BIO12 - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
testes (testicles - 2)
produce sperm & sex hormones
- made of connected tissues w/ seminiferous tubules
scrotum
holds test away from body @ cooler temp (34C)
- skin (balls)
- ideal temp for spermatogenesis
epididymis
carries & stores sperm cells from testes; helps sperm mature
- coiled tubules behind testes
vas deferens
transports mature sperm to urethra to prep for ejaculation
- tubules
prostate gland (1)
produces fluid to nourish & transport sperm (seminal fluid)
- muscular tube
SEMINAL FLUID: basic fluid containing bicarbonate (HCO3) to neutralize vagina's acidity
cowper's gland (2)
produces thick clear mucus before ejaculation (seminal fluid)
- small glands bellow prostate
SEMINAL FLUID: mucus rich fluid for lubrication
penis
copulation organ
- connective tissue
seminal vesicle
provides sperm w sugary fluid for movement
SEMINAL FLUID: basic fluid for acidity of vagina; fructose for sperm energy; prostaglandins (hormone) to contract female uterus
Spermatogenesis
formation of sperm in seminiferous tubules in testes
spermatocyte
makes up tubules
- undergoes meiosis to produce sperm & supported by sertoli cells
sperm structure
HEAD:
nucleus (chromosomes & DNA)
acrosomes (enzymes 4 outer layer egg penetration)
MIDPIECE:
circular mitochondria (energy 4 movement)
TAIL:
microtubules (flagellum)
interstitial cells
between seminiferous tubules
- secrete male sex hormones androgen & testosterone
sperm pathway
TESTES - sperm maturation
EPIDIDYMIS - sperm storage
VAS DEFERENS - sperm transport & some storage
URETHRA - penis 4 ejaculation
semen makeup & gland contributors (3)
SEMEN = sperm + seminal fluid
1. seminal vesicles
2. prostate gland
3. cowper's glands
penis structure & function
