Lecture 3: Cell Adhesion
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
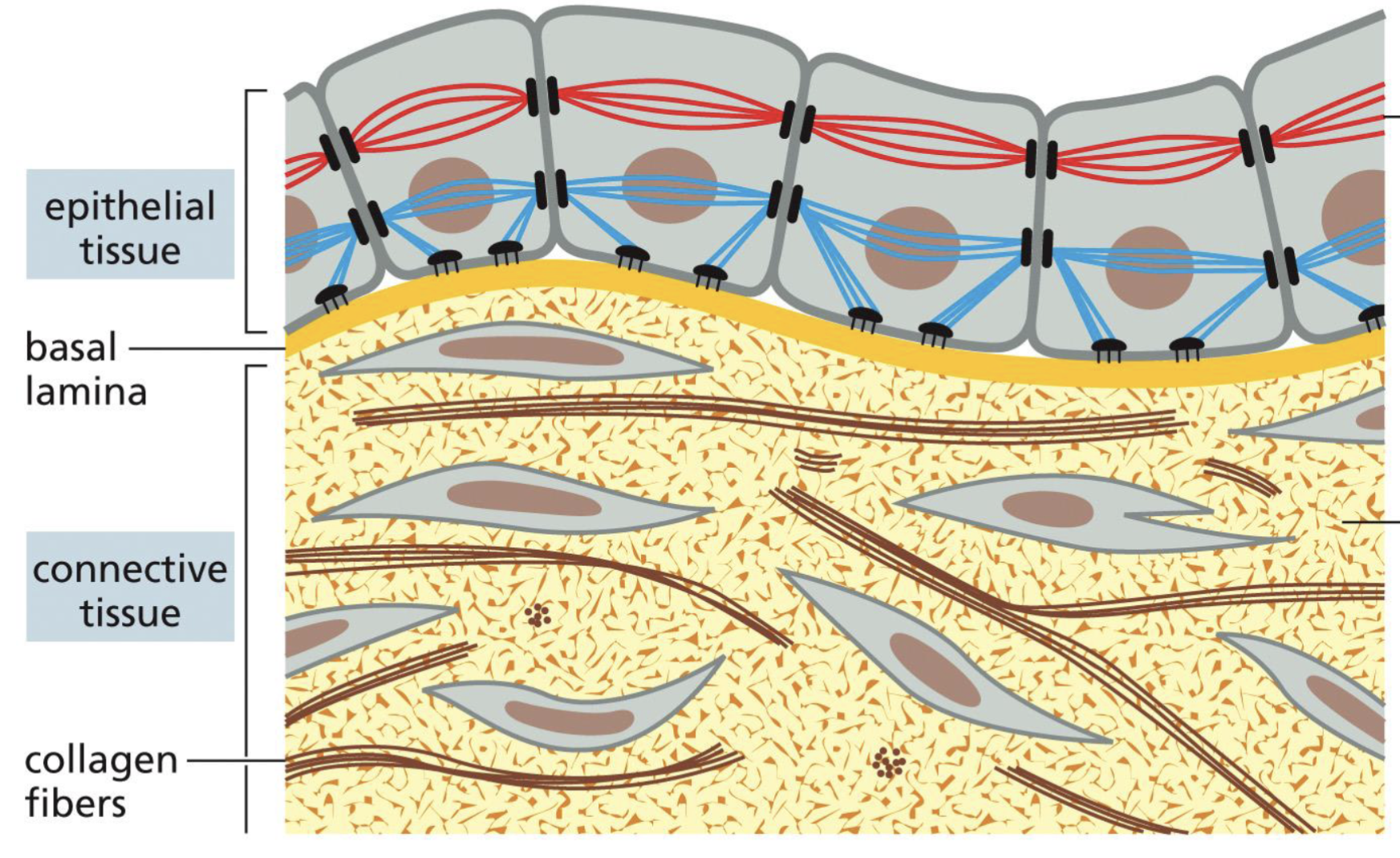
What are epithelial cells?
Cells that line surfaces, cavities, and organs
What are epithelial tissue?
Cells that are directly connected to each other (sometimes include basal lamina)
Ex) skin, digestive tract, etc.
