CH 101 Varner
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
when atoms of similar electronegativity (generally 2 nonmetals) share electrons
Covalent bonds
Electrostatic attraction between a cation and anion Oftentimes (but not always), this is between a metal cation and non-metal anion
Ionic bonds
1) Each atom that requires an octet has an octet
2) The total number of atoms with nonzero formal charges is minimized
Resonance Structure Hierarchy Rules:
Pi bonds are only if there is more than one bond between two molecules
Sigma vs Pi bonds
just p
Pi orbital hybridization is
1) # of atomic orbitals in = # of molecular orbitals out
2) The lower energy molecular orbital is termed a bonding orbital
3) The higher energy molecular orbital is termed an antibonding orbital and is labeled with “*”
Molecular Orbitals (MO)
BO = ½(BE-ABE*)
MO Bond Order
Molecule has at least one unpaired electron
Paramagnetic
Exist within a single molecule. The covalent or ionic bonds between atoms.
Intramolecular Forces
Exist between 2 or more molecules. The attractive forces between two molecules that keep them close together.
Intermolecular Forces
the larger the molecule, the larger the amount of London dispersion forces.
All molecules possess dispersion forces. However,
Requirements One molecule with a H-N, H-O, or H-F covalent bond. A second molecule with a N, O, or F atom.
The δ+ H atom of one molecule is attracted to the δ- N, O, or F atom of a second molecule
Hydrogen Bonding
Gases = thermal > intermolecular
Liquid = equal
Solid = thermal < intermolecular
Thermal vs intermolecular forces
the higher the melting point or boiling point
The greater the number of intermolecular forces
easy escape from liquid phase
Low atmospheric pressure =
difficult escape from liquid phase
High atmospheric pressure =
Sublimation
Solid to gas
deposition
Gas to solid
condensation
Gas to liquid
evaporation
Liquid to gas
freezing
Liquid to solid
melting
Solid to liquid
Nonpolar solutes are soluble in nonpolar solvents.
Polar solutes are soluble in polar solvents
“Like Dissolves Like”
hydrophobic
Nonpolar solutes are
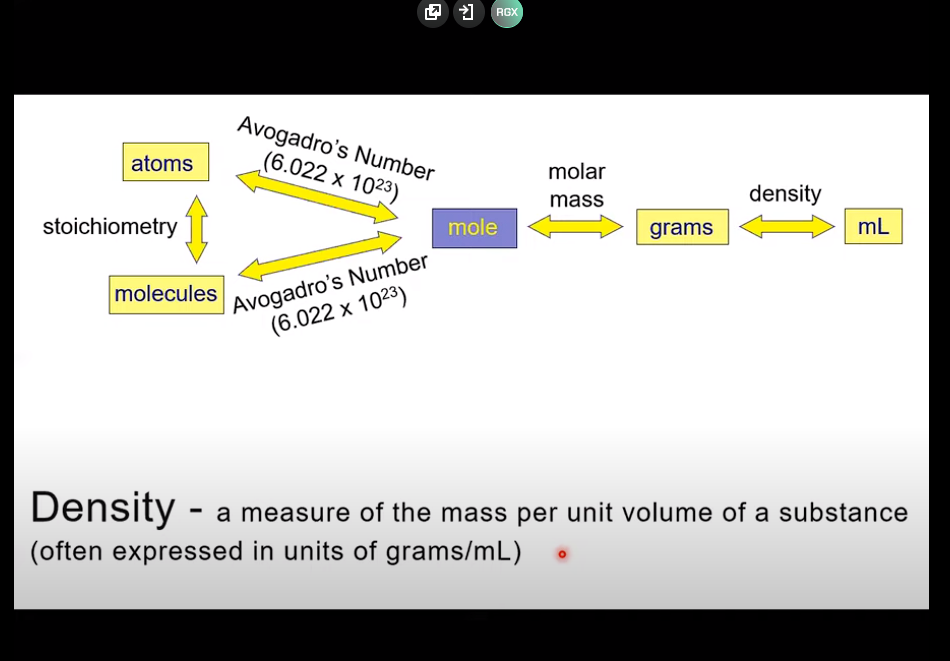
Molar concertation (moles solute / liters solution)
What does “M” stand for?
grams/mL
Density
London dispersion are effected by
Mass and # of molecules, not electronegativity
Vapor Pressure is opposite
Boiling point
Hydrophobic
No polar
Hydrophilic
Polar
Rows 3a and below
Can break octet rule