EKG Part 1 of 2: Basics and Recording EKG
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
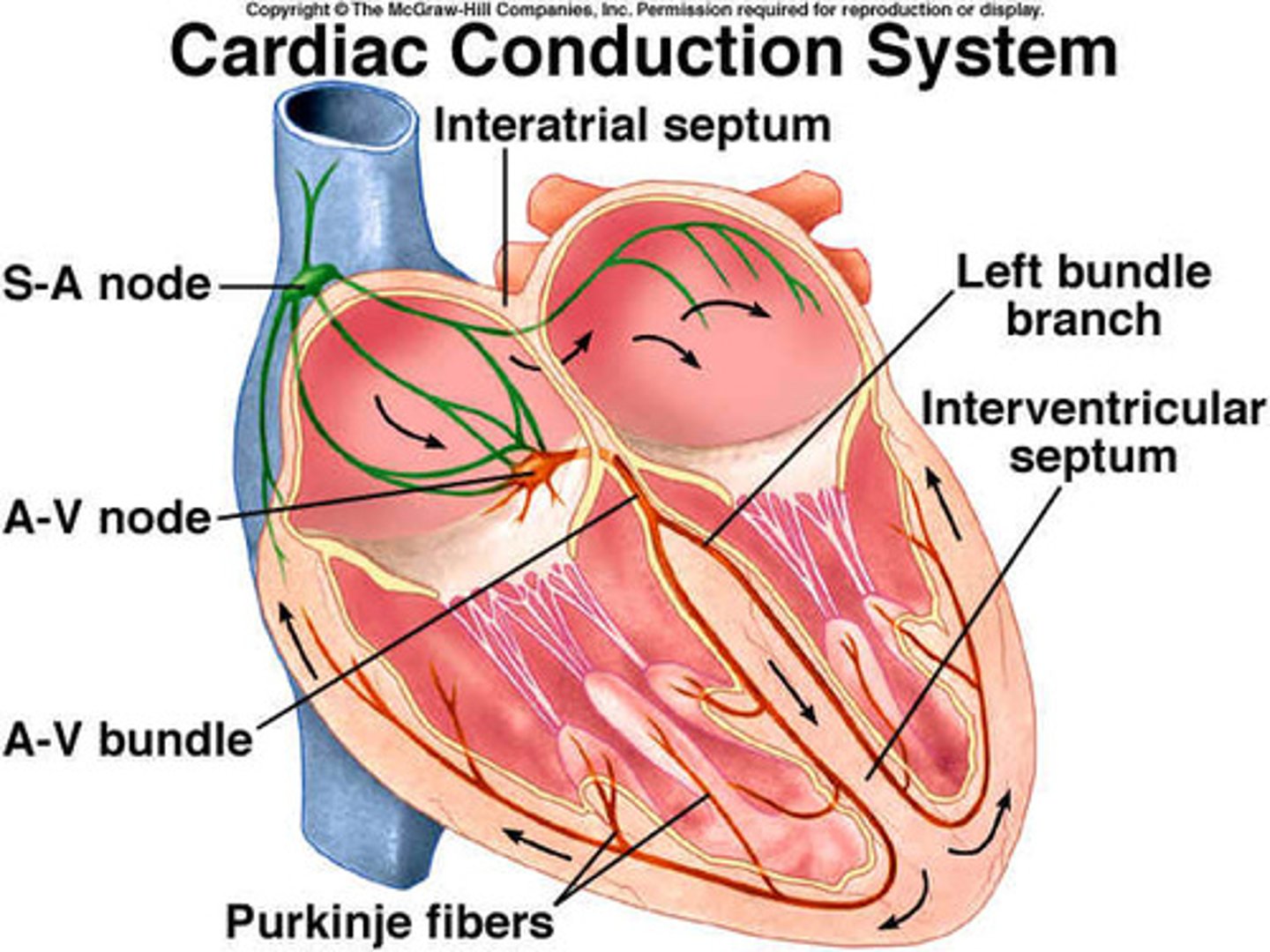
Cardiac conduction pathway (5)
1.) SA node
2. ) AV node
3.) Bundle of His (AV bundle)
4.) AV bundle branches (LBB and RBB)
5.) Purkinje fibers
SA node
The pacemaker of the heart.
Responsible for "sinus rhythm" of heart.
Has automaticity.
Where is the SA node located?