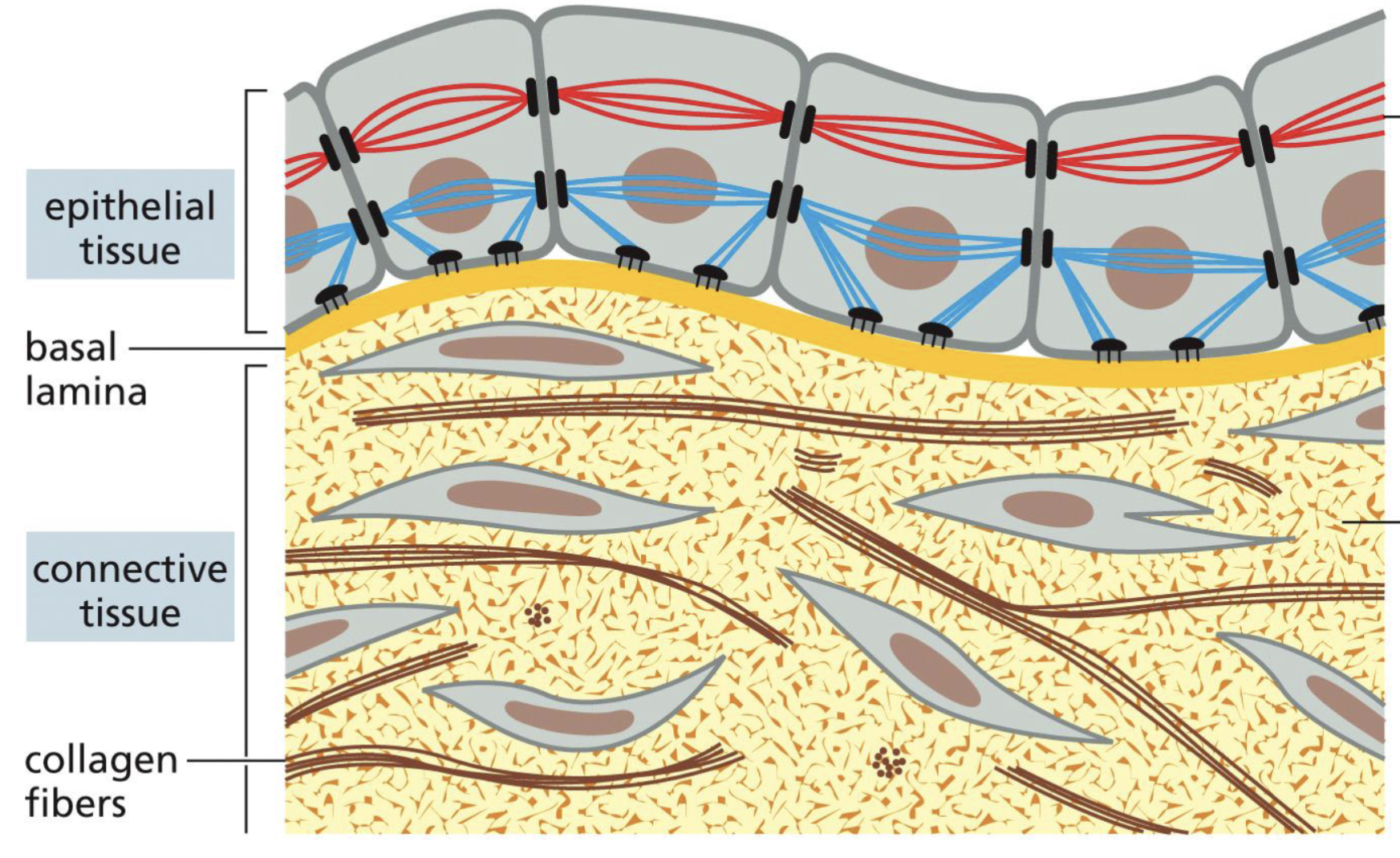
Connective Tissue
Cells that are dispersed through the extracellular matrix
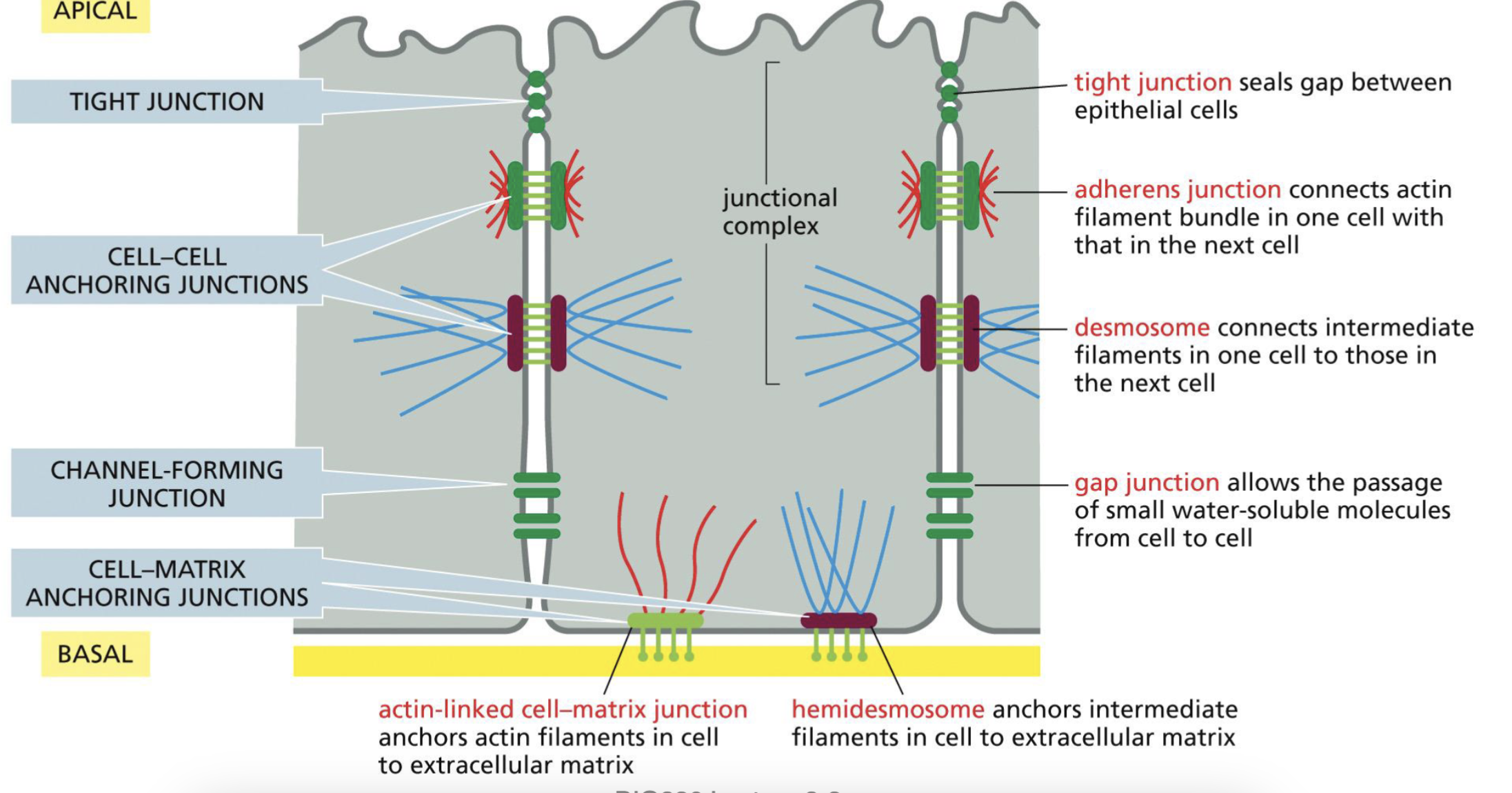
Epithelial structure that holds the cells together: Tight Junction?
Seals gap between epithelial cells
form sealing strands, and are all along between two cells.
