Vas week 4: LE ABI and analog pedal artery waveforms bookwork
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Which of the following risk factors is exclusive to arterial disease?
hyperlipidemia
Which of the following is an appropriate indication and shows medical necessity for performing an arterial pressure exam?
Preoperative assessment of healing potential
The most common mechanism of disease affecting the arterial blood supply is
Atherosclerosis
what is paresthesia?
sensation of “pins and needles”
What is the suggested amount of time to “rest” a patient before the exam in order to stabilize blood pressures?
5-10 min
what is the appropriate CW Doppler frequency to use for ABI analysis on an obese patient?
4 MHz
An ABI less than _____ suggests multilevel disease
0.50
A change in the ABI of >0.15 from one study to the next is _____.
Significant
The left brachial pressure is 142mmHg. the right brachial pressure is 118mmHg. the right dorsalis pedis pressure is 138mmHg. the right posterior tibial pressure is 128mmHg. Calculate the ankle-brachial index using the dorsalis pedis pressure.
0.97 (138/172)
A waveform pattern that is describe as triphasic would have
strong forward flow in late systole followed by flow reversal below the baseline
Arterial pressures can be _____ distally if the patient has developed good collateralization in the leg.
normal
Arterial pressures may be falsely _____ if taken with the patient in the sitting position.
elavated
ankle cuffs should be wrapped _____ cm(s) above the medial malleolus
2-3
avoid sampling the dorsalis pedis artery too close to the toes so as not to record a signal from the _____ instead
Plantar arch or a digital vessel
when taking the ankle pressures on the right leg, use the _____ arm brachial pressure to calculate the index
highest
If brachial pressures differ greatly, sample the _____ artery to check flow direction and rule out a subclavian steal
vertebral
The purpose of the ABI is to evaluate the _____ of disease
presence & severity
A hemodynamically significant lesion almost always causes a _____ in the ankle pressure
decrease or reduction
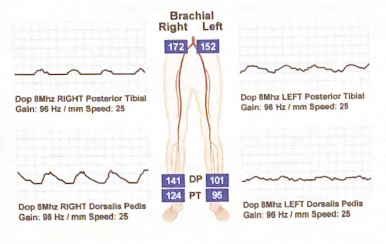
Calculate the ABI for each pedal artery bilaterally
Right PTA: 0.72 Left PTA: 0.55
Right DPA: 0.82 Left DPA: 0.59

Describe this pedal waveform:
Absent or non pulsatile
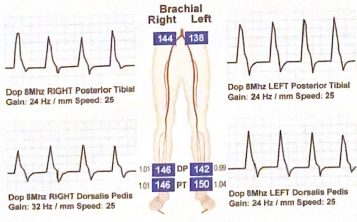
What would be the interpretation for this case? Describe the pedal waveform patterns and categorize the severity of the ABI
All waveforms are triphasic and all ABI’s are normal
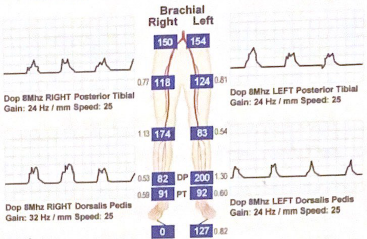
Describe the left dorsalis pedal artery waveform pattern and categorize the severity of the ABI
Waveform is monophasic
200/154=2.6 : since the ABI is above 1.3 it is calcific and considered non-diagnostic
Explain the discrepancy between the ABI and waveform documented for the left DP
Artery is calcified which falsely elevates pressure measurements
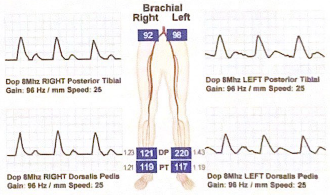
Explain why the brachial pressures are low compared to the ankle pressures. What 2 disease processes could be going on?
upper extremity atherosclerosis or lower extremity calcification. there is no significant difference between the absolute pressures in the arms. so arterial calcification is a concern since the pedal waveforms would be called biphasic in some labs
How are arterial pressures affected by a critical narrowing of the arterial lumen?
Pressures decrease significantly
Define “Poikilothermia”
Ice cold limbs
If the dorsalis pedis arterial signal is not identified at the ankle, how else would you try to obtain pressure information?
Go to anterior tibial signal more proximally on the leg or study the peroneal artery instead
After hearing the initial pulse, why is it important to make sure the pulse continues before recording the systolic pressure value?
the first sound may be from motion artifact if it does not continue as a true pulse