Variation, classification, natural & artificial selection
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
Interspecific variation is?
Between species
Intraspecific variation is?
Within species
What is a phenotype?
physical characteristics of an organism
What is a genotype?
genetic makeup of an organism
What is genetic variation?
Mixture of alleles inherited affect the phenotype of organism
Why can genetic variation occur?
DNA mutations-->
crossing over during P1 meiosis
independent assortment during M1 meiosis
random fertilisation
Random mutations-->
chromosomes or DNA
What is environmental variation?
Phenotypic variation caused by differences in environment, i.e. diet, climate, lifestyle
Examples of environmental variation?
Etiolation-plants grown without enough light grow tall and spindly with long internodes
Chlorosis-plants develop yellow leaves due to lack of chlorophyll or magnesium or light
What is discontinuous variation?
Phenotypes fall into distinct and discrete categories with no)or very few) intermediate values
How is discontinuous variation displayed?
bar chart
What affects discontinuous variation?
-->Often controlled by one gene(monogernic)
-->includes codominant and multiple alleles
-->may be controlled by 2 genes which are epistatic
-->not affected by environment
Examples of discontinuous variation?
Often qualitative data
blood group
tongue rolling
peas colour
What is continuous variation?
A continuous range of values between two extremes, usually forming a normal distribution curve
What affects continuous variation?
-->genes tend to provide additive effect on phenotype
-->smaller effects of each allele causes quantitive variation in phenotype
-->polygenic characteristics influenced by environment more than monogenic characteristics
Examples of continuous variation?
height
weight
leaf size
immune system strength
What is a species?
Group of organisms, similar in appearance, anatomy, physiology, biochemistry and genetics. They can interbreed to produce fertile offspring
What is phylogeny?
Study of evolutionary relationships between species, showing how closely related they are
How can relationships between species be displayed?
Phylogenetic tree
"cladogram"
In a phylogenetic tree what does the point at which two lines diverge from one another represent?
Last common ancestor, now extinct
What is convergent evolution?
Evolution of similar features in distantly related species. This creates analogous structures with similar form or function but have evolved separately
What is taxonomy?
System of classifying organism to their observable features or genetic characteristics
How is classification hierarchy?
Organism classified into large groups which are then subdivided into increasingly smaller groups
What is classification by carl lineaus?
Hierarchy, taxonomy, phylogeny
What is the binomial naming system?
UNDERLINE BOTH

What does classical linnaean classification rely on?
observable featrures
What are the taxons
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species
Donkey Kong Put Carrots Over Family Guy Special
Why is the binomial system being universal beneficial?
-->organisms can have more than one 'local' name
-->organism can be referred to as different names in different parts of world
-->local names can cover wide range of organisms
-->translation of languages/dialects may give different names
What is carl woese 3 domain system?
Above kingdom, organism organised into archea, bacteria, eukarya
What is an autotroph?
Can make its own food, i.e. photosynthesis, opposite to a heterotroph who consumes other organisms
What are prokaryotes Kingdom?
No nucleus
Loops of naked DNA(no histonse) not arranged in chromosomes
No membrane bound organelles
Smaller
Free living or parasytic
What are protoctists Kingdom?
Eukaryotic
Single celled or groups of similar cells
Wide variety of forms(dont fit into any other of four kingdoms)
Display various plant-like/animal-like features
Mostly free-living
Autrotrophs or heterotrophs
What are fungi Kingdom?
Eukaryotic
Exists as single cells(i.e. yeast) or have mycelium that consist of hyphae
Chitin cell walls
Cytoplasm is multi-nucleate
Mostly free living
Saphrophytic nutrition(use extracellular enzymes to break down matter and absorb nutrients)
most store food as glycogen
What are plant Kingdom?
Eukaryotic
Autotroph
Multicellular
Cellulose cell wall
Contain chlorophyll(mostly)
Store food as starch
What are animal Kingdom?
Eukaryotic
Heterotroph
Multicellular
Usually able to move around
Nervous system
Store food as glycogen
Why does modern classification rely heavily on molecular evidence?
Using only observable features could lead to incorrect taxonomic classification
Classical classification?
Observable features-morphology(external apperance), anatomy(internal structure), behaviour, fossil record, breeding method
Modern classification?