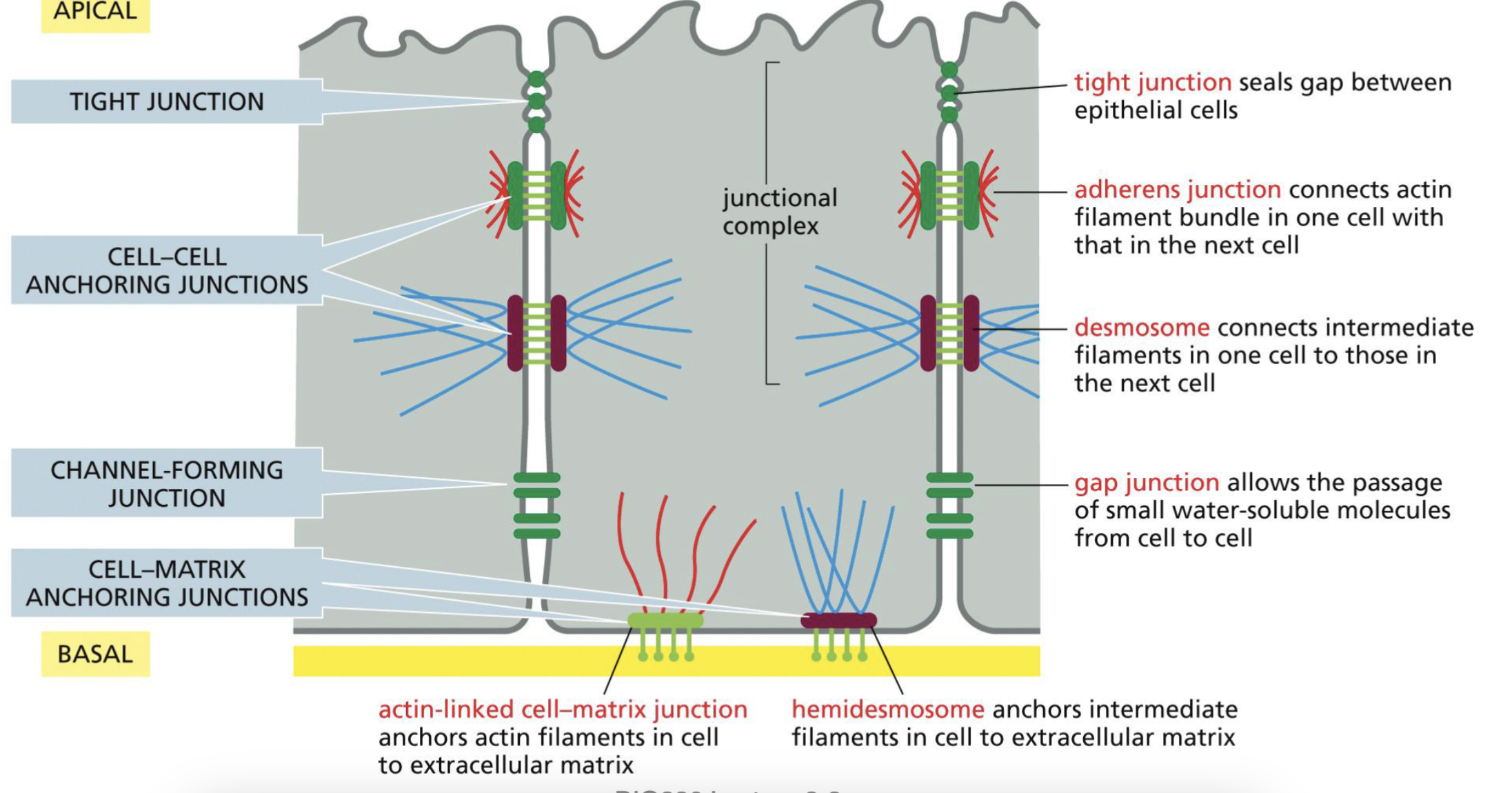
Epithelial structure that holds the cells together: Cell-Cell Anchoring Junctions? (2 types)
Adherens Junction: connect actin filament bundles on neighboring cells, form adhesion belts
**actin filaments do not go through, but anchors on the surface
Desmosome: connects intermediate filaments on neighboring cells
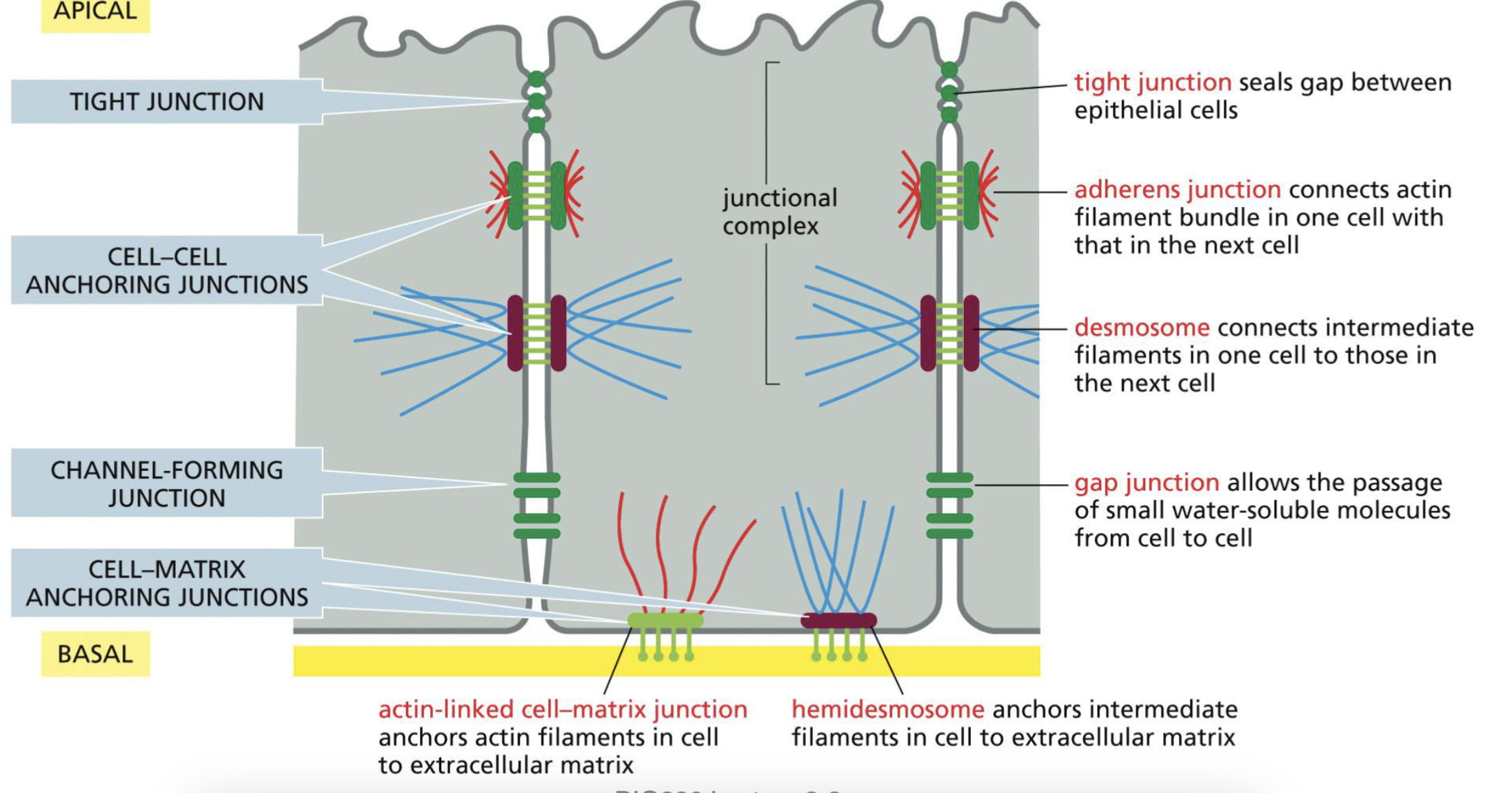
Epithelial structure that holds the cells together: Channel Forming Junction
