12- Liver Metabolism and Urea Cycle
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Direct Bilirubin
Normal Amount: <0.2 mg/dL
Dissolves in water
Conjugated
Indirect Bilirubin
Normal Amount: <1.0 mg/dL
Insoluble in water
Unconjugated
Hyperbilirubinemia
Above 1.2 mg/dL
Jaundice
Bilirubin >2.0 mg/dL
Icterus
Bilirubin >3.0 mg/dL
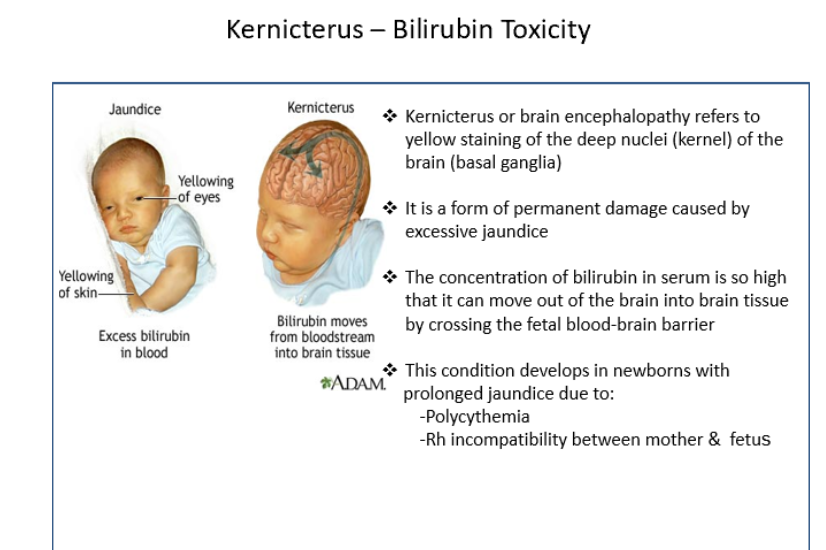
Kernicterus
Unconjugated Bilirubin 12-20 mg/dL
Enters CNS, mental retardation, motor issues, brain damage, cerebral palsy
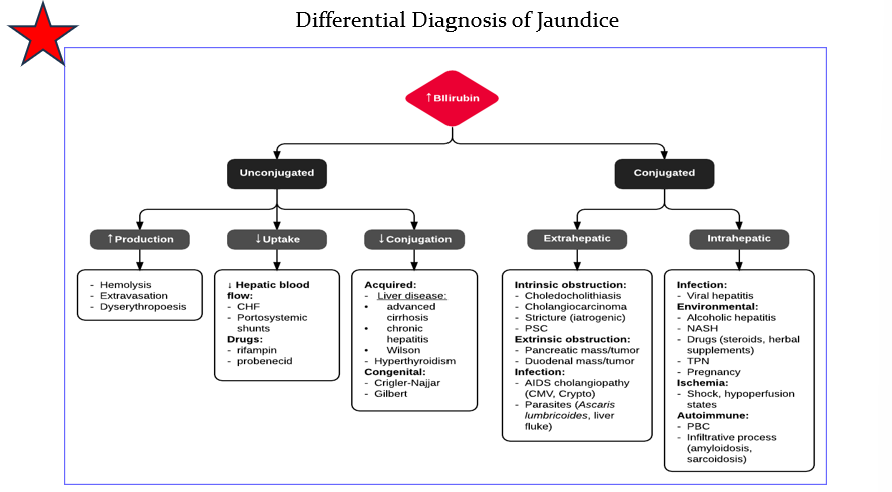
DDX Jaundice Conjugated
Extrahepatic
Intrahepatic
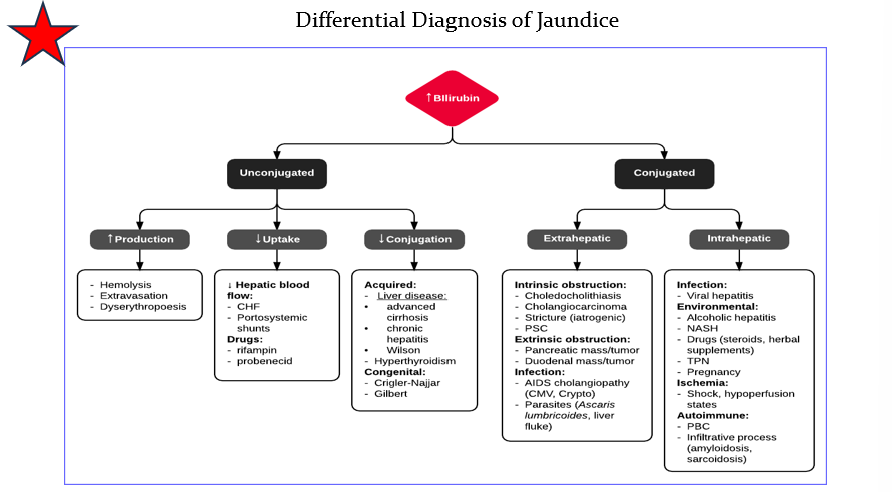
DDX Jaundice Unconjugated
Increased production
Decreased uptake
Decreased conjugation