Upper posterior wall of right atrium
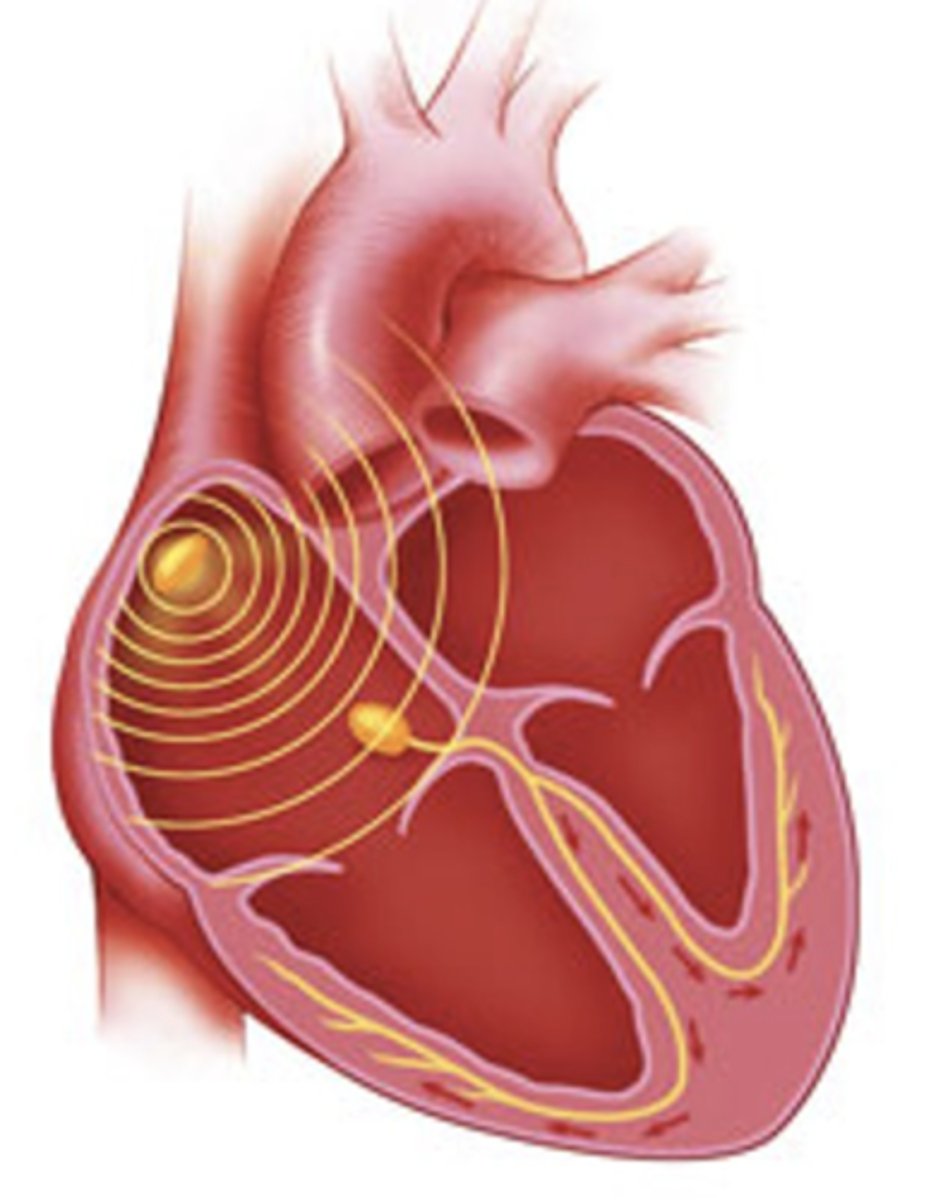
__________________ spreads outwards from SA node like the waves created from a pebble dropped in a lake.
Depolarization spreads outwards from SA node like the waves created from a pebble dropped in a lake.
The interiors of resting myocytes are negative, but when these cells are ___________, their interiors become _________ and the cells __________.
The interiors of resting myocytes are negative, but when these cells are depolarized, their interiors become positive and the cells contract.
The myocyte interiors regain their resting ______ charge during the ________ phase.
The myocyte interiors regain their resting negative charge during the REpolarization phase.