Gap Junctions: allows small water-soluble molecules to pass through. Doesn’t go outside of the cell, goes to the next cell
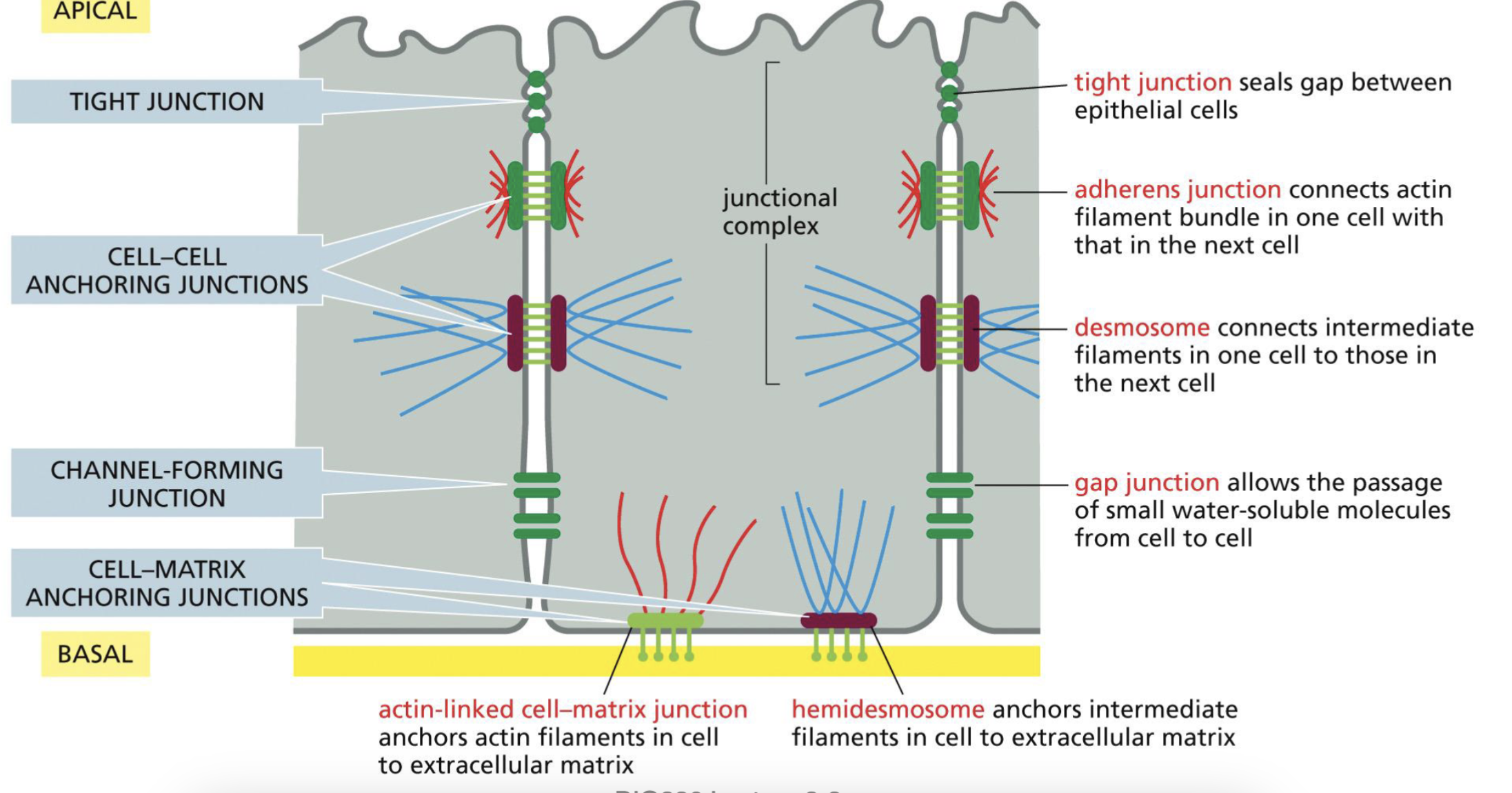
Epithelial structure that holds the cells together: Cell-Matrix Anchoring Junctions
Actin-linked cell matrix junction: anchor actin filaments in cell to extracellular matrix
Hemidesmosome: anchors intermediate filaments in cell to extracellular matrix
Cell-Cell Anchoring Junctions mediated by…
cadherins (transmembrane proteins) → adherens junctions
