MBHS Unit 5: Mental and Physical Health
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
Eustress
A positive stress that energizes a person and helps a person reach a goal

Distress
negative stress

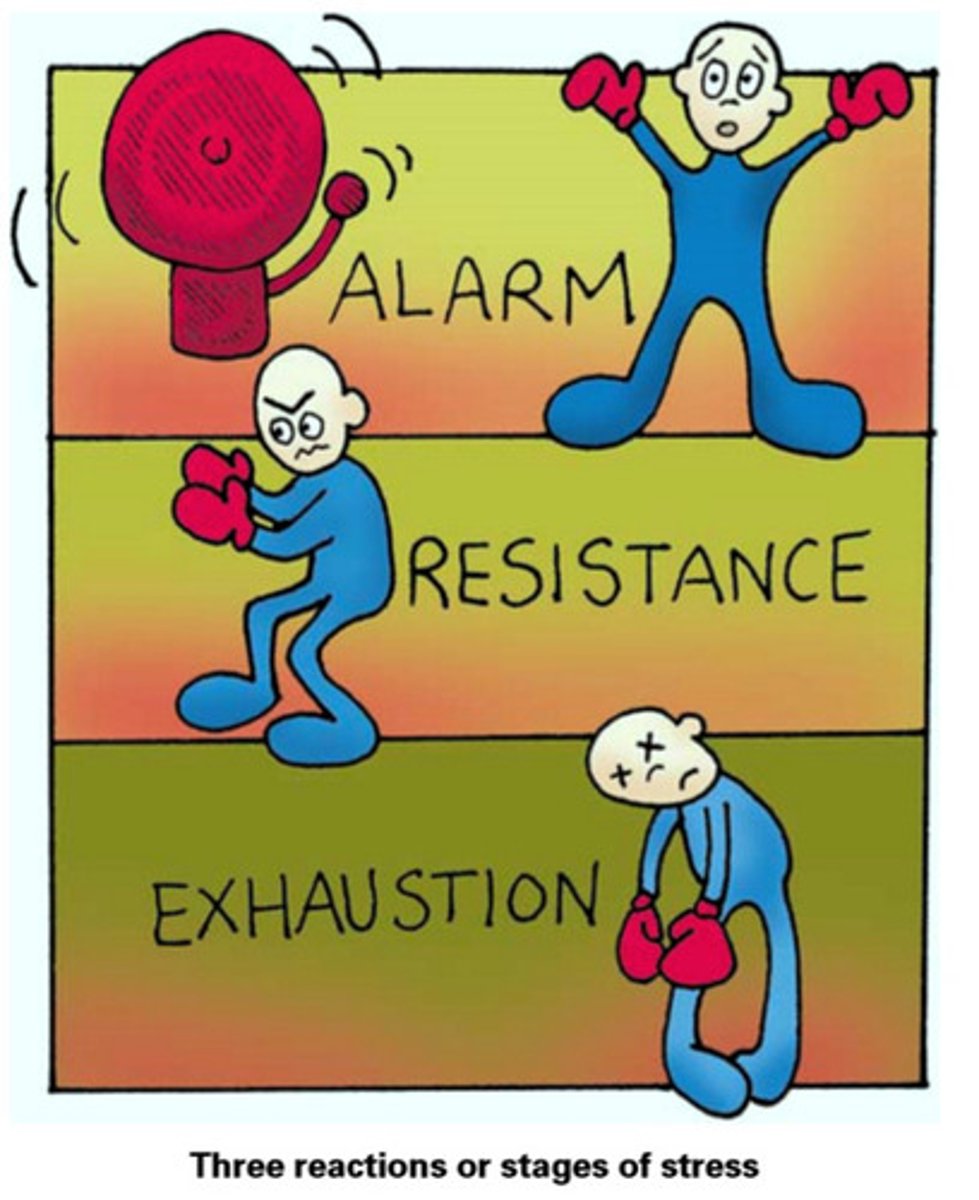
General Adaptation Syndrome
Seyle's concept that the body responds to stress with alarm, resistance and exhaustion
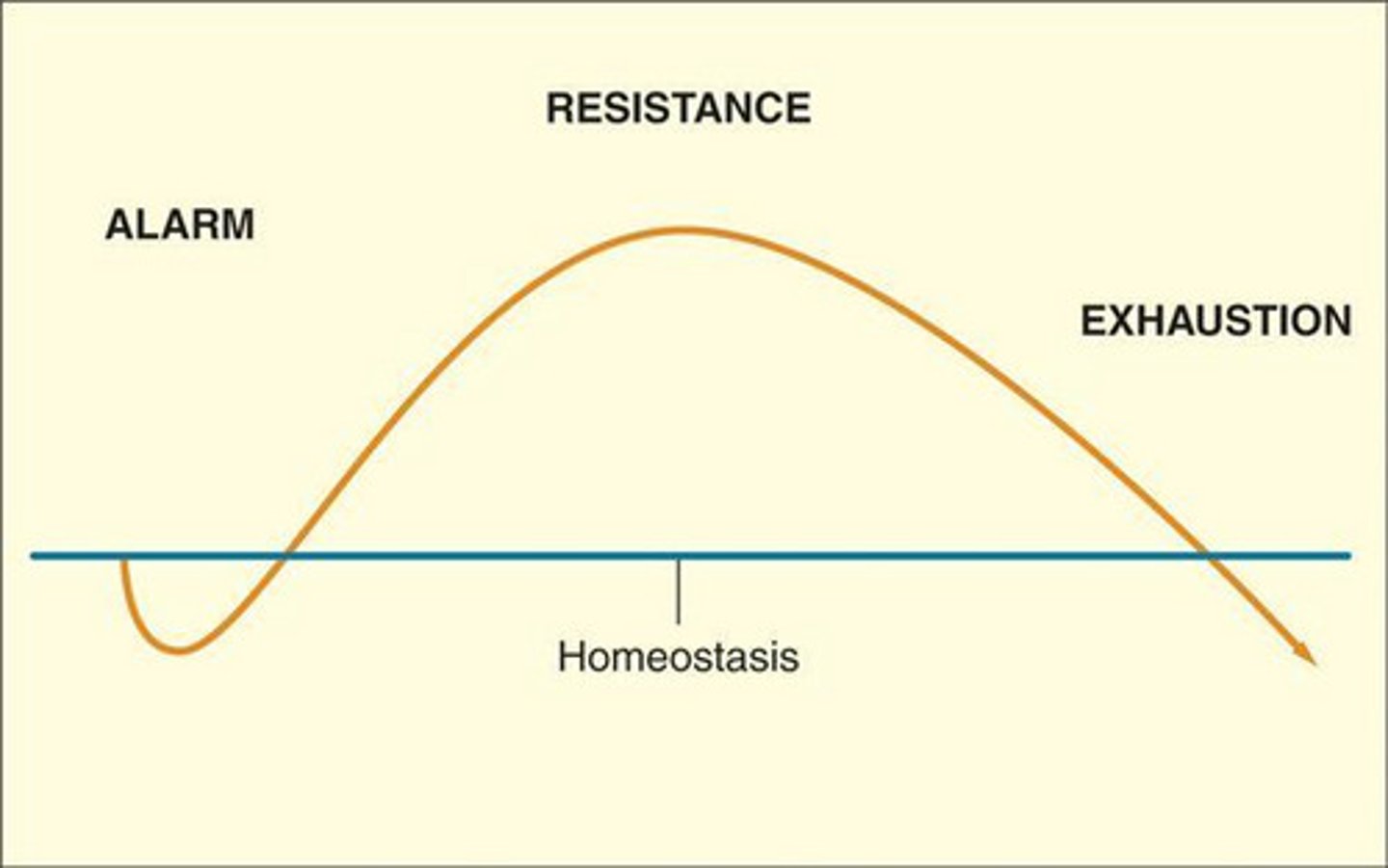
Alarm GAS stage
occurs when stress is encountered (fight-flight-freeze response)

