ORAL COM FIRST HALF
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Wood (2004)
Communication as defined by _____ is a systematic process in which individuals interact with and through symbols to create and interpret meanings. Wood’s definition suggests the qualities that are inherent in communication.
Rogers (1996, 2000)
Communication as defined by ____ is a process in which participants create information with one another to reach mutual understanding.
Gerbner (1967)
For ________, communication is a “social interaction through messages.”
Stevens (1950)
For ____, communication is “the discriminatory response of organism to a stimulus.”
Berelson & Steiner (1964)
________ defined communication as “the transmissions of information, ideas, emotions, skills, etc., by the use of symbols – words, pictures, figures, graphs, etc.
Cronkhite (1976)
For _____, “human communication has occurred when a human being responds to a symbol.”
giving and receiving information
Communication is the process of __________ between a human source and a human receiver using words, symbols, and actions.
Communication is a PROCESS
refers to the transmission or passage of information or message from the sender through a selected
channel to the receiver overcoming barriers that affect its pace.
It is creative, continuing condition of life, a process that changes as the communicator’s environments
and needs change.
Many words have become obsolete, trite, or altered in their meanings
while new words have evolved
Communication is SYSTEMATIC
It occurs within systems of interrelated and interacting parts.
The communication process involves many parts of a larger system including:
Communication is SYMBOLIC
Symbols, verbal or non-verbal, are the basis of language
It involves a sound (word), a mark, an action / behavior, a picture which represents something
Communication involves MEANINGS
Meanings are assigned, given or invented, not received
It is the production of meaning rather than the production of messages that identifies communication
speaker/sender
message
medium
channel
listener/receiver
context
feedback
noise
What are the elements of communication
senders
an element of communication that conveys messages by converting their thoughts into symbols of observable signals such as words
codification
the process of conveying messages by converting thoughts into symbols of observable signals such as words
receivers
an element that hears the signals and convert the symbols into their thoughts
decoding, deciphering, or interpretation
the process of hearing the signals and converting the symbols into their thoughts
messages
these are the ideas or thoughts that are transmitted from sender to receiver
schema/field of experience
the culture and experience together are called ___
symbols
observable signals transmitted from sender to receiver. can be spoken, read, seen, or felt
verbal
when symbols come in the form of utterances coming from the mouth of a speaker, they are considered _____
nonverbal
if symbols come from body movements other than that of the mouth they’re considered as _________
channel
refers to the medium through which the message is sent
noise
anything that reduces the quality of signal sent by the sender through the channel, weakening the communication between sender and receiver
feedback
the message transmitted by the receiver in response to the message of the speaker
intrapersonal
interpersonal
types of communication
intrapersonal comm.
a communicator’s internal use of language or thought. occurs in the mind of the individual in a model which contains a sender, receiver, and feedback loop
interpersonal comm.
it is communication between a min. of two parties in which meaningful exchange is intended with the sender trying to effect a response from a person or group
Communication models
are systematic representations of the process which helps in understanding how communication works can be done
Aristotle’s Model (300 B.C.), Laswell’s Modelof Communication, Shannon & Weaver Communication Model, David Berlo’s SMCR Model, and Schramm’s Model.
enumerate the basic models of communication
Speaker —→ Speech ——> Occasion —→ Audience —→ Effect
Aristotle’s communication model is mainly focused on speaker and speech. It can be broadly divided into 5 primary elements (in order):???
logos
soundness of argument
uses facts, statistics, examples and authoritative statements
pathos
emotional power of language
appealing to readers’ needs, values, and attitudes thru word choice
ethos
credibility and integrity
presenting a logical, reasoned argument that takes opposing views into account
establishing character
pros: organized speech, shows importance of speaker’s roles in comm., useful for pub. speaking
cons: no direct feedback, no concept of comm. failure, only applicable for pub. speaking
pros and cons of Aristotle’s model
linear
Laswell’s communication model is a ____ model
Laswell’s comm. model
a comm. model that is straightforward and tells you that communication originates from someone, their message flows through a channel, either through sound waves or light waves, and that someone on the other end receives the message with a corresponding effect.
WHO —→ SAYS WHAT —-→ IN WHICH CHANNEL —→ TO WHOM —→ WITH WHAT EFFECT
laswell’s comm. model order
pros: it is easy and simple, it suits almost all types of communication, the concept of effect
cons: Feedback not mentioned, Noise not mentioned, Linear model
pros and cons of laswell’s comm. model
SHANNON and WEAVER’S COMMUNICATION MODEL
a comm. model that incorporates the concept of noise, which
is anything that interferes with the message
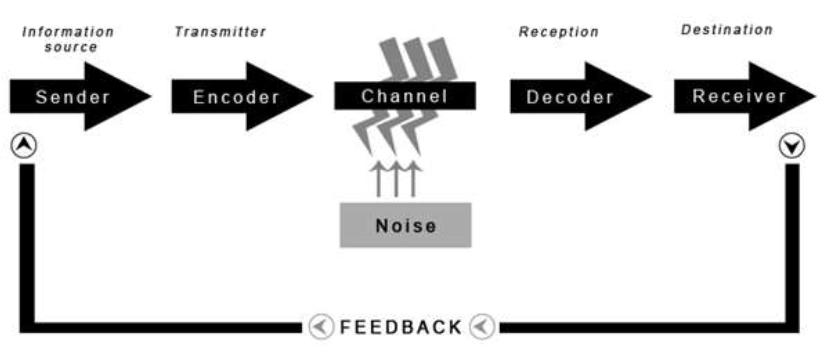
Shannon-weaver’s comm. model
David Berlo’s comm. model
a comm. model where communication is an open process, which means that messages sent and received are open to various interpretations and based on context and the culture of the receiver.
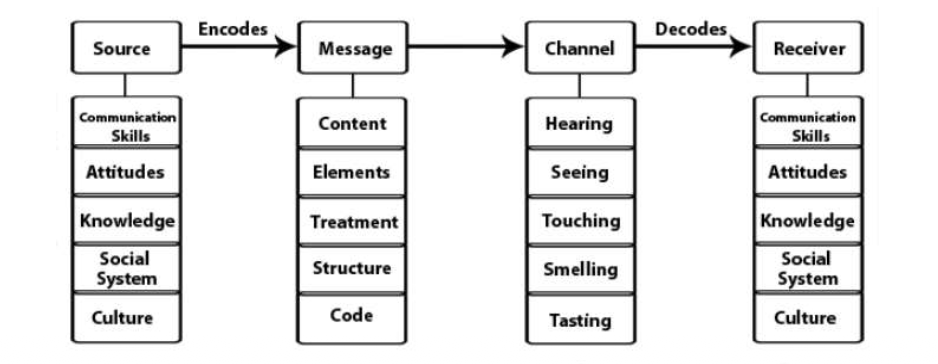
David Berlo’s Comm. Model
OSGOOD- SCHRAMM MODEL OF COMMUNICATION
This model suggests that communication is something circular in nature where both the sender and receiver are involved in the encoding and decoding, and are equal partners in exchange process.