“cadherin family members” → desmosome
Cell-extracellular matrix junctions mediated by…
integrins (transmembrane proteins)
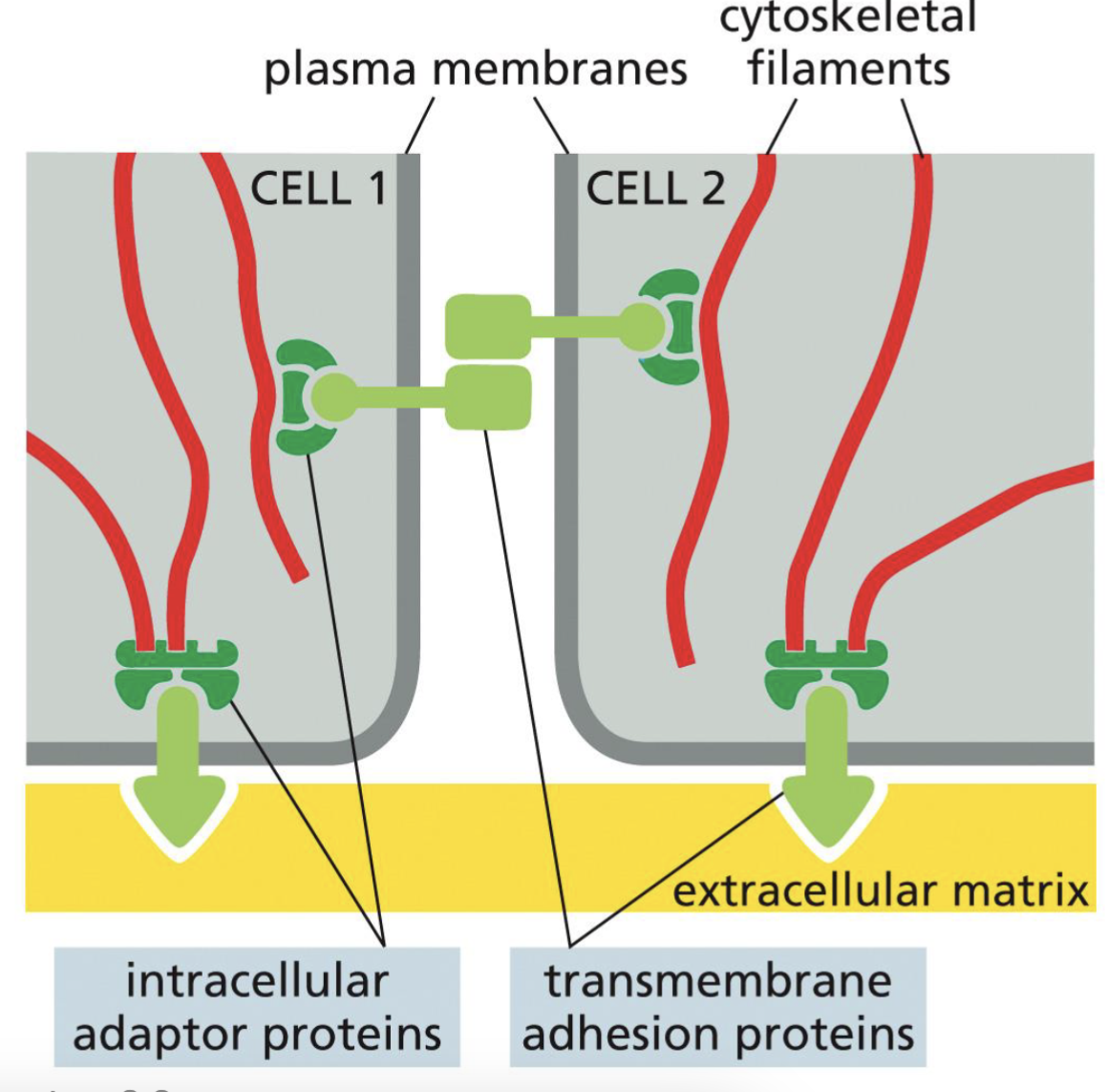
In General, Layout of junctional complexes linking to cytoskeleton
transmembrane adhesion proteins link to cell/extracellular matrix
intracellular adaptor proteins link to the transmembrane adhesion proteins and to the cytoskeletal filamemts
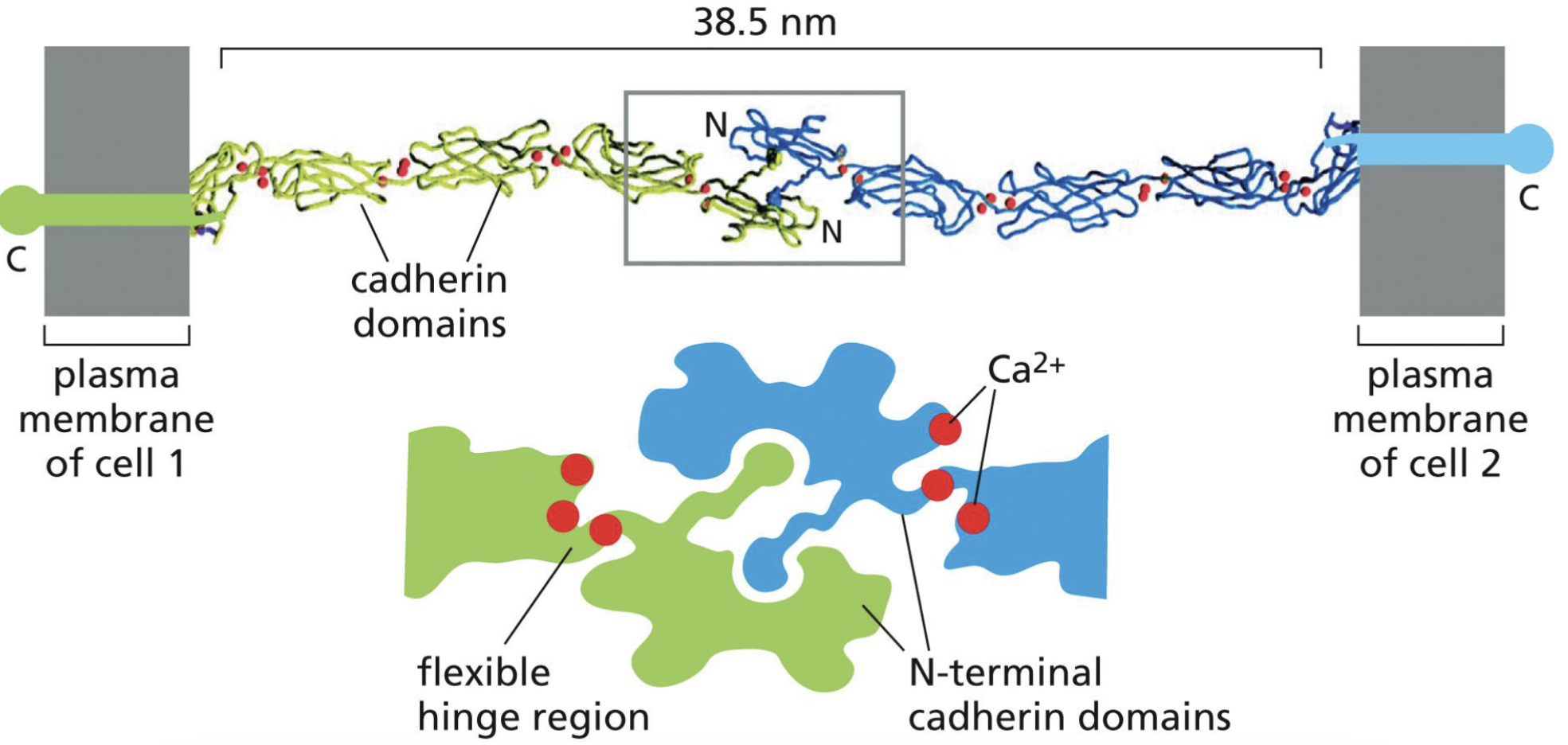
How do cadherins interact between each cell?
