X-Ray Interaction in Tissue
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards based on X-Ray Interaction in Tissue lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What are the three main ways X-ray photons interact with a patient?
Penetration, absorption, and scatter
What is a valence electron?
Electron on the outer shell of nucleus, has more energy but weaker binding energy
What is the relationship between binding energy and atomic number?
Binding energy is directly proportional to atomic number.
In the context of X-rays, what happens during penetration?
X-ray photons go through the patient and hit the detector.
In the context of X-rays, what happens during absorption?
X-ray photons interact with something and are absorbed by the patient, not reaching the detector.
In the context of X-rays, what happens during partial absorption?
X-ray photon loses energy in patient and hits detector
In the context of X-rays, what happens during scatter radiation?
X-ray photon has interactions and bounce off from patient, not reaching the detector
List the five types of attenuation discussed in the lecture.
Coherent scattering, photoelectric absorption, Compton scattering, pair production, and photo-disintegration.
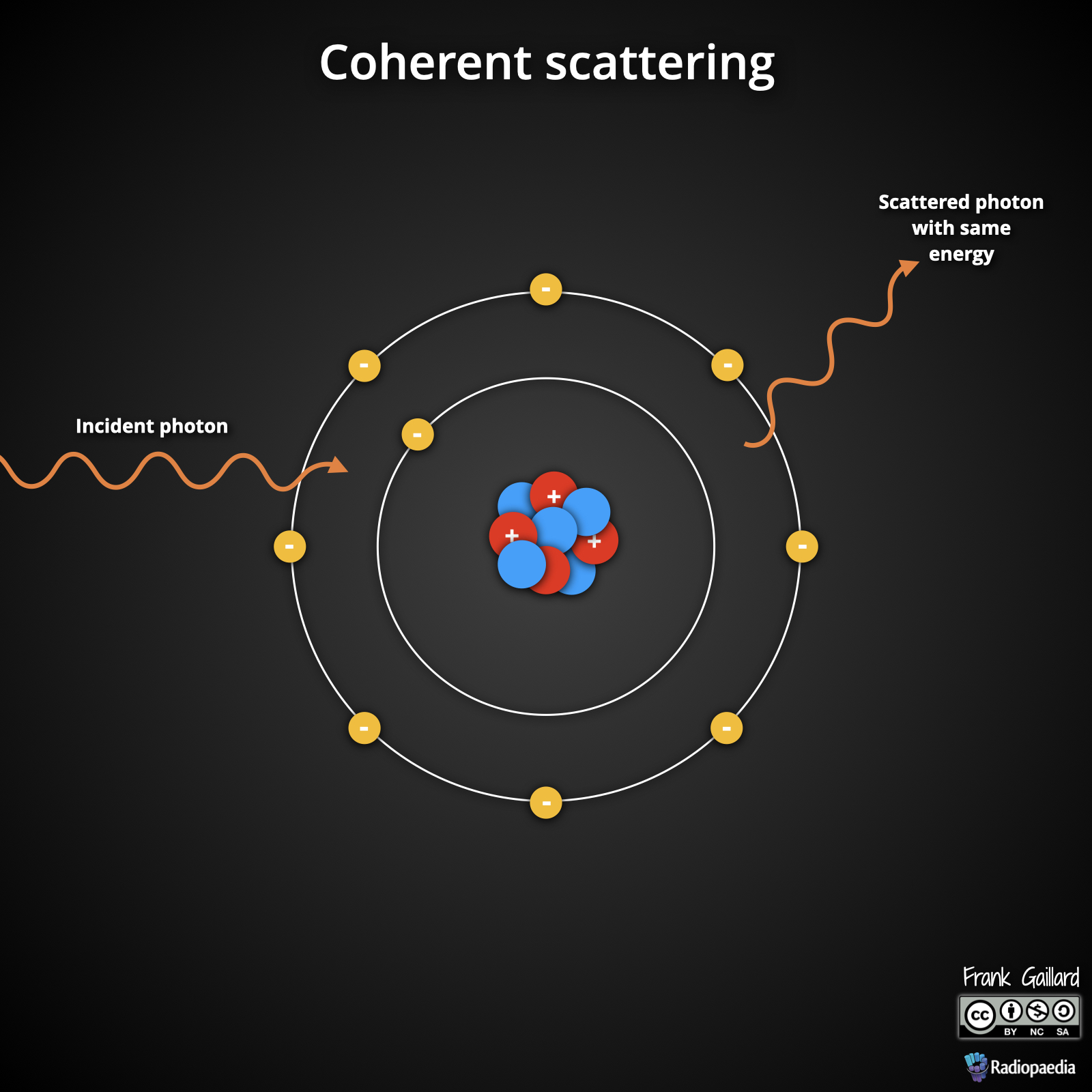
Describe what happens during coherent scattering.