- foreskin cover (unless circumsized)
- spongy erectile tissue compressed when arteries fill w blood (erection)
- sphincter controls contractions 4 ejaculation when semen in urethra & prevents urine from entering
- post ejaculation, returns to flaccid state during refractory period
male orgasm
1. penis erectile tissue fills w blood, becomes erect for intercourse (erection)
2. sperm release (ejaculation) approx 4million/3.5mL of semen
3. orgasm physiologically & psychologically experienced by brain & reproductive organs
neuroendocrine control in male reproductive system (flowchart)
Hypothalamus -> Gonadotropic
Releasing Hormone (GnRH) -> anterior pituitary -> 2
FOLLICLE STIMULATING HORMONE (FSH) -> spermatogenesis & hormone production (seminiferous tubules) -> sperm + inhibin
(inhibin has negative feedback loop to hypothalamus & anterior pituitary)
LUTENIZING HORMONE (LH) -> androgen + testosterone (interstitial cells) -> sperm maturation + secondary sex characteristics (voice, facial hair, big ass Adam's apple)
(testosterone has negative feedback loop to hypothalamus & anterior pituitary)
ovaries
produce eggs + sex hormones
- connective tissue
oviducts
transports eggs
- tubules
uterus
houses developing embryo
- muscular sac
cervix
connects vagina to uterus
- muscle/muscular
vulva
external parts of vagina
- skin (labium minora & majora)
clitoris
erectile tissue, leads to female orgasm
- tissue
vagina
copulation organ & birth canal
- muscular tube
labium minora & majora
VULVA
MINORA: internal small folds covering vagina
MAJORA: external big folds covering vagina
ovaries structure & function
protects developing ova (eggs)
- where follicles undergo oogenesis
oogenesis
2 million follicles located in outer cortex of ovaries @ birth
