Cycles Quiz - Honors Bio
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Carbon
The element found in all living things

Carbon dioxide
A form of carbon that exists in the atmosphere that is MOST abundant in our atmosphere.
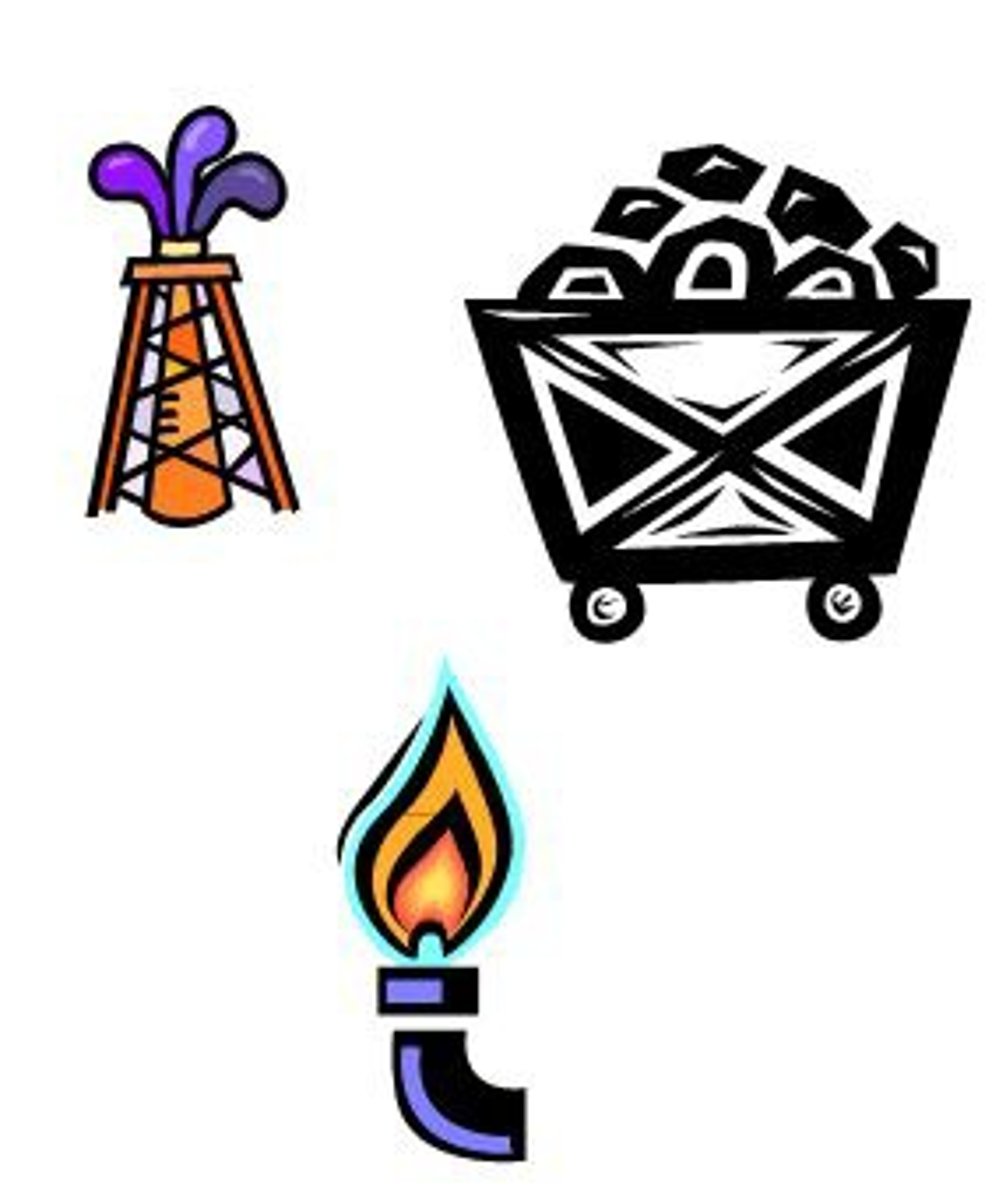
Fossil fuel
Coal, oil, natural gas, and other fuels that are made from the decay of plants and animals.

Carbon cycle
The movement of carbon around all the Earth's systems.