Resistance GAS stage
You try to cope by focusing your energy on the task

Exhaustion GAS stage
The body's organs and immune system become weakened and damaged.
tend and befriend
under stress, people (especially women) often provide support to others (tend) and bond with and seek support from others (befriend)

problem focused coping
Attempting to alleviate stress directly by changing the stressor or the way we interact with that stressor.

emotion focused coping
attempting to alleviate stress by avoiding or ignoring a stressor and attending to emotional needs related to one's stress reaction

positive psychology
the scientific study of optimal human functioning; aims to discover and promote strengths and virtues that enable individuals and communities to thrive

Adverse childhood experiences (ACES)
Stressful or traumatic experiences, including abuse, neglect, and a range of household dysfunction, such as witnessing domestic violence or growing up with substance abuse, mental disorders, parental discord, or crime in the home.
Deviant
differing from the norm
Distressful
behavior that prevents a person from thinking clearly or making rational decisions
Dysfunctional
not operating normally or properly
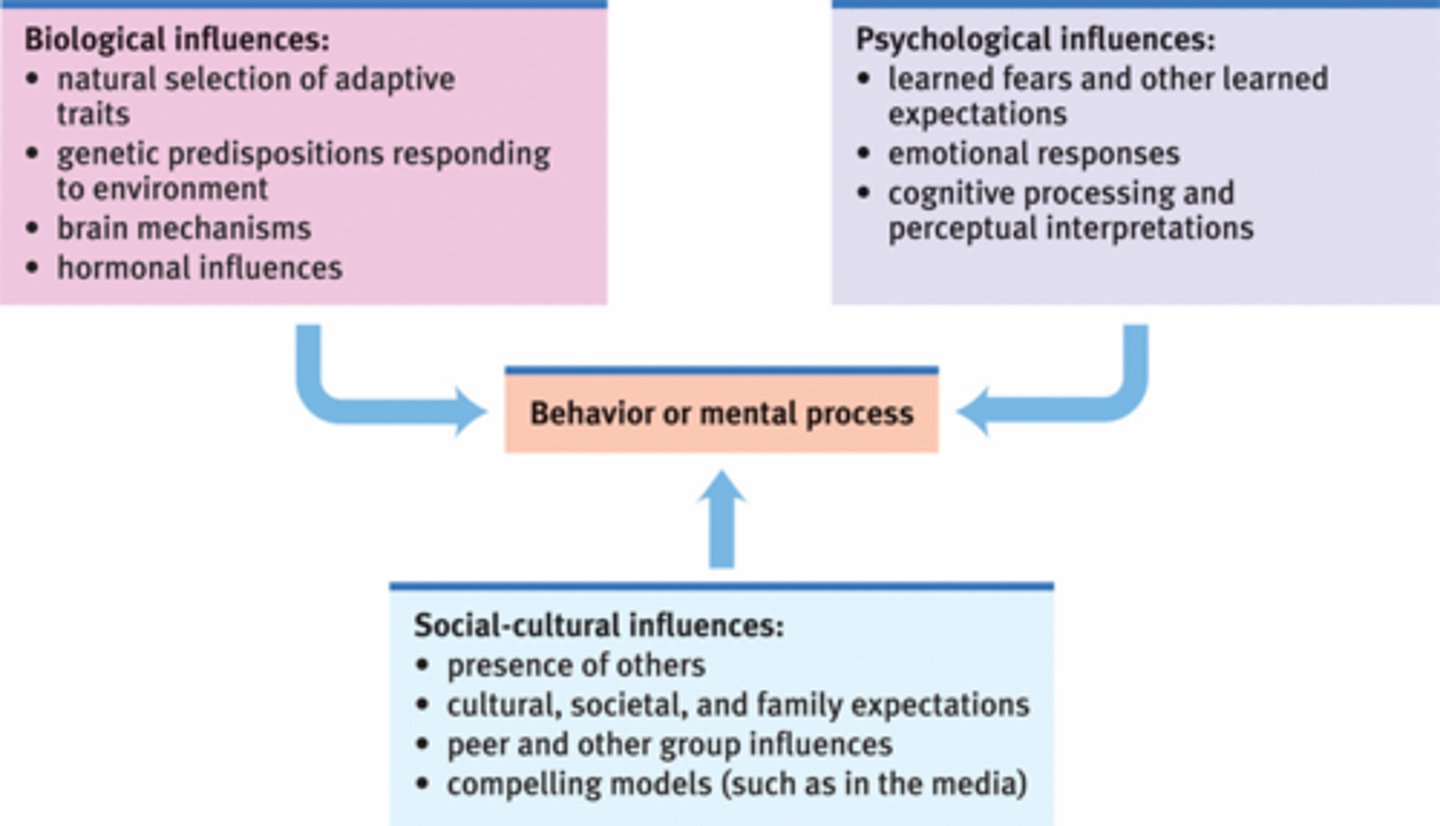
Biopsychosocial theory
the theory that the interaction of biological, psychological, and cultural factors influences our mental health
International Classification System of Mental Disorders
Developed by The World Health Organization to classify mental disorders
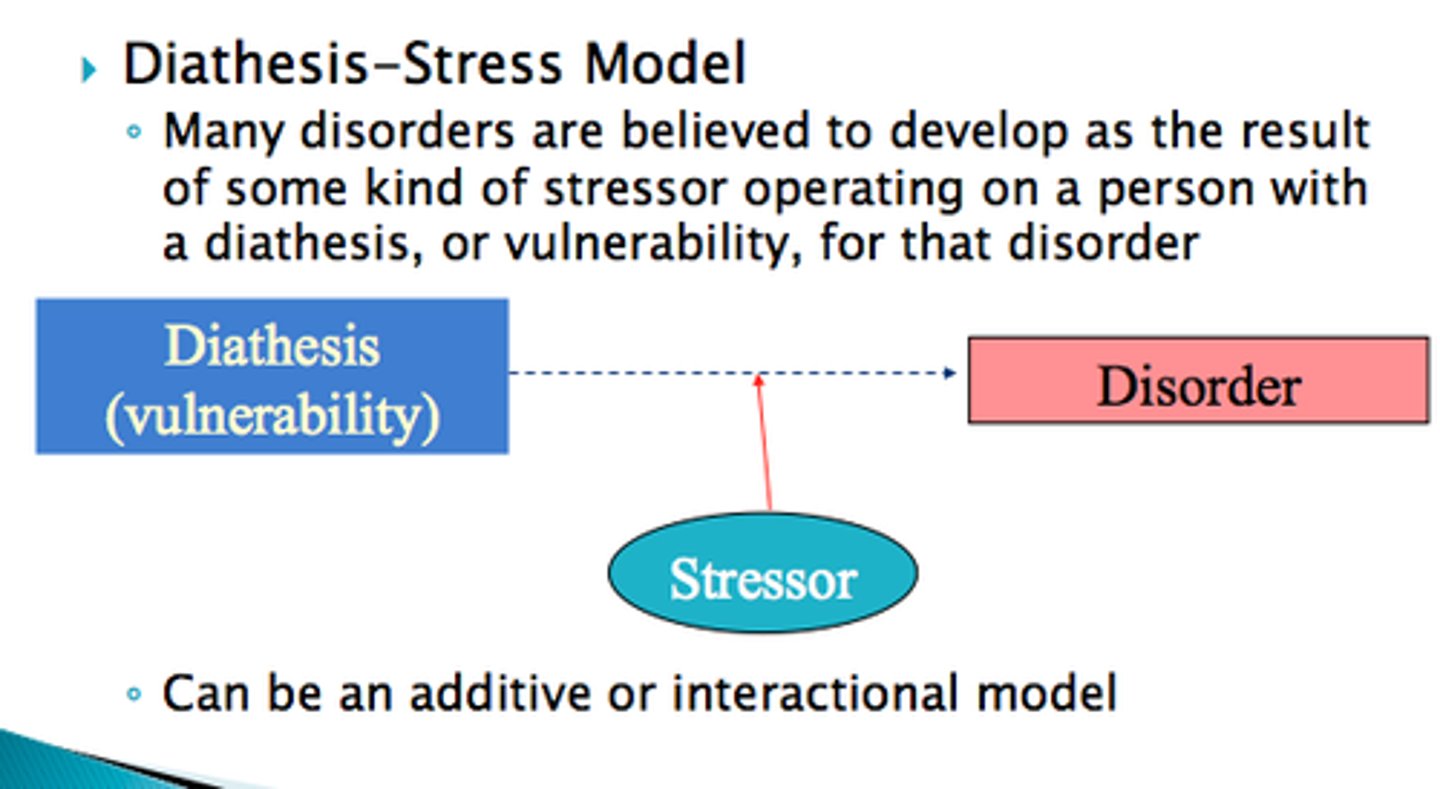
diathesis-stress model
a diagnostic model that proposes that a disorder may develop when an underlying vulnerability is coupled with a precipitating event
DSM-5-TR
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th Edition, Text Revision

