Deserts Geography A-Level
1/120
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
121 Terms
what are the inputs in a desert system?
Things that enter the system
-water from exogenous rivers
-precipitation
-sediment carried in water
-energy can come from the sun, wind or rain
what are the outputs in a desert system?
things that leave the system
-water evaporates
-sediment leaves in water
-runoff
what are the flows and transfers in a desert system?
movement of energy or matter between stores in a system
-wind blown sand
- surface runoff
-sediment transfer
what are the stores in a desert system?
where energy or matter is kept
-landforms (stores of sediment) e.g. a sand dune
-water may be stored in the ground or in rivers.
-playas
-rivers
what type of system are deserts?
Deserts are open systems
What is dynamic equilibrium- give eg in desert
state of balance between inputs and outputs from a system.
in some desert areas, seasonal changes in wind can result in small scale and short term changes to sand dune profiles however in longer term profiles remain the same
what is a negative feedback loop- give eg
when a system responds to a change by returning to its original state- counteracts change
high rates of weathering of a slope leads to a build up of scree which then protects lower part of the slope from weatheing
what is a positive feedback loop?
amplifies changes in a system
removal of vegetation will reduce moisture which may lower rainfall which means a reduction in vegetation cover.
what can positive feedback loops cause in terms of dynamic equilibrium?
positive feedback loops cause the formation of a new state of dynamic equilibrium
what are the 3 sources of energy in a desert?
-insolation (sunlight)
-runoff (water)
-winds
why is insolation so strong in deserts?
-no clouds to block out heat
-more insolation is transferred to the ground because of the latitude of deserts.
what is the diurnal temperature range?
Basically means that deserts are hot in the day and freezing at night (due to no clouds)
what is the precipitation normally like in deserts when it does rain?
often flash floods and rainstorms. Often severe because of lack of plants to intercept. Also, the land is often baked hard, meaning the water is not absorbed/ infiltrated but just flows as runoff.
what causes wind?
Movement of air from an area of high pressure, to an area of low pressure. When there is a high gradient, winds can be very strong.
What are prevailing winds?
winds that blow in the same direction over large areas of Earth
give a reason why winds can be so powerful in deserts
lack of vegetation means that they can blow over the landscape, without any obstruction and thus increasing their force.
why is there so much sediment in deserts?
Because they used to form part of the sea bed. Then that evaporated, leaving just the sediment.
where can sediment also come from?
sediment also comes from weathering of the underlying parent material. Rivers bring sediment into deserts. Wind carries sediment in the air, which is then deposited.
How can deserts be a source of sediment?
Deserts make dust clouds.
what is the sediment budget?
The balance between the input, output and storage of sediment within a desert budget over time.
This helps determine if that system has an overall surplus (accretion) or deficit (erosion) of material, and therefore whether parts of a system are in balance/equilibrium
hot desert sediment budget usually have low sediment inputs because of the very limited erosion of hill slopes by water.
Wind erosion is usually the dominant transfer though flash floods can erode significant amounts of sediment
What is the importance of the sediment budget?
They determine what type of landforms can form. More depositional landforms when positive, and more erosional when negative.
What is the aridity index?
This basically looks at how dry an area is.
When is there a water surplus?
P (precipitation)>PET (potential evapotranspiration)
when is an area classified as a desert?
when there is a value below 0.2 on the aridity index
what latitude are most deserts found at?
Most deserts are found 30 degrees North and South of the equator.
what parts of the continents tend to be the driest?
the central parts tend to be the driest. Because as you move further inland, the air loses its water as precipitation.
Why are deserts sometimes found beside mountain ranges?
-tall mountains force air upwards
-air cools and condenses
-moisture dropped as precipitation
-the air is then dry
(Known as the rain shadow effect)
how do cold ocean currents cause deserts to form?
-cold ocean currents run along the coasts
-wind loses its ability to hold water as it travels over cold water.
