SACE STAGE 2 : BIOLOGY
1/195
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
196 Terms
Gene
A certain sequence of nucleotides in DNA/RNA that is located on a chromosome
Genetic information
The hereditary information about DNA sequences contained in chromosomal DNA/RNA
Chromosomes
Consists of single molecule DNA bonded to proteins
Sister chromatids
The identical copies (chromotids) former by the DNA replication of a chromosome
Cytosol
The fluid in which organelles of the cell reside
Nucleotide
An organic molecule that is the building block of DNA/RNA
Nucleotide region
Is where cytosol and DNA is located
Double helix
The structure formed by double stranded molecules of nucleic acid
Nucleus
A large membrane bounded organelle that contains the genetic material in the form of many linear DNA molecules, controls all cell activity and regulates transcription of genes
Complementary base pairing
The pairing of the two complementary base nucletides.
In DNA, A pairs with T and C pairs with G
In RNA, A pairs with U and C pairs with G
Adenine
Thymine
Cytosine
Guanine
Uracil
Eukaryotic cells
Complex and have multiple linear chromosomes eg. plants, animals and fungi
Prokaryotic cell
Simple and have singular circular chromosomes eg, bacteria
DNA replication (semi-conservative)
1: Helix bonds broken by enzyme
2: DNA polymerase enzyme assists as a catalyst
3: Results in two DNA molecules, contain 1 old and 1 newly synthesised strand
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid, it stores and transmits information, is self replicating and is made from sugar, phosphate and base
Chromotin
A mass of genetic material composed of DNA and histones that are the condensed into chromosomes
Enzymes
Organic catalysts which speeds up a biochemical reaction in a cell without being changed
Catalyst
Substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction
Specificity
Unique binding of one molecule to another. one substrate to one enzyme
Active site
Region on an enzymes surface where the substrate binds in a complementary fashion
Induced fit model
Model where the substrate induces a fit into the active site where it did not initially fit
Activation energy
Amount of energy necessary for a chemical reaction to occur
Metabolism
All of the biochemical reactions occurring within an organism
Metabolic pathway
A series of biochemical reactions occurring in cells, each catalysed by a specific enzyme
Competitive inhibitor
An inhibitor whose structure is so similar to the structure of the substrate that it binds to the active site of enzyme and prevents substrate from binding
Non-competitive inhibitor
A chemical which combines with an enzyme, but not at the active site, but changes the shape of the active site, preventing the substrate from binding
RNA
Ribose nucleic acid
Cytoplasm
Contents of an eukaryotic cell, excluding the nucleus and other organelles
Exons
Intronoding segment of DNA which carries bases which are transcribed (expressed)
Intron
Section of non-coding DNA which carries non-coding bases, segments are spliced out of RNA
rRNA (ribosomal RNA)
Ribosomal RNA; type of RNA that makes up part of the ribosome
mRNA (messenger RNA)
Messenger RNA; type of RNA that carries instructions from DNA in the nucleus to the ribosome
tRNA (transfer RNA)
Transfer RNA; type of RNA that carries amino acids to the ribosome
Polypeptide
Long chain of amino acids held together by peptide bonds
Template strand
Coding strand in DNA helix and contains genes that are transcribed into mRNA
Complementary strand
A strand of DNA that is one of the strands of the double helix and complements the coding of template strand
DNA base triplet
Three nucleotides bases code for one amino acid
Codon
A three base sequence on mRNA molecule that provides codes for a particular amino acid
Anticodon
A three-base sequence on the tRNA that is complementary to the mRNA codon
Amino acids
A molecule consisting of an amino and acid part which is joined by peptide bonds in long chains to form polypeptides and proteins
Ribosome
An organelle in the cytoplasm which has a vital role in translation
Transcription
Process which occurs in the first part of protein synthesis in the nucleus of a cell in which DNA make a copy of mRNA
Translation
Second stage of protein synthesis that occurs in ribosomes in which the base sequence in ,mRNA is used to make an amino acid sequence in a polypeptide
RNA splicing
Process in which mRNA bases are produced as a result of transcription, introns are removed and the remaining mRNA bases (exons) are joined together
Antibody
A protein made by a plasma cell in the blood as a response to the presence of a specific antigen
Antigen
A non-self marker protein or carbohydrate, that stimulates production of an antibody
Peptide bond
Chemical bonds that link amino acids in a polypeptide chain or protein molecule
Alpha helix
Secondary structure of polypeptides with a coiled, helical shape
Beta pleated sheet
Secondary structure of polypeptides with a folded sheet shape
Enzyme
Organic catalyst which is able to speed up a biochemical reaction in a cell without being changed itself
Hormones
Chemical released from endocrine gland and carried in blood.