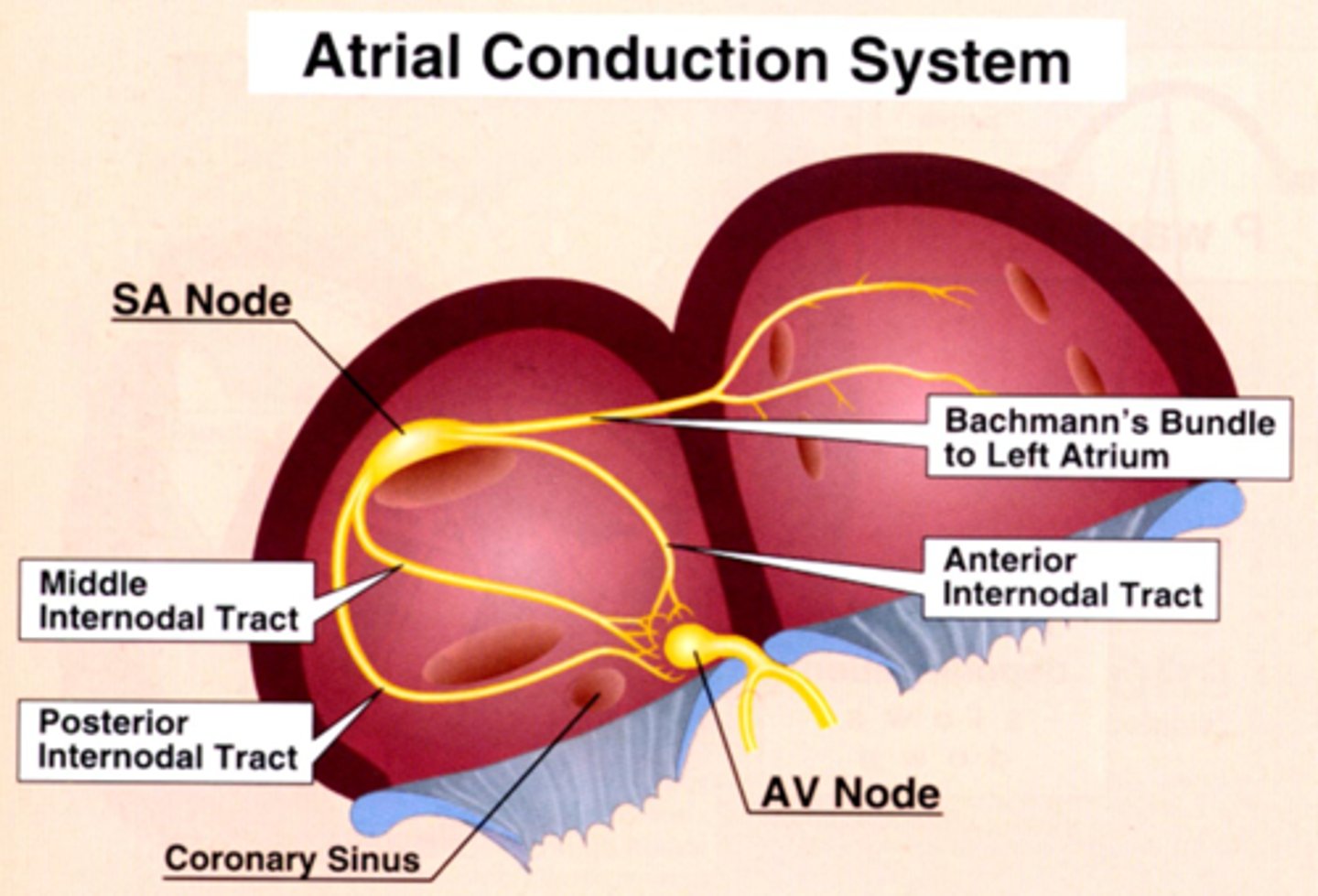
Atrial conduction system
Internodal tracts (located in RA)
- Anterior internodal tract
- Middle internodal tract
- Posterior internodal tract
Conduction tract (innervates LA)
-Bachmann’s Bundle
P-wave represents
R and L atrial depolarization (contraction)
**atrial meaning SA and AV node.
Internodal tracts depolarization course is from where to where?