An incident photon excites an electron as it passes by and is deflected with the same energy.
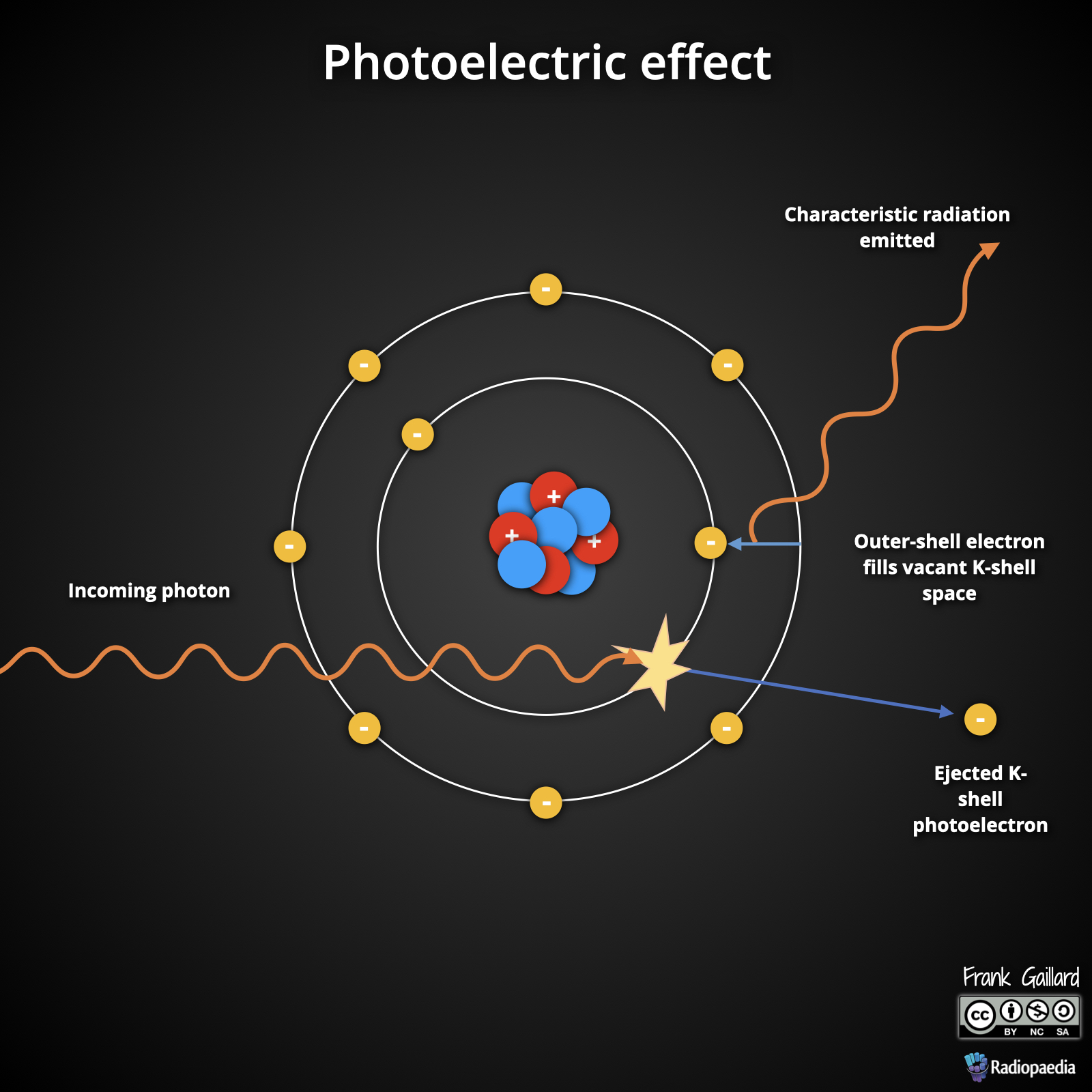
How does photoelectric absorption occur?