Decomposition
The process of breaking down organic material, such as dead plant or animal tissue
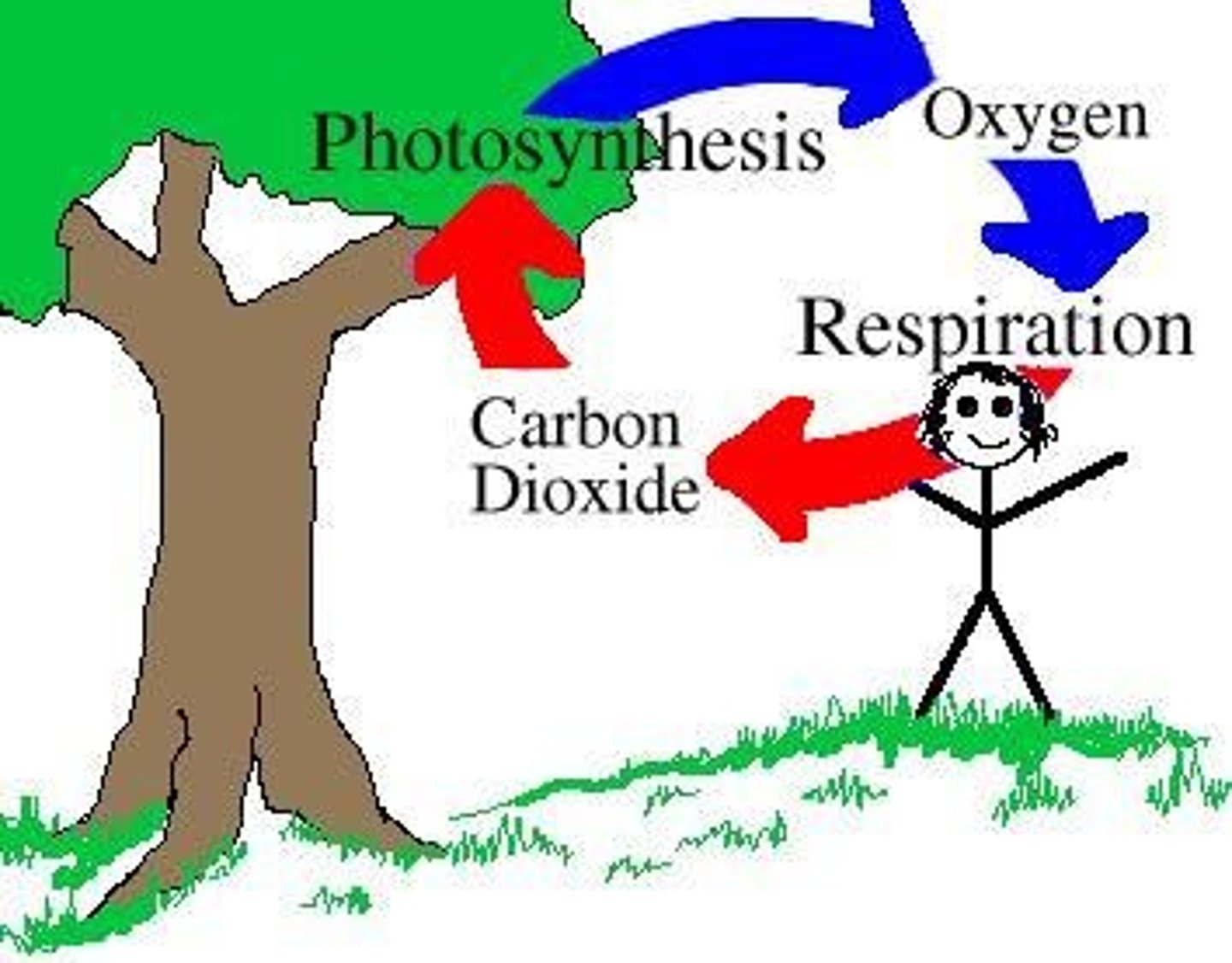
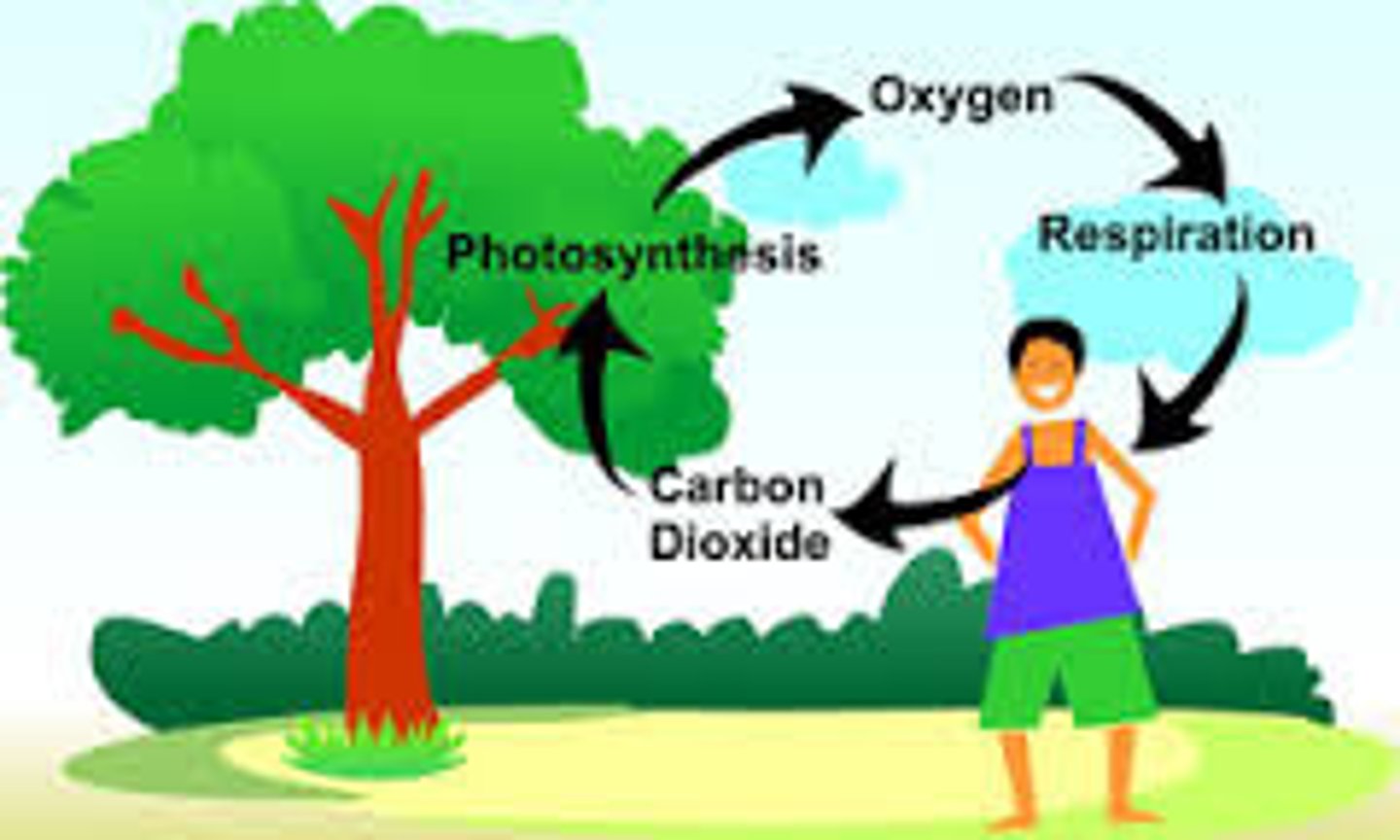
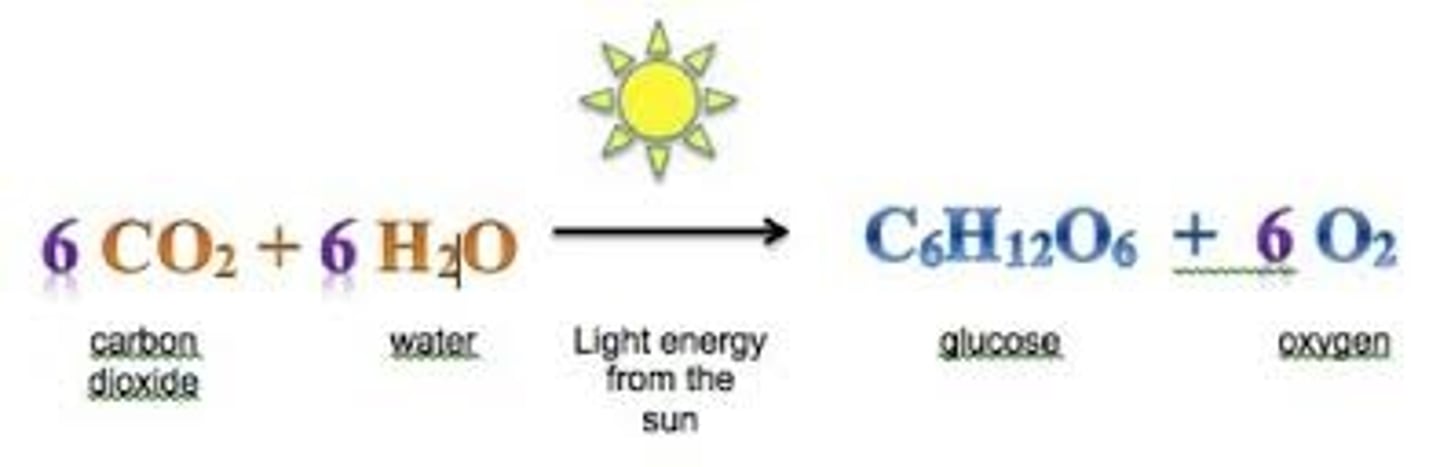
Photosynthesis
Plants use the sun's energy to convert water and carbon dioxide into sugars
Cellular respiration
metabolic process used to acquire energy in living systems; releases CO2