SA node to AV node
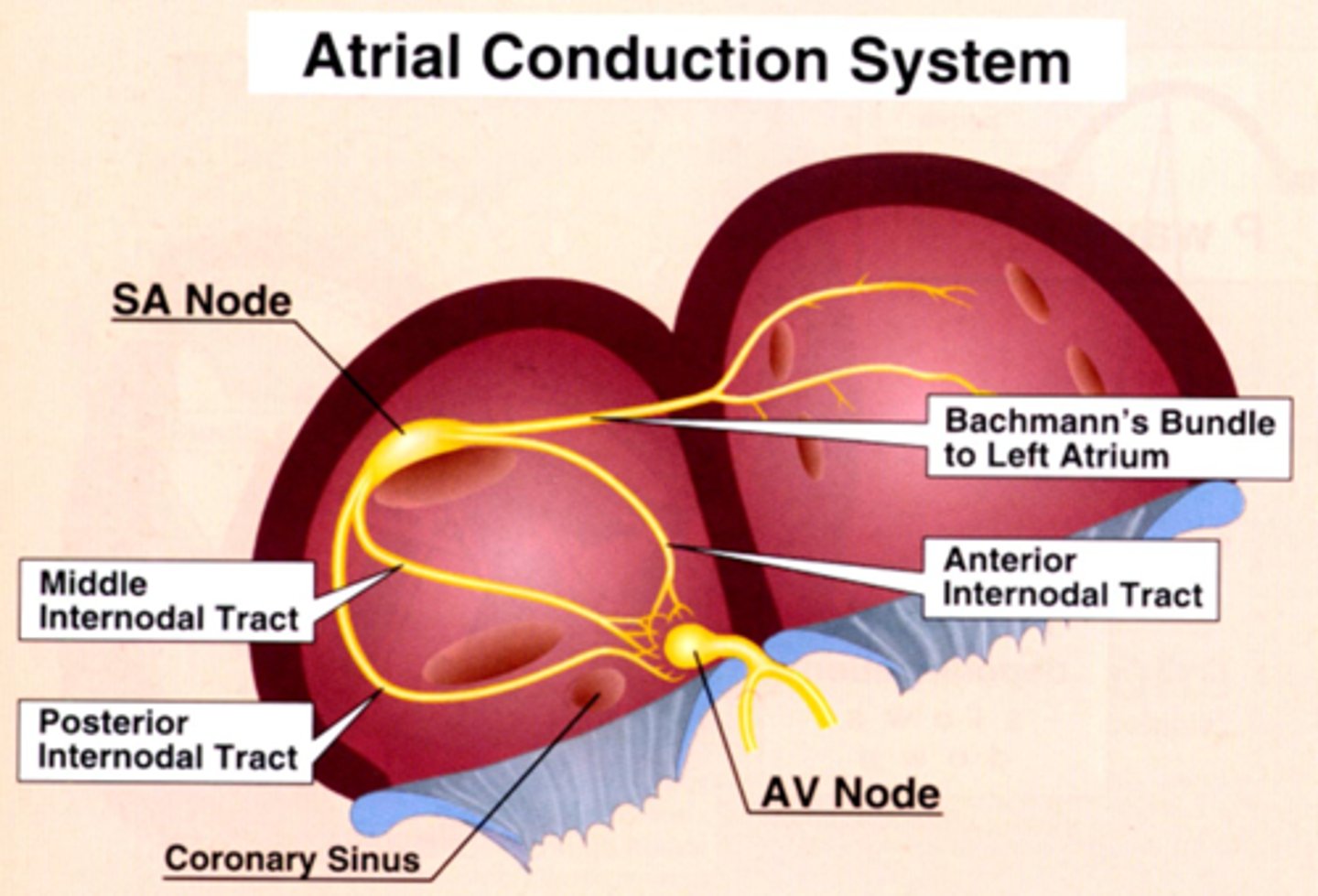
Bachmann's Bundle depolarization course is from where to where?