Cadherins interact homophillically in extracellular domains. (only Cadherin “E” will interact with Cadherin “E”)
Interaction requires Calcium ions to lock the flexible hinge regions
What happens due to the homophilic interactions of cadherins?
Different cadherins sort itself out, and form separate groups that do not interact with one another.
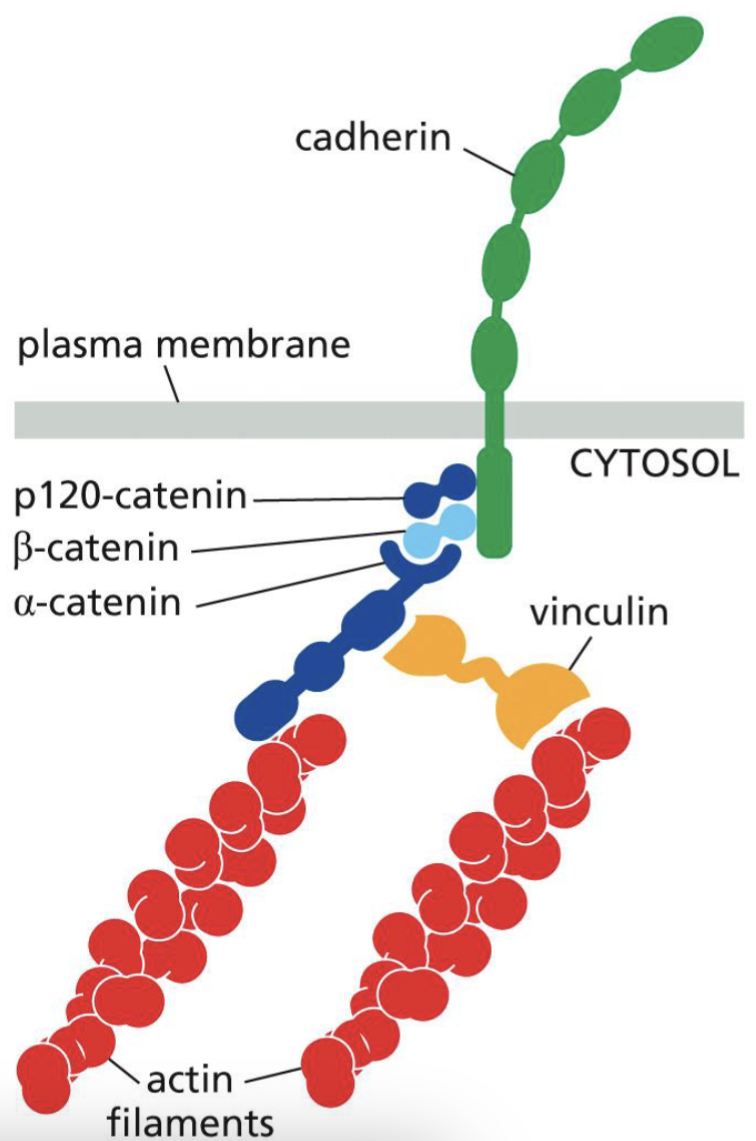
How cadherin domains interact with actin filaments
Cadherin directly links to adjacent cell’s cadherins
Cadherin (inside the cell) indirectly interact with actin filaments
This causes indirect links of the actin cytoskeleton between adjacent cells → adhesion belts form.
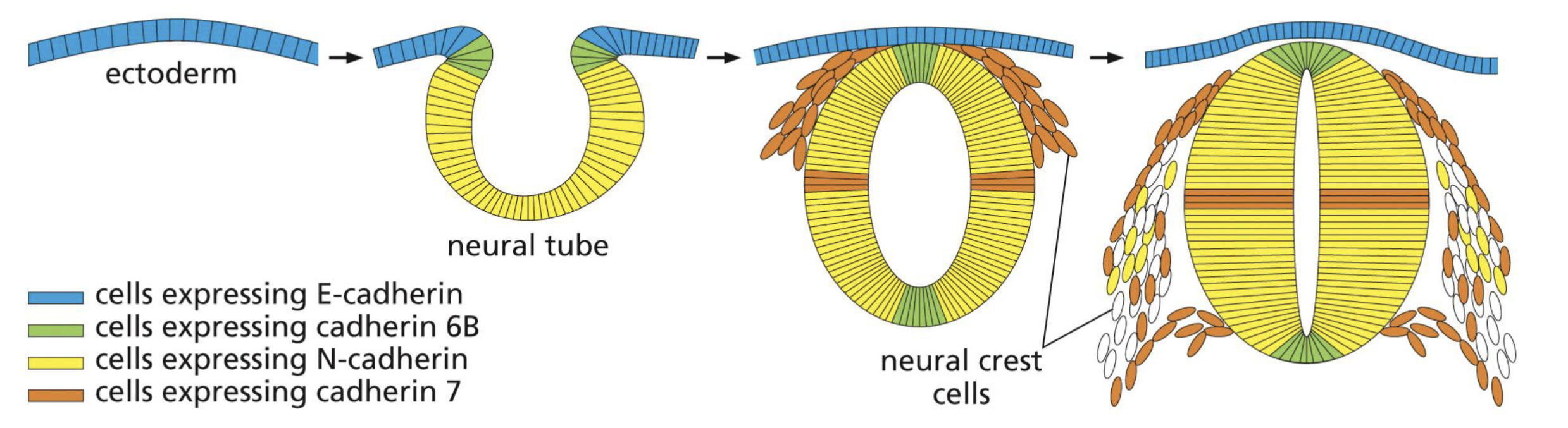
How do adhesion belts mediate morphogenesis?
Invagination of epithelial sheet → tightens the adhesion belts in selected regions, causes the tube to pinch off.
Adhesion belt forming a tube example: Neurons/Nervous System
Adhesion belt contraction pulls cells to form a tube.
form neural tube for nervous system
Apical Domain, Basal domain, basolateral domain
Apical: faces faces surface, cavity or organ
Basal: faces the inside of the body
Basolateral domain: Basal + lateral domain
How are the different domains maintained?
via tight junctions → they keep correct proteins on the correct side of the domains.