Embryology, Scanning electron microscopy, biomolecule analysis
What is embryology?
How the embryo develops
What is Cytochrome C(universal?)
All organisms that respire must have this, but the protein is not the same in all species.
By comparing amino acid sequence, can conclude how related species are, based on similarities between sequences
Greater number of differences between two sequences(cytochrome C)?
Greater evolutionary distance and thus less related the two species are
How is DNA/RNA used as evidence for classification?
Certain biomolecules are found in all molecules, the DNA(or RNA) that codes for these proteins is the same in all organisms.
Changes to the DNA sequence of bases are called mutations and occur randomly over time for many reasons. Analysing DNA sequences and looking for differences .
Evidence for classification?
Cytochrome C
DNA/RNA
What is the three domain system?
Organisms are divided into archaea, bacteria and eukaryotes, by Carl Woese
What did Woese do to the kingdom prokaryotae?
Were all once grouped together but labelled eubacteria or archaebacteria, after a gene study for RNA that makes ribosomes and observable features, he decided to split group in half to provide accurate view of how these organisms evolved
In three domain system what did each thing become?
Eubacteria became modern bacteria
Archaebacteria became the archea
The rest became eukarya
These are called domains and come at top of hierarchy of taxa
How are archaea different from modern bacteria?(argued by Woese)
Bacteria have;
=different cell membrane structure
=different RNA polymerase
=no histones
=different DNA replication mechanism
Why are archaea more similar to eukaryotes?(argued by Woese)
Similar RNA polymerase
Similar DNA replication mechansim
Produce histones
Bacteria domain(first half of prokaryotes kingdom)
MOst diverse and widespread prokaryotes
Domain archea(second half of prokaryotes kingdom)
most prokaryotes in this domain are extremophiles
Prototista(eukarya kingdom)
unicellular and simple multicellular
Plantae(eukarya kingdom)
multicellular that photosynthesise
Animalia(eukarya kingdom)
multicellular that ingest other organism
Fungi(eukarya kingdom)
partly definded by its members absorbing nutrients after deocmposing organic material
What were Darwin's observations that helped him form the theory of Evolution by natural selection?
Species over reproduce as offspring dont all survive
Populations tend to remain fairly stable
There is variation within a species(wide gene pool)
Offspring often resemble parents characteristics
What were Darwin's deductions(survival of the fittest)?
1.There is a struggle for survival. Individuals get eaten or die of disease or competition for resources.
2.Individuals with characteristics that best adapt for their environment are most likely to survive and reproduce
3.If these characteristics can be inherited then organism pass them onto offspring
Who was Wallace?
Independently concluded the same as Darwin. Made collections in the Amazon and south east Asia. Wallace and Darwin first published joint papers on evolution by Natural selection
How do fossil records provide evidence for evolution?
Fossilised remains show;
-species getting more and more complex with time(while retaining similarities)
-excinction and arrival of new forms
-allows phylogenetic trees to be made
What are some problems with the fossil record?
-->often fossil record is incomplete
-->usually only hard parts of animal fossilize and many organisms dont have hard parts
-->fossils can be destroyed and damaged by rock movements
-->fossils only form in specific conditions
What is some more recent evidence for evolution?
Biological molecules
Protein variation
DNA
Mitochondrial DNA
How do biomolecules provide evidence for evolution?
Many biomolecules are found in all organisms. This suggests that all species arose from one common ancestor
Closely related=more similar
How do protein variation provide evidence for evolution?
Vital proteins such as DNA and RNA polymerase are found in all living organisms. Higher organisms have added subunits to improve regulation.
Cytochrome C(used in respiration) shows patterns of changes
How do DNA provide evidence for evolution?
Sequencing the bases in DNA allows for comparison
How do mitochondrial DNA provide evidence for evolution?
Mitochondria are passed to offspring in the egg during sexual reproduction.
Mutations are more common in mitochondrial DNA than nuclear DNA(as less checking). So variations can be used to trace evolution
What is an adaptation?
Feature enhancing survival and long term reproductive success
What should a well adapted organism be able to do?
-find enough food/photosynthesise enough
-find enough water and mineral ions
-defend itself from predators and diseases
-survive physical conditions of its environment such as temperature, ph and light intensity
-respond to environmental changes
-be able to reproduce succesfully
What is a behavioural adaptation?