Behavioral Perspective
An approach to the study of psychology that focuses on the role of learning in explaining observable behavior.

Psychodynamic Perspective
how behavior springs from unconscious drives and conflicts

Humanistic Perspective
the psychological view that assumes the existence of the self and emphasizes the importance of self-awareness and the freedom to make choices

Cognitive Perspective
A psychological approach that emphasizes mental processes in perception, memory, language, problem solving, and other areas of behavior

Evolutionary Perspective
how the natural selection of traits has promoted the survival of genes

Sociocultural Perspective
perspective that focuses on the relationship between social behavior and culture

Biological Perspective
view that psychological disorders like depression and schizophrenia are associated with imbalances in one or more neurotransmitter systems

Post traumatic stress disorder
characterized by haunting memories, nightmares, social withdrawal, jumpy anxiety, and/or insomnia that lingers for four weeks or more after a traumatic experience

Bipolar 1 Disorder
a type of bipolar disorder marked by full manic and major depressive episodes
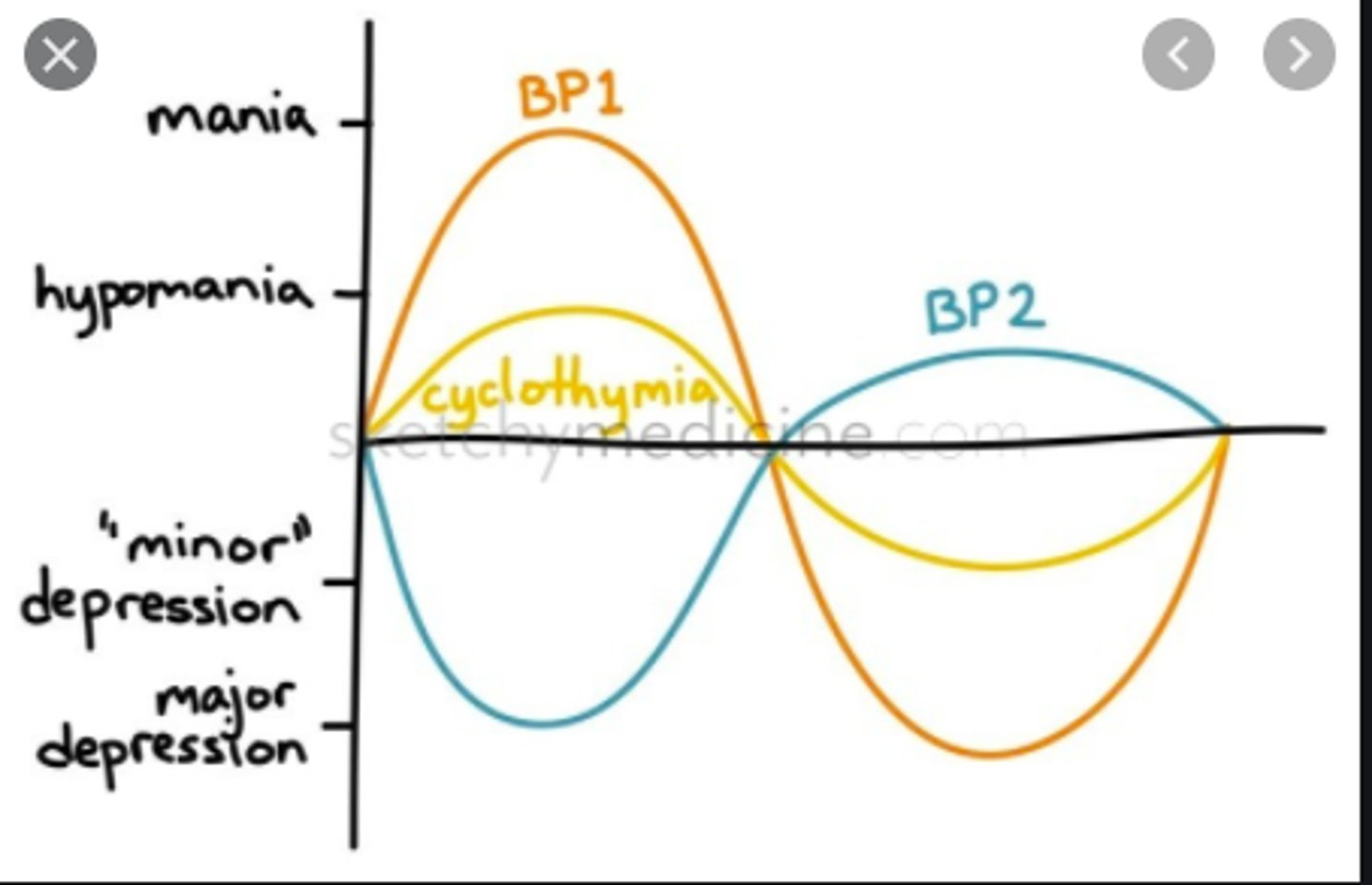
Bipolar 2 Disorder
a disorder characterized by alternating periods of extremely depressed and mildly elevated moods