-this means it loses its water as precipitation prior to reaching land
-there is now only mostly dry air, meaning a desert.
what are desert soils like
soils contain very little organic matter as very few plants can survive the lack of percipitation and high temps
decomposition rates are very low due to lack of water
desert soils lack structure annd are easily eroded by wind
generally infertile
upper layer of desert soils suffer from salinisation and have high mineral content
what are the temp ranges in the deserts?
up to 50 degrees in the summer, and below 0 in the winter and at night. Down to dry desert air, meaning no clouds.
climate in hot deserts and margins
- high summer temps and low rainfall
-lack of cloud cover results in diurnal temp
-low winter temps so overnight frost and snow can occour
-rising air creates localised low pressure regions drawing in strong winds from surrounding high pressure
-convection currents can trigger thunderstorms
is biomass high in a desert?
low. Due to limited water.
give some adaptations of the cacti, which allow for it to survive.
- smaller leaves or spines instead of leaves to reduce water loss
- thick waxy cuticles which reduces water loss
- deep root systems which allow plants to tap into deep groundwater sources
-succulence-have water storing tissues in stems
-stomata only opens to take in co2 at night which reduces water loss as temps are cooler
-halophytes- plants often able to grow in salinised soils
Is desert soil very fertile?
no. Due to high temps, which make them dry and low amount of organic matter.
what is the soil like in desert margins?
more fertile. Due to greater amount of water here.
How does desert climate affect the soil?
infrequent rain and high temps= poor soil quality (infertile). Evaporation draws salt to the surface, but it's just left on the top layer because it can't evaporate.
how does climate affect vegetation?
lack of precipitation means that vegetation cover is sparse. Only species that are highly adapated can survive e.g. the cactus.
how does soil affect climate?
soil erosion leads to dust clouds forming which reduce the formation of raindrops and thus precipitation.
How does vegetation affect climate?
less rainfall because less transpiration from plants. Also high temps because lack of evaporative cooling from plants. Finally high wind speeds because of lack of vegetation to slow the wind down.
how does soil affect vegetation?
soils are dry, salty and mostly infertile. This means a lack of vegetation. They have a lack of vegetation.
how does frost shattering cause rocks to break down?
Otherwise known as freeze-thaw weathering. Water enters into the cracks, freezes and expands at night due to sub zero temps, and then causes the rock to weaken/ partly break.
Why do deserts have a slower rate of weathering
slow rates due to the lack of water so mechanical weathering is more important than chemical whethering
how does chemical weathering cause rocks to break down?
mainly by hydration. This is when moisture combines with minerals in rocks, especially rocks containing salt, causing them to swell and eventually break.
chemical whethering- how does salt crystilization cause rocks to break down?
High temps draw saline groundwater
to the surface and water evaporates,
leaving behind salt crystals
Salt crystals grow between pores and
joints and lead to granular and block
disintegration
chemical whethering- what is hydration
Salt minerals expand when water is
added to them. This is called hydration.
The expansion can be as great as 300%.
2. The increased volume created by rock
minerals absorbing water produces physical
tensions within the rock and the pressures
can break the rock
mechanical wheathering- What is exfoliation?
For rocks with layers of different mineral compositions, outer layers expand in the day while inner layers remain cooler. At night, outer layers contract/ decrease in size more than inner layers, resulting in the peeling away of thin sheets from the rock surfacd
mechanical whethering- how does thermal fracture cause rocks to break down?
The diurnal temperate causes rocks to expand and contract causing cracks in the rock surface. Over time, repeated heating and cooling cause rocks to weaken and break apart.
Mechanical whethering- what is block and granular disintegration?
