Chapter 6: Muscular System (Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology, Marieb)
1/141
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
142 Terms
Muscles
A type of tissue which is responsible for movement in body. This movement produces heat as a byproduct.
Skeletal Muscle
One of the three types of muscles. Muscles move voluntarily and are attached by tendons to bones. They are long, multinucleate (have multiple nucleus), appear striated (due to arrangement of actin and myacin), and are surrounded and bundled by connective tissue. (which supplies nutrients)
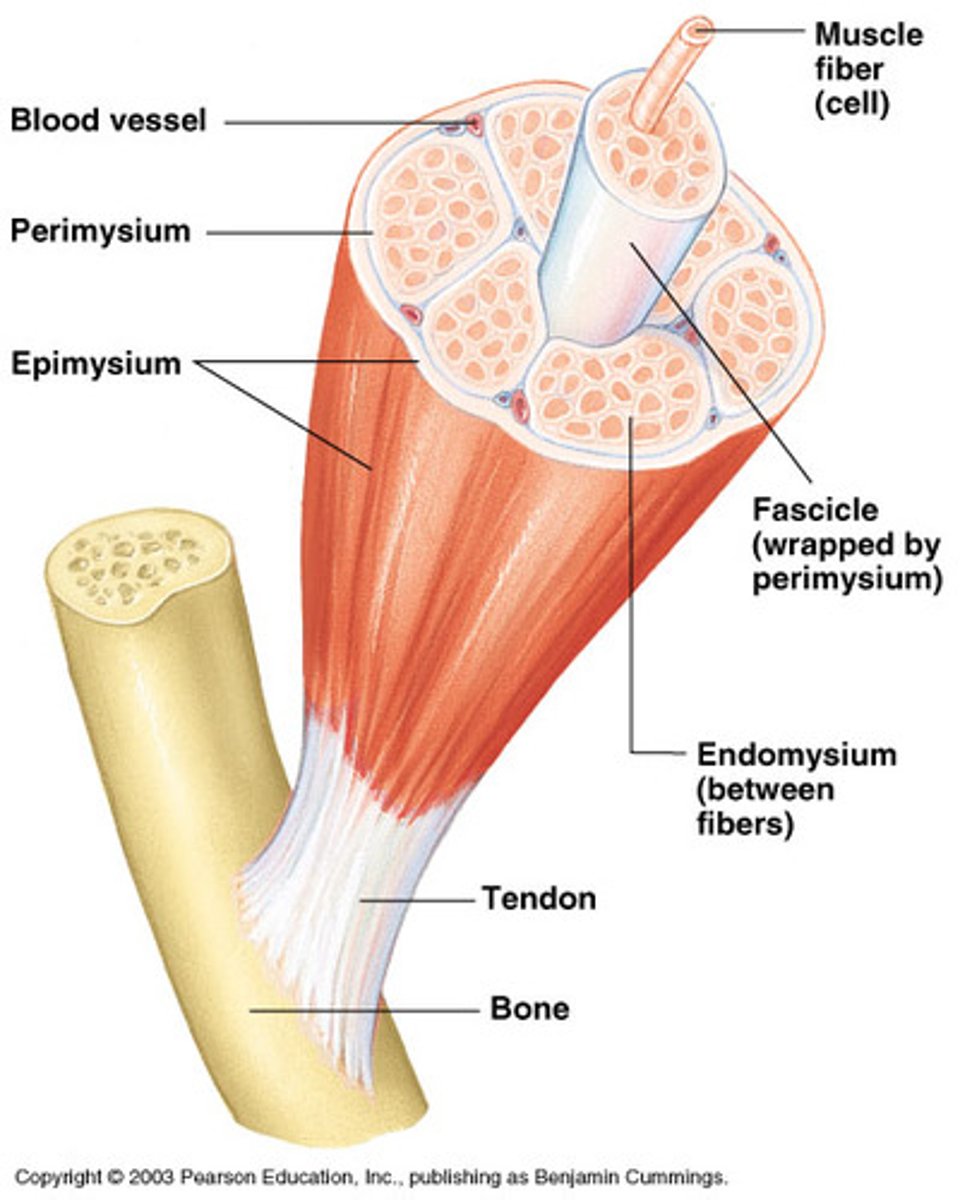
Endomysium
A connective tissue wrapping which wraps itself around a single muscle cell/fiber.
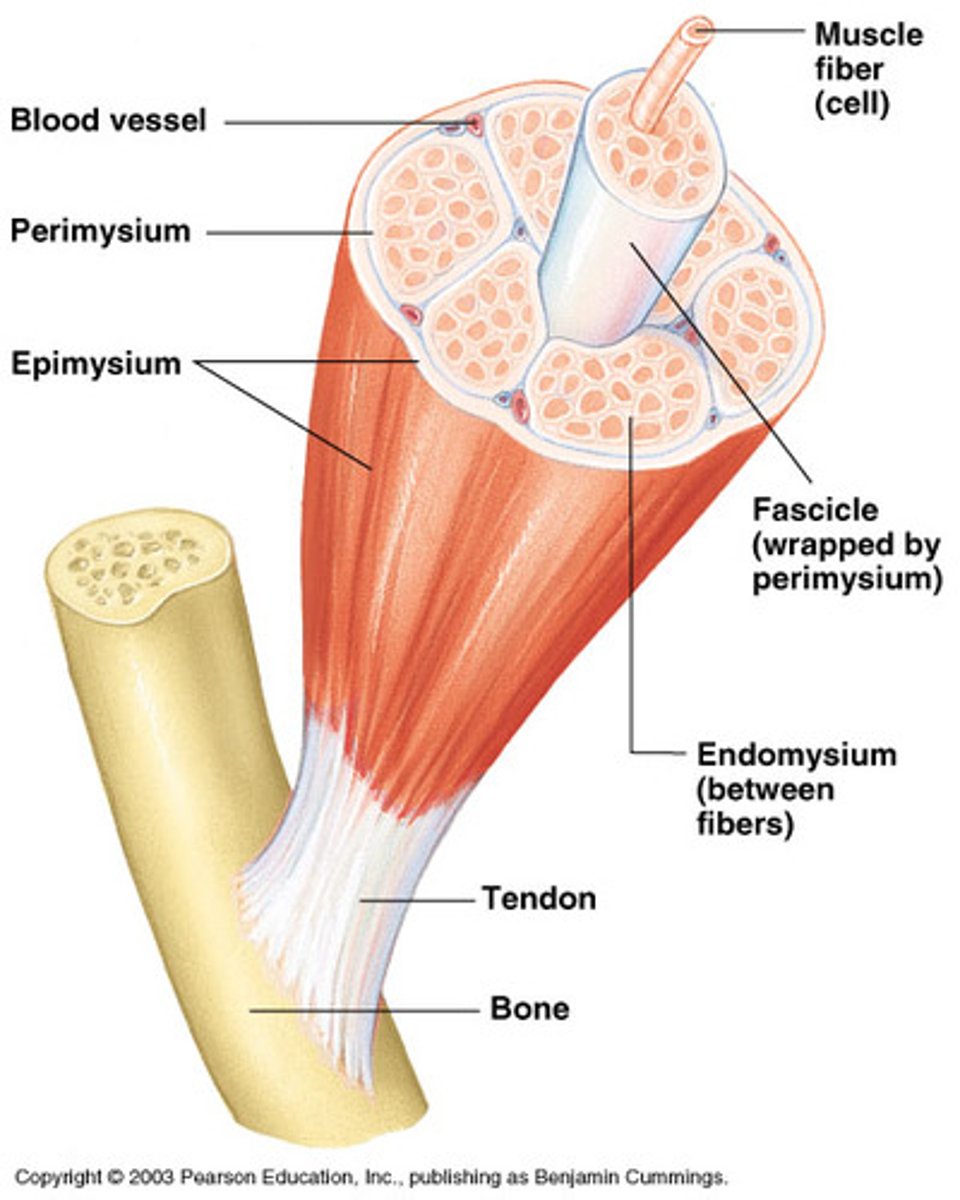
Perimysium
A connective tissue wrapping which wraps itself around a fascicle (bundle) of cells/fibers.
