid organisms, a pair of chromosomes that are the same size and shape and contain the same genes in the same positions.
66
New cards
nondisjunction
An error that can occur during meiosis or mitosis; it results in one daughter cell receiving two copies of a particular chromosomes while the other daughter cell receives none.
67
New cards
sister chromatids
The paired, double-stranded DNA copies of a recently replicated chromosomes.
68
New cards
Sexual reproduction
A process in which two haploid gametes unite to form a genetically unique diploid cell.
69
New cards
Monosomy
The condition of having a diploid chromosome complement in which one chromosome lacks its homologous partner.
70
New cards
Trisomy
The condition in which there are three copies of the a chromosomes type instead of the normal two.
71
New cards
Life cycle
The sequence of events that produces another generation of organisms
72
New cards
generates genetic diversity in 3 ways
random fertilization, independent assortment, and crossing over
73
New cards
when does crossing over happen
prophase 1
74
New cards
what happens in random fertilization
gametes fuse independently of their genetic information
75
New cards
principles of chromosome theory of inheritance
1. DNA is genetic material
2. Chromosomes are inherited as units from parents to offspring
3.Diploid cells contain pairs of homologous chromosomes( 1 maternal and 1 paternal)
4.During Meiosis I-homologs separate and sort independently of whether they are maternal or paternal
5. Gametes are haploid--> carry one set of chromosome
2. Chromosomes are inherited as units from parents to offspring
3.Diploid cells contain pairs of homologous chromosomes( 1 maternal and 1 paternal)
4.During Meiosis I-homologs separate and sort independently of whether they are maternal or paternal
5. Gametes are haploid--> carry one set of chromosome
76
New cards
How is DNA organized?
chromosomes
77
New cards
how else are chromosomes inherited?
cell to cell through mitosis and from pare4nts to offspring
78
New cards
What do homologous chromosomes carry?
a set of complimentary genes
79
New cards
Gene expression
|Gene-->|protein-->| characteristic|
80
New cards
What is a gene?
Unit factor passed on from generation to generation)(ex. eye color seed color)
81
New cards
What is an allele?
variant form of a gene
82
New cards
character
a distinguished feature of a group or organism that is heritable and controlled by genes
83
New cards
what is a trait
variation of a character controlled by alleles
84
New cards
Genotype
description of
the genetic makeup of
an individua
the genetic makeup of
an individua
85
New cards
Phenotype
observable, measurable
characteristics in an
individual
(described by adjectives)
characteristics in an
individual
(described by adjectives)
86
New cards
diploid organisms carry
y two alleles per gene
(one in a each chromosome within a pair of homologs)
(one in a each chromosome within a pair of homologs)
87
New cards
RR or rr
> homozygous (two identical alleles)
88
New cards
RR
--> homozygous dominant
89
New cards
rr
--> homozygous recessive
90
New cards
Rr
--> heterozygous (two unequal alleles)
91
New cards
capitalized letter
dominant
92
New cards
lower case letter
recessive
93
New cards
punnet square
tool for predicting outcome of a
genetic cross
genetic cross
94
New cards
square
male
95
New cards
circle
female
96
New cards
filled in circle or square
affected
97
New cards
empty circle or squar
unaffected
98
New cards
recessive trait
*unaffected individuals may have effected children
*may skip generations
*heterozygous individuals are carriers
* males and females effected with equal frequency
*may skip generations
*heterozygous individuals are carriers
* males and females effected with equal frequency
99
New cards
sex linked genes
found only on sex chromosomes
100
New cards
y chromosome
75 genes mostly in masculenity