The combined effect of thermal fracture and different minerals expanding and contracting at different rates. This can cause rocks to split into blocks(along joints) or to crumble as mineral grains separate.
granualar- made up of mica and white quartz minerals which heat up and cool down at different rates leading to stress in rock and disintergration
block- repeated heating and cooling of well joined rocks such as limestone. The rocks break along joints that are the main area of weakness
what is suspension?
when very small particles are picked up and carried by the wind.
what is surface creep?
when larger particles are hit and pushed along the ground by particles being moved by saltatiterm-98on.
what is saltation?
bouncing of small particles along the ground that are temporarily lifted from the ground.
how does sediment availability affect wind transportation
hamada- bare rock- areas have little sediment available for wind transportation, regardless of wind strength
how does particle size and shape affect wind transportation
fine, well sorted sand grains are more easily lifted by the wind compared to larger particles.
Round and smooth grains also have higher mobility than angular and rough grains as they offer less resistance to wind
how does wind strength affect wind transportation
strong high energy winds can pick up and transport more and larger sediment
features of aerolian wind erosion- What is desert pavement?
Desert pavements are sheet-like surfaces of rock particles that are left
behind after the wind, or the water has removed the fine particulate matter
or sand. A desert pavement is covered by closely packed, rounded rock
fragments of the pebble. The rock pebbles are intermixed with silt that is
devoid of any vegetation.
How does surface roughness affect wind transportation