An aspect of the behaviour of the organism which allows it to survive where it lives
What is a physiological adaptation?
Internal and biochemical features that ensure correct functioning of cell processes
What is an anatomical adaptation?
Any structure enhancing survival of organism
What are the anatomical adaptations of marram grass?
Long roots
Roots spread over wide area
Curled leaves-create warm humid microclimate
Lower epidermis covered in hairs and folded
Stomata placed in pits
Low density of stomata
Leaf covered in thick waxy cuticle
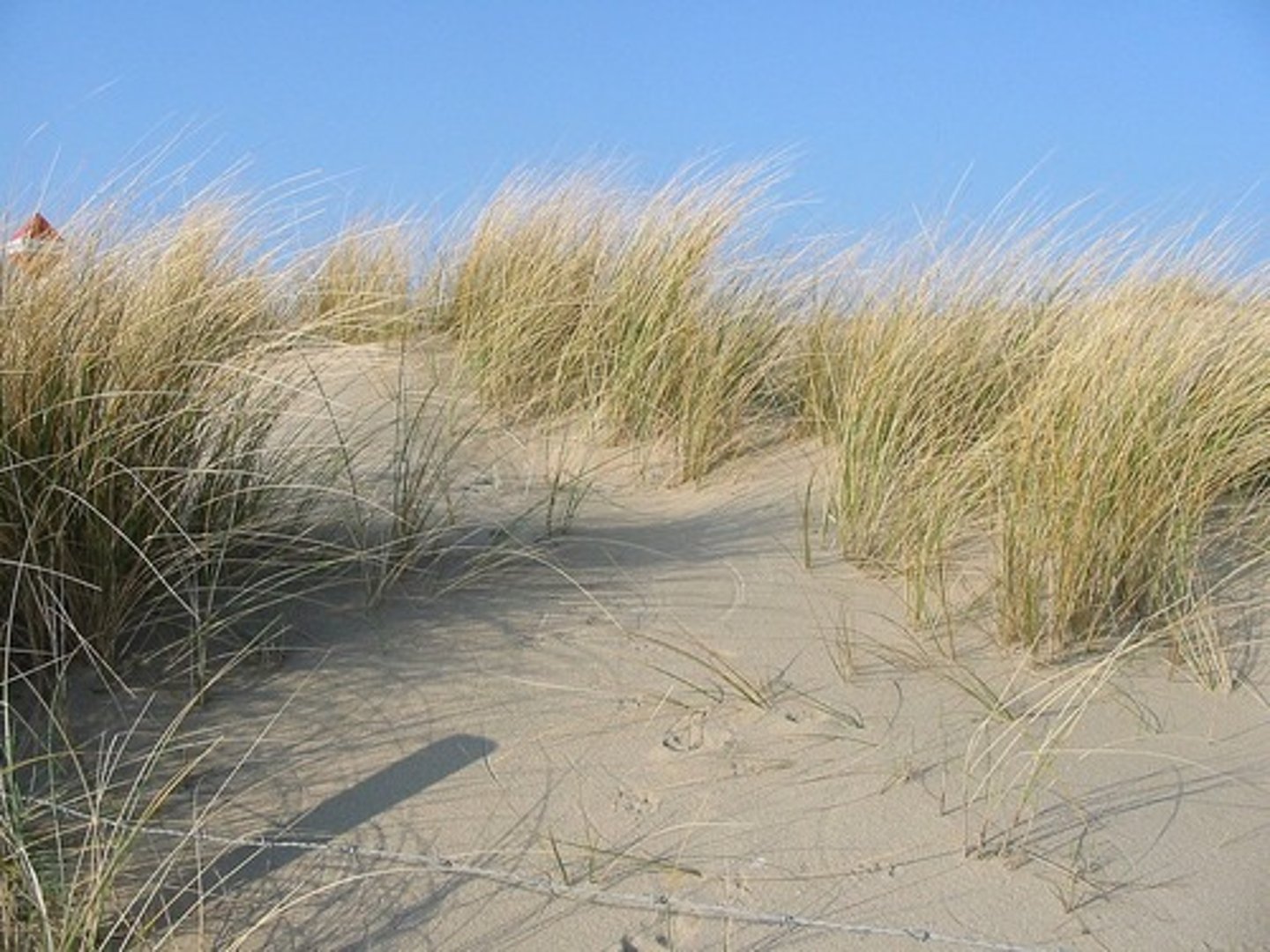

What are the behavioural adaptations of marram grass?