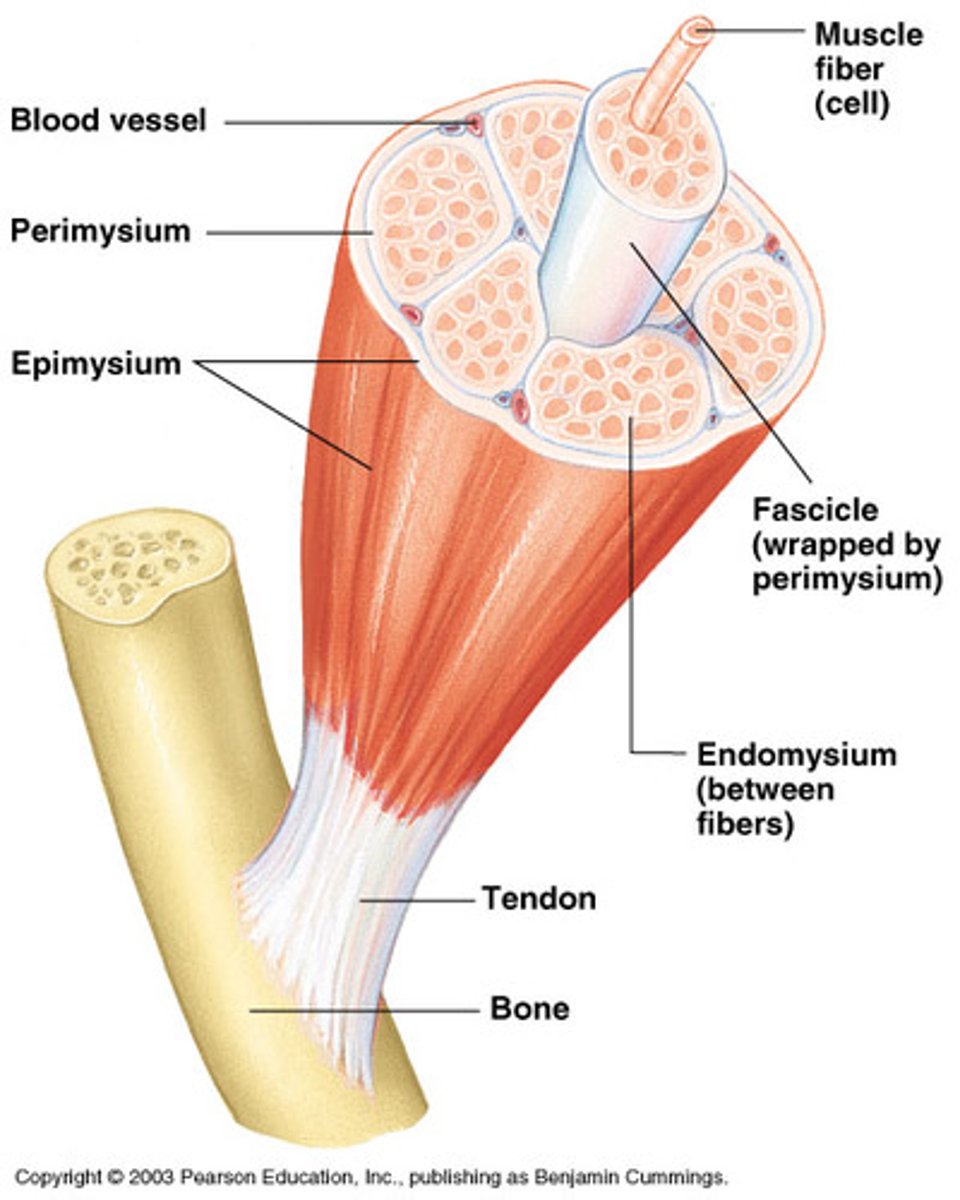
Epimysium
A connective tissue wrapping which covers the entire skeletal muscle.
