Theorieis of reflective practice and basic schools of psychology
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
Kolb - Kolb’s experiential learning theory
Kolb’s experiential learning style theory is typically represented by a four-stage learning cycle in which the learner “touches all the bases
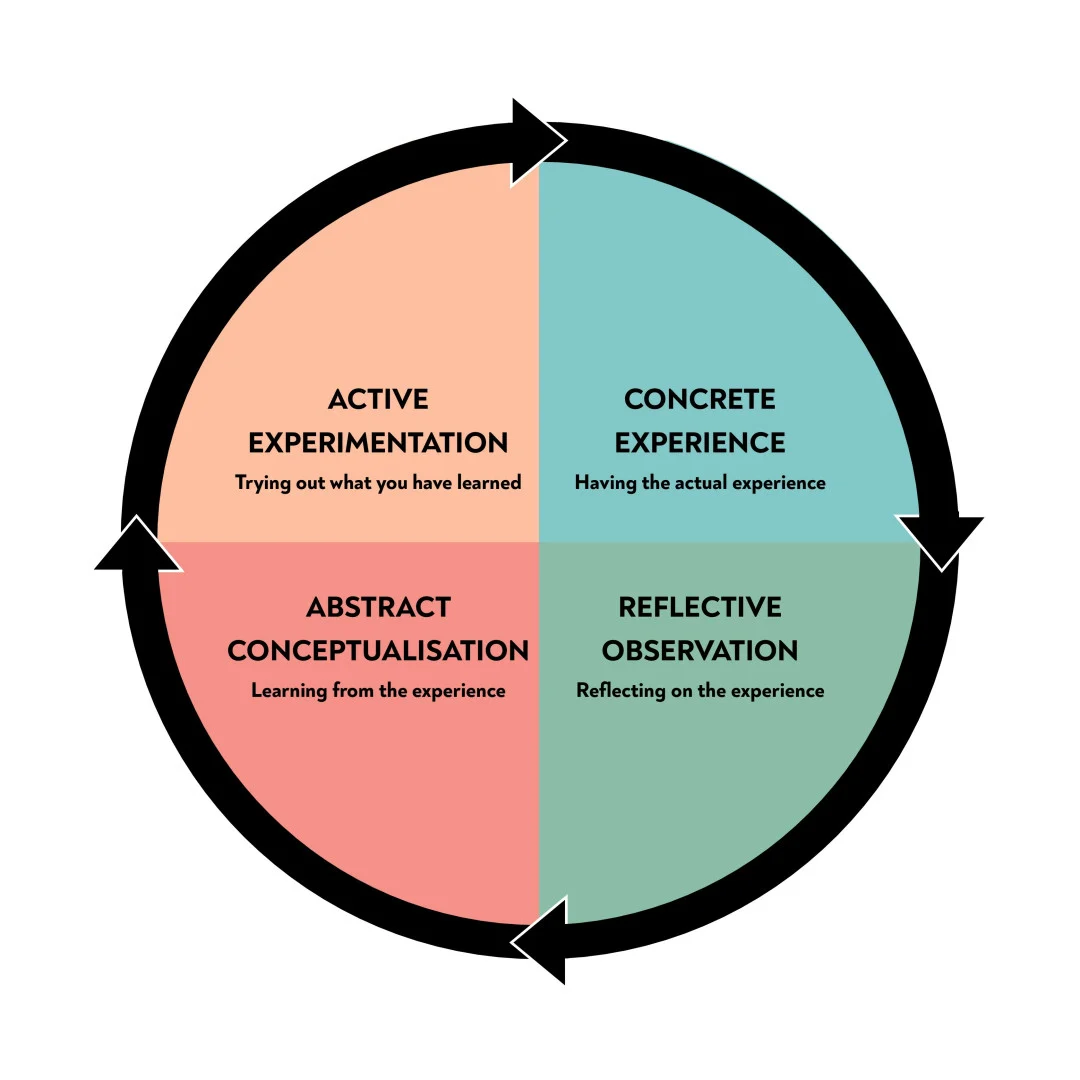
Gibbs - Gibbs' reflective practice
Gibbs' reflective practice model is a framework for structured reflection, consisting of six stages: description, feelings, evaluation, analysis, conclusion, and action plan. In the application of this model, linguistic interpretation is key to understanding and articulating experiences during reflection.
Schön - Schön's reflective practice model
Schön's reflective practice model emphasizes the importance of reflection in action and reflection on action, focusing on learning from experience and adapting practices.
Behaviorism
A school of psychology that focuses on observable behaviours and the ways they can be learned or unlearned through conditioning.
Cognitive Psychology
A branch of psychology that studies mental processes such as perception, memory, problem-solving, and decision-making.
Psychoanalysis
A school of thought developed by Sigmund Freud, emphasizing the influence of the unconscious mind on behavior and the importance of childhood experiences.
Humanistic Psychology
A psychological perspective that emphasizes the study of the whole person and the uniqueness of each individual's experience, fostering personal growth and self-actualization.
Gestalt Psychology
A psychological approach that focuses on understanding the organization of the mind and behaviors as a whole, rather than as individual components.
Neuroscience
Neuroscience is the scientific study of the nervous system, encompassing the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves, and seeks to understand how these structures influence behavior, cognition, and emotions.