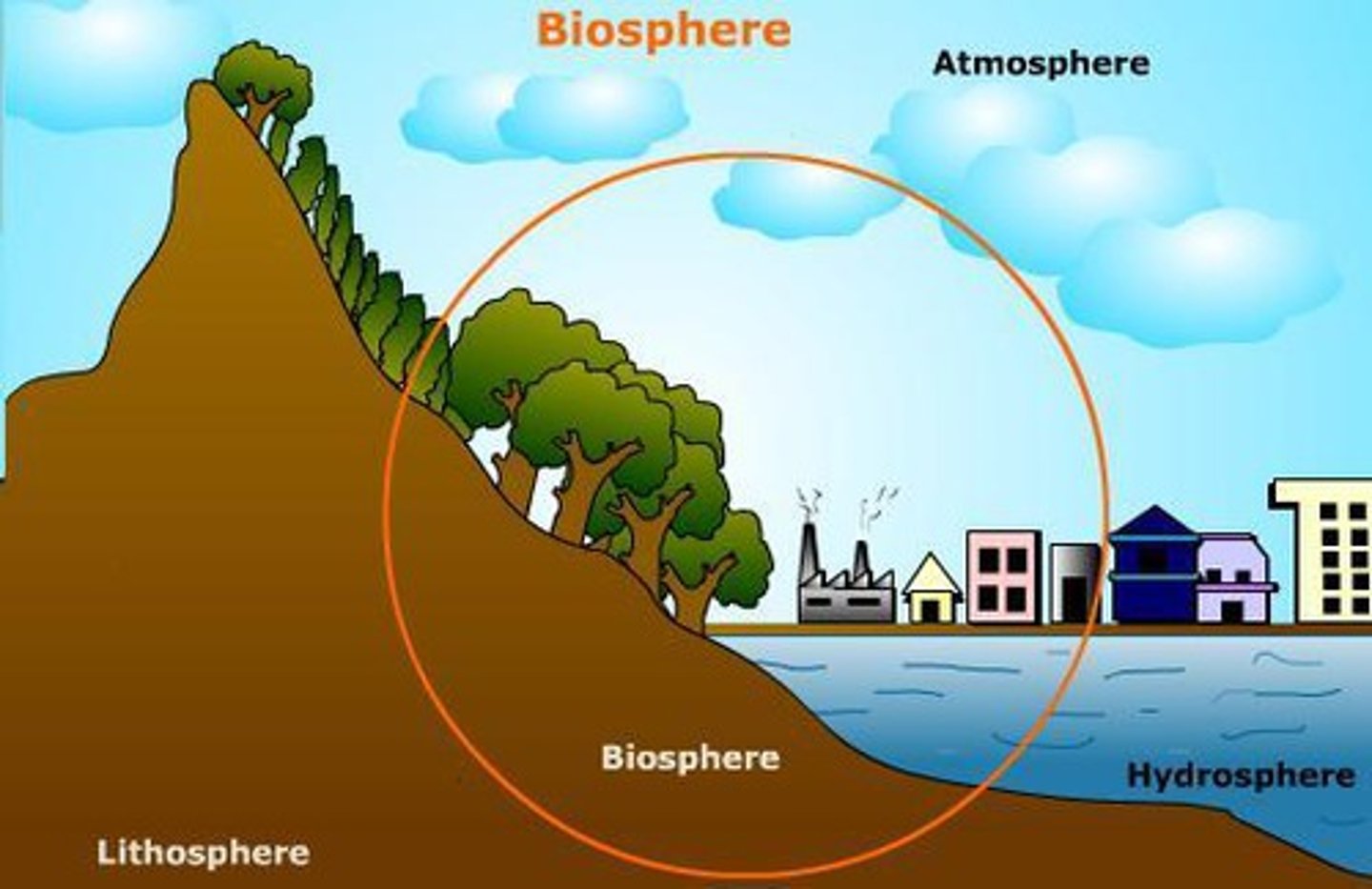
Atmosphere
the envelope of gases surrounding the earth or another planet.
Biosphere
Consists of all life on Earth and all parts of the Earth in which life exists, including land, water, and the atmosphere.
Carbon is taken out of the atmosphere by...
photosynthesis
Combustion
The process of burning, releases carbon compounds (CO2). The creation of fire
Carbon is added to the atmosphere by...