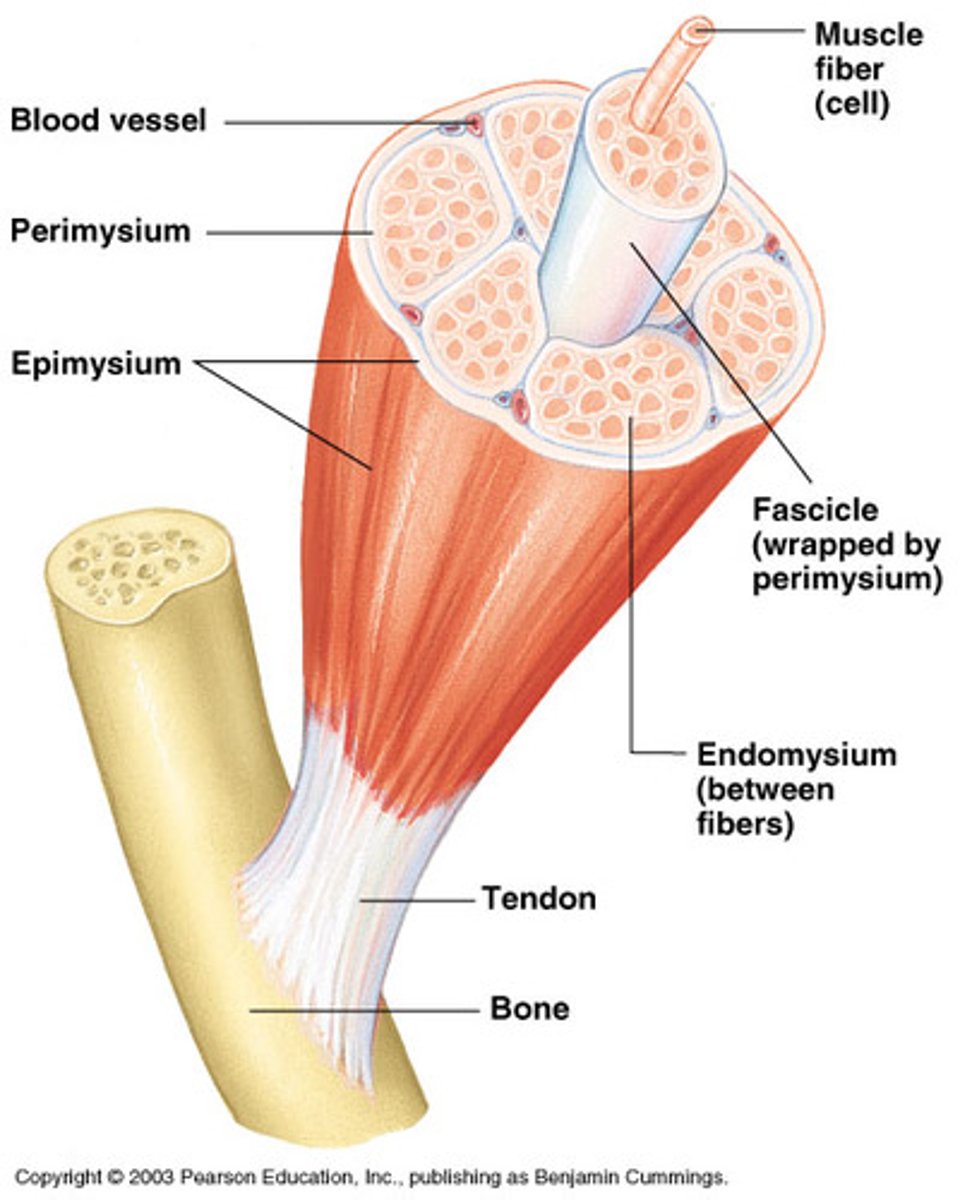
Tendon
Is a cord like structure which connects muscles to bones. It is formed by epimysium blending into connective tissue attachments.
Aponeurosis
A sheet like structure whose primary function is to join muscles to the body parts (bone or muscle) the muscles act upon.Is formed by epimysium blending into connective tissue attachments.
Collagen Fibers of the Skin
A type of connective tissue formed when epimysium blends into particular connective tissue attachments.
Smooth Muscle
One of the three different types of muscle tissue. This muscle has no striations and is formed from spindle shaped cells, they possess a single nucleus, move involuntarily, and are found mainly in the walls of hollow organs.
Cardiac Muscle
One of the three types of muscle tissues. These have striations, usually a single nucleus, are joined together by another muscle cell by an intercalated disc, function involuntarily, and are found only in the heart.
Sarcolemma
The cell membrane of a striated muscle cell.
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
The special type of smooth endoplasmic reticulum found in smooth and striated muscle fibers whose function is to store and release calcium ions.
Myofibrils
Microfilaments of actin and myosin in repeating subunits.
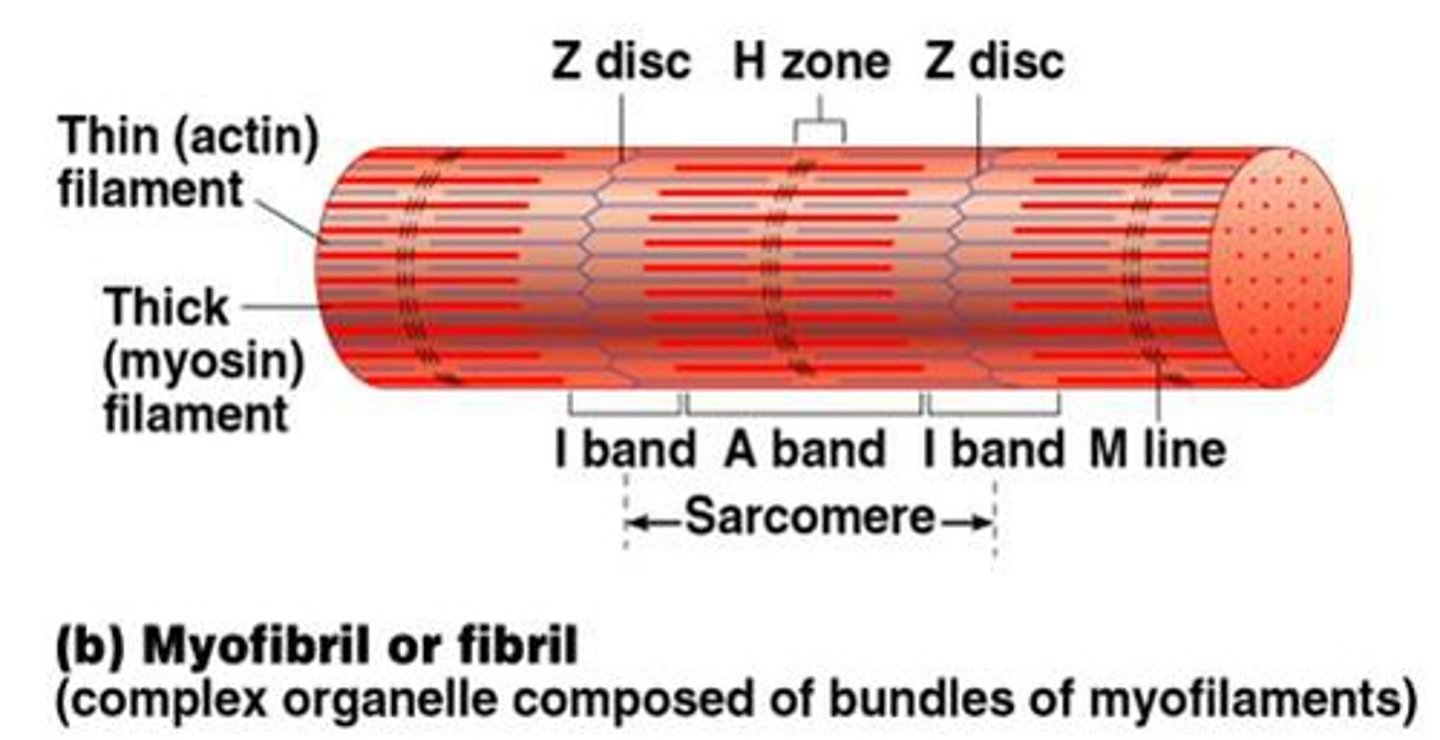
Sarcomere
The contractile unit of a myofibril consisting of Z-discs, A-bands, and I-bands.