Close stomata and leaves curl when little water available
Open stomata only at night(cooler and more humid)
Elongates stem and grows quickly
What are the physiological adaptations of marram grass?
Leaves contain lignified cell walls(maintains turgidity even when no water)
Guard cells
Lower cell water potential than most plants so can survive salty conditions
Roll leaves using hinge cells
Why does convergent evolution come about?
Adaptations are controlled by the environment. Thus if evolutionary distinct species that live in similar habitats or exploit similar ecological niche, often evolve similar adaptations
What is a niche?
Role of organism in ecosystem
Why does natural selection come around?
Genetic variation
Selection pressure
Reproductive success
Repeated over many generations
How does genetic variation lead to natural selection?
Random mutations in DNA cause different alleles. Causing intraspecific variation. Very occasionally new alleles are beneficial
How does a selection pressure lead to natural selection?
Organisms compete for survival. There are environmental factors that confer greater chances of survival for some members of a population than others
How does reproductive success lead to natural selection?
Organisms with the advantageous adaptations are most likely to survive and reproduce passing on alleles coding for beneficial characteristics to offspring. Thus beneficial allele frequency increases within population
Why does natural selection take many generations and eventually may create a new species?
Beneficial alleles passed down, process repeated so beneficial allele frequency increases within population, eventually become genetically different enough that cant interbreed to produce fertile offspring
What is pesticide resistance(implication of evolution for human population)?
The use of pesticides by human creates a selection pressure for those individuals with some form of resistance.
How can pesticide resistance develop?
Resistance may be developed;
-insects may be able to metabolise the insecticide
-target receptor proteins on the plasma membrane may be modified
What are the problems arising due to pesticide resistance?
-->many insect species carry diseases thus infection rate inc.
-->pesticide becomes concentrated in food chain-bioaccumulation
-->insects can cause a great deal of damage before insecticide resistance is recognised by farmers(crop loss)
-->broader and stronger insecticides may need to be used(killing beneficial/benign insects
-->resistance leads to new insecticide development(costly)
What are the implications of antibiotic resistance for humans?
-overuse and misuse of antibiotics
-leads to multiple resistant strains developing
-eventually strain will be resistant to all known antibiotics
-resistance only lost if antibiotic take out of circulation and thus no selection pressure
--need to develop new antibiotics
Model answer for response on how new species arises?
Selection pressure means beneficial set of characteristics
Random genetic mutations lead to beneficial alleles
Increase chance of survive and reproduce'
Pass on beneficial alleles to offspring
Increased frequency of beneficial allele over time
Repeated over generations
Becomes so distinct they can no longer breed to produce fertile offspring=new species
What is a gene pool?
all the alleles of all the genes in an interbreeding population.
