Gene Expression
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Amino acid
A protein "building block." There are 20. Amino acids float in cytoplasm. Specific tRNA molecules collect specific amino acids, then bring to ribosome. Peptide bonds form between amino acids and a polypeptide chain forms, creating proteins.
Complementary base pairs
A-T and G-C in DNA, A-U and C-G in RNA
Enzyme
A specific type of protein that controls all of the chemical reactions in the body. Can be affected by temperature, pH, poisons etc…
Gene
A section of DNA along a chromosome which codes for a particular protein.
Peptide bond
A bond that forms between two amino acid molecules during protein synthesis, creating a polypeptide chain.
Nucleotide
A 'building block' of DNA or RNA. Consists of a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.
Polypeptide
A chain of amino acids. One or more forms a functional protein
Protein
An organic molecule made up of amino acids linked together (polypeptide) in a particular order, determined by the DNA sequence.
RNA
Ribonucleic acid, a single stranded nucleic acid that is involved in the synthesis of proteins
Codon
Three bases along an mRNA molecule.
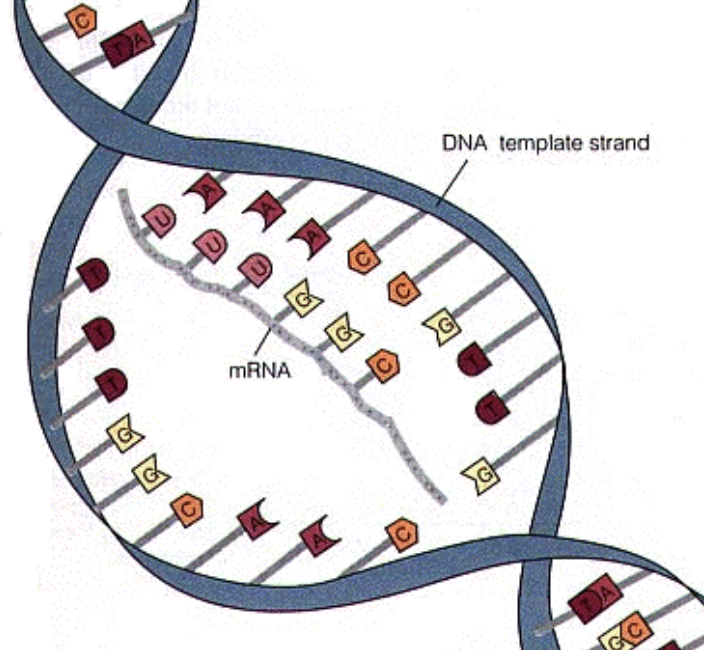
mRNA
Messenger RNA
- RNA polymerase attaches complementary RNA nucleotides to the template strand, forming mRNA molecule. (nucleus)
- Carries a complimentary copy of the DNA to the ribosome for protein synthesis (cytoplasm)
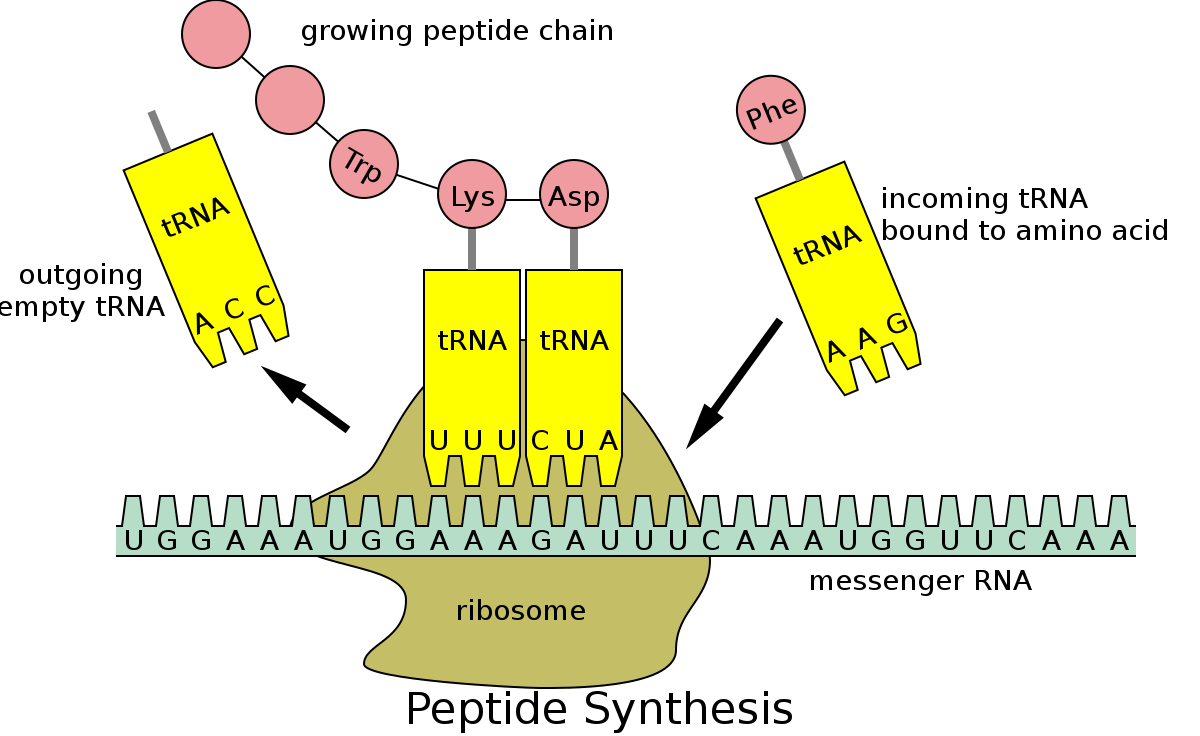
Protein synthesis
The process where the genetic code is used to construct a protein.
Transcription and Translation.
Ribosome
The cell's 'protein factory,' the site for protein synthesis
- Consisting of 2 units of rRNA
rRNA
Ribosomal RNA, this forms part of the structure of a ribosome
Triplet
Three bases along a DNA molecule
Transcription
The process where the template strand of DNA is used to form a strand of mRNA during protein synthesis.
Anticodon
Three bases on a tRNA molecule
Deletion mutation
A mutation that involves the loss of one or more bases, causing a frame shift
Frame shift