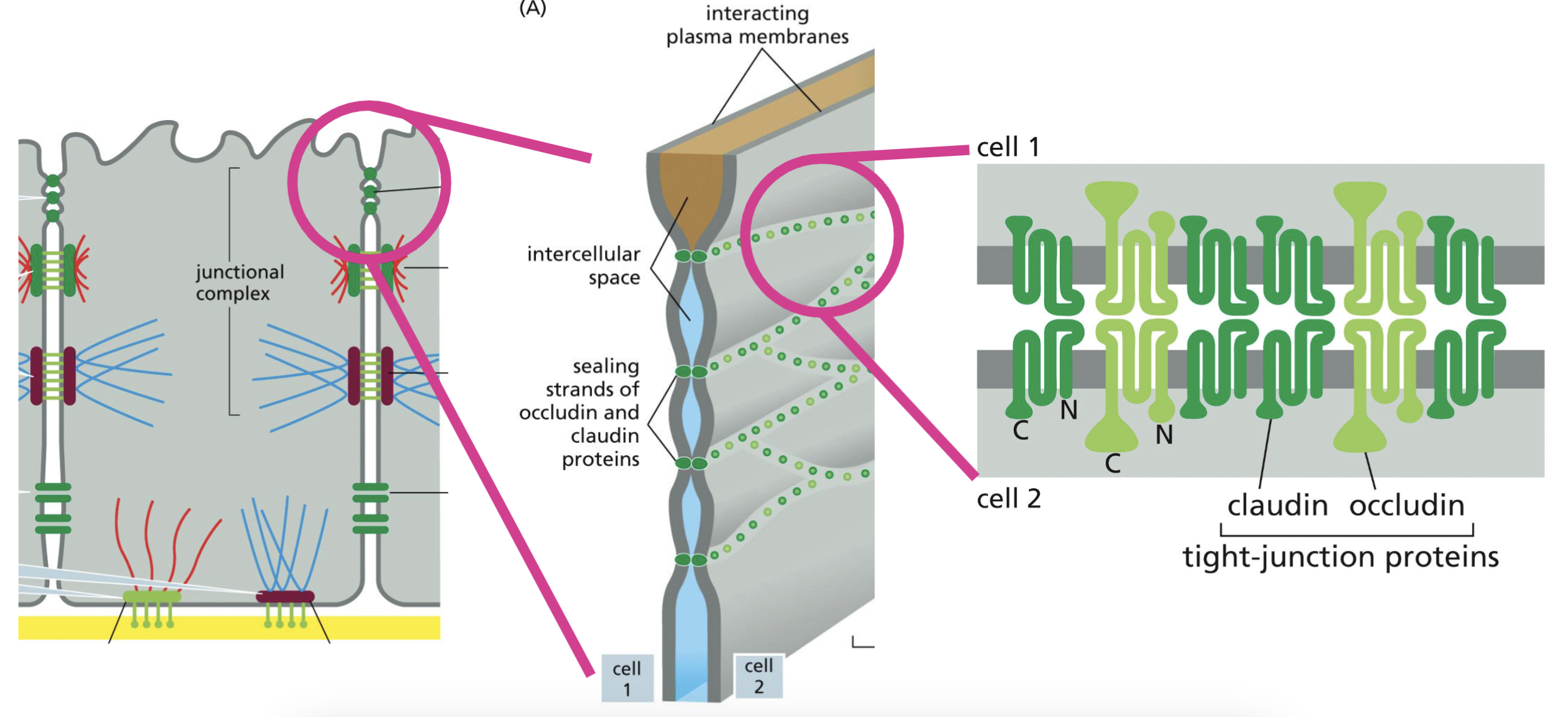
Tight Junctions structure
Occludin and Claudin form homophilic interactions directly link to adjacent cells (4 pass transmembrane proteins)
→ a lot of interactions like this → all through out the layer, = sealing strands
Example of Tight Junctions regulating what enters an organism (Moving glucose from lumen into the blood)
In the intestinal epithelial cells…
Lumen of gut: a lot of sodium ions. There are sodium ion driven glucose transporter → uses energy to transport glucose from the lumen into the cell
In the cell: a lot of glucose (high [glucose]) → passive carriers allow glucose to diffuse out of the cell into connective tissue/blood (diffusion)
Tight junctions keep correct transporters in the correct domains
![<p>In the intestinal epithelial cells…</p><p>Lumen of gut: a lot of sodium ions. There are sodium ion driven glucose transporter → uses energy to transport glucose from the lumen into the cell</p><p>In