Schizophrenia
a psychological disorder characterized by delusions, hallucinations, disorganized speech, and/or diminished, inappropriate emotional expression
Dopamine Hypothesis
the idea that schizophrenia involves an excess of dopamine activity
Positive Symptoms
Schizophrenic symptoms that involve behavioral excesses or peculiarities, such as hallucinations, delusions, bizarre behavior, and wild flights of ideas.
Negative Symptoms
symptoms of schizophrenia that are marked by deficits in functioning, such as apathy, lack of emotion, and slowed speech and movement
Delusions
false beliefs, often of persecution or grandeur, that may accompany psychotic disorders
Hallucinations
false sensory experiences, such as seeing something in the absence of an external visual stimulus
Catatonia
state of immobility and unresponsiveness lasting for long periods of time
Flat Affect
a lack of emotional responsiveness
Major Depressive Disorder
A mood disorder in which a person experiences, in the absence of drugs or a medical condition, two or more weeks of significantly depressed moods, feelings of worthlessness, and diminished interest or pleasure in most activities.
Persistent Depressive Disorder
a chronic form of unipolar depression marked by ongoing and repeated symptoms of either major or mild depression
Obsessive Compulsive Disorder
a disorder characterized by unwanted repetitive thoughts (obsessions) and/or actions (compulsions)

Obsession
an unwanted thought or image that takes control of the mind
Compulsion
uncontrollable urge to perform an act repeatedly
Hoarding Disorder
Persistent difficulty discarding or parting with possessions, regardless of their actual value
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
an anxiety disorder in which a person is continually tense, apprehensive, and in a state of autonomic nervous system arousal

Panic Disorder
An anxiety disorder marked by unpredictable minutes-long episodes of intense dread in which a person experiences terror and accompanying chest pain, choking, or other frightening sensations.
Agoraphobia
fear or avoidance of situations, such as crowds or wide open places, where one has felt loss of control and panic

Specific Phobia
a disorder that involves an irrational fear of a particular object or situation that markedly interferes with an individual's ability to function

Social Anxiety Disorder
intense fear of social situations, leading to avoidance of such

Ataque de nervios
a self-labeled syndrome found in Latinos in which they experience a mixture of anxiety, panic, depression, and anger
Taijin Kyofusho
a form of social anxiety common in Japan involving a fear of offending or embarrassing others with one's odor, eye contact, or appearance.
Dissociative Identity Disorder
A rare dissociative disorder in which a person exhibits two or more distinct and alternating identities
Dissociative Amnesia
Dissociative disorder characterized by the sudden and extensive inability to recall important personal information, usually of a traumatic or stressful nature.

Dissociative Fugue
disorder in which one travels away from home and is unable to remember details of his past, including often his identity

Cluster A Personality Disorders
odd or eccentric
paranoid, schizoid, schizotypal
Paranoid Personality Disorder
type of personality disorder characterized by extreme suspiciousness or mistrust of others
Schizoid Personality Disorder
a personality disorder characterized by persistent avoidance of social relationships and little expression of emotion
Schizotypal Personality Disorder
a psychological disorder characterized by several traits that cause problems interpersonally, including constricted or inappropriate affect; magical or paranoid thinking; and odd beliefs, speech, behavior, appearance, and perceptions
Cluster B Personality Disorders
dramatic, emotional, erratic
antisocial, borderline, histrionic, narcissistic
Antisocial Personality Disorder
Disregard for the rights of others,
Manipulative, deceitful behavior,
Lack of empathy or remorse for harmful actions,
Impulsive behavior
Histrionic Personality Disorder
a personality disorder characterized by excessive emotionality and preoccupation with being the center of attention; emotional shallowness; overly dramatic behavior
Narcissistic Personality Disorder
characterized by a grandiose sense of self-importance, a preoccupation with fantasies of success or power, and a need for constant attention or admiration
Borderline Personality Disorder
a personality disorder characterized by lack of stability in interpersonal relationships, self-image, and emotion; impulsivity; intense fear of abandonment
Cluster C Personality Disorders
Anxious, fearful
avoidant, dependent, obsessive compulsive
Avoidant Personality Disorder
A personality disorder characterized by consistent discomfort and restraint in social situations, overwhelming feelings of inadequacy, and extreme sensitivity to negative evaluation.
Dependent Personality Disorder
A personality disorder characterized by a pattern of clinging and obedience, fear of separation, and an ongoing need to be taken care of.
Obsessive Compulsive Personality Disorder
a personality disorder characterized by preoccupation with orderliness, perfection, and control
Neurodevelopmental Disorders
a group of conditions manifested early in development that are characterized by developmental deficits that produce impairments of personal, social, academic, or occupational functioning
ADHD
a psychological disorder marked by the appearance by age 7 of one or more of three key symptoms: extreme inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity
Autism Spectrum Disorder
A disorder characterized by deficits in social relatedness and communication skills that are often accompanied by repetitive, ritualistic behavior.
Therapy ethical standards
nonmaleficence, fidelity, integrity, respect for the rights of others
Free Association
in psychoanalysis, a method of exploring the unconscious in which the person relaxes and says whatever comes to mind, no matter how trivial or embarrassing

