Humanities stuff 2.0 (copy) (copy)
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
jienna chan thank u
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Horizon O (organic matter)
thin layer of decomposing organic matter, humus, and material
Horizon A (topsoil)
nutrient rich, darker soil nearest to the surface where most plant roots and soil organisms are found
Horizon B (subsoil)
plant litter isn’t present so minimal humus is found, nutrients from topsoil accumulate in this layer
Horizon C (parent material)
weathered rock not broken down enough to be soil
Horizon D
underlying layer of solid rock
climate influences
The distance from the equator, distance from the sea, altitude, location of mountain ranges, direction of prevailing winds
main 5 types of biomes
Tundra, grasslands, desert, forest, aquatic biomes
Atmosphere
Gases surrounding the Earth
Lithosphere
Crust and upper mantle
Hydrosphere
the sum of earth’s water in the ocean, ground, on the surface, and vapours in the air
Biosphere
Regions of the earth where organisms live
Flora
the plants characteristic of a region, period or special environment
Fauna
all of the animal life present in a particular region or time
deserts
arid or semi arid regions of the world with little amounts of rainfall
grasslands
regions inhabited by grazing animals and little to no trees
mountains effect on biomes
pose as barriers to moisture laden prevailing winds, affecting the amount of precipitation that reaches in land areas
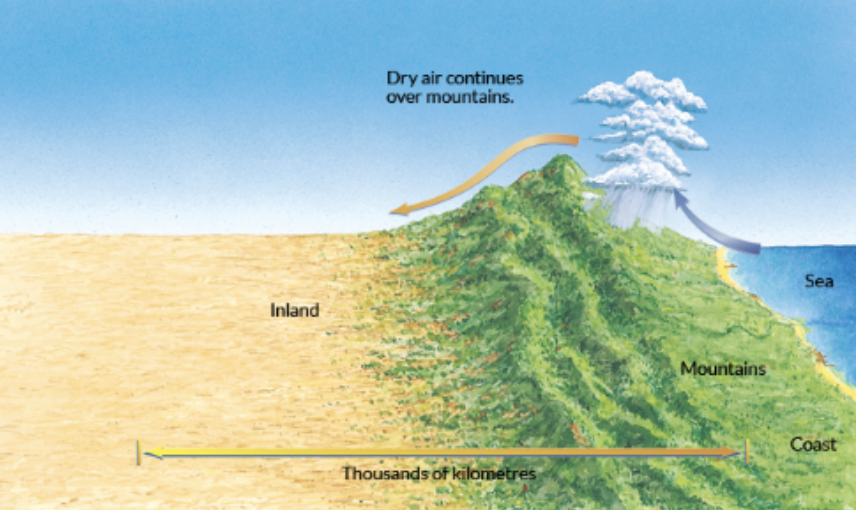
mountains
high elevations that influence climate and ecosystems
latitudes influence on biomes
Sun’s rays are more direct at equator while at the poles it’s more spread out
fire stick farming
indigenous land management strategy using small, controlled fires to clear out land to facilitate hunting or agriculture and develop the growth of plant species.
Biome
a large ecological area with distinct flora and fauna adapted to its environment
climate
The long-term pattern of weather in a particular area
overfishing impacts on biosphere
reduce fish populations and alter ocean life
clearing forests impact on biosphere
destroys animal habitats and release carbon dioxide
overgrazing animals impact on biosphere
vegetation won’t have time to grow back and animals won’t have food
climate of deserts
hot, arid regions with little rainfall
flora of deserts
cactus, tumbleweed, succulents, acacia, weathered trees
fauna of deserts
camels, donkeys, meerkats, scorpions, hawks
climate of grassland
wet and dry seasons, moderate temp and rainfall
flora of grasslands
shrubs, sunflowers, clovers, acacia, buffalo grass
fauna of grasslands
sheep, cows, elephants, zebras, lions
how a change in a sphere affects another
air pollution in atmosphere can harm plants and animals
land degradation
process of land decreasing in biological productivity, unable to have the ability to support organisms
weather
short term atmospheric conditions