SA node to Left atrium
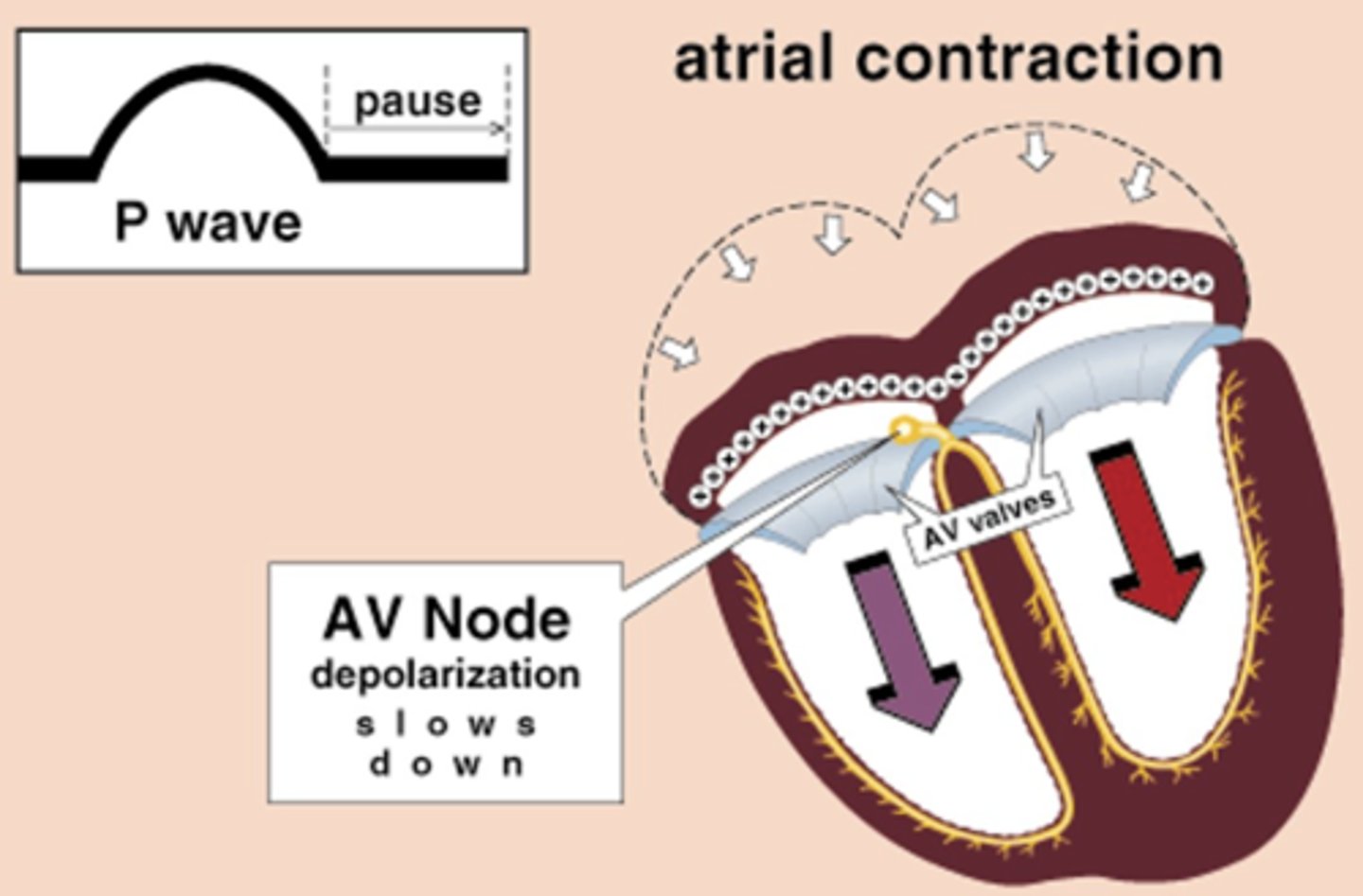
When wave of atrial depolarization enters the AV node, depolarization slows, producing a ______ on EKG known as the ______ interval.
This allows time for blood to enter _______.
When wave of atrial depolarization enters the AV node, depolarization slows, producing a pause on EKG known as the PR interval.
This allows time for blood to enter ventricles.
Automaticity
The ability of the heart to generate and conduct electrical impulses on its own.
Ability to generate pacemaking stimuli.
This is why heart can beat when taken out of body.
SA/AV node action potential
When membrane voltage increases, cell is less negative.. depolarized (contract).
When membrane voltage decreases, cell is more negative.. repolarized.
After a slow depolarization through the AV node, depolarization shoots rapidly through the ________ conduction system.
After a slow depolarization through the AV node, depolarization shoots rapidly through the ventricular conduction system.