Manifest Content
according to Freud, the remembered story line of a dream

Latent Content
according to Freud, the underlying meaning of a dream

Client Centered Therapy
a humanistic therapy, developed by Carl Rogers, in which the therapist uses techniques such as active listening within a genuine, accepting, empathetic environment to facilitate clients' growth. (Also called person-centered therapy.)

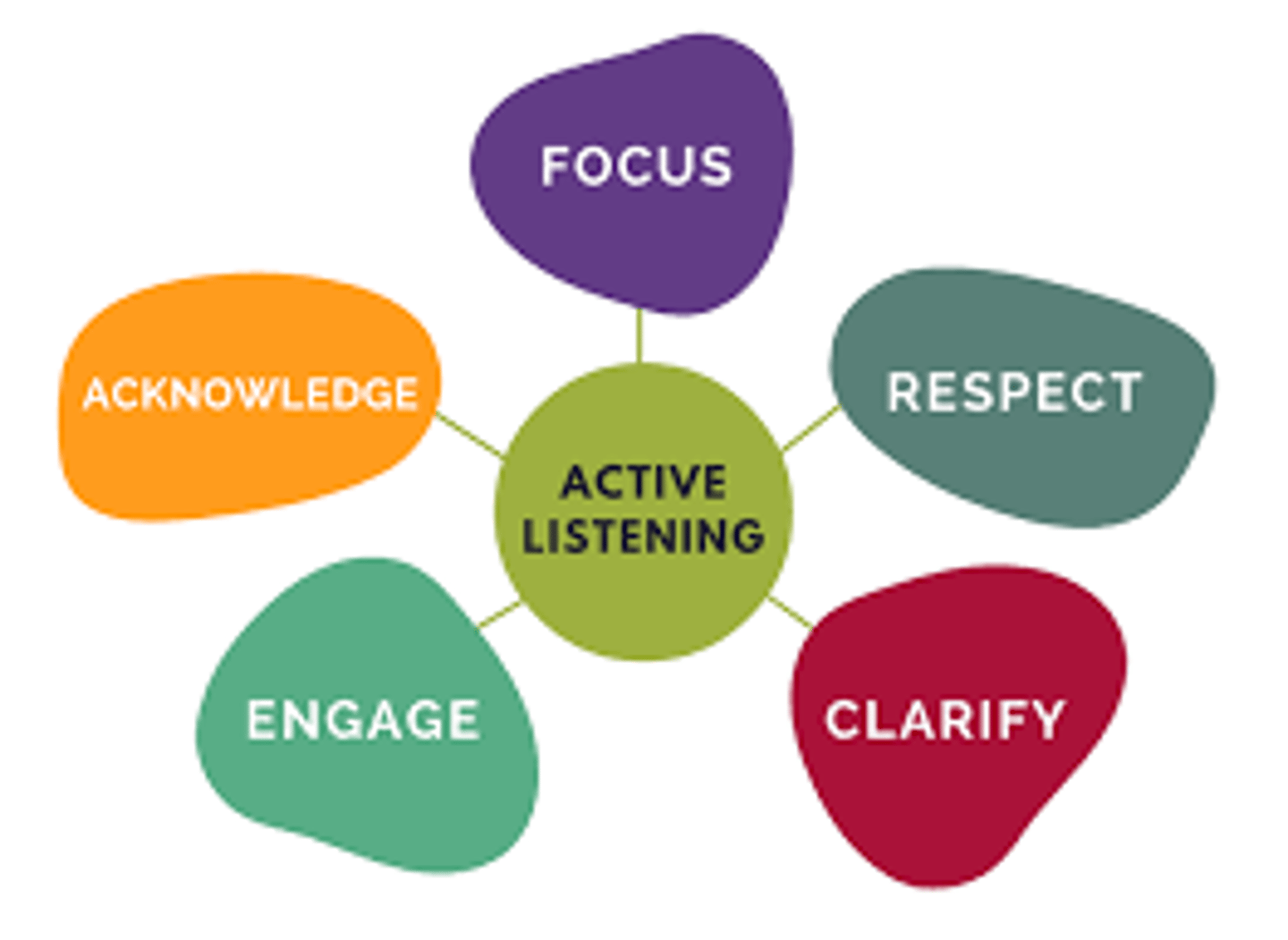
Active Listening
Empathetic listening in which the listener echoes, restates, and clarifies. A feature of Rogers' client-centered therapy.
Unconditional Positive Regard
according to Rogers, an attitude of total acceptance toward another person

Cognitive Restructuring
a therapeutic approach that teaches clients to question the automatic beliefs, assumptions, and predictions that often lead to negative emotions and to replace negative thinking with more realistic and positive beliefs

Fear hierarchies
feared objects, activities or situations are ranked according to difficulty. They begin with mildly or moderately difficult exposures, then progress to harder ones.

cognitive triad
The three forms of negative thinking that Aaron Beck theorizes lead people to feel depressed. The triad consists of a negative view of one's experiences, oneself, and the future.

Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
a popular integrative therapy that combines cognitive therapy (changing self-defeating thinking) with behavior therapy (changing behavior)

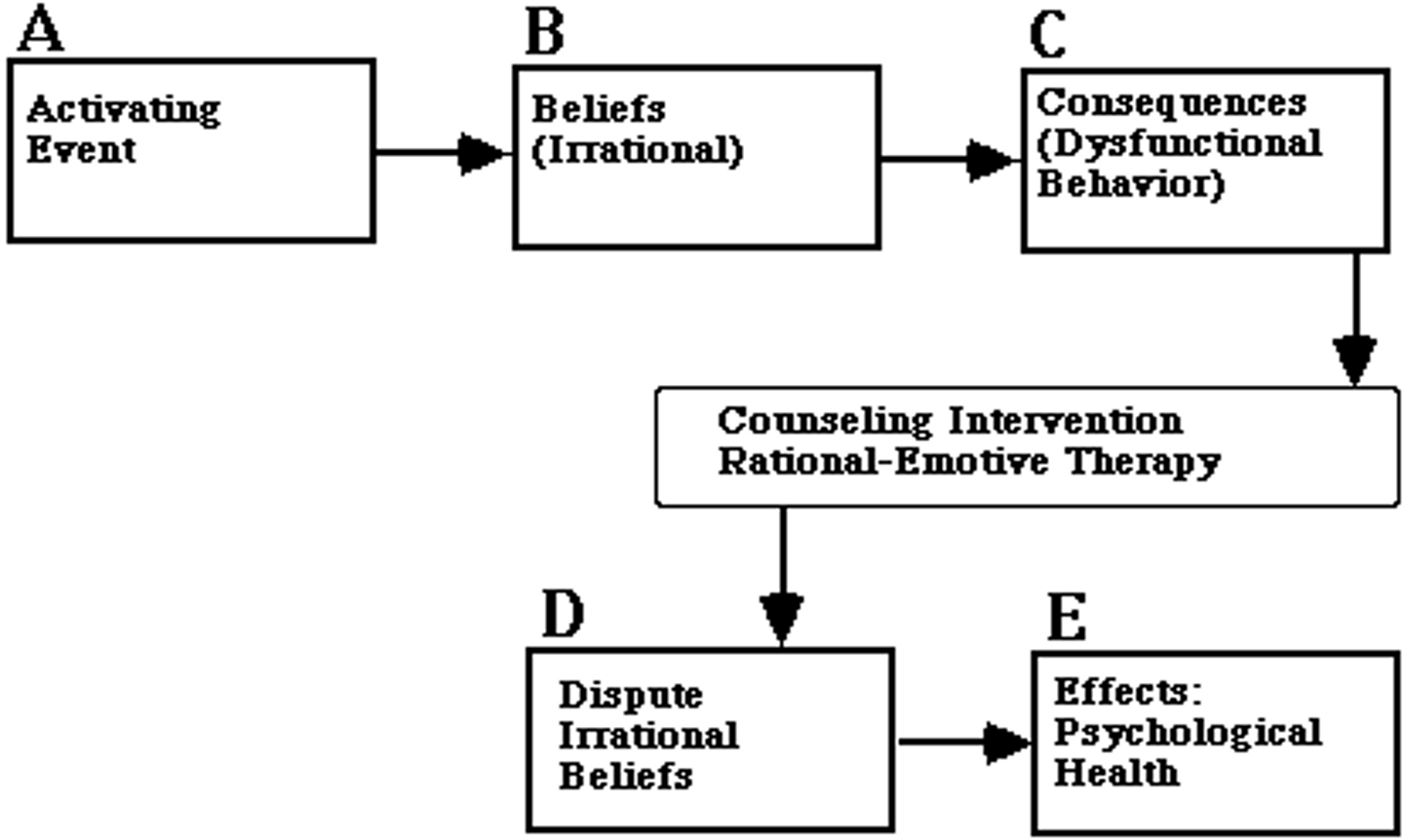
Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy
a confrontational cognitive therapy, developed by Albert Ellis, that vigorously challenges people's illogical, self-defeating attitudes and assumptions
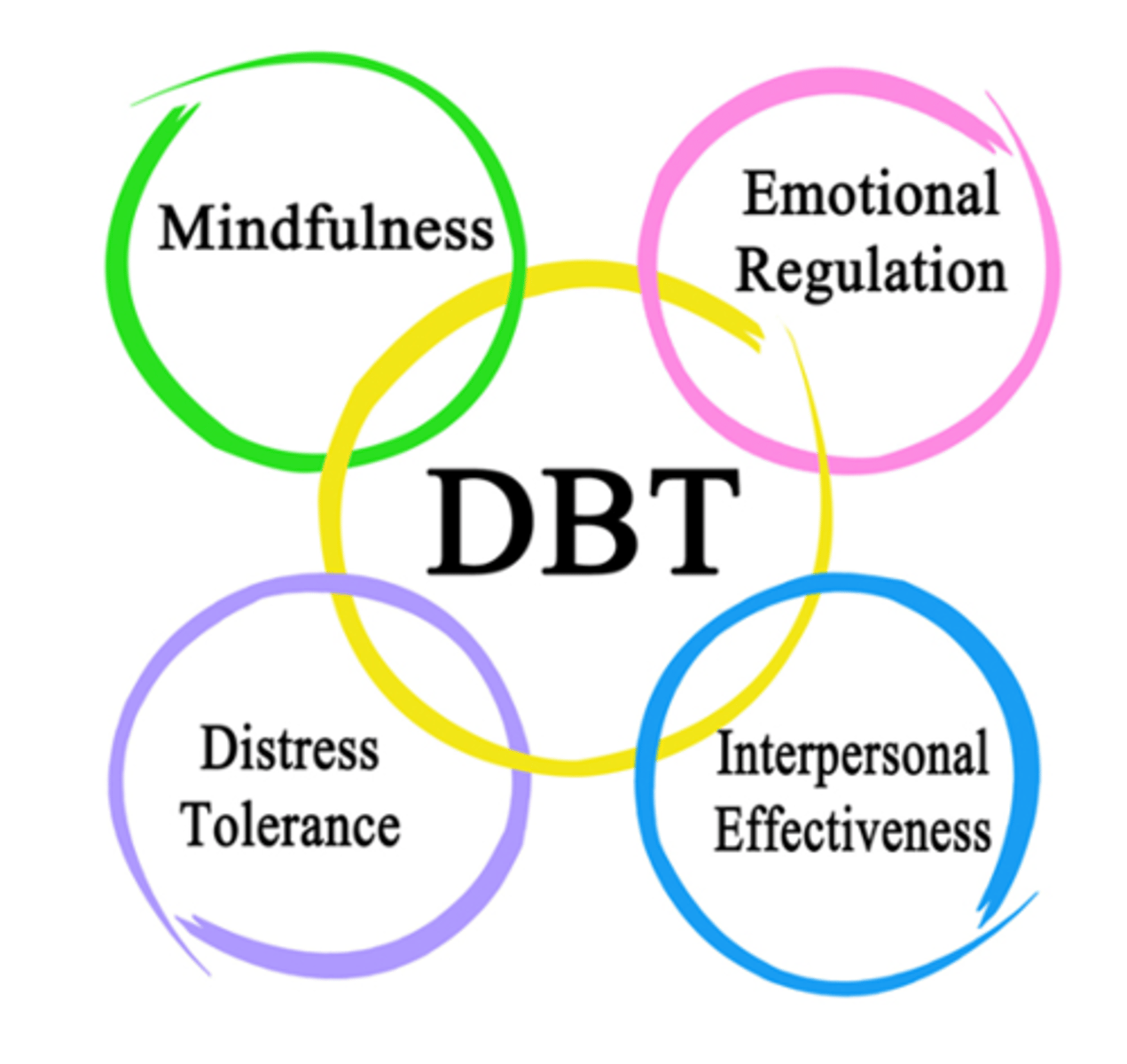
Dialectical Behavior Therapy
cognitive-behavioral intervention aimed at teaching problem-solving skills, interpersonal skills, and skill at managing negative emotions
Systematic Desensitization
A type of exposure therapy that associates a pleasant relaxed state with gradually increasing anxiety-triggering stimuli. Commonly used to treat phobias.