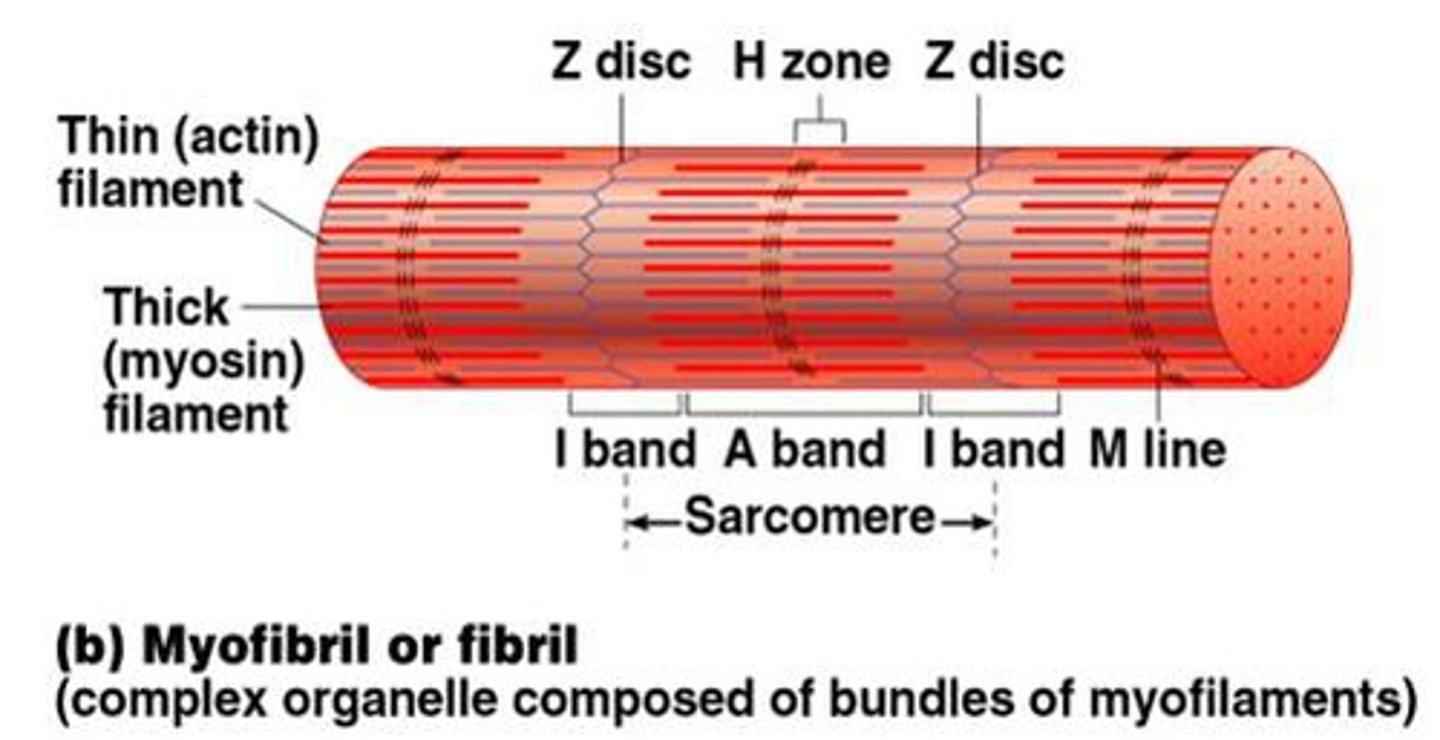
Z Disc
A structure within a unit of myofibril. It is a membrane which actin is embedded in.
Neuromuscular Junction
The place at which the nervous system is connected to the muscular system through a synapse. It is here in which the muscle cells are simulated by a single neuron.
ATP
A unit of stored energy which muscles use initially for contraction. Only 4-6 seconds of ATP energy is stored by muscles. The bonds within ATP are broken in order to release the energy.
Origin
A place where a muscle attaches on a bone that is not moved by that muscle.
Insertion
A place where a muscle attaches on a bone that is moved by the muscle.
Flexion
Movement in the saggital plane that decreases the angle of the joint and brings two bones closer together.
Extension
Opposite of flexion; movement in the saggital plane that increases the angle of the joint or distance between two bones or parts of the body.
Rotation
Movement of a bone around its longitudinal axis.
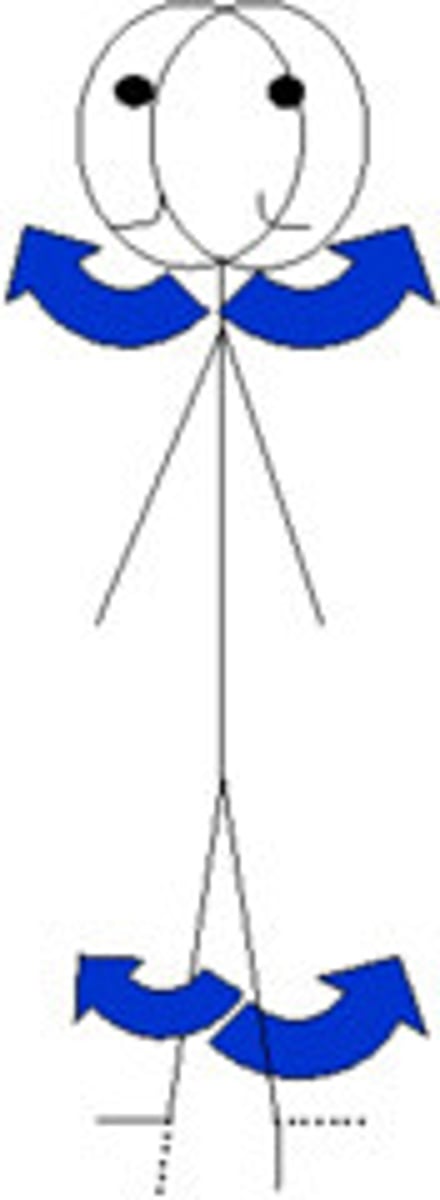
Abduction
moving a limb away in the frontal plane from the median plane of the body, spreading the fingers apart
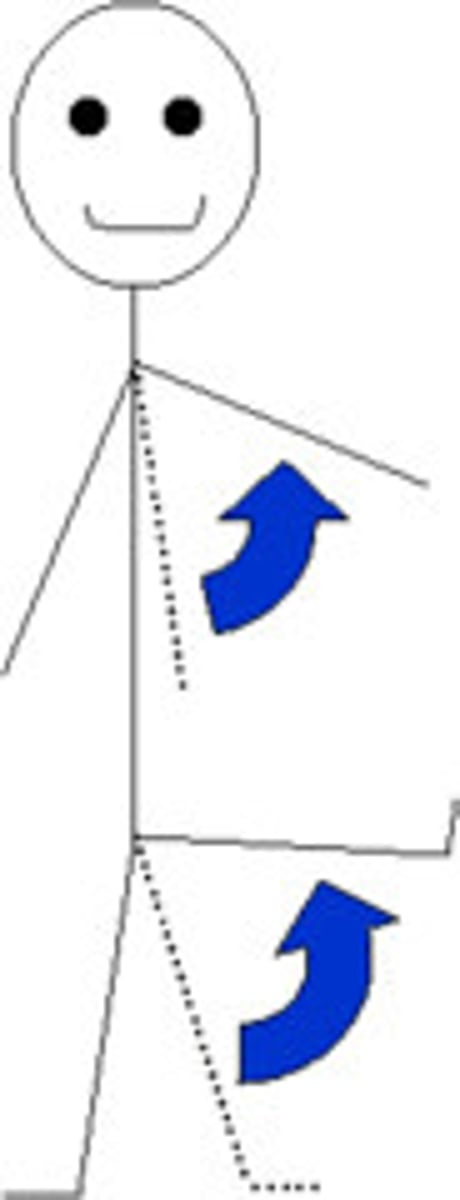
Adduction
Opposite of abduction; movement of a limb toward the body midline
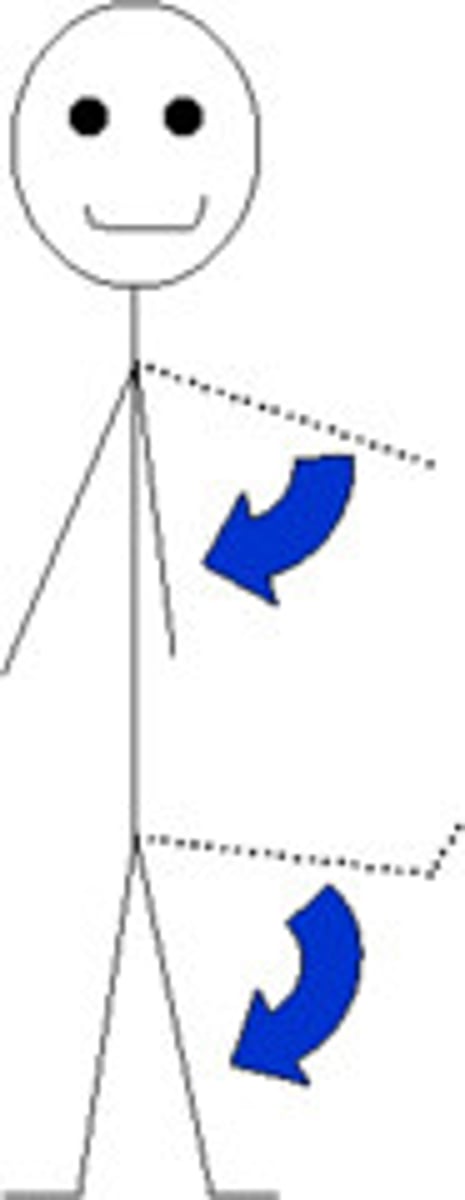
voluntary
Cardiac and Smooth are involuntary while skeletal is _______
skeletal muscle
moves the bones of the face
smooth