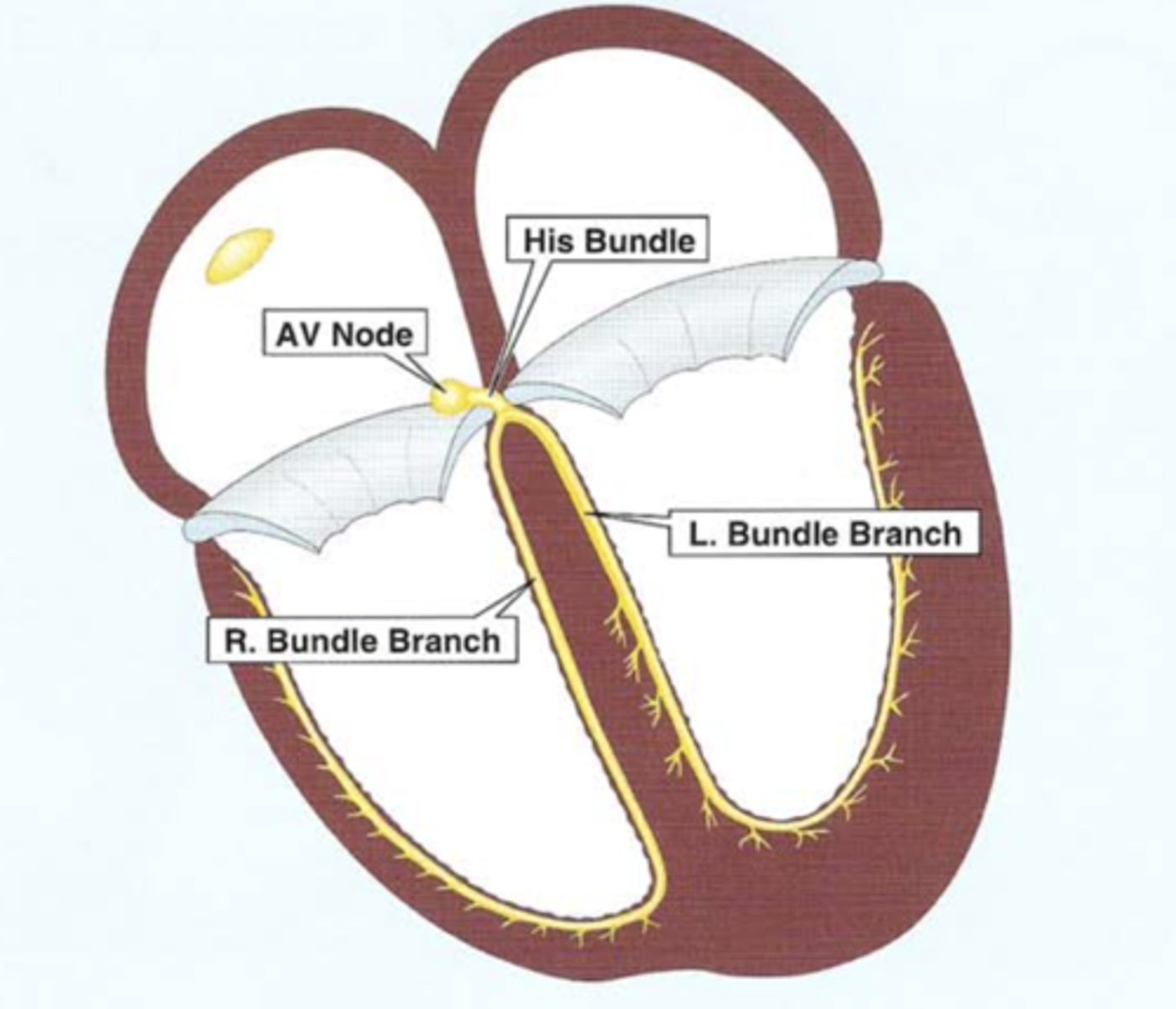
____________ conduction system originates in the Bundle of His.
Ventricular conduction system originates in the Bundle of His
Ventricular depolarization and contraction produces a _____ ________ on EKG.
Ventricular depolarization and contraction produces a QRS complex on EKG.
***In reality ventricular contraction lasts longer than the QRS complex
Bundle of His immediately bifurcates in the interventricular septum into the _____ and ______
Bundle of His immediately bifurcates in the interventricular septum into the RBB and LBB
Ventricular depolarization begins midway down the interventricular septum, where the LBB produces ______ ________ _________.