Aversive Conditioning
a form of treatment that consists of repeated pairings of a stimulus with a very unpleasant stimulus

Token Economy
an operant conditioning procedure in which people earn a token of some sort for exhibiting a desired behavior and can later exchange the tokens for various privileges or treats

Biofeedback
a system for electronically recording, amplifying, and feeding back information regarding a subtle physiological state, such as blood pressure or muscle tension

Antipsychotics
a class of psychotropic medications used for the treatment of schizophrenia and other disorders that involve psychosis
Tardive Dyskenisia
Shaking and involuntary movements side effect of treatment with early antipsychotic drugs
Antianxiety medication
medication that reduces anxiety via depression of central nervous system activity
Antidepressants
drugs that combat depression by affecting the levels or activity of neurotransmitters in the brain
Mood stabilizers
drugs used to control mood swings in patients with bipolar mood disorders (commonly used-lithium)
Light Exposure therapy
therapy that involves a timed daily dose of intense light; used for SAD
Electroconvulsive Therapy
a biomedical therapy for severely depressed patients in which a brief electric current is sent through the brain of an anesthetized patient
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
a treatment that involves placing a powerful pulsed magnet over a person's scalp, which alters neuronal activity in the brain
Psychosurgery
surgery that removes or destroys brain tissue in an effort to change behavior
Group Therapy
therapy conducted with groups rather than individuals, permitting therapeutic benefits from group interaction