- 400 of 2M follicles mature via oogenesis (changing from follicles to eggs to implant into uterus)
ovum
mature egg cell from follicles developed during puberty
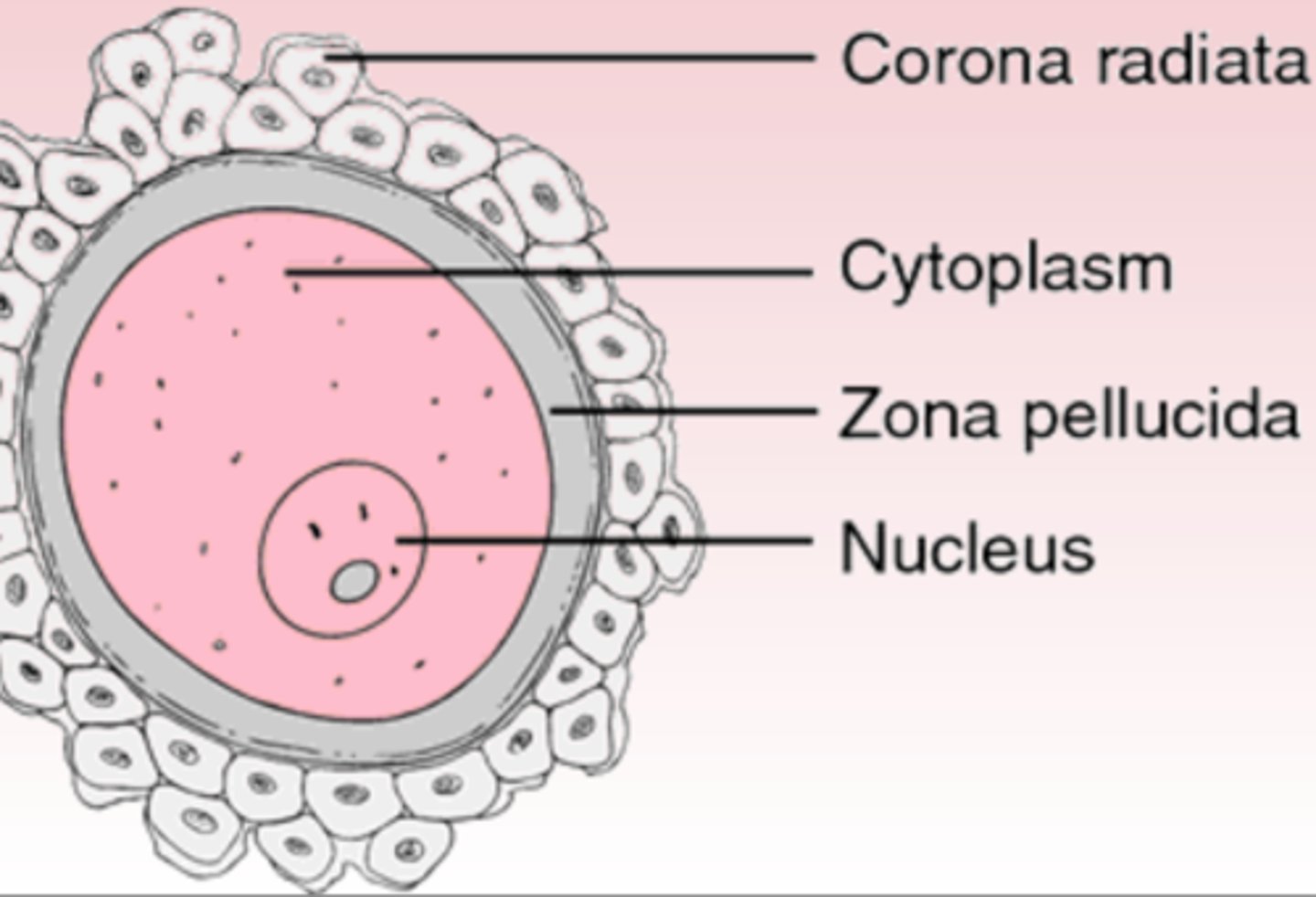
corpus luteum
from follicles
FERTILIZED: persists for 3-6 months producing female hormones (estrogen & progesterone)
- degenerates in 10 days
UNFERTILIZED: degenerates in 10 days
ovum path
OVARIES - produced
OVIDUCT - transport
UTERUS - implants if fertilized
VAGINA - period if not fertilized
female orgasm
1. erectile tissue (clitoris, labia minora, vaginal wall) fill with blood, clitoris is erect
2. vaginal wall blood vessels release fluid lubricating vagina for sex
3. no ejaculation, wide range of physiological & psychological sensations in reproductive organs + brain
neurendocrine control of female sexual development & hormones (flowchart)
Hypothalamus -> Gonadotropic
Releasing Hormone (GnRH) -> anterior pituitary -> 2
FOLLICLE STIMULATING HORMONE (FSH) -> follicles -> estrogen + egg maturation growth & thickening of endometrium (uterine lining)
(estrogen is negative feedback loop to hypothalamus & anterior pituitary)
LUTENIZING HORMONE (LH) -> corpus lutenum -> progesterone grows + thickens uterine lining
(progesterone is negative feedback loop to hypothalamus & anterior pituitary)
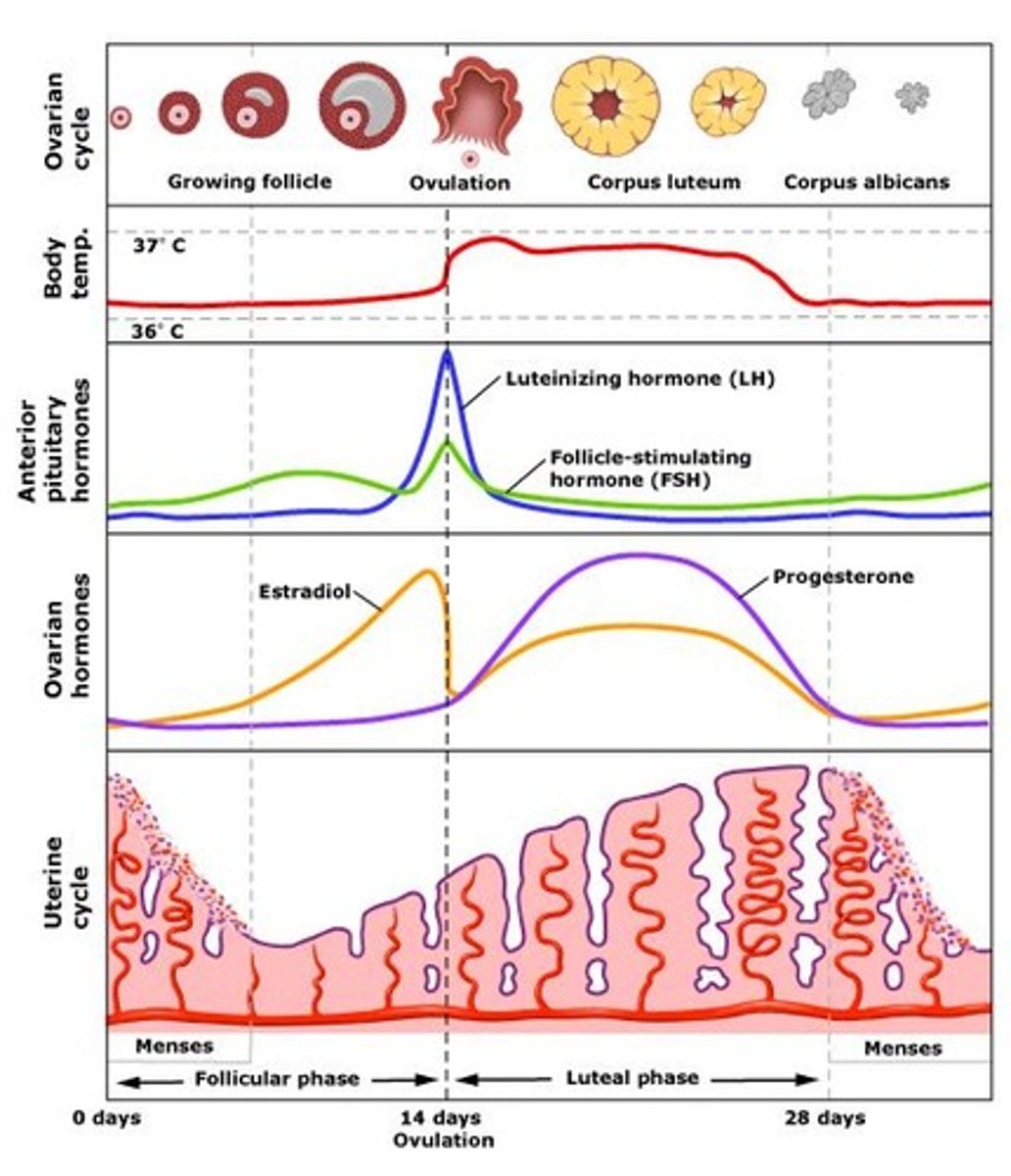
ovarian cycle
day 1-13:
FOLLICULAR PHASE - FSH -> follicle -> estrogen grows endometrium & egg (uterine lining)
day 14:
OVULATION - peak FSH & LH levels
day 15-28:
LUTEAL PHASE - follicles become corpus luteum -> progesterone growth & thickens endometrium
- continues for 3-6 months if pregnant
- last ~10 days b4 degeneration
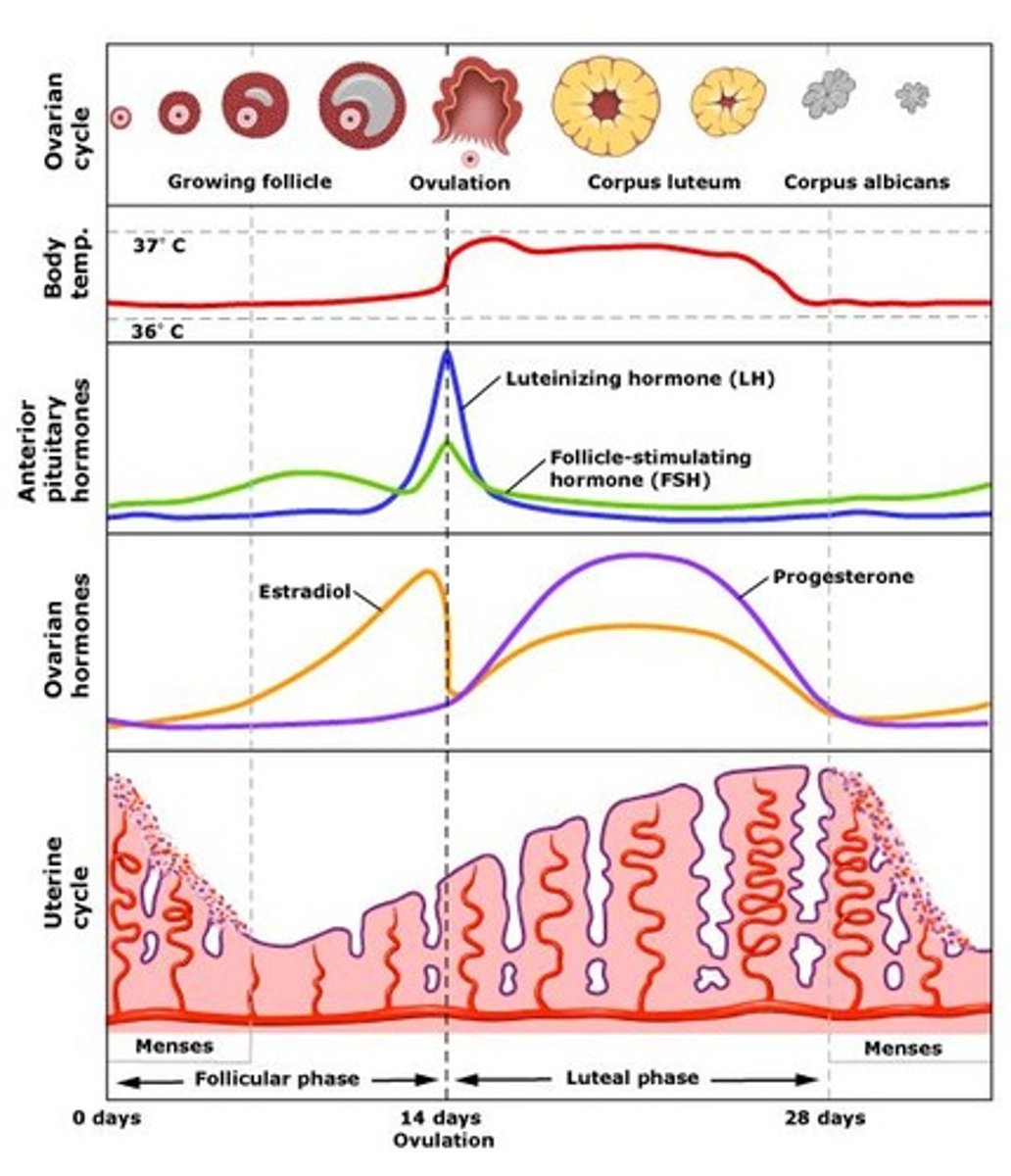
uterine cycle
day 1-5:
MENSTRUATION - estrogen + progesterone decrease & shedding of endometrium
day 6-13:
PROLIFERATIVE PHASE - estrogen increase -> growth/regrowth + thickening of endometrium
day 14:
OVULATION - peak FSH & LH levels
day 15-28:
SECRETORY PHASE - progesterone increase -> growth + thickening of endometrium
NOT FERTILIZED - menstruation starts & cycle repeats
pregnancy
fertilization occurring in oviducts
1. zygote (fertilized egg) goes from oviduct to uterus
2. zygote implants into endometrium
3. develops outer membrane producing Human Chorionic Gonadotrophic Hormone (HCG)
4. HCG prevents corpus luteum degradation
placenta development
blood vessel network to exchange nutrients + wastes
- responsible for producing HCG hormone & progesterone + estrogen (negative feedback signal 2 anterior pituitary to stop GnRH production so new follicles don't mature to maintain endometrium)
birth (flowchart)
"water breaks" - release of mucus plug from cervix
1. cervix dilates
2. hypothalamus
3. posterior pituitary
4. oxytocin
5. uterine contractions
(5 -> 1 positive feedback system until baby is out)
female breasts
MAMMARY DUCT: 15-25 lobules, leads to nipples
NIPPLES: surrounded by areola + contains saliva resistant lubricant
AREOLA: contains glands containing saliva resistant lubricant
milk production
hypothalamus
prolactin releasing hormone
anterior pituitary
prolactin hormone
milk production in mammary
(circles back to hypothalamus - positive feedback for suckling infant)
milk release
hypothalamus
posterior pituitary
oxytocin
contraction of lobules
release milk
(circles back to hypothalamus - positive feedback areola stimulation by infant)
menopause
ovarian & uterine cycles stop (45-55)
- hormones are produced but ovaries don't respond, leads to decreasing hormone lvls over time