An incident photon knocks off an electron from the K or L shell, and an outer-shell electron fills the vacancy, emitting characteristic radiation.
How does high atomic number affect photoelectric absorption?
Increases probability of photoelectron absorption
Describe Compton scattering.
A high-energy photon interacts with an outer shell electron, ejecting it and losing energy to become a lower-energy scattered photon.
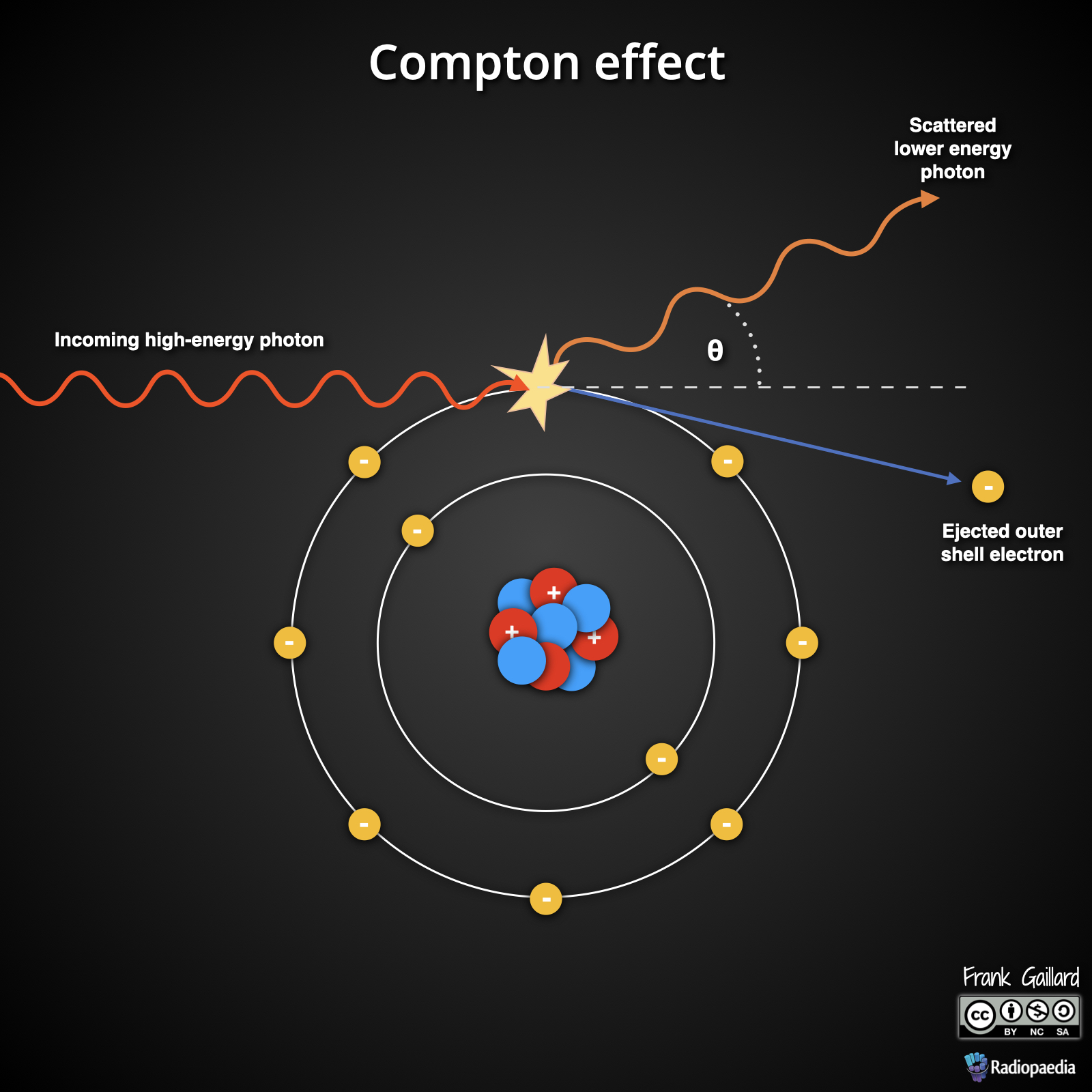
What is the impact of Compton Scatter?