Breathing, burning fossil fuels, forest fires, volcanoes
Assimilation
The absorption and incorporation of carbon compounds into the tissues of living organisms
Deposition
Deposition is the laying down of sediment carried by wind, flowing water, the sea or ice
Sedimentation
when organisms die, their carbon is added to ocean sediments, which over time produce limestone
water cycle
the continuous process by which water moves from Earth's surface to the atmosphere and back
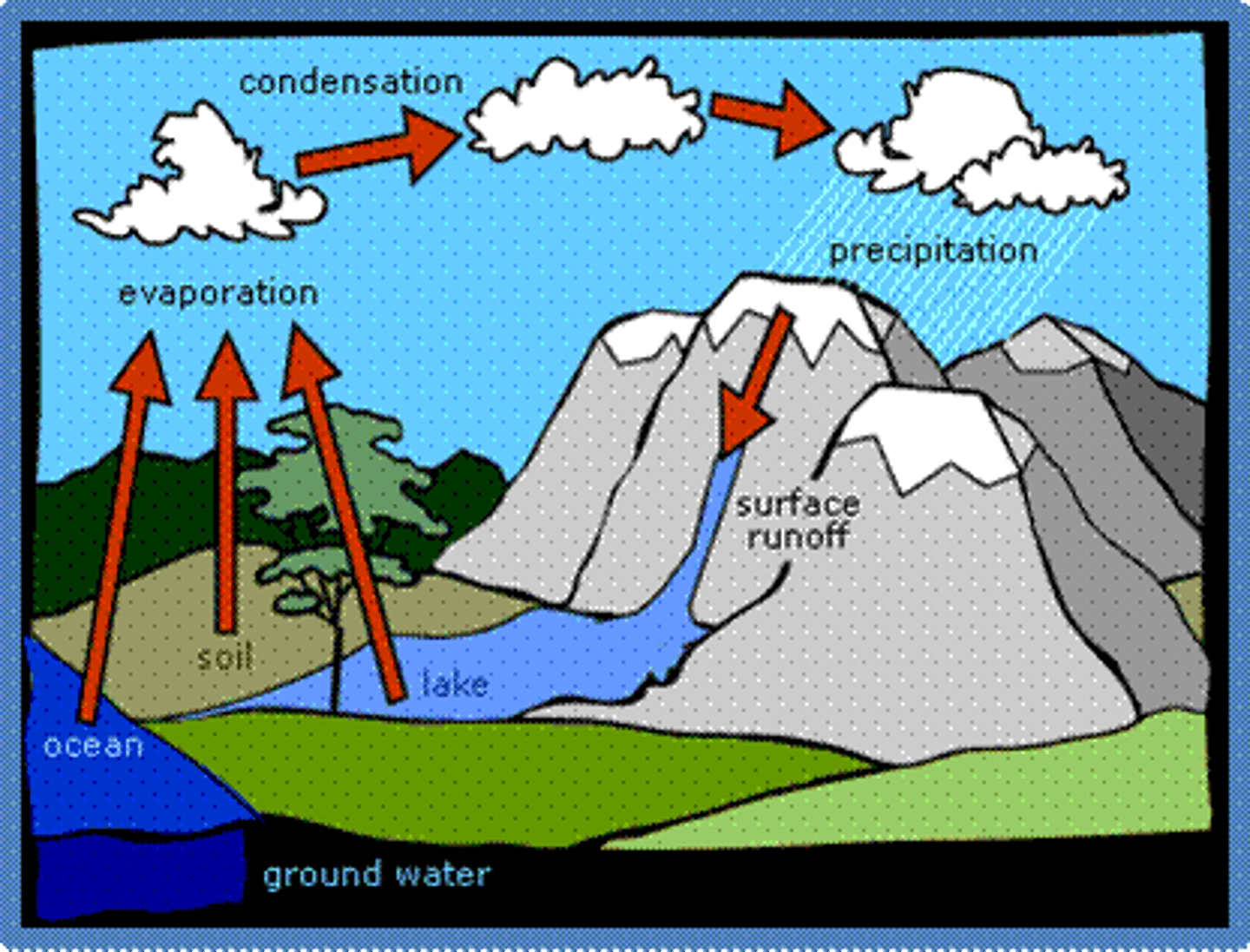
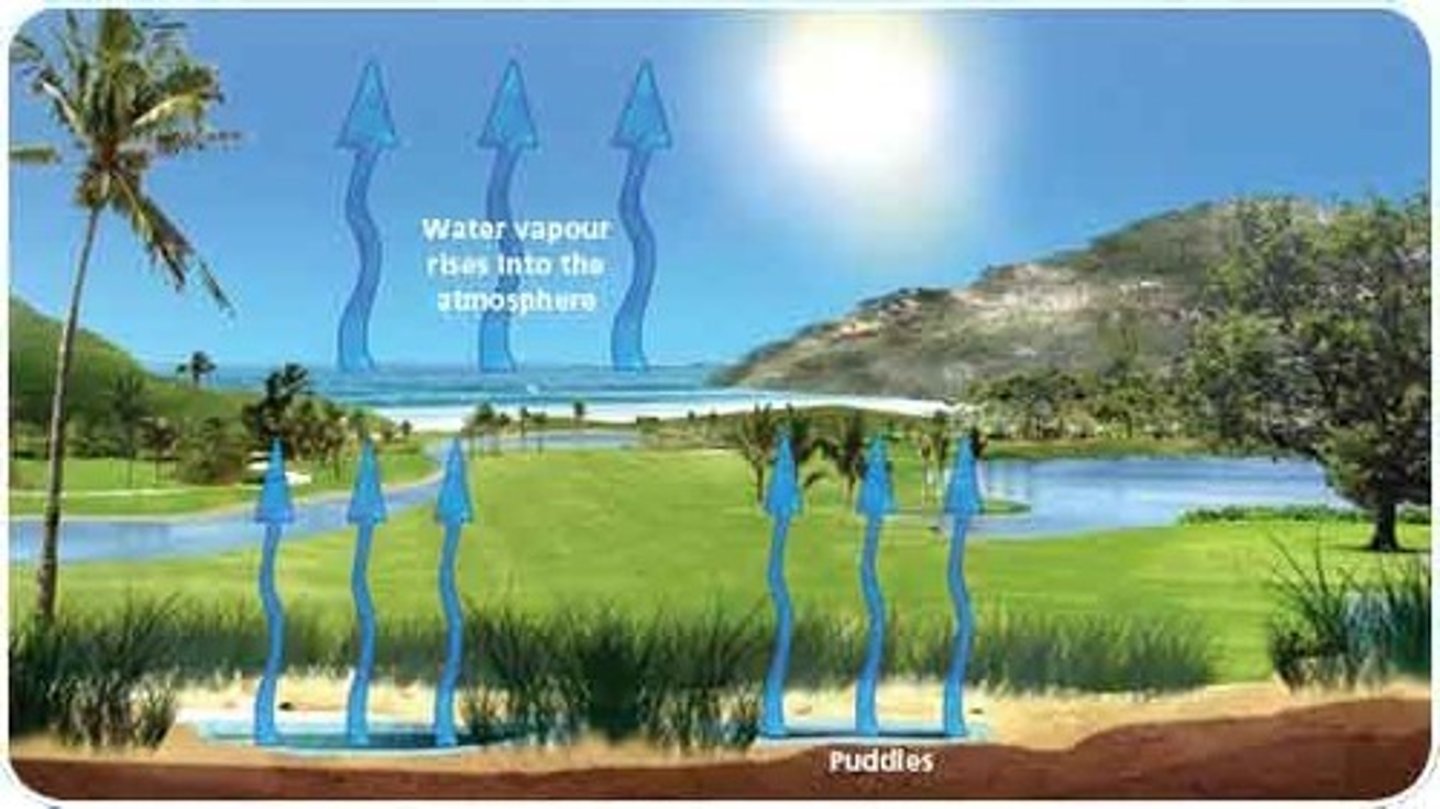
evaporation
a process at which molecules at the surface of a liquid absorb enough energy to change to the gaseous state

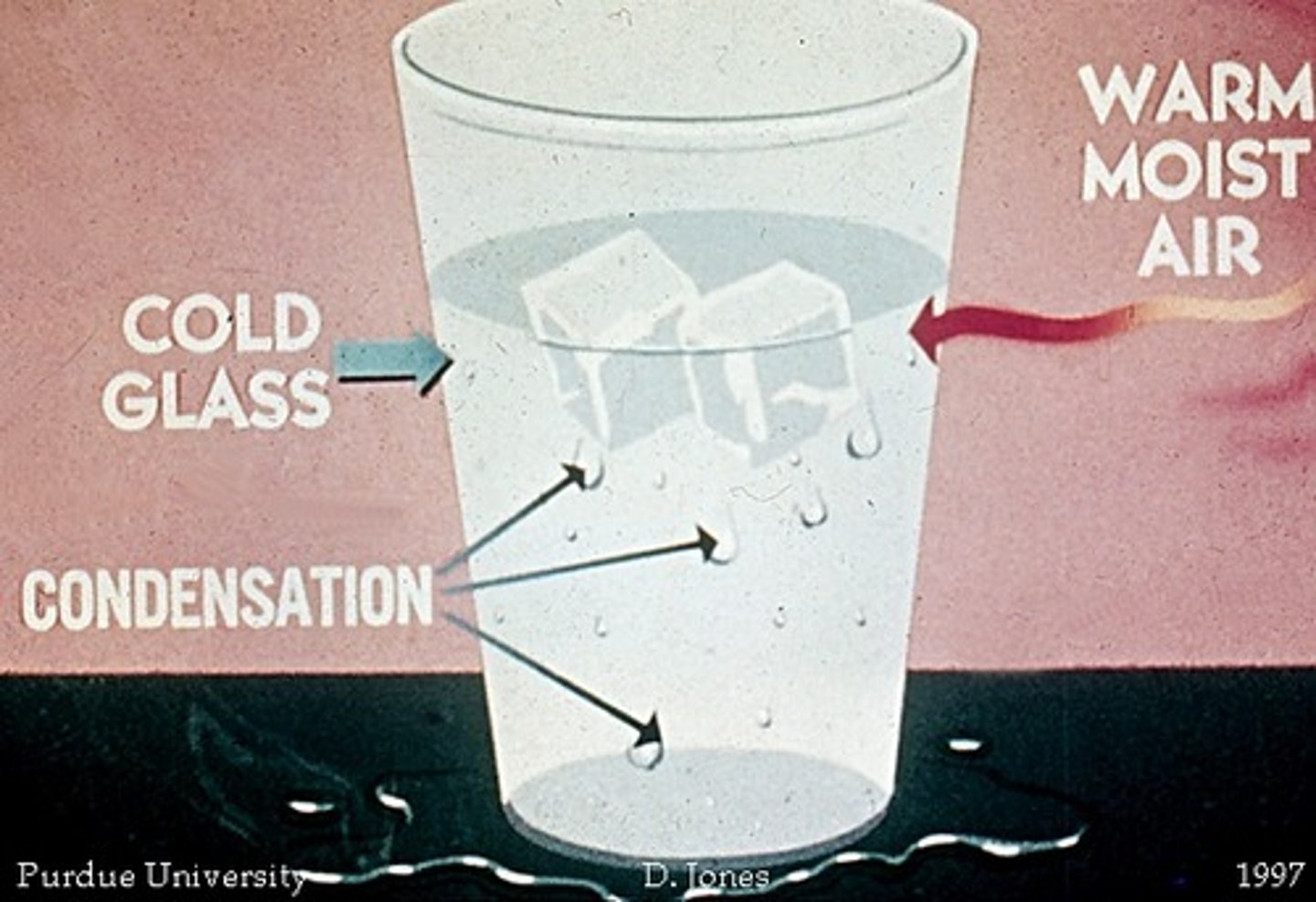
