Neuro Exam #1: Action potentials-conductance
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
sodium
before action potential is reached, which ion is moving into the neuron membrane?
potassium
after action potential is reached, which ion is moving out of the neuron membrane?
-80- -70 mV
what is the range for a neuron's resting potential?
Na+ channels open
what occurs once the threshold level is reached?
Na +channels close, K+ channels open
what occurs when action potential is reached?
sodium
what channels are open during depolarization?
potassium
what channels are open during repolarization?
into
Na+ channels allow ions to move _____ the cell
out of
K+ channels allow ions to move _____ the cell
K+ channels remain open after resting potential
what occurs during hyperpolatization?
E Na+
During depolarization, Em moves toward _______
E K+
During repolarization, Em moves toward _______
threshold
the opening voltage for both channels is ________
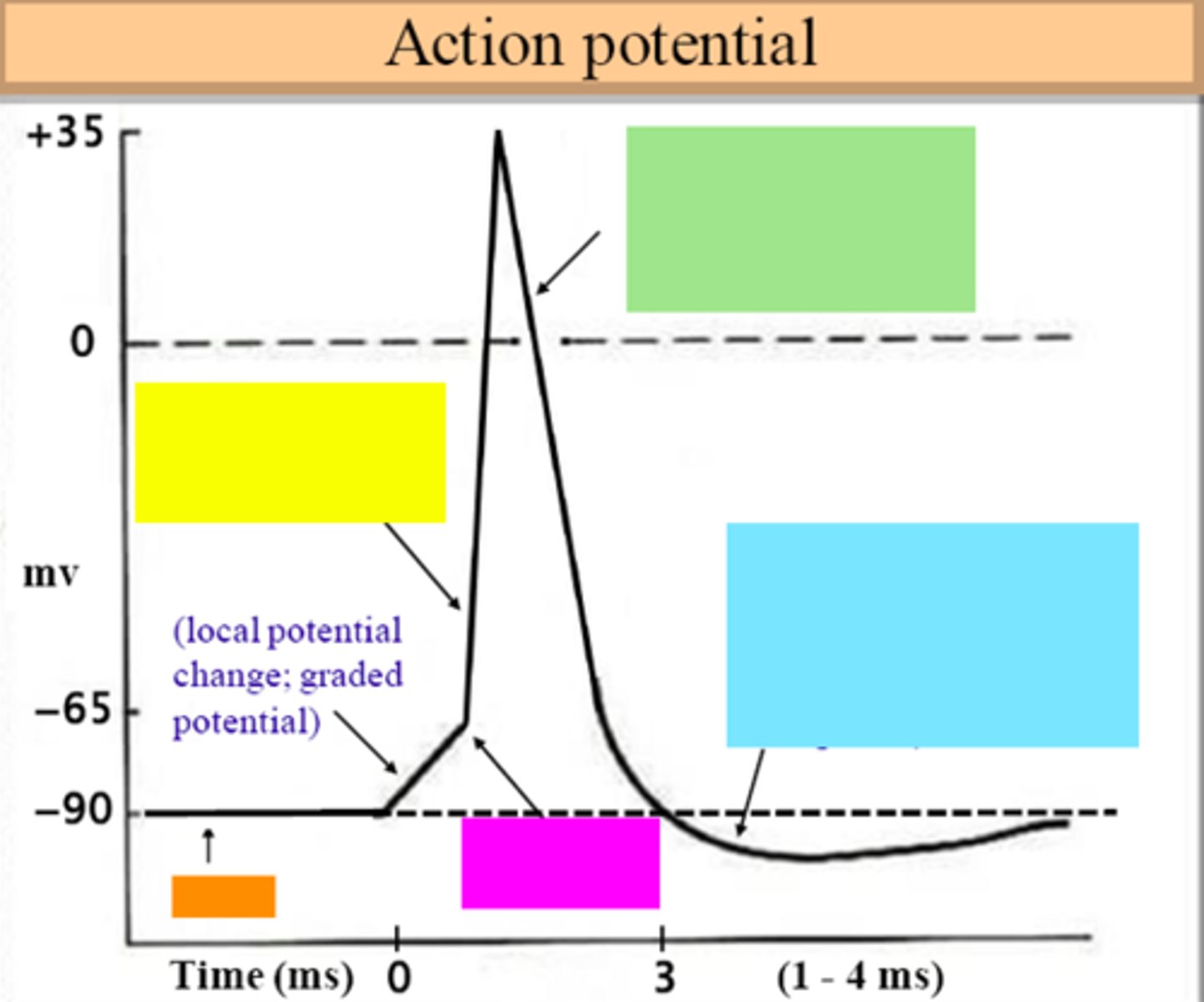
threshold
ID the purple box:
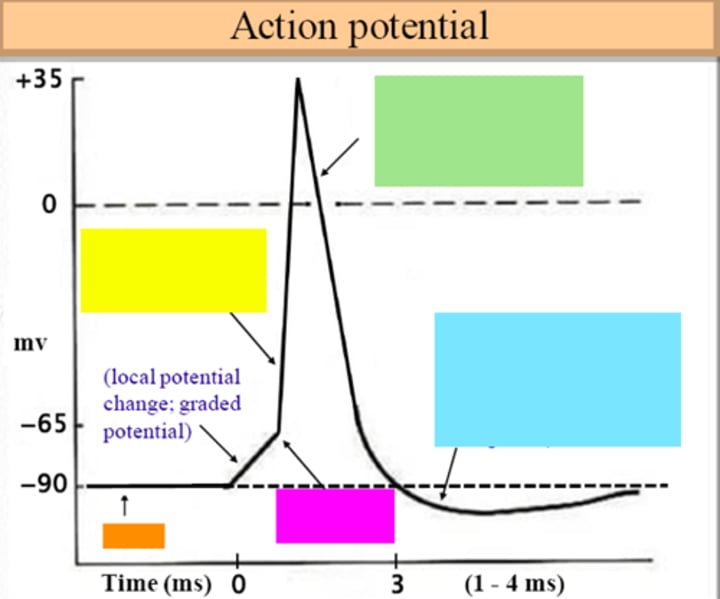
hyperpolarization
ID the blue box:
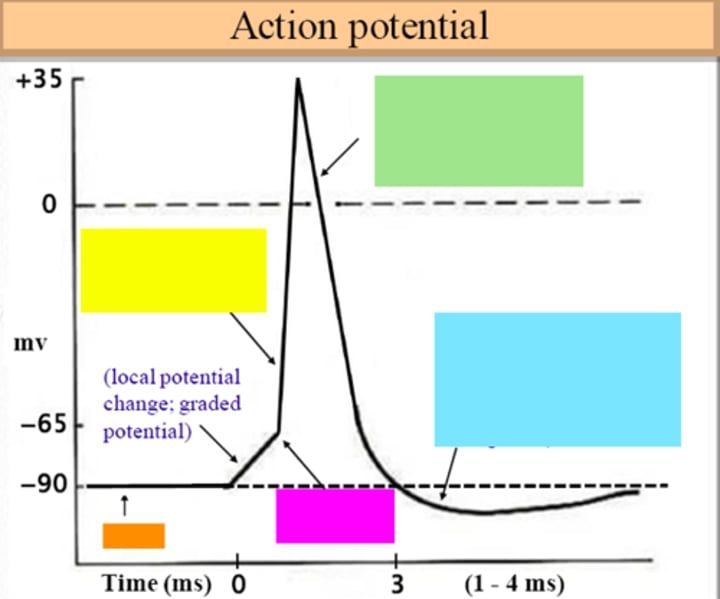
repolarization
ID the green box:
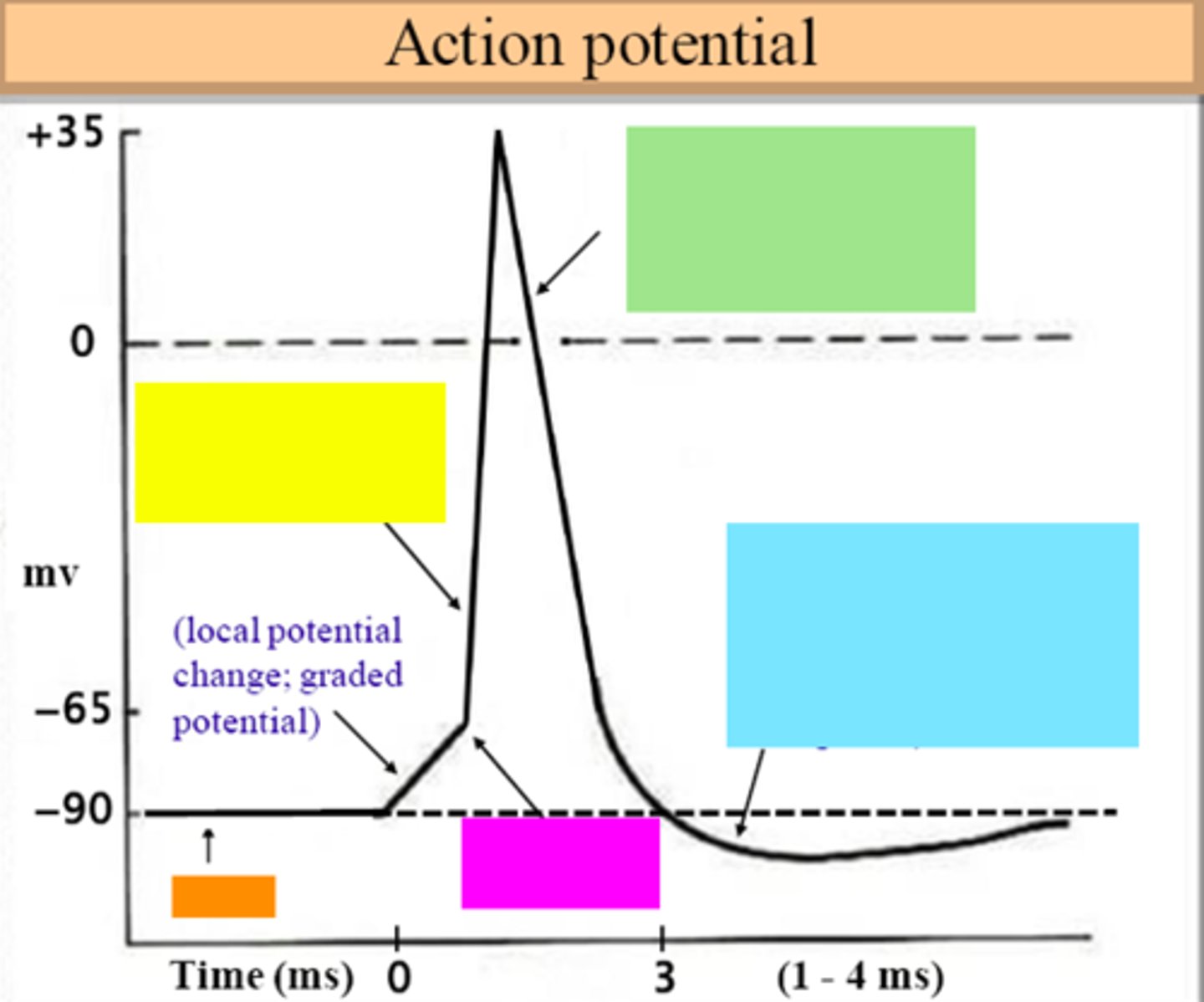
depolarization
ID the yellow box:
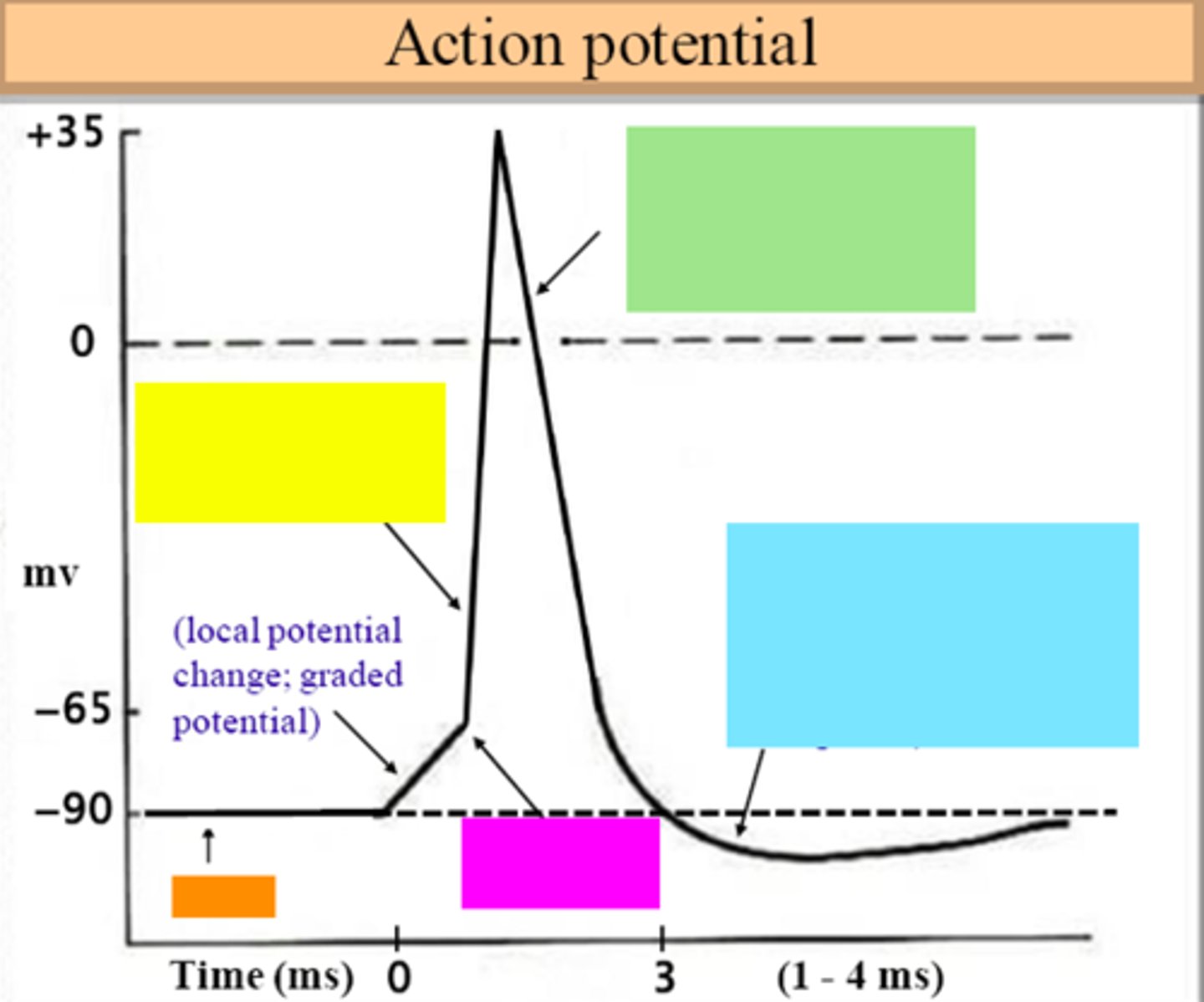
resting membrane potential
ID the orange box:
all-or-none principle
once threshold is reached, an action potential reaches full amplitude:
absolute refractory period
the time during which it is impossible to generate a second action potential:
relative refractory period
the time during which a second action potential can be generated but would require a stronger stimulus to reach threshold:
sodium channel inactivation
what is the molecular mechanism of the absolute refractory period?
false
t/f: with enough stimulus, the sodium channel that is in inactivation state can be opened again
larger stimulus
after Na+ channel reactivation, it is possible to generate another action potential but a ___________ is necessary to open enough Na+ channels to override the efflux of K+ whose permeability is still above the resting state
true
t/f: Action potentials are "all-or-none"
Na+ channels
local dental anesthesia lidocaine works on______
inactive
lidocaine acts at a defined site on Na+ channels and lock the channel in its _________ conformation
false
t/f: when a Na+ channel is in inactive form, it remains open and ions continue to diffuse in
regenerative current
Propagation of an action potential in an excitable cell:
nodes of Ranvier
the myelin sheaths are discontinuous and are separated by areas of bare axonal membrane called:
saltatory conduction
for myelinated neurons, ion flux passes only through the Nodes of Ranvier where there are functional channels, thus the action potential "jumps from node to node. This is called:
length constant (lambda)
quantifies the distance that a graded electrical potential can travel passively down an axon - before it decays to ~ 37% of its original amplitude:
membrane resistance
the force that impedes the flow of ions from the outside of the membrane to the inside, and vice versa:
axial resistance
the force that impedes current flow through the axoplasm (down the axon), parallel to the membrane:
# of channels
what determines the membrane resistance?
axon diameter
what determines the axial resistance?
greater
the fewer number of channels, the ______ the membrane resistance
lower
the more number of channels, the ______ the membrane resistance
lower
the greater the diameter of an axon, the ____ the axial resistance
greater
the smaller the diameter of an axon, the ____ the axial resistance
greater
a nerve with a large axon will have a ______ conduction velocity
greater
axons that are myelinated will have a ______ membrane resistance
lower
axons that are unmyelinated will have a ______ membrane resistance
large diameter, myelinated
Which type of axon will have the fastest conduction velocity?
- large diameter, unmyelinated
- large diameter, myelinated
- small diameter, unmlyelinated
- small diameter, myelinated
low axial resistance, high membrane resistance
Which type of axon will have the fastest conduction velocity?
- low axial resistance, low membrane resistance
- high axial resistance, high membrane resistance
- low axial resistance, high membrane resistance
- high axial resistance, low membrane resistance
high axial resistance, low membrane resistance
Which type of axon will have the slowest conduction velocity?
- low axial resistance, low membrane resistance
- high axial resistance, high membrane resistance
- low axial resistance, high membrane resistance
- high axial resistance, low membrane resistance
small diameter, unmlyelinated
Which type of axon will have the slowest conduction velocity?
- large diameter, unmyelinated
- large diameter, myelinated
- small diameter, unmlyelinated
- small diameter, myelinated
true
t/f: the ionic current injected into the axon will follow the path of least resistance
axon diameter and myelination
The length constant is a function of:
demyelinating
multiple sclerosis is a _______ disease
membrane resistance
when it comes to the length constant, patients with multiple sclerosis have a biological defect that will affect what variable?
decrease
patients with multiple sclerosis have a biological defect that will ________ the membrane resistance of their neurons