Occurs when one or more bases are inserted or deleted in the DNA, changing how the triplets are read
Gametic mutation
A mutation occurring in gametes (sex cells) that can be by offspring if the sperm or egg with the mutation is the one that is fertilized/fertilizing
Insertion mutation
A mutation in which there is an addition of an extra base, or bases in the DNA strand which causes a frame shift to occur
Metabolic block
The failure of a reaction on a metabolic pathway due to a non-functional enzyme
Mutagen
A physical or chemical agent that changes the DNA of an organism or increases the frequency of mutations
Mutation
A random and permanent change in the DNA of a cell
Redundant/degenerate code
Where an amino acid may be coded for by more than one mRNA codon
RNA polymerase
The enzyme that joins new nucleotides onto the template strand of DNA to make mRNA
Template strand
The strand of DNA that is copied (transcribed) when mRNA is produced
Base substitution mutation
A mutation where one base in DNA is substituted for another
Coding strand
The strand of the DNA molecule that stores the genetic code for making a protein
Metabolic pathway
A series of enzyme controlled chemical reactions occurring within a cell. In a metabolic pathway, a starting chemical (substrate), is converted by a series of different enzymes into a final product
Somatic mutation
A mutation that occurs in a body cell, these can not be inherited by the offspring and will only affect the individual with the mutation
Recessive condition
A genetic condition arising from a mutation that produces a recessive allele. Both parents must carry the allele for it to be expressed in the offspring
Phenotype
The physical expression of the genotype/what the trait looks like
Dominant condition
A genetic condition arising from a mutation that produces a dominant allele. Only one copy of the allele is needed for it to be expressed in the phenotype
Gene mutation
A change in the base sequence of a gene which results in a new allele. May involve base substitution, insertion, or deletion
Genotype
The genetic make up of an organism/the two alleles it has for a particular gene