the cell: a lot of glucose (high [glucose]) → passive carriers allow glucose to diffuse out of the cell into connective tissue/blood (diffusion)</p><p><strong>Tight junctions keep correct transporters in the correct domains</strong></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/979138fc-08ba-43d6-af9a-4e86e48f3c41.png)
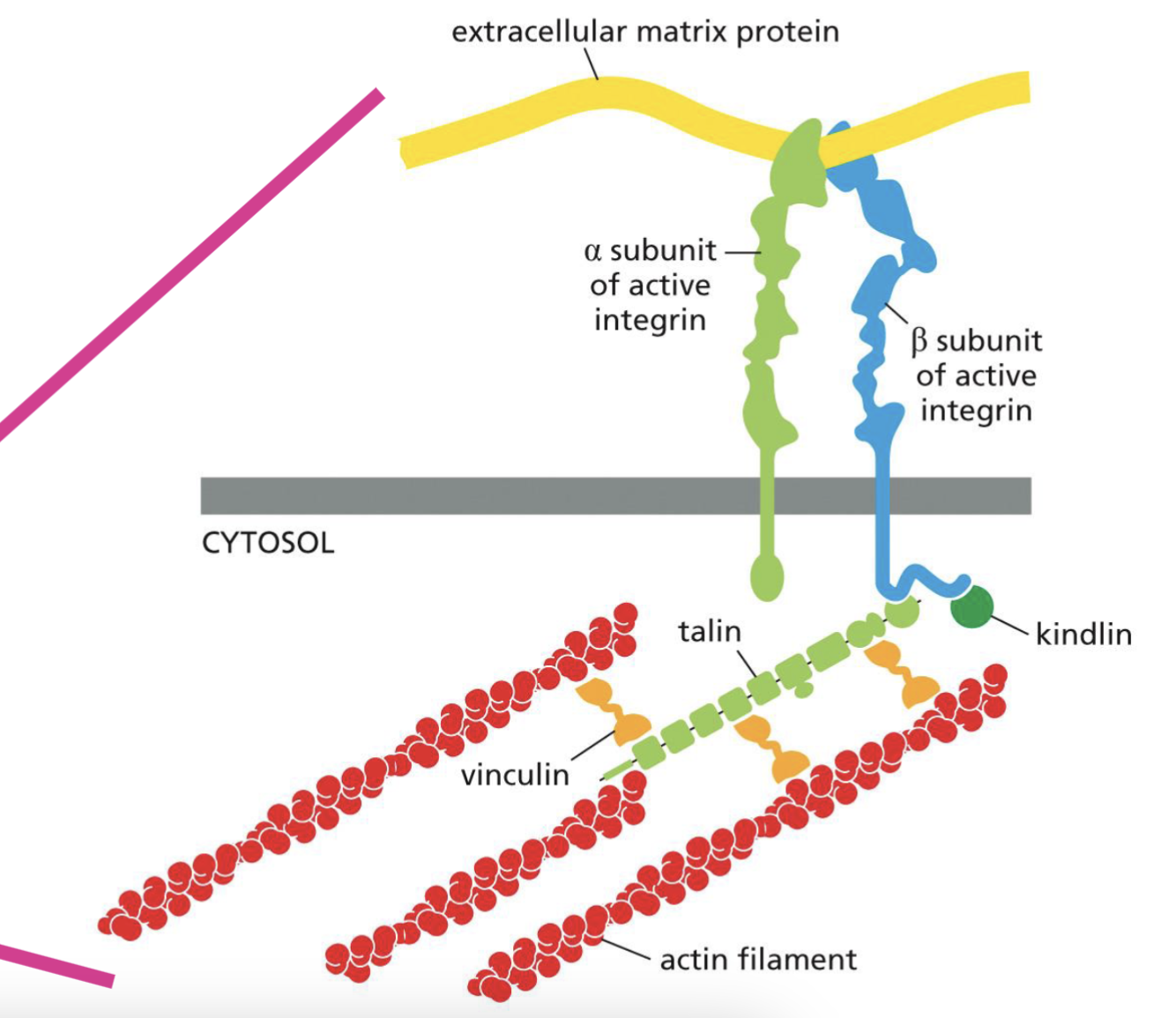
Role of Integrin
integrin directly bind to extracellular matrix protein (floor)
Transmembrane domain of integrain indirectly interact with actin filaments
This interaction helps to provide adhesion necessary for cell migration
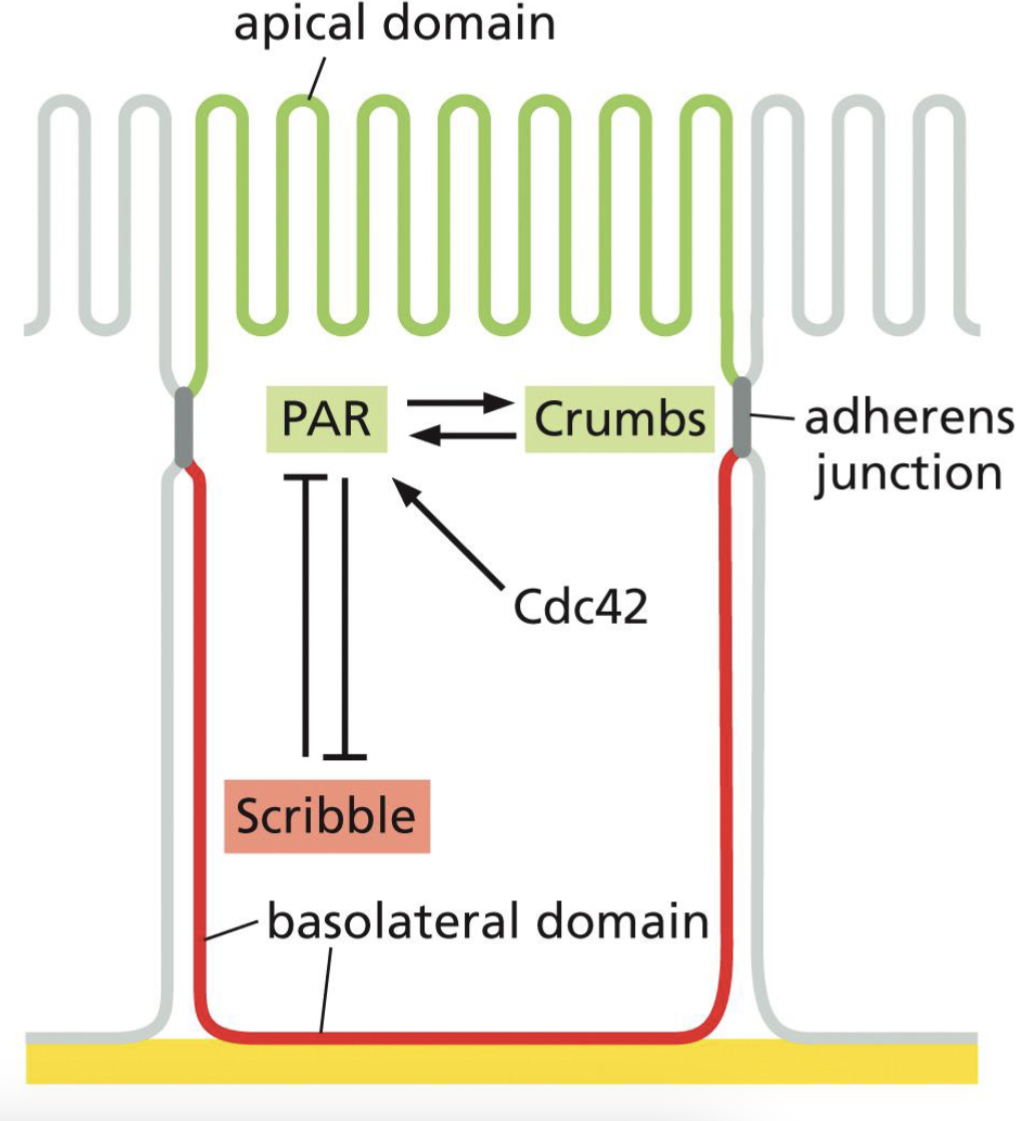
Polarity Cue
Because adherens junctions is very sticky, forms first
Adherens junctions provide polarity cues to make that side apical, and to define the other side as basolateral domain.
Adherens junction activates Crumbs and PAR signal → apical
Scribble signal activated for basal domain, and the PAR is inhibited on that side.