bind to surface receptor in the cell membrane and bring about specific functions
Receptor
An organelle which is able to detect a stimulus and send a message through sensory neurons to the central nervous system
Repressor protein
A protein that switches off genes by making them inaccessible for transcription
Activator protein
Protein that switches on genes by making them more accessible for transcription
Gene expression
Process that results in information stored in DNA being used to make a gene-product, usually a polypeptide or RNA molecule
Promoter
Specific base sequence near the start of a gene, which RNA polymerase binds too, to start transcription
Transcription factors
A variety of proteins involved in the process of converting, or transcribing, DNA into RNA
Phenotype
The appearance of an organism which is determined by its genotype and the effect of the environment
Cell differentiation
The process by which cells become different in structure and function
RNA polymerase
The enzyme that catalyses the production of mRNA in transcription
Chromatin
Granular material found in the nucleus of a cell during interphase, consists of unwound chromosomes and DNA molecules
Histones
Small proteins around which DNA is wrapped to form chromosomes in eukaryotic cells
Zygote
A cell which is formed in result of the fertilisation of a male and female gamete (sperm and ovum)
Stem cell
A type of unspecialised cells that is able to divide and produce different types of cells
may be pluripotent or multipotent.
Methylation
Attachment of methyl groups to section of DNA that may interfere with gene expression
One of several factors involved in epigenetic.
Epigenetics
Inheritance if traits caused by modification of gene expression rather than simple transmission of genetic information
Cancer
General name of cells which grow uncontrollably and are malignant and will invade and kill other tissues in the body
Auto-immune system
A complex organization within the body that is designed normally to "seek and destroy" invaders of the body, including infectious agents.
Mutation
A random and permanent change in the sequence of bases in the DNA which may be expressed as a change in the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide.
Not all mutations are bad and can lead to improving chance of survival and consequently increase population
Point mutation
A type of mutation in which only one base in a gene in substituted
Frameshift mutation
A type of mutation in which DNA bases are inserted or deleted therefore causing DNA triplets to be read in a different sequence after the change
Base substitution
A mutation where one base is replaced by another.
Base insertion
A mutation where a base is added
Base deletion
A mutation where a base is removed.
Mutagen
Any chemical, radiation or other agent which increases the rate of mutation in an organism.
Germline cell mutation
A mutation in a sperm or ovum cell which may be included in the zygote and therefore in all cells of the resultant organism.
Somatic cell mutation
A type of mutation which occurs in normal body cells, may sometimes give rise to a cancer.
Genetic engineering
Deliberate manipulation of genetic material in order to change some of characteristics or produce useful products
Gene probe
Artificially prepared DNA or RNA sequence used to located particular base sequence or gene.
Restriction enzymes
An enzyme used to cut DNA into different segments over 1000 known and each one cuts DNA at a specific restriction site.
DNA ligase
Enzyme that can be used to join one fragment of DNA to another
Recombinant DNA
A DNA molecule formed by joined segments of DNA from different species
PCR
Polymerase chain reaction, reaction in which millions of copies of the DNA can be made in a short period of time
DNA primer
Short sequence of DNA bases used to control PCR
DNA polymerase
Enzyme that catalyses the production of new DNA strand during replication
Gel electrophoresis
A technique used to separate large molecules using an electric field, based on size and charge
DNA profiling
Technique that compares DNA from different sources by cutting it into fragments with restriction enzymes and then separating these fragment into visible bands using gel electrophoresis.
Microinjection
A technique using micro-pipette to transfer genes between species.
Virus vector
A virus that is used to transfer genes from species to another
CRISPR
Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats, gene editing technology that permits the genes of an organisms to be permanently altered
Cas-9
Enzyme that recognizes guide RNA and binds here and cuts the DNA
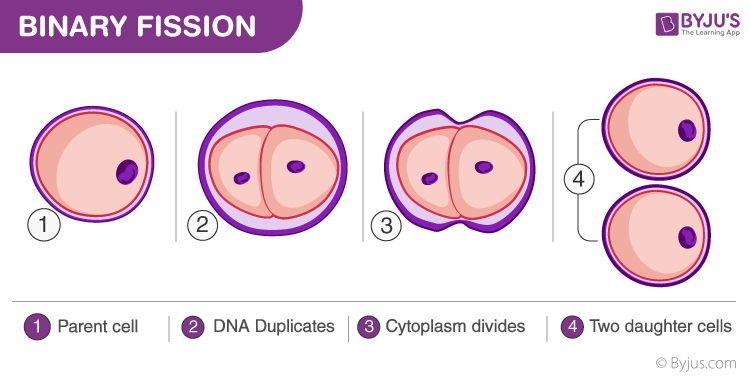
Binary fission
Division process of prokaryotic cells
Heterotroph
Organisms that consume other organisms for chemical energy.