condensation
water vapor cools and becomes a liquid
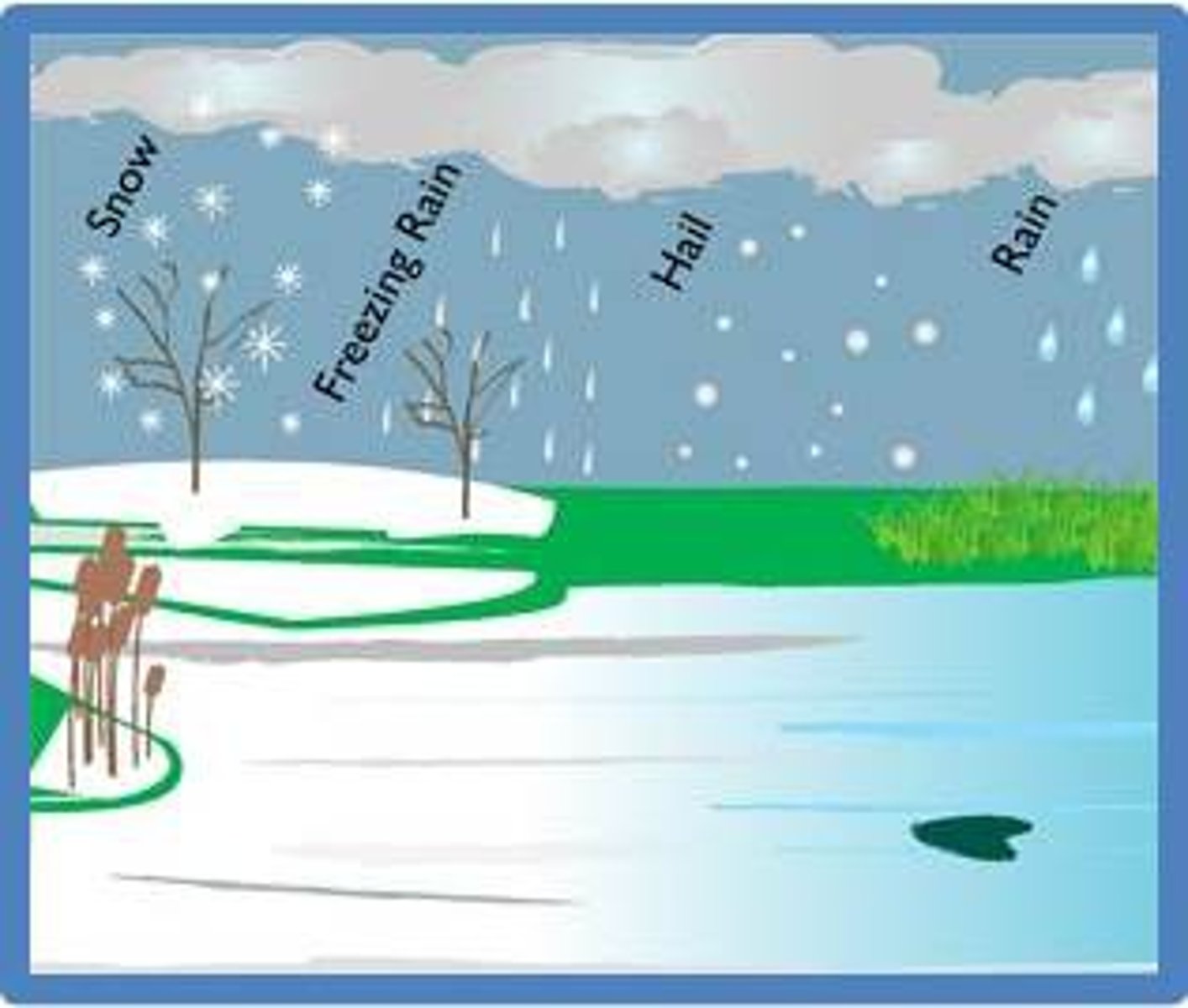
precipitation
when water in the form of ice, rain, sleet, hail, or snow, falls to Earth
transpiration
the water that plants give off as part of their respiratory process (they "breathe" in carbon dioxide and "breathe" out oxygen - in this process, they also make water)
