Hematology Lecture Disorders of Iron Kinetics & Heme Metabolism
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Impaired Red Cell Production
Anemias associated with iron & heme
Iron Restricted anemia
Iron is the limited factor; Iron Deficiency Anemia (IDA); Anemia of Inflammation (AI)
Porphyria
Build up of porphyrins
SIderoblastic anemias
Failure to incorporate iron in protoporphyrin causing excess iron accumulation in developing RBCs
Hemochromatosis
Excess accumulations in iron
Iron-loading anemias
Impaired iron kinetics
Iron Deficiency Anemia Etiology
Deficient total body iron to uphold normal physiologic function
Functional iron deficiency (IDA)
Iron stores are adequate, but iron is not available to support normal erythropoiesis
Impaired absorption (IDA)
Inability to absorb iron through enterocyte into the blood causing a deficiency or iron in the body;
Chronic loss of hemoglobin (IDA)
Blood loss resulting in small amounts of heme iron from the body over a prolonged period
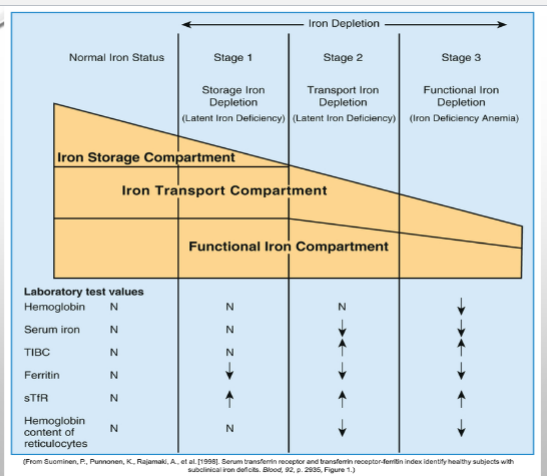
Stage 1 IDA
Progressive loss of storage iron but RBC production are normal; serum ferritin levels decrease; testing is not performed yet as patients appear healthy & this stage is common
Stage 2 IDA
Exhaustion of iron storage pool, but RBC production is normal as it is using the transport compartment & iron being recycled from cells (latent iron deficiency)
Stage 3 IDA
Iron stores, mobile iron, & serum iron are depleted preventing normal RBC development (frank anemia); serum ferritin levels are low; Hepcidin decreased; patient exhibits fatigue, weakness, & shortness of breath; pica
Iron Deficiency Anemia
Menstruating Females - IDA RISK
Females lose red blood cells during period; compounded by increased iron needs associated with growth
Pregnant/nursing females - IDA RISK
Leads to loss of nearly 1200mg of iron
Growing children - IDA Risk
Infants need iron supplemented formula by 6 months. Before that, breast milk is needed
CBC IDA
Anisocytosis, microcytosis, hypochromia in proportion to anemia severity
Decreased
Serum iron during IDA
Increased
TIBC during IDA
Decreased
Transferrin saturation during IDA
Decreased
Serum ferritin during IDA
Decreased
Hemoglobin content of retics during IDA
IDA Treatment
First therapy is to treat any underlying contributing cause; oral supplements of ferrous sulfate; intravenous iron
Anemia of Inflammation (AI)
Associated with systematic diseases - Chronic inflammatory conditions (rheumatoid arthritis), chronic infections (tuberculosis), & malignancies
Impaired ferrokinetics - Etiology of AI
Increased levels of hepcidin decreased iron absorption in the intestines & sequester iron in macrophages & hepatocytes causing bone marrow macrophages to show abundant stainable iron but developing erythroblasts show inadequate iron
Porphyrias
Disease that interfere with the production of protoporphyrins can also produce anemia; both hereditary and acquired; an enzyme in heme synthesis is missing causing excess porphyrins which are leaked from the cell as they age or die
Congenital Erythropoietic Porphryia
Autosomal recessive inheritance causing an uroporphyrinogen III synthase deficiency; patients have a decrease in heme production
Erythropoietic Protoporphyria
Autosomal recessive inheritance causing a ferrochelatase deficiency; increases in protoporphyrin in RBCs & feces; findings include photosensitivity, liver involvement, gallstones, and symptoms exacerbated by alcohol
X-Linked Erythropoietic Protoporphyria
Dominant inheritance causes ALA synthase 2 gain of function; increases in protoporphyrin in RBCs & possible feces; findings include photosensitivity, microcytic, hypochromic anemia with retic response is possible
Sideroblastic Anemias
Characterized by the presence in the bone marrow of ring sideroblasts; erythroblasts when stained with prussian blue show a ring of blue iron deposits around the nucleus
Acquired sideroblastic anemia
X-linked (paternal) - X-linked sideroblastic anemia
Mitochondrial (maternal) - pearson marrow-pancreas syndrome
Autosomal - erythropoietic protoporphyria