nonstriated muscle
intercalated discs
gap junctions that promote rapid conduction of electrical signals throughout the heart
irritability
muscle's function to response to stimuli
origin
_____ of the muscle attaches to the stationary (unmovable) bone
insertion
_____ of the muscle attaches to the more movable bone
synergist
also known as "helper muscles", that assist the primer mover. can produce same movement or stabilize joints across where prime mover acts, preventing undesirable movements
antagonist
muscles that oppose the action of another muscle
fixator
designed to stabilize a joint during movement. fixators groups in ankle prevent them from wobbling when standing
atrophy
response when muscles are not used as much and they decrease in size
motor unit
all the muscles that one neuron controls
Sliding Filament Theory
Sliding means contraction
When muscle fibers are stimulated by nervous system
ATP attaches and detaches making parts of the myosin act as oars
Pulling on the actin
Ca ions triggers the myosin to bind with the actin
When the action potential ends the Ca is reabsorbed into storage areas and muscle relaxes.
Few thousandths of a second
muscle fatigue
unable to contract even though it is being stimulated
isotonic contractions
the myofilaments are successful in the sliding movements.
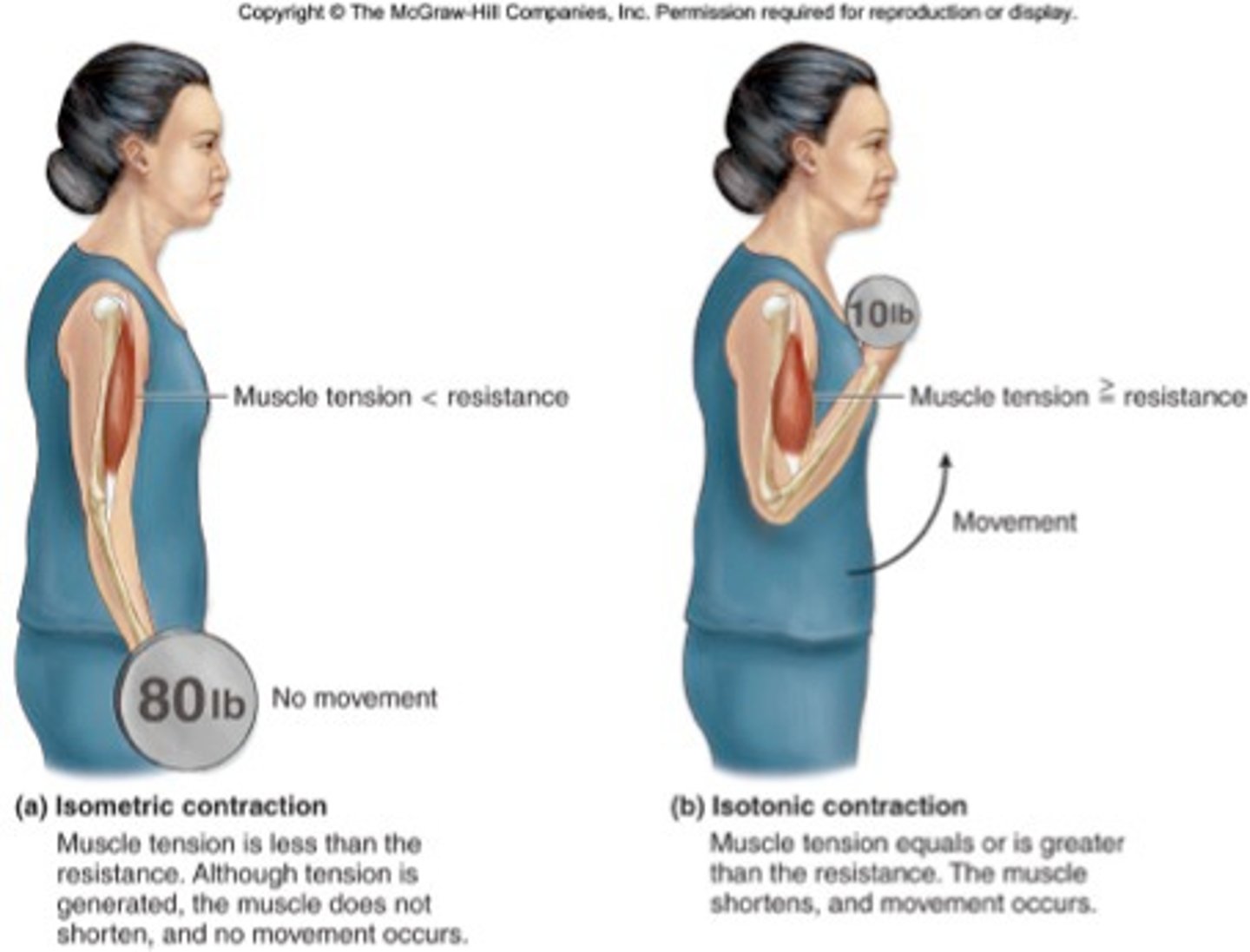
Isometric contractions
contractions will the muscles do not shorten (no movement)