Ventricular depolarization begins midway down the interventricular septum, where the LBB produces fine terminal filaments
**because LV is bigger, needs more pathways.
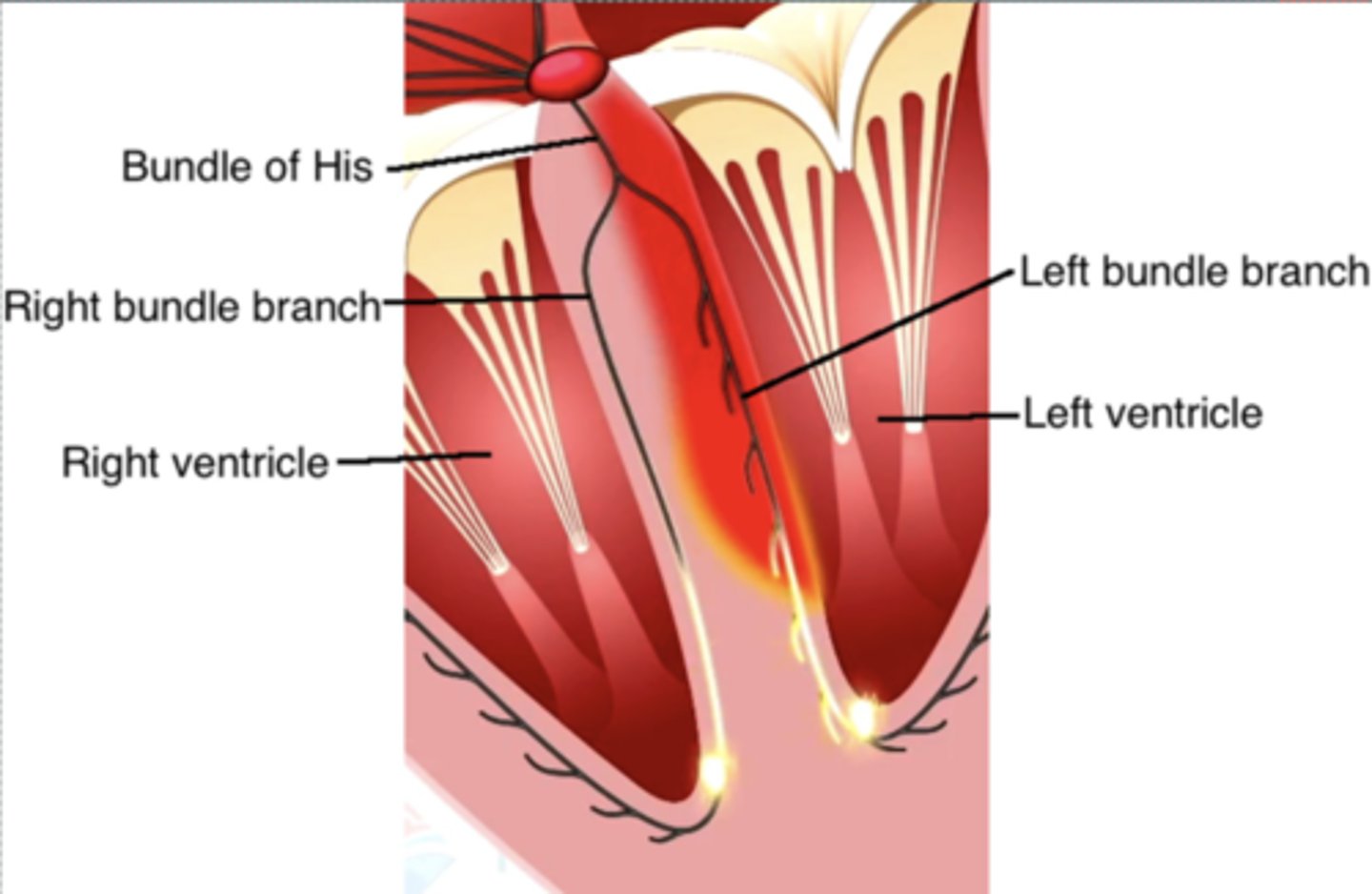
The RBB does ____ produce terminal filaments in the septum. So ______ ___ _______ depolarization of septum occurs before the rest of the ventricular myocardium depolarizes.
The RBB does NOT produce terminal filaments in the septum. So left-to-right depolarization of septum occurs before the rest of the ventricular myocardium depolarizes.