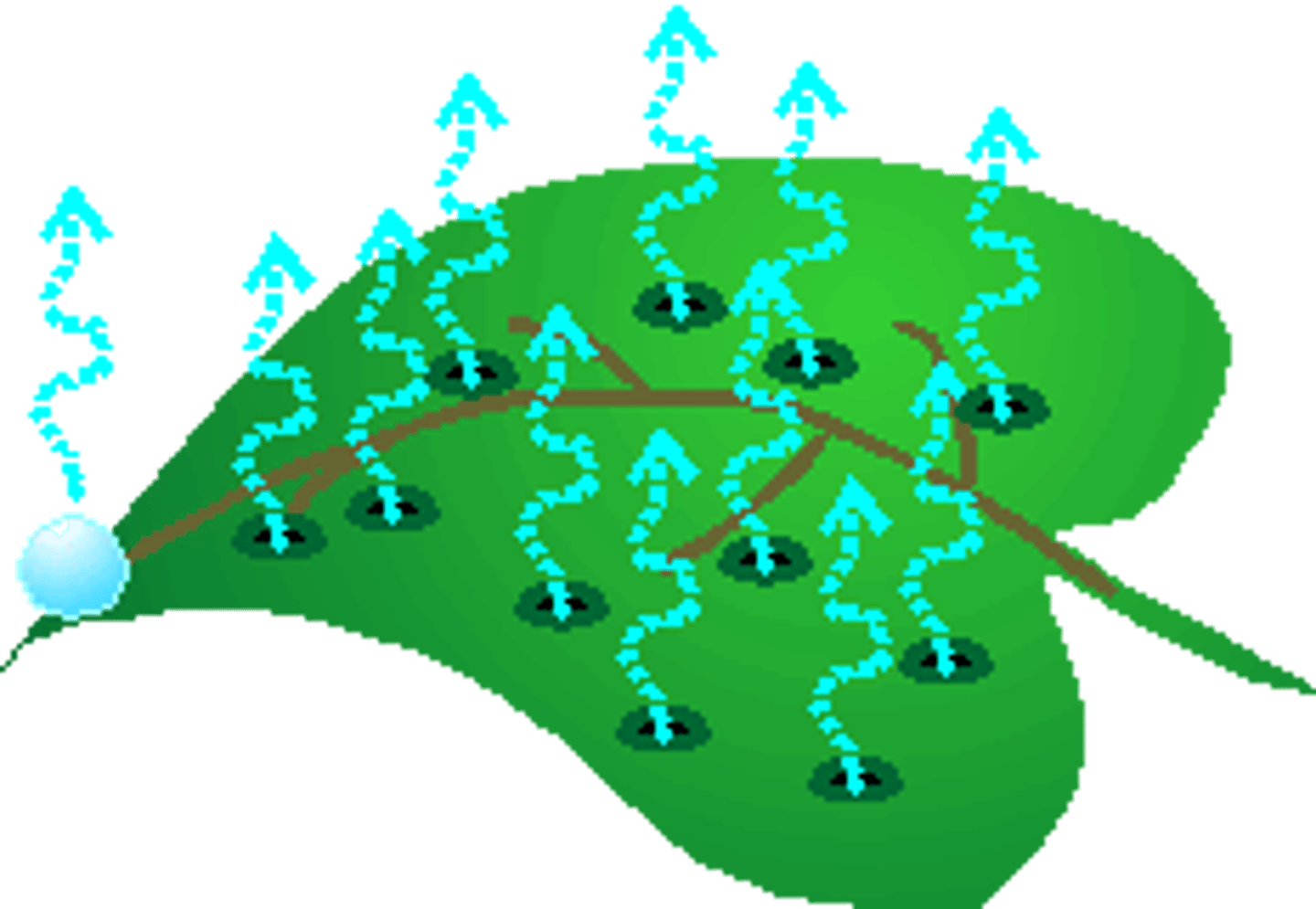
surface runoff
when precipitation hits the ground, it is either absorbed, or it flows over the surface of the earth

water vapor
water in its gas form

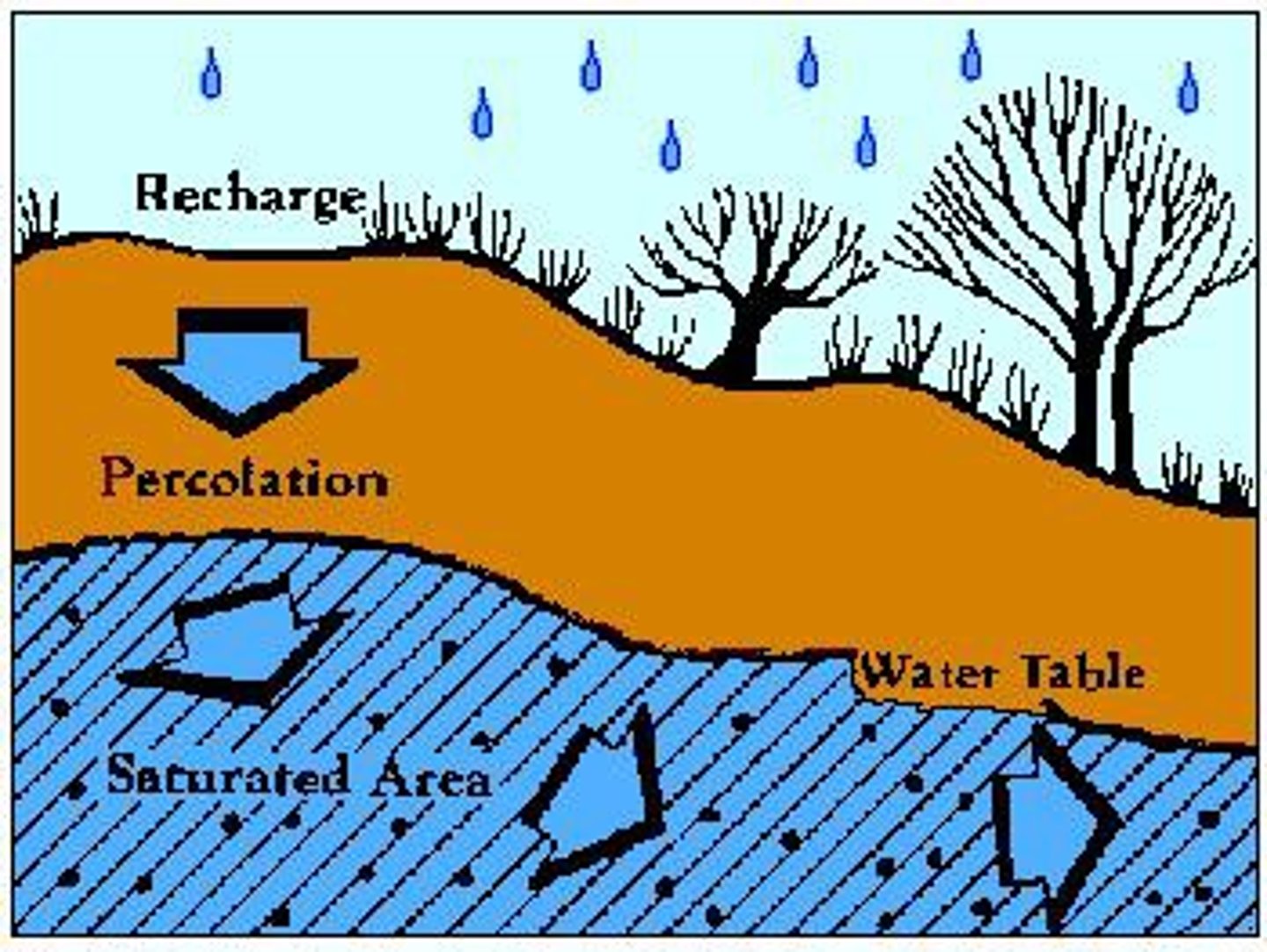
groundwater
water that is in the ground
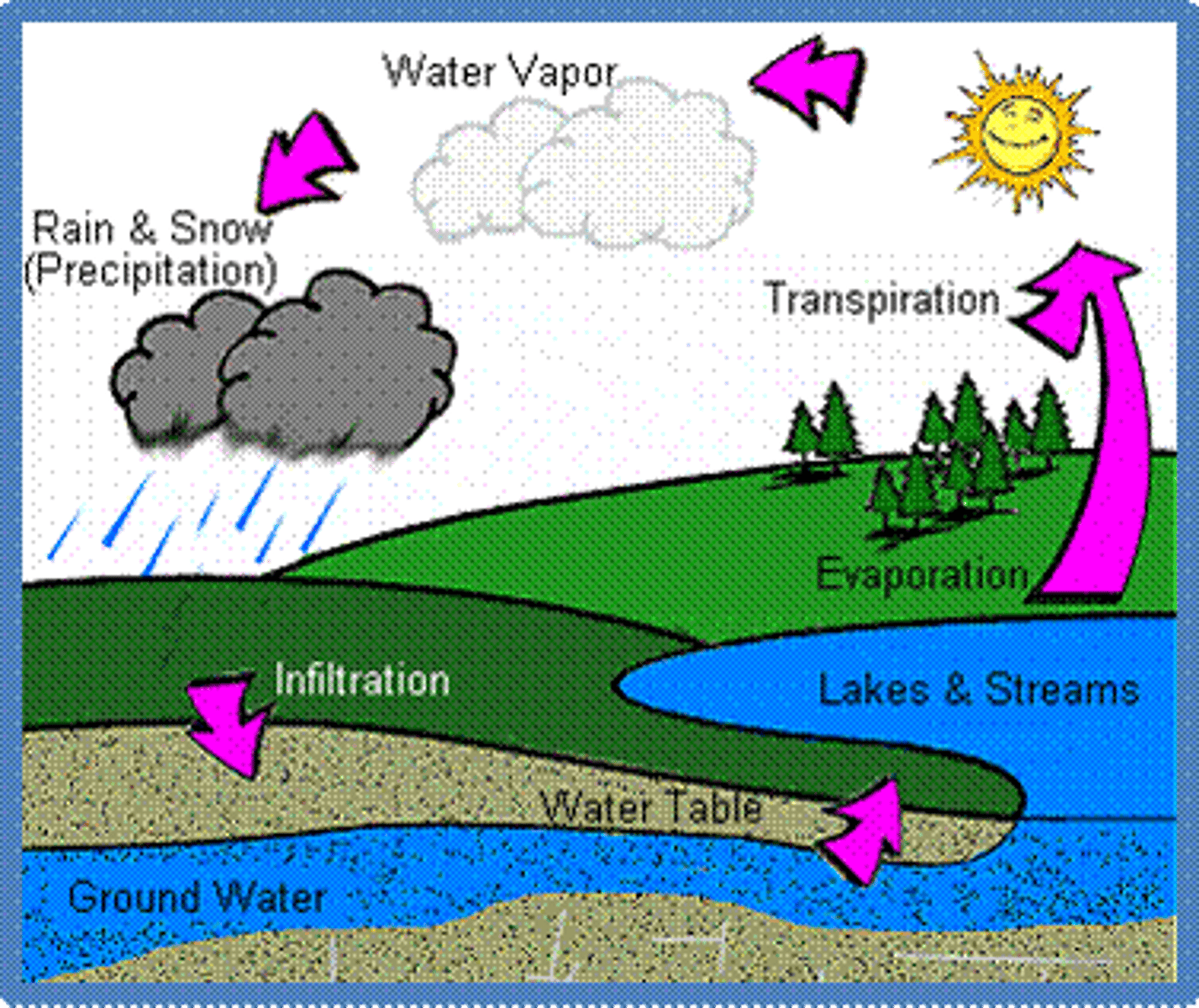
What 2 factors drive the water cycle?