The 5 Golden Rules of Skeletal Muscle Activity
1. With a few exceptions, all muscles cross at least one joint
2. Typically the bulk of the muscles lies proximal (near center) to the joint crossed.
3. All muscles have at least two attachments: the origin (is the part of the muscle that is connected to a bone and does not move) and the insertion (where the muscle connects to the bone).
4. Muscle can only pull; the never push
5. During contraction, the muscle insertion moves toward the origin.
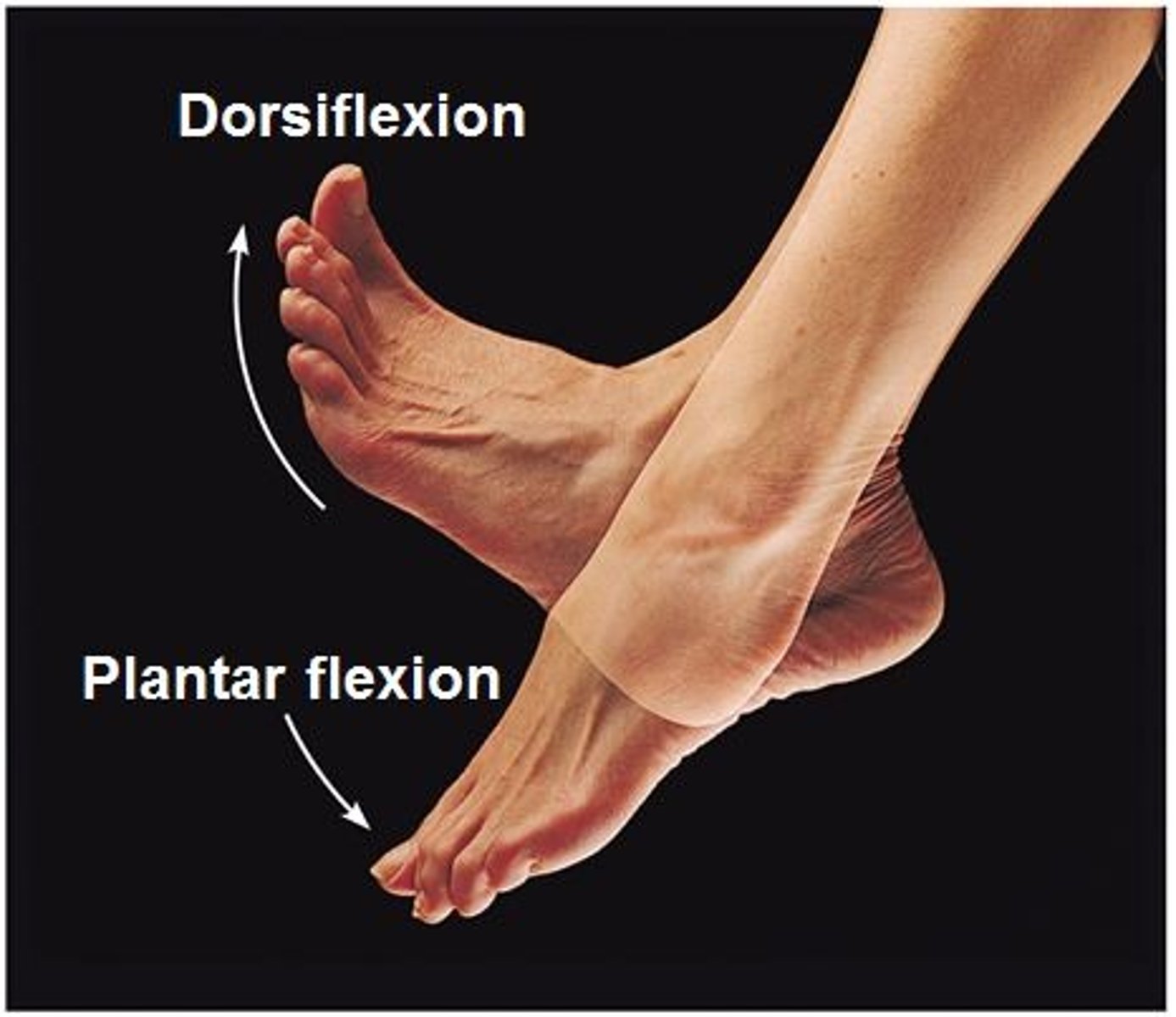
Dorsiflexion / plantar flexion
Up and down movement of the foot at the ankle
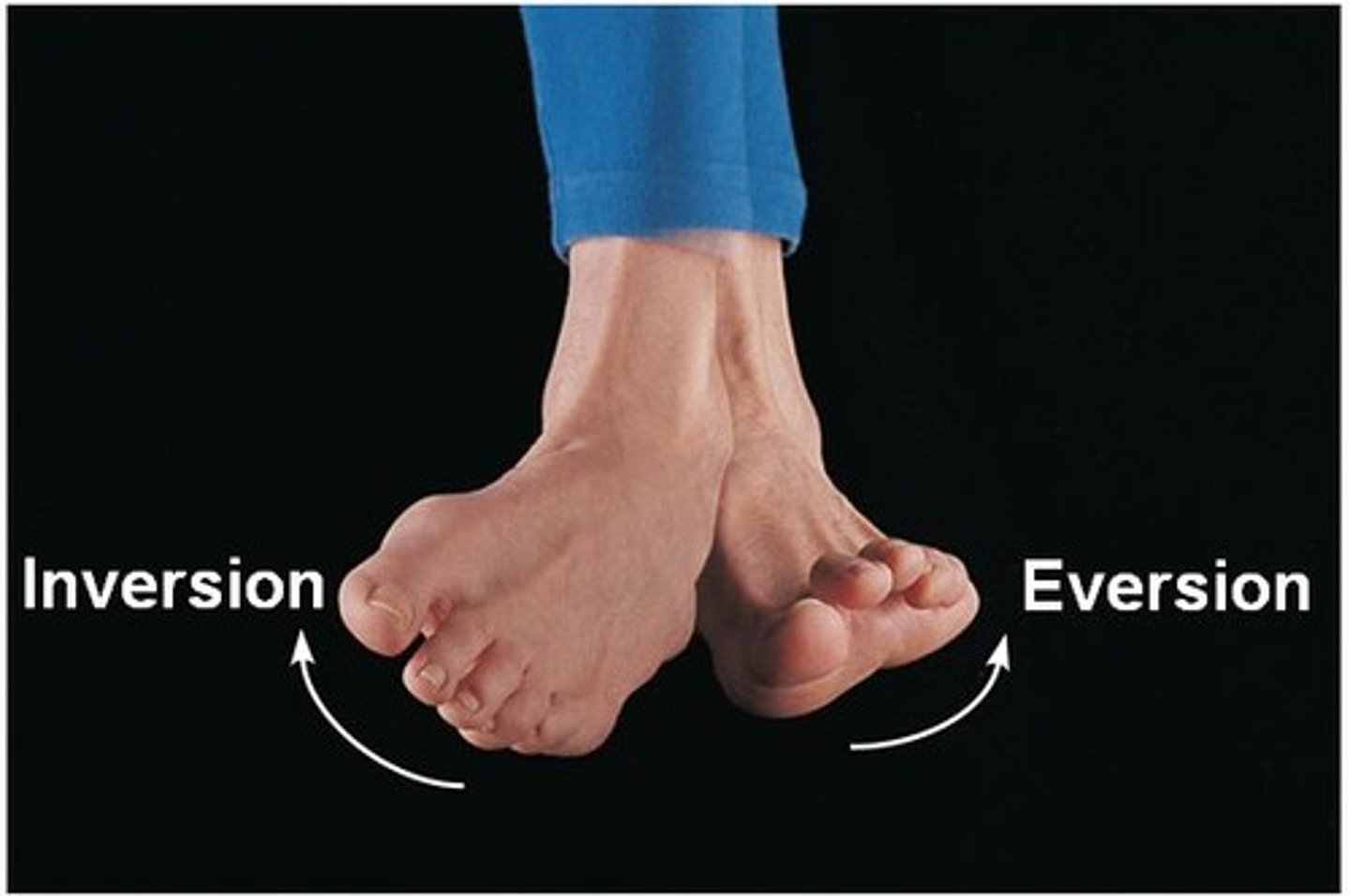
Inversion / Eversion
Allows your foot to move side to side
prime mover
is a muscle that major responsibility is for causing a particular movement.
What makes up nearly 1/2 of the body's mass?
Muscle
What is the essential function of muscle? What does this ability make it responsible for?
Contraction (shortening); All body movement
Which two muscle cell types are elongated? What are their cells called because of this?
Skeletal and smooth; muscle fibers
Whenever you see the prefixes ---, and ---, and -----, you will know that ------ is being referred to:
For example, in muscle cells the ________ is called ___________:
myo; mys; sarco; muscle; cytoplasm; sarcoplasm
______ ______ ______ are packaged into the organs called ___ ____ that attach to the body's _____:
Skeletal muscle fibers; skeletal muscles; skeleton
Largest of the muscle fiber types:
Skeletal Muscle
Contraction of muscles is due to the what?
Movement of microfilaments
Which muscle type is subject to conscious control? That means it is called what?
Skeletal Muscle; voluntary
Which two muscle types are striated (their fibers have obvious stripes)?
Skeletal and Cardiac Muscle
________ muscle is mostly attached by ______ to _____:
Skeletal; tendons; bones
What is Skeletal Muscle wrapped by? What does this give it?
Connective Tissue; strength and support
Connective tissue that encloses a single muscle fiber:
Endomysium
Connective tissue that wraps around a fascicle (bundle) of muscle fibers:
Perimysium
Connective tissue that covers the entire skeletal muscle:
Epimysium
Connective tissue on the outside of the epimysium:
Fascia
The epimysium blends into either the strong, cordlike ______ or into ______ __________, which attach _______ indirectly to ______, _______, or ___ _____ ___.