a smooth flat surface encourages transportation as wind speed is higher because obstacles reduce wind speed so may result in deposition
What is wind deposition?
as wind energy drops, transported sediment is deposited. This occours when the wind encounters an obstacle that causes its velocity to decrease.
how does saltation threshold affect wind transportation
the minimum wind speed required to initiate saltation. Smaller, lighter particles have lower saltation thresholds than larger particles.
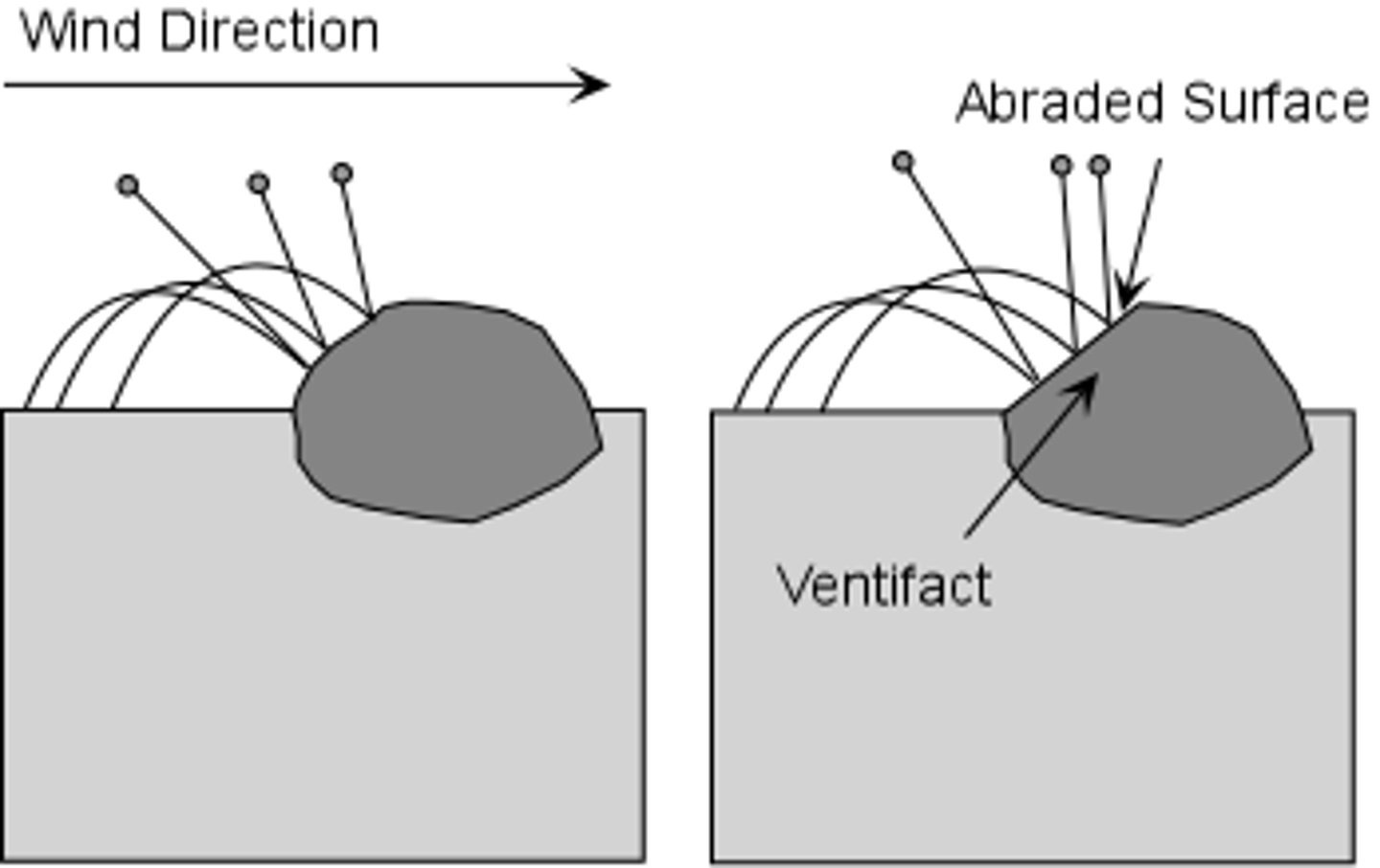
landforms by aeolian processes- ventifacts
- stones with sides (facets) that have been abraded by wind driven sand.
- a result of abrasion
- found in areas of little vegetation and frequent strong winds
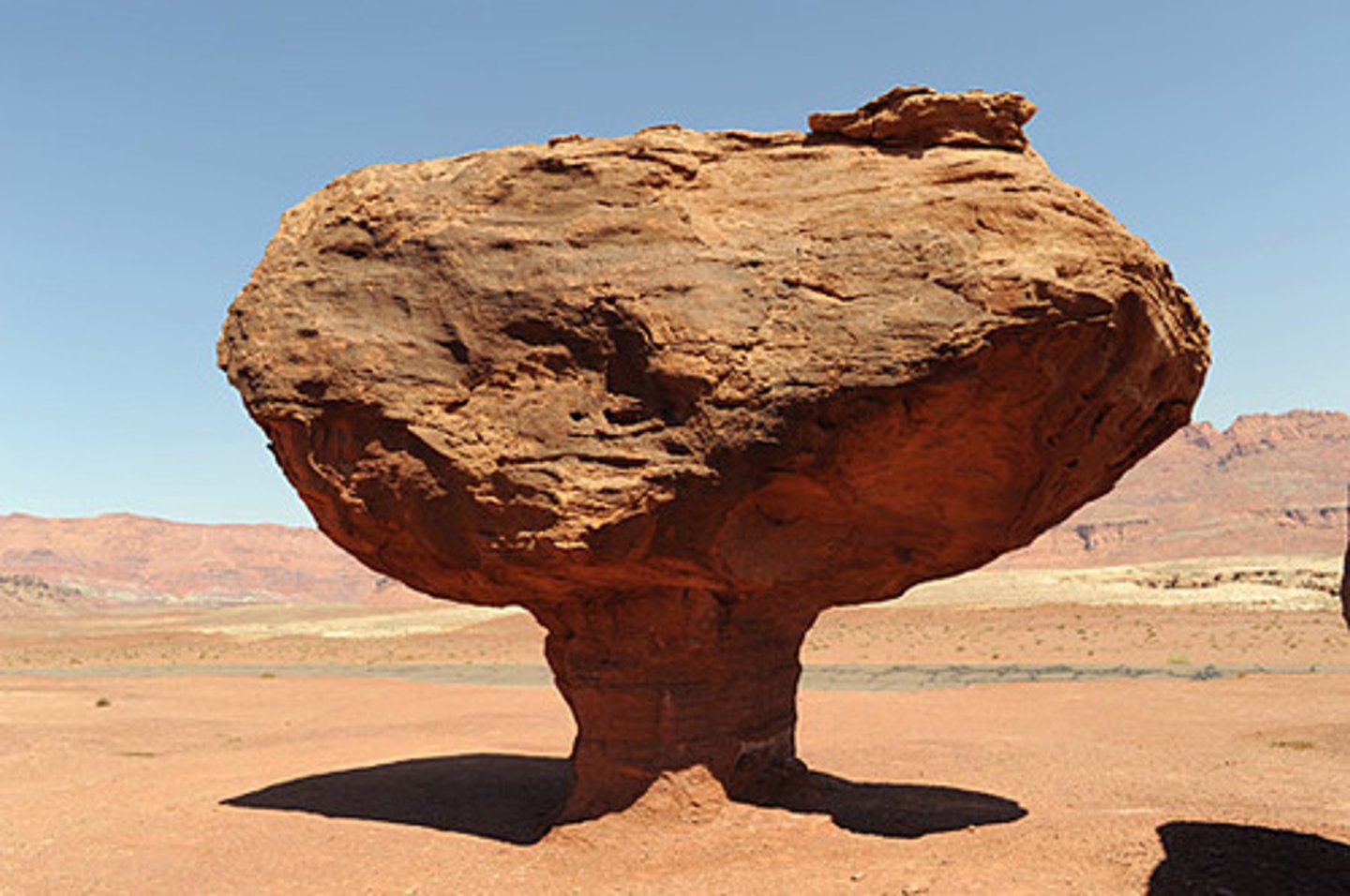
rock pedestal
a mushroom-shaped rock formed by the erosion of the rock's base
a type of ventifact

What are yardangs?
Yardangs are streamlined, wind-eroded ridges typically found in desert environments.
They form parallel to the prevailing wind direction due to the abrasion and deflation processes caused by windborne sand particles.
characteristics of yardangs
What is a flash flood?
A sudden, violent flood that occurs within a few hours, or even minutes, of a storm.
Why do flash floods occur?
They occur because all of the rainfall and precipitation cannot be infiltrated into the dry, hard desert soil.
Are flash floods strong?
Flash floods are really powerful and can move large amounts of rock by traction. The rocks within the water erode each other by the processes of attrition (basically rocks attacking each other).
By what process does the material carried by the flash flood erode the channels?
Abrasion
What is a sheet flood?
A slow-moving, even flow of water over land (the difference is that this flow of water isn't confined to a channel).