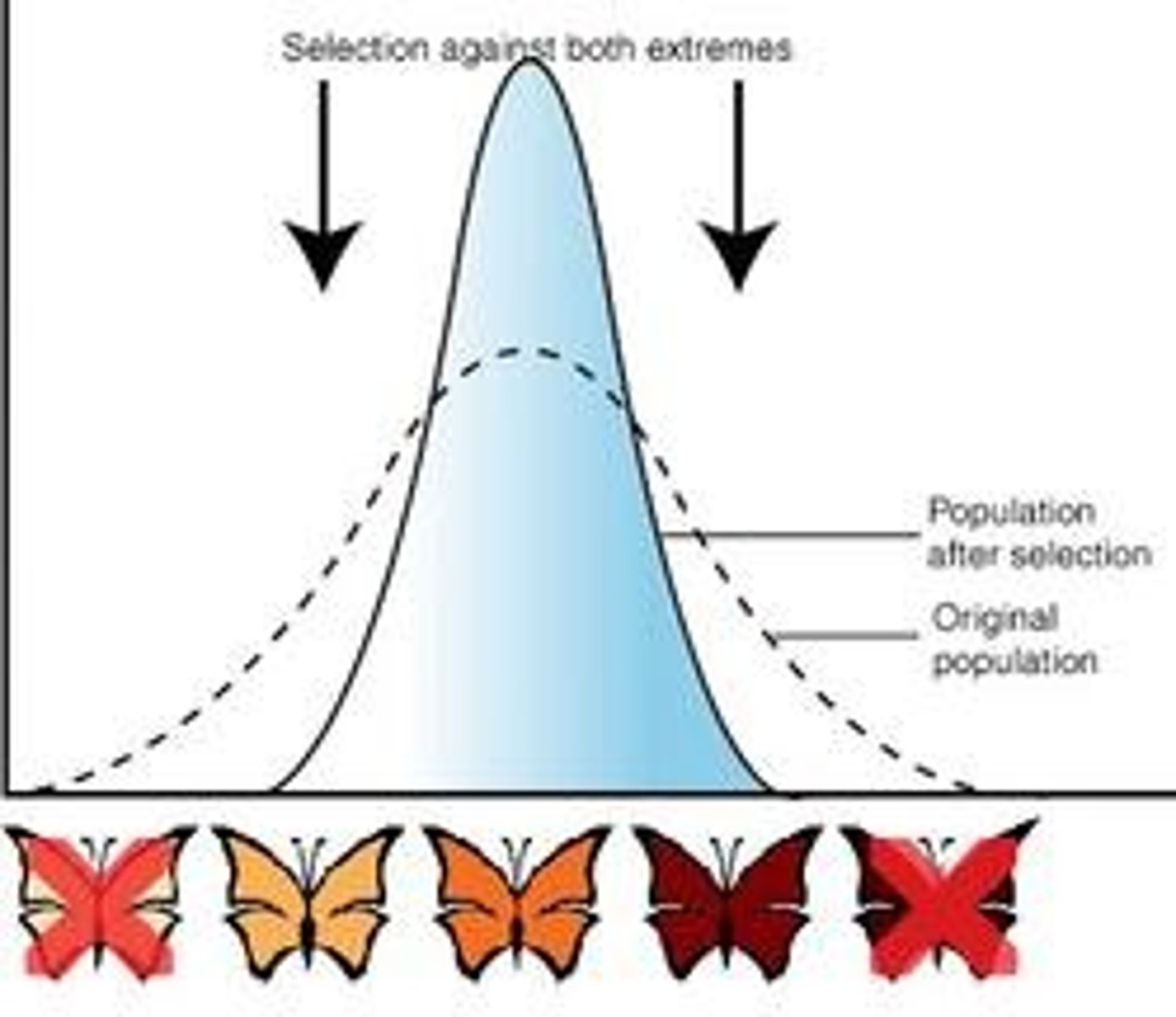
What is stabilising selection?
If the environment is stable, then this occurs;
-same alleles selected for in every successive generation and thus gene pool of population remains roughly the same
-extremes of phenotypes selected against and intermediate phenotypes selected for
What is directional selection?
If the environment changes then the selection pressure changes and this occurs;
-directional selection is an evolutionary force of natural selection
-one extreme will be selected against and the other for(selective advantage)
-over time the allele frequency shifts towards and extreme
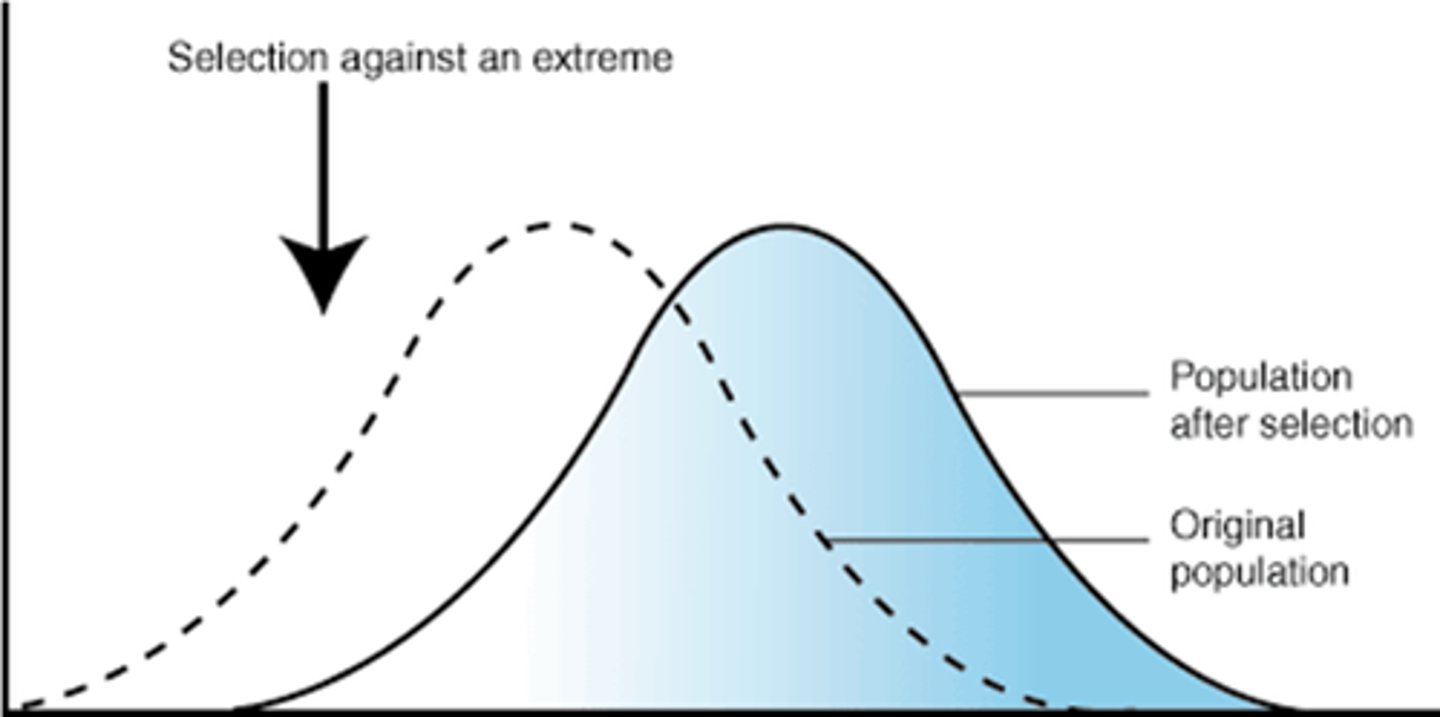
Example of directional selection?
if only large seeds were available, birds with larger beaks could eat while the birds with small beaks will have a harder time to eat. The birds with larger beaks would be more successful in surviving and passing on genes. So over time beaks increase in size
Example of stabilising selection?
natural human birth mass, babies of very low body mass are more susceptible to fatal diseases and those of a very high birth mass encounter difficulties passing the mothers pelvis
What is genetic drift?
Random fluctuations can occur in allele frequency within a population, purely by chance. Most likely in small populations i.e. island where populations are geographically separated
Why does genetic drift occur?
Randomness of reproduction
What may happen in extreme cases of genetic drift?
Allele may be eradicated from a population entirely. Making the population more venerable to extinction of environment changes as smaller gene pool
What is a genetic bottleneck?
Natural disaster or disease pandemic may kill a large % of population. Leading to particular alleles lost from population. Less genetic diversity. Population inc again but from smaller gene pool, so less variation
What is the founder effect?
When a new population is started from only a few individuals it may show loss of genetic variation. Alleles lost from population. So smaller gene pool
Why is a smaller gene pool dangerous?
Chance of survival of an individual will have a proportionally larger effect on whole populations. Less likely some members of population are adapted to different things such as diseases or climate change. Thus greater variety in alleles in population allows better adaptation to changing environment
What are alleles?
different forms of the same gene found at the same locu(position on chromosome)
Low genetic diversity can lead to problems associated with?
Inbreeding(recessive conditions)
How can genetic biodiversity be increased/gene pool be widened?
Interbreeding
Mutations
How can genetic biodiversity be decreased/gene pool be shrunk?
Selective breeding, captive breeding, cloning, genetic bottle necks, founder effect and genetic drift
What are monomorphic genes?
All members of population have the same allele.
Basic structures and biochemistry are constant within species
What is a polymorphic gene?
Two or more alleles of a gene in a population(genetic variation).