tendons; sheet-like aponeuroses; muscles; bones; cartilage; connective tissue coverings
What are the sites of muscle attachment? (3x)
-Bones
-Cartilages
-Connective tissue coverings
_______ Muscle:
-No __________
-______________
-Found mainly in the walls of _______ visceral _______ such as the ________, ______ ______, and respiratory passages.
-Propels _______ along a definite tract within the body
Smooth; striations; Involuntary; hollow; organs; stomach; urinary bladder; substances
Muscle that is visceral, non striated, and involuntary:
What shape is this muscle? ____ ________ ___:
Smooth Muscle; spindle-shaped cells;
What are the two muscle types that are uninucleate?
Cardiac and Smooth Muscle
Muscle arranged In circular and longitudinal layers
Slow and sustained contraction
Smooth Muscle
________ muscle is only found in the _______, where it forms the _____ of the _____ ____; the ____ serves as a _____, propelling _____ into the ______ ___ and to all the _____ of the body:
Cardiac; heart; bulk; heart; walls; heart; pump; blood; blood vessels; tissues;
Muscle fibers that are arranged in spiral or figure 8-shaped bundles:
Cushioned by small amounts of soft connective tissue
Cardiac Muscle
Cardiac muscle cells are joined to each other at what?
Intercalated discs
The term muscular system applies specifically to what?
Skeletal Muscle
Name the four Skeletal Muscle Functions:
-Produce movement
-Maintain posture
-Stabilize joints
-Generate heat
What type of muscle accounts for at least forty percent of body mass? THis fact makes it most responsible for what?
Skeletal Muscle; heat generation
Specialized plasma membrane in skeletal muscle cells:
Sarcolemma
Long organelles inside muscle cell:
Aligned to give distinct bands
myofibrils
Specialized smooth endoplasmic reticulum inside muscle cells:
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
Inside the muscle cell: alternating ____ ( __) and ___ (__) ________ along the length of the perfectly aligned _______ give the _ __ as a whole its ____ appearance:
light; I; dark; A; bands; myofibrils; muscle cell; striped
The __ band is the ___ band which contains only thin _______:
I; light; filaments
Inside myofibrils, the ______ band is the _____ band which contains the ___ ___ of the ___ ______:
A; dark; entire length; thick filaments
Which band has a midline interruption? That midline interruption is a ___ __ called what?
