PARASITIC DISEASE, HELMINTHS, ARTHROPODS
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
Aspergillosis
brooder pneumonia
Aspergillosis
a fungal disease with high morbidity and mortality rates in young birds affecting the respiratory system
Aspergillus fumigatus
cause of Aspergillosis
transmission of Aspergillosis
Air borne; common in hatcheries and brooder houses
Moldy feeds
Contaminated drinking water
Inhalation of fungal spores
symptoms of Aspergillosis
Lung infection Numerous nodules in lung tissues
Loss of appetite, sleepiness, gasping and sometimes convulsion, and death
Sneezing, coughing, other respiratory signs are absent in chronic cases
No other signs except for semi-blindness and high mortality
prevention for Aspergillosis
Remove moldy feed and litters
Thorough cleaning of feeders and waterers
Disinfection
Mycotoxicosis
a poisoning with toxic substances of fungal origin
Aflatoxin, Ochratoxin, Trichothecenes (T-2)
cause of Mycotoxicosis
Aflatoxin
hepatotoxin produced by the molds Aspergillus flavus and A. parasiticus
Ochratoxin
a nephrotoxin produced mainly by A. ochraceus but also by some species of Aspergillus and Penicillium
Trichothecenes
a mycotoxin having an epithelionecrotic effect produced by Fusarium spp. of mold
Poultry Litter, Moldy Cereal
common sources of mycotoxin
Aspergillosis, Mycotoxicosis
poultry fungal disease
Coccidiosis
a disease caused by protozoan parasites called coccidia, which enter, multiply, and destroy the cells lining the intestinal tract.
Eimeria tenella
cause of Cecal coccidiosis
E. acervulina, E. necatrix, E. maxima and other species
cause of Intestinal coccidiosis
transmission of Coccidiosis
Ingestion of sporulated oocyst in fecal-contaminated feed, water, and litter
Mechanical transmission by contaminated footwear and farm equipment
Mechanical carriers such as rodents, flies, beetles, and wild birds
symptoms of Coccidiosis
Symptoms vary greatly depending on the severity of the infection and species of Eimeria.
Depression, ruffled feathers, loss of appetite
Blood-stained feces
Decreased feed efficiency and growth rate
prevention for coccidiosis
Apply coccidiostat in the feed or drinking water.
Observe strict sanitation. Provide footbath with disinfectant at the entrance of poultry houses.
Change or remove damp litter, especially during brooding
Leucocytozoonosis
a parasitic disease of chickens caused by a blood parasite that invade, multiply, and destroy cells of various internal organs and red blood cells
Leucocytozoon caulleryi
cause of Leucocytozoonosis
transmission of Leucocytozoonosis
Transmitted by tiny blood sucking insects (biting midges).
It is most prevalent during wet season
symptoms of Leucocytozoonosis
weakness, depression
Greenish diarrhea Loss of appetite
Death due to internal hemorrhage and red blood cell destruction
Hemorrhagic spots in skeletal and visceral organs
Large roundworm, Cecal worm, Gizzard worm, Tapeworm
Helminths
Ascardia galli
Large Roundworm
Small Intestine
large roundworms are found in
symptoms of large roundworm
Setback in weight gains; loss of egg production; death in heavy infections, paleness
Heterakis gallinae
Cecal Worm
Ceca
cecal worms are found in
symptoms of cecal worm
Unthriftiness, weakness, emaciation; ceca inflamed, thickened
Acuraria sp.
Gizzard Worm
Gizzard
gizzard worms are found in
symptoms of gizzard worm
Impaired digestion due to gizzard damage
Raillietina spp., Hymenolepis spp.
Tapeworm
Small Intestine
tapeworms are found in
symptoms of tapeworm
Loss of appetite; loss of weight, eventual emaciation, diarrhea, decrease egg production
Pediculosis
Louse infestation
Menacanthus stramineus
body louse
Goniocotes gallinae
fluff louse
Menopon gallinae
shaft louse
Lipeurus caponis
wing louse
Goniodes dissimilis
brown louse
Goniodes gigas
large chicken louse
Body louse (Menacanthus stramineus)

fluff louse (Goniocotes gallinae)

shaft louse (Menopon gallinae)
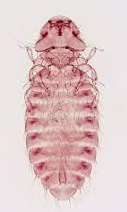
wing louse (Lipeurus caponis)

brown louse (Goniodes dissimilis)
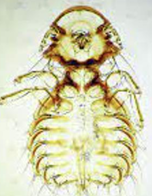
large chicken louse (Goniodes gigas)