This interaction can irradiate others
How are Dark and White areas defined in X-rays?
Dark area = lots of photons reaches detector, lots of transmission/ penetration. White area = high Z therefore high probability of PEA
Define Differential Absorption
Difference in x-ray interactions with matter
In the context of X-rays, what happens at lower kVs?
Increased probability of PEA and better contrast
In the context of X-rays, what happens at higher kVs?
Probability of Compton scatter increase and contrast is worse
Describe pair production.
A high-energy photon interacts with the nucleus, splitting it into a positron and an electron, followed by annihilation at 180 degrees.
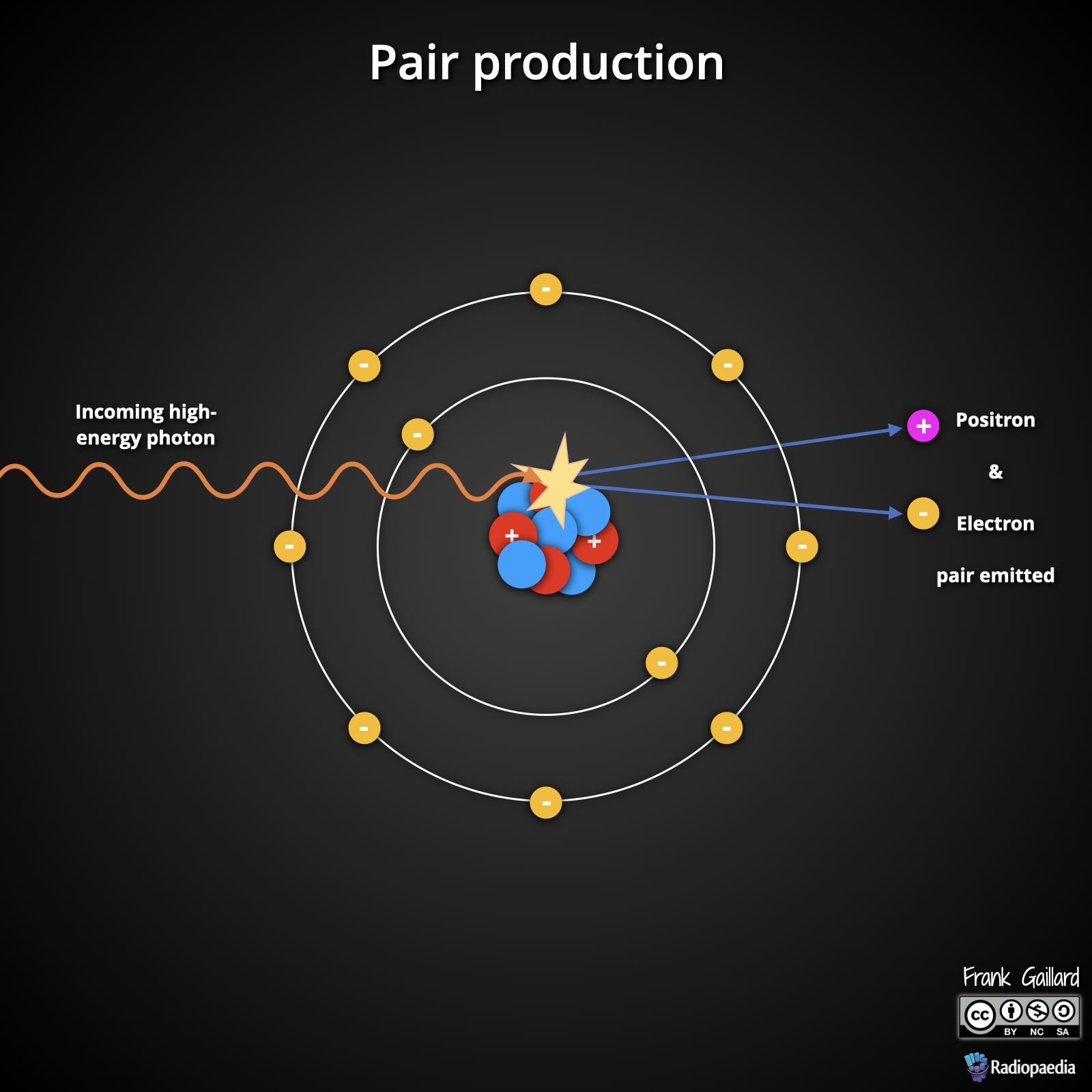
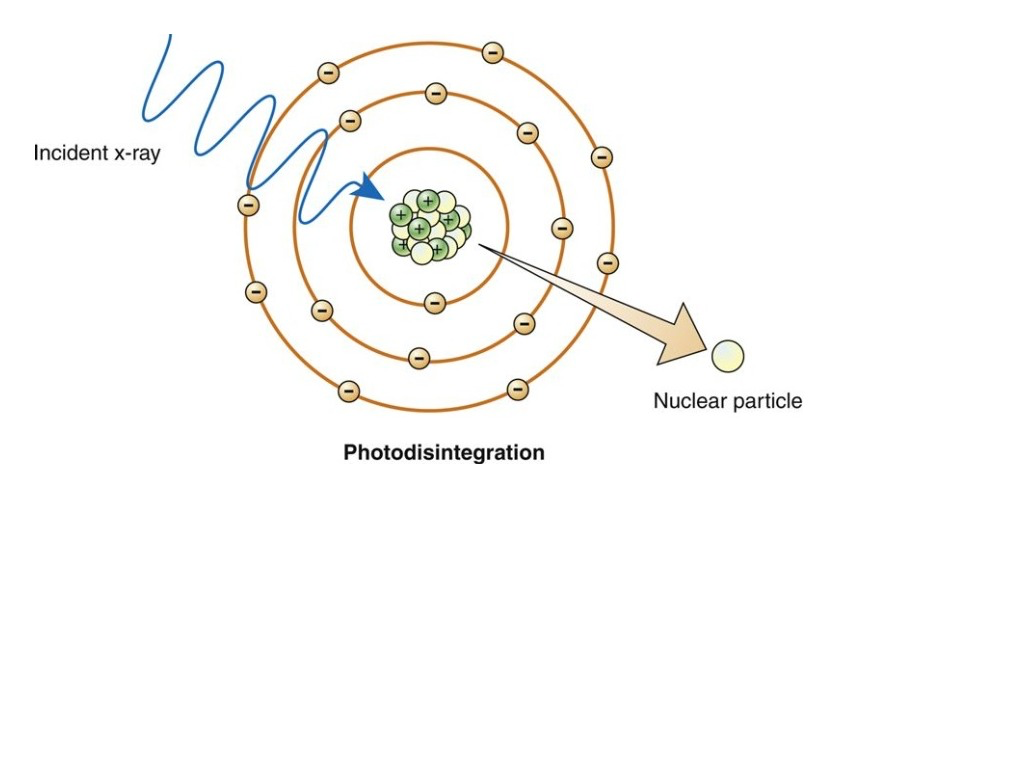
Describe photo-disintegration.
An incident x-ray interacts with the nucleus, making it unstable and causing it to eject nucleons.