Vacuole
Single membrane-bound sac which stores food/nutrients to be broken down in animal cells and is a support structure of plant cells that holds water and salt
Vesicle
Transports substances in/out of cell by endo/exocytosis
Mitochondria
Site of aerobic respiration, making ATP molecules that stores energy for cell to use
Golgi Body
Stack of flattened membrane-bound sacs that are not linked to each other
involved in the processing and packaging of molecules into vesicles for movement out of the cell by exocytosis
Ribsomes
Made up of proteins and RNA, free or attached to the rough ER, site of protein synthesis
Rough ER
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum.
Flattened membrane sacs with ribosomes attached to surfaces
Intra-cellular transport, site of protein synthesis of ribosomes
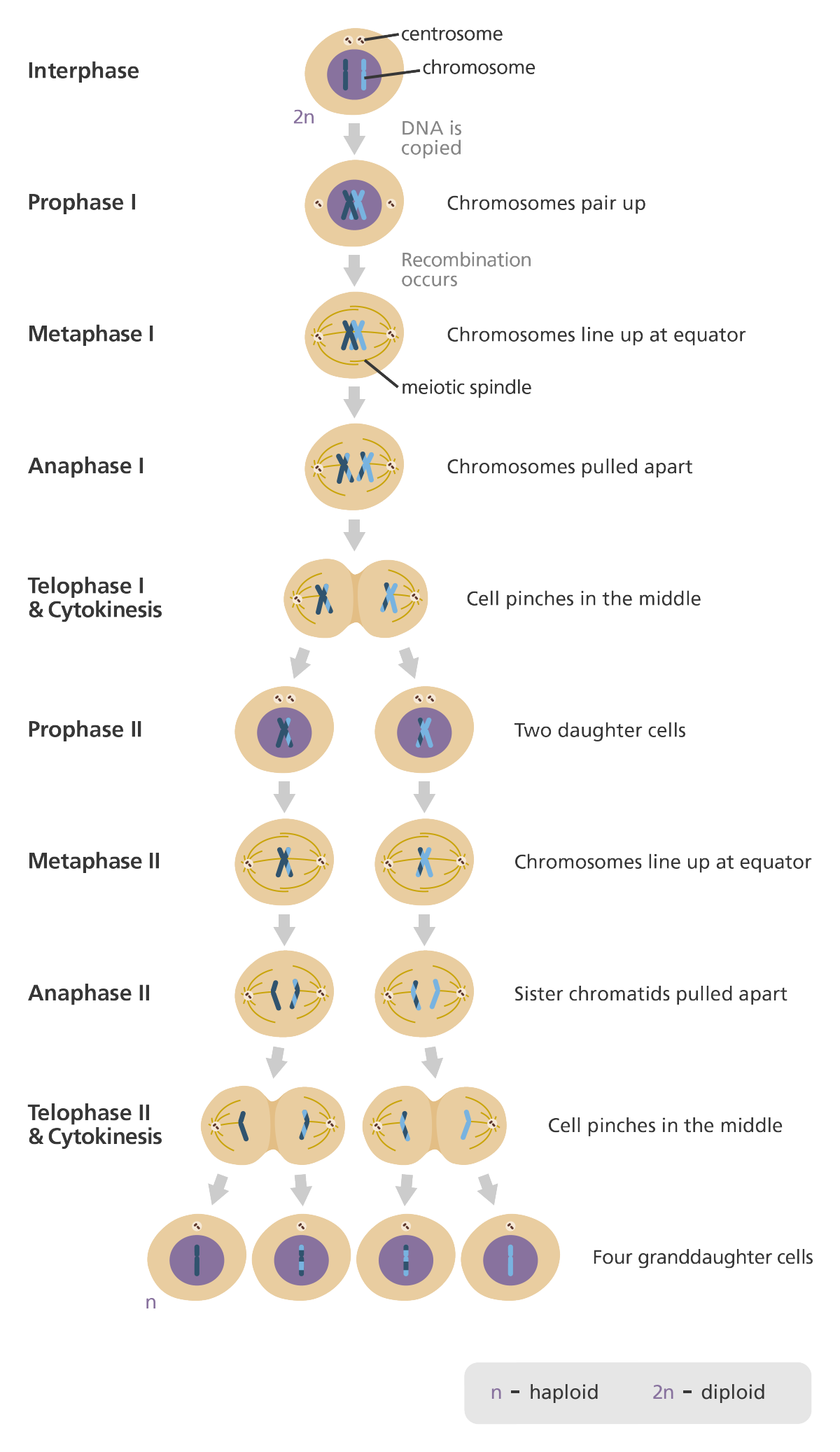
Meiosis (def)
Sexual cell reproduction that produced 4 daughter gametes
Chloroplast
Stacks of internal membrane structures called grana (contains chlorohpyll)
site of photosynthesis, usually in the cells of the leaves of a plant