I band; darker area; Z disc
Skeletal muscle cells: The ______ A ____ has a ______ central area called the ____ ____:
Dark; band; lighter; H zone
Skeletal muscle cells: In the dark ____ band, the ____ line in the center of the H _____ contains tiny protein rods that hold adjacent ______ ______ together:
A; M; Zone; thick filaments
The banding pattern along the length of the aligned myofibrils in a muscle cell reveal the what?
working structure of the myofibrils
Contractile unit of a muscle fiber:
sarcomere
Smaller structures within sarcomeres that actually produces the banding pattern:
Myofilaments
_____ are chains of tiny _______ units called _____, which contain an arrangement of even smaller structures called _______ that actually produce the ____ ____:
Myofibrils; contractile; sarcomeres; myofilaments; banding pattern
What are the two types of threadlike protein myofilaments within the sarcomeres?
Myosin and actin filaments
List the two types of myofilaments present in sarcomeres:
-Which one is thick? Which one is thin?
Myosin and Actin filaments; Myosin filaments; Actin filaments
Thick filaments=____ filaments
-Composed of the protein _________
-Have _______ enzymes
-Have ________ (extensions or cross bridges)
- ______ and _________ ______ somewhat
Myosin; ATPase; heads; Myosin; Actin; overlap
The small projections on the ends of the thick (myosin) filaments are called ________ _______ when they link the thick and thin filaments together during _____:
Cross bridges; contraction
What contractile protein helps to compose thin filaments?
Actin
Thin filaments =____ filaments
-Composed of the _______ ______:
-Anchored to the _____ ______
actin; protein actin; Z disc
The I band only contains parts of two adjacent sarcomeres and what type of filaments?
Thin filaments
Complex organelle composed of bundles of myofilaments
Myofibril (or fibril)
Thin filaments:
The thin filaments do not extend into the middle of a relaxed _______, and thus the central region--the __ _, which lacks __ __ and looks a bit _____--is sometimes called the ______ _____:
sarcomere; H Zone; actin filaments; lighter; bare zone
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum (SR)
-Important ________ ________ organelle
-Its tubules and sacs surround each ____
-_____ and releases _____
-Surrounds the ________
muscle fiber; myofibril; stores; Calcium; myofibrils;
Why is the sarcoplasmic reticulum so important in a muscle fiber?
It stores ______ and releases it on demand when the muscle ____ is stimulated to _______:
What provides the final "go" signal for contraction?
Calcium; fiber; contract; Calcium
Inside muscle cells, myofibrilsare aligned to give distinct bands: what are they? which band is light and which is dark? What do the light bands contain? What do the dark bands contain? The thin filaments are composed of what protein? What about the thick filaments?
I and A band; I; A; thin filaments; thick filaments; actin; myosin
Muscle Function
Producing movement, maintaining posture and body position, stabilizing joints and generating heat.
Skeletal Muscle
One of the three types of muscles. Muscles move voluntarily and are attached by tendons to bones. They are long, multinucleate (have multiple nucleus), appear striated (due to arrangement of actin and myacin), and are surrounded and bundled by connective tissue. (which supplies nutrients)
Endomysium
A connective tissue wrapping which wraps itself around a single muscle cell/fiber.
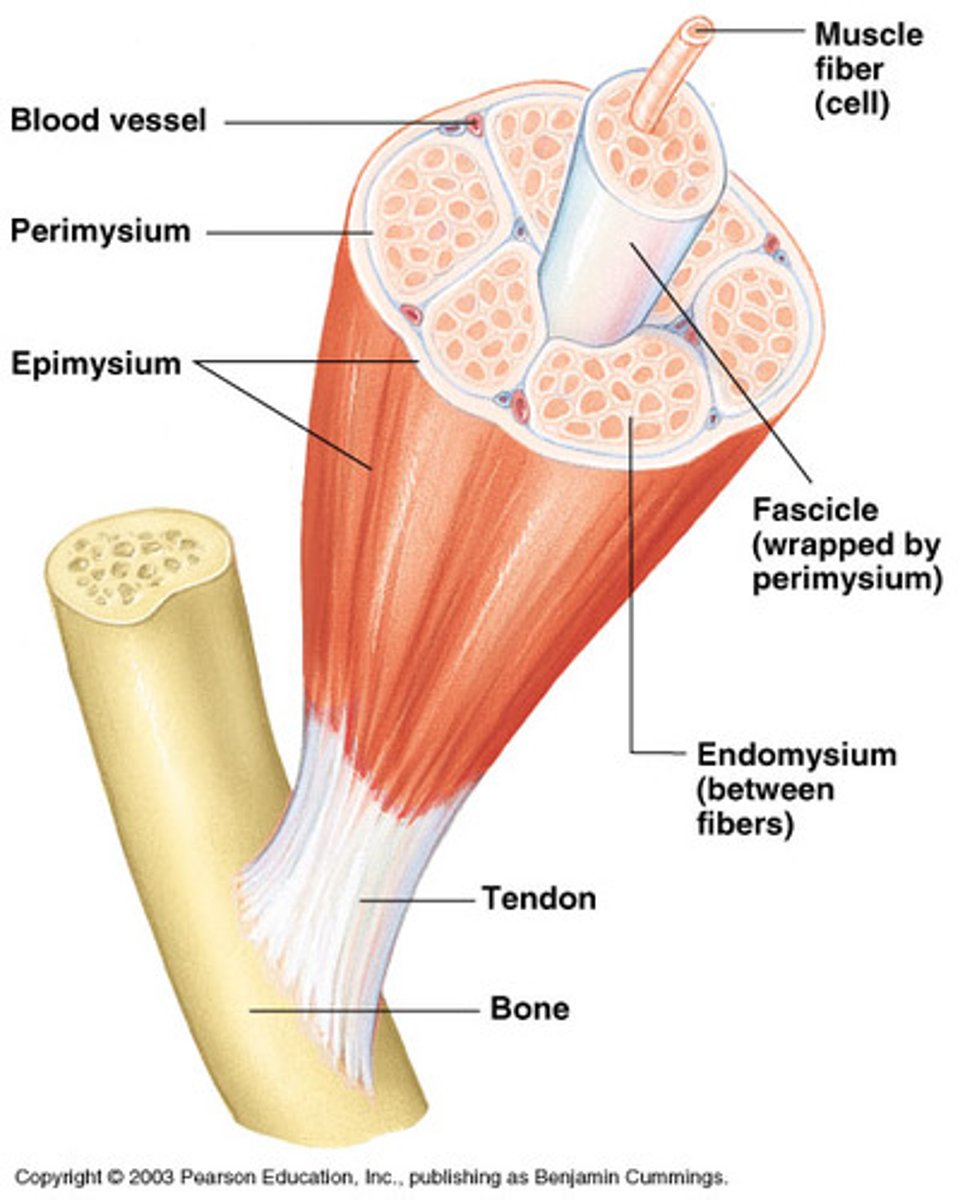
Perimysium
A connective tissue wrapping which wraps itself around a fascicle (bundle) of cells/fibers.