Neonatal Jaundice
Pre-Hepatic (hemolysis & decreased conjugation)
Decreased UDP (decreased conjugation)
Precipitates in basal ganglia
Causes of Neonatal Jaundice
ABO Incompatibility
Breast Milk Jaundice
ABO Incompatibility
This form of jaundice occurs when there is incompatibility between blood types of the mother and fetus
This leads to increased bilirubin levels from the breakdown of the fetus red cells (hemolysis)
Breast Milk Jaundice
This form of jaundice occurs in breastfed newborns and usually appears at the end of the first week of life.
Certain chemicals in breast milk are thought to be responsible for inhibition of UDP Glucuronyl transferase.
It is usually a harmless condition that resolves spontaneously
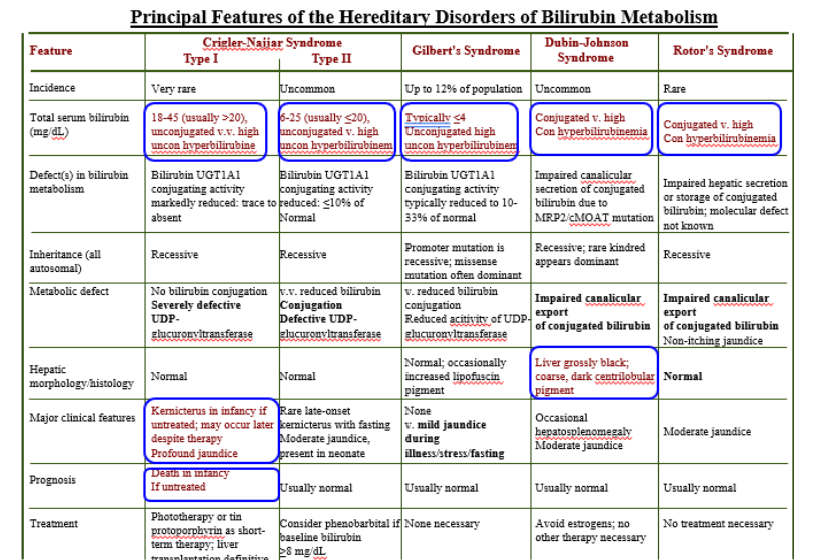
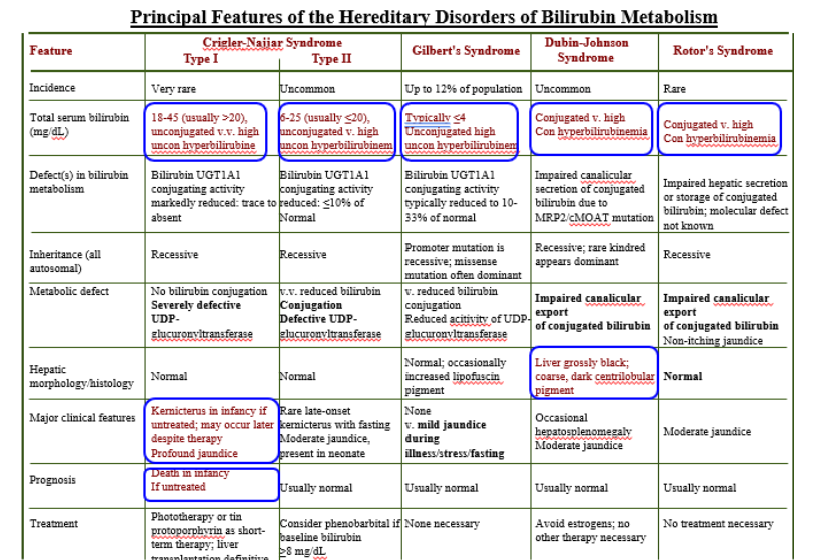
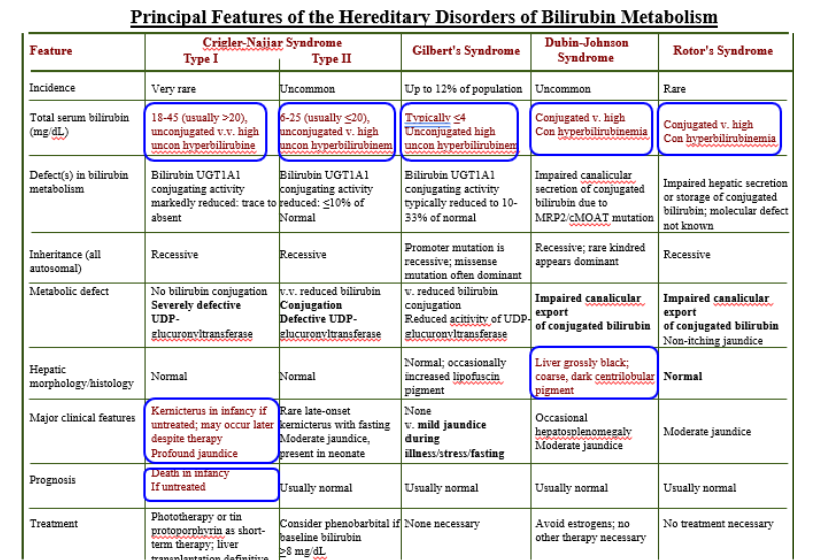
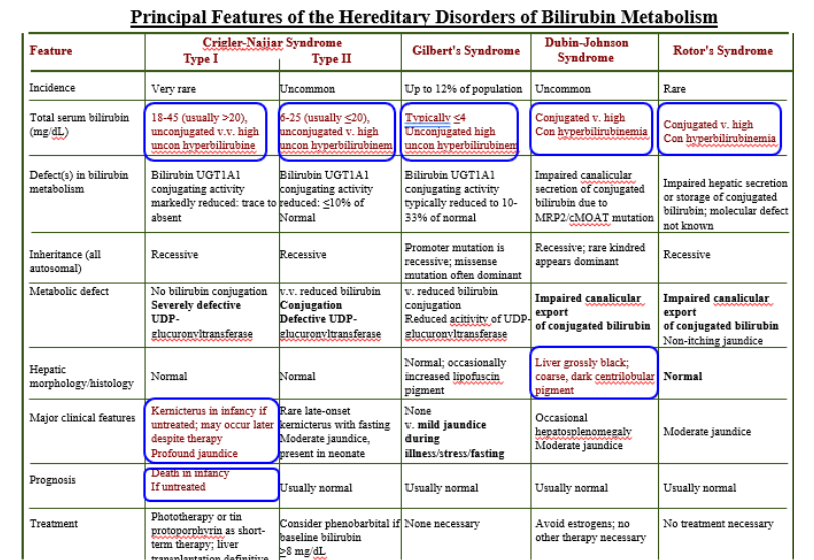
Inherited Disorders of Bilirubin Metabolism
Gilbert’s Syndrome
Crigler-Najjar (Type I)
Crigler-Najjar (Type II)
Dubin-Johnson
Rotor’s Syndrome
Crigler-Najjar Syndrome Type I
Total Serum Bilirubin: 18-45 (>20)
Unconjugated is high
Severely defective UDPGT
Kernicterus in infancy if untreated
Death in infancy
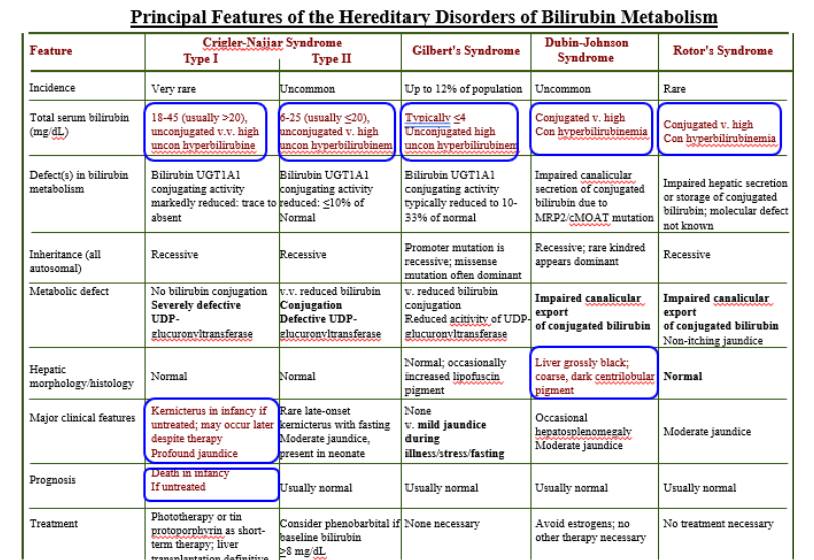
Crigler-Najjar Syndrome Type II
Total Serum Bilirubin: 6-25 (<20)
Unconjugated high
Conjugation Defective UDPGT
Gilbert’s Syndrome
Total Serum Bilirubin: <4