Gravity and energy from the sun
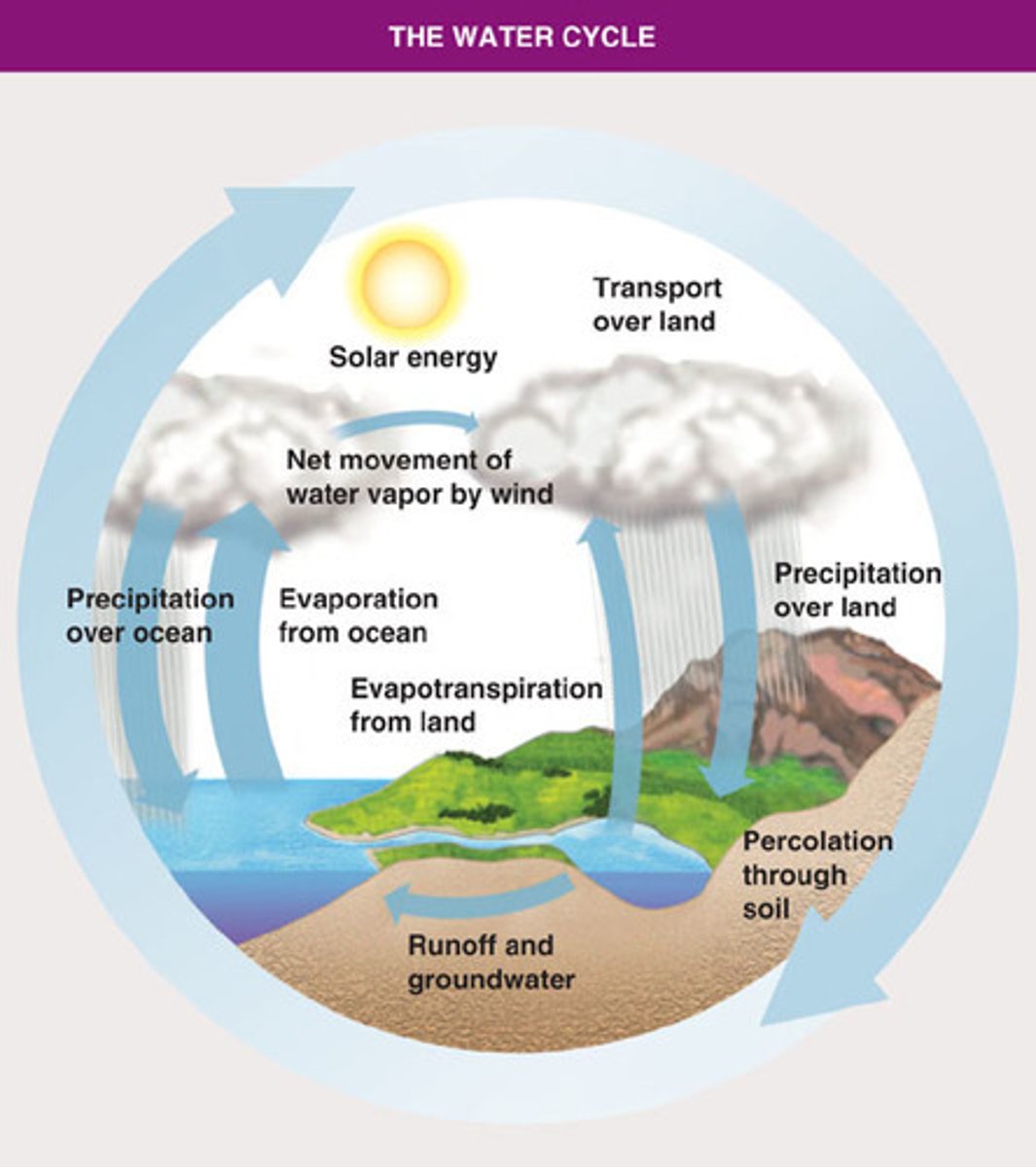
How does water evaporate?
Water heats up from the sun causing the water to change from a liquid to a gas and rises into the atmosphere.

How does condensation happen?
Condensation is formed when water vapor in the atmosphere cools and turns from a gas to a liquid.

Infiltration
the process by which water on the ground surface enters the soil
Nitrogen Cycle
The circulation and reutilization of nitrogen in both inorganic and organic phases
Where is nitrogen found?
In proteins
RNA and DNA
Nitrogen is so essential to life because it is a key component of amino acids and nucleic acids. Even ATP, the basic energy currency of living things, contains nitrogen.
5 main processes
Nitrogen Fixation, Ammonification, Assimilation, Nitrification, and Denitrification
How much of earth's atmosphere is nitrogen
78% of earths atmosphere is nitrogen which is a majority
Can we use atmospheric nitrogen (N2)?
Plants and animals cannot use it!
legumes
Certain kids of plants that have small bumps on their roots called nodules. These nodules have nitrogen-fixing bacteria.
Why is nitrogen important?
the availability can affect the rate of key ecosystem processes(primary production and decomposition)
Nitrogen Fixation
Bacteria change Nitrogen into a useable form
Ammonification
Decomposers convert organic waste into ammonia (NH3).
Nitrification
Ammonium converted into nitrate (NO3-) and nitrite (NO2-) through work of nitrifying bacteria.
Denitrification
Process where Dinitrogen (N2) is formed and heads back into the atmosphere
Assimilation
absorbing Nitrogen into one's body (normally by consumption for animals)