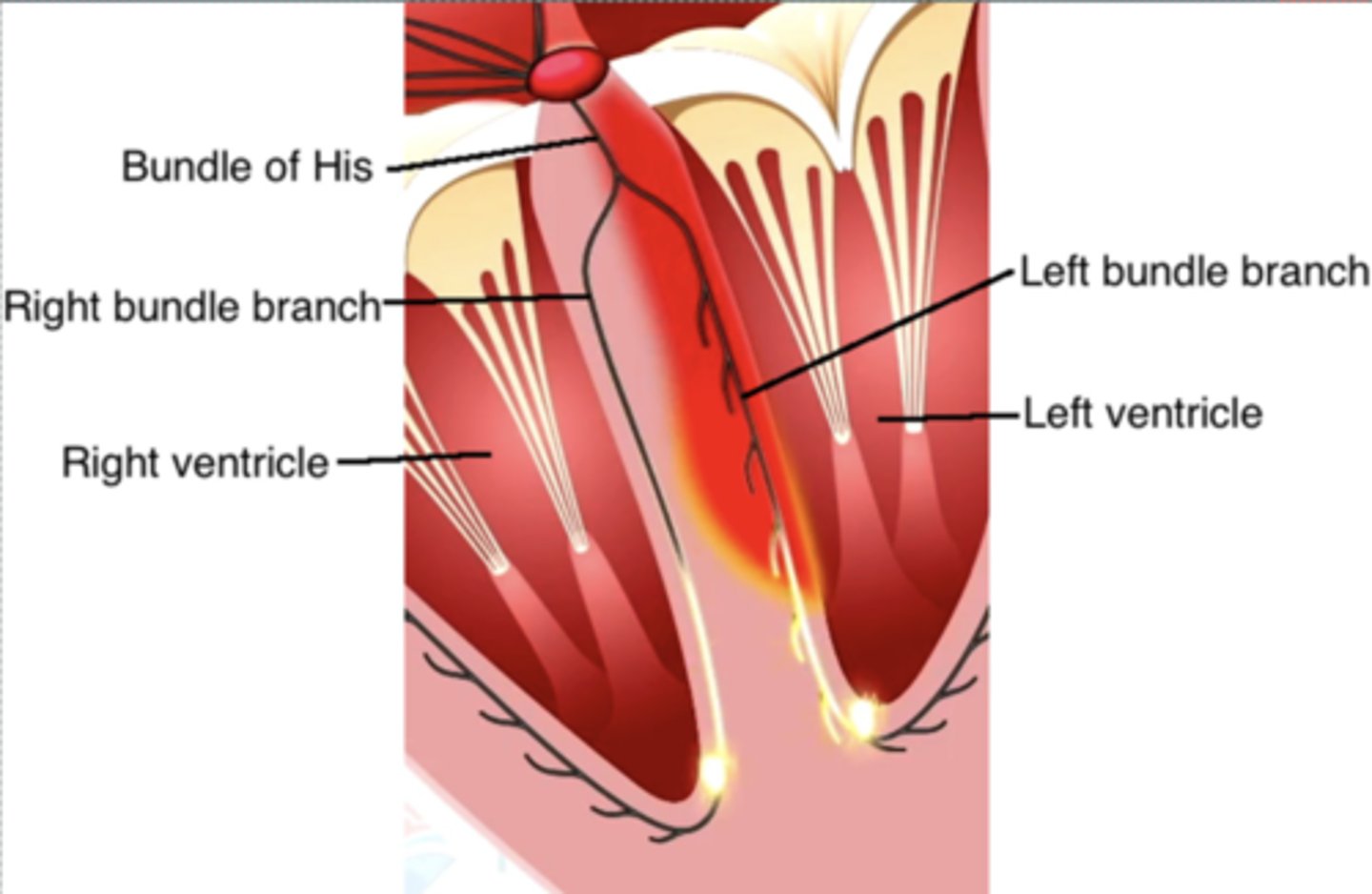
Terminal filaments of __________ rapidly distribute depolarization to ventricular myocytes, initiating ventricular ____________.
Terminal filaments of Purkinje fibers rapidly distribute depolarization to ventricular myocytes, initiating ventricular contraction.
Rapid repolarization of the ventricles is represented by _______ on EKG.
Rapid repolarization of the ventricles is represented by T-wave on EKG.