Unconjugated high
Mild jaundice during illness/stress/fasting
Dubin-Johnson Syndrome
Conjugated high
Impaired canalicular export of conjugated bili.
Liver grossly black!
Rotor’s Syndrome
Conjugated high
Impaired canalicular export of conjugated bili.
Normal Liver!
Hyperammonemia
Ammonia is highly toxic to the liver
Normal number is <50µmol /L, and an increase to only 100 µmol /L can lead to consciousness issues
200 µmol /L is associated with coma and convulsions
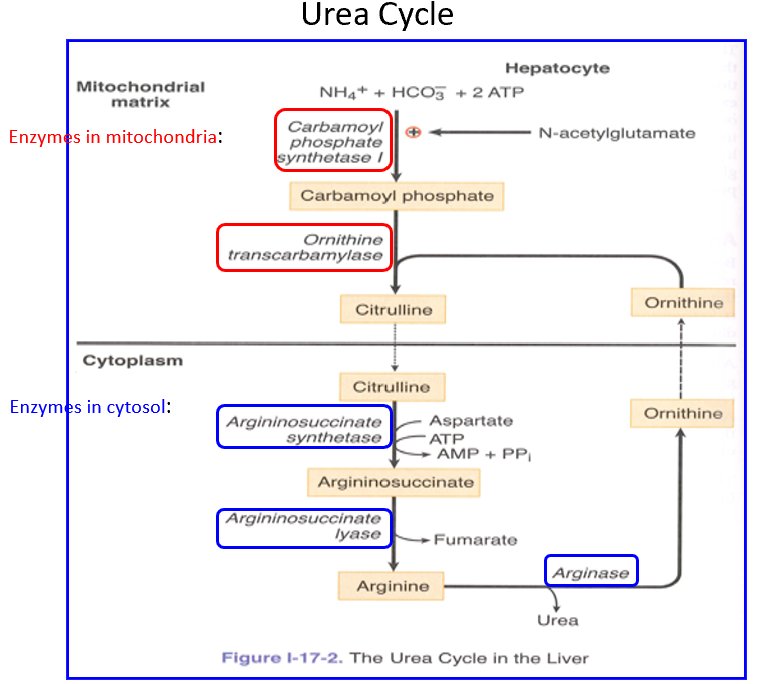
Mitochondria
Cytosol
The first 2 reactions of the urea cycle happen in THIS, the rest in THIS.
Kidneys
Urea from liver is transported to the blood and then to THIS where it is excreted into the urine.