When do sheet floods occur?
Sheet floods occur after periods of intense rainfall, where the water will collect over the dry, impermeable land.
Are sheet floods powerful?
Sheet floods are still powerful, but not as much as flash floods. They can still transport pebbles, gravel and sand by suspension and saltation.
What is deposition?
Deposition is the process of dropping material
When does deposition occur?
When water/ air carrying sediment slows down so that it isn't moving fast enough to carry so much sediment
When does wind and water slow down?
Wind and water can slow down when they hit an object e.g. a piece of vegetation. If water spreads out, it also loses energy and deposits the sediment it is carrying.
What is mass movement?
This is the downward movement of material down a slope, due to the force of gravity. This is common in landforms with steep slopes e.g. inselbergs and the sides of wadi's.
When is mass movement most common?
Most likely to happen after a period of rainfall, when the material becomes heavier and encounters less friction.
What is a rockfall?
an event that results in a large amount of rock splitting off of a landform
what are landscapes made up of?
landscapes are made up of landforms
what are the types of landforms that can form in a desert?
These can be erosional or depositional, fluvial or aeolian.
Do landscapes always stay the same?
landscapes are always changing, and they are changed by various processes.
What are some of the things that can change the desert landscape?
changes in the levels of input can change the landscape of a desert. For example more water coming into the desert, means that more fluvial land forms will be formed. This causes change to the landscape.
Can landscapes formed in the past still experience change?
Yes. For example a wadi is something that could have formed thousands of years ago. Despite this, it continues to change with the input of water.
why is the landscape formation process longer in deserts?
Because of the lack of water in deserts. Lots of landforms in the world environment require lots of water, something that isn't always readily available in a desert.
What is desertification?
this is the degradation of semi-arid land through human activities and changes in climate. In the most basic terms, it means desert areas getting bigger.
what fraction of land is at risk of desertification?
1/3 of land worldwide is at risk of desertification.
how many people are currently affected by desertification?
250 million people.
what % of Africa is at risk of desertification?
46% of Africa is at risk of desertification
how does climate change cause desertification?
lower rainfall means that there is less opportunity for plants to grow, meaning lack of nutrients and subsequently soil erosion occurs. This is due to lack of water in the soil. Also higher temperatures mean that the rate of evapotranspiration increases. This means the soil dries out, leading to soil erosion and death of vegetation.
what human activities cause desertification?
overgrazing (reduces vegetation= more soil erosion)
overcultivation (less productivity and more soil erosion due to lack of nutrients)
deforestation (removing trees and their roots make soil prone to erosion)
population growth (increases pressure on land and is likely to erode soils through overcultivation and trampling)
what landscape changes come as a result of desertification?
land surface is more prone to erosion because of increasing wind speeds. Less vegetation = greater wind speeds. Land dries out because moisture leaves the soil quicker when there isn't vegetation covering it. Plant roots that help to bind the sediment are lost.
how does increased soil erosion have an impact on ecosystems?
less plants because less fertile soils. Less plants also means less animals can survive, meaning less biodiversity. These species either die out or have to migrate, meaning a change in the distribution of biodiversity. Additionally desertification can release carbon stored in the soil, into the atmosphere, driving climate change.
how do changes to landscapes and ecosystems cause knock-on effects to the human population?
reduction is soil fertility means that farmers cannot sell enough crops to feed their families, which means that they will need to move (migrate). This also puts pressure on the land in the place where they are migrating to. If people cannot move, famine may take place. Health of people can be affected. This happens because dust from soil erosion can cause respiratory diseases etc.
how will climate change in the future cause desertification?
global temps expected to rise means deserts become hotter and less wet. Extreme weather e.g. heat waves and droughts are likely to be increase in frequency.
what are the risks if desertification continues?
the rate of desertification will increase, meaning that things like famine and malnutrition are likely to also increase. Food security would be compromised. People trying to move away leads to overcrowding and the spread of diseases. Conflict is also likely over as less food for more people.
how can humans stop desertifcication?
locally people can plant vegetation to bind soils and act as wind break (slow down the wind to prevent further erosion). Globally we need to all fight climate change. Need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
How can humans reduce the impacts of desertification?
locally farmers can use different farming methods and farm sustainably (to avoid overcultivation). Also farmers can have fewer animals to avoid overgrazing.
what is an example of how we have tried to fight against desertification?
Great green wall in the Sahara and Sahel is a plan to plant trees that extend 8'000 kilometres across the whole of the Sahel.
Why might schemes like the Great Green Wall not be massively effective?
Because trees can take a very long time to grow, which may mean to people actually cutting down the tree's used in the project for their own purposes in times of shortage or crisis.
what does aerolian mean
wind
factors that impact the amount of aerolian erosion
Strength & duration of wind
Wind direction
Particle size
Moisture content of rock
Veg cover
Structure/composition of rock
explain the aerolian process of deflation
Wind blows away fine sediments, lowering the desert floor.
Coarser gravel and hardened crust (duricrust) are left behind, forming desert pavement.
This pavement prevents further wind erosion and creates a "reg" desert.
Strong winds can carve out small depressions, called deflation hollows or blowouts.
These hollows are usually small but can grow to several square kilometers.
explain the process of abrasion
Wind carrying sand sculpts rocks through sandblasting, mostly near the ground.
Wind strength, duration, and direction affect how fast abrasion happens.
Softer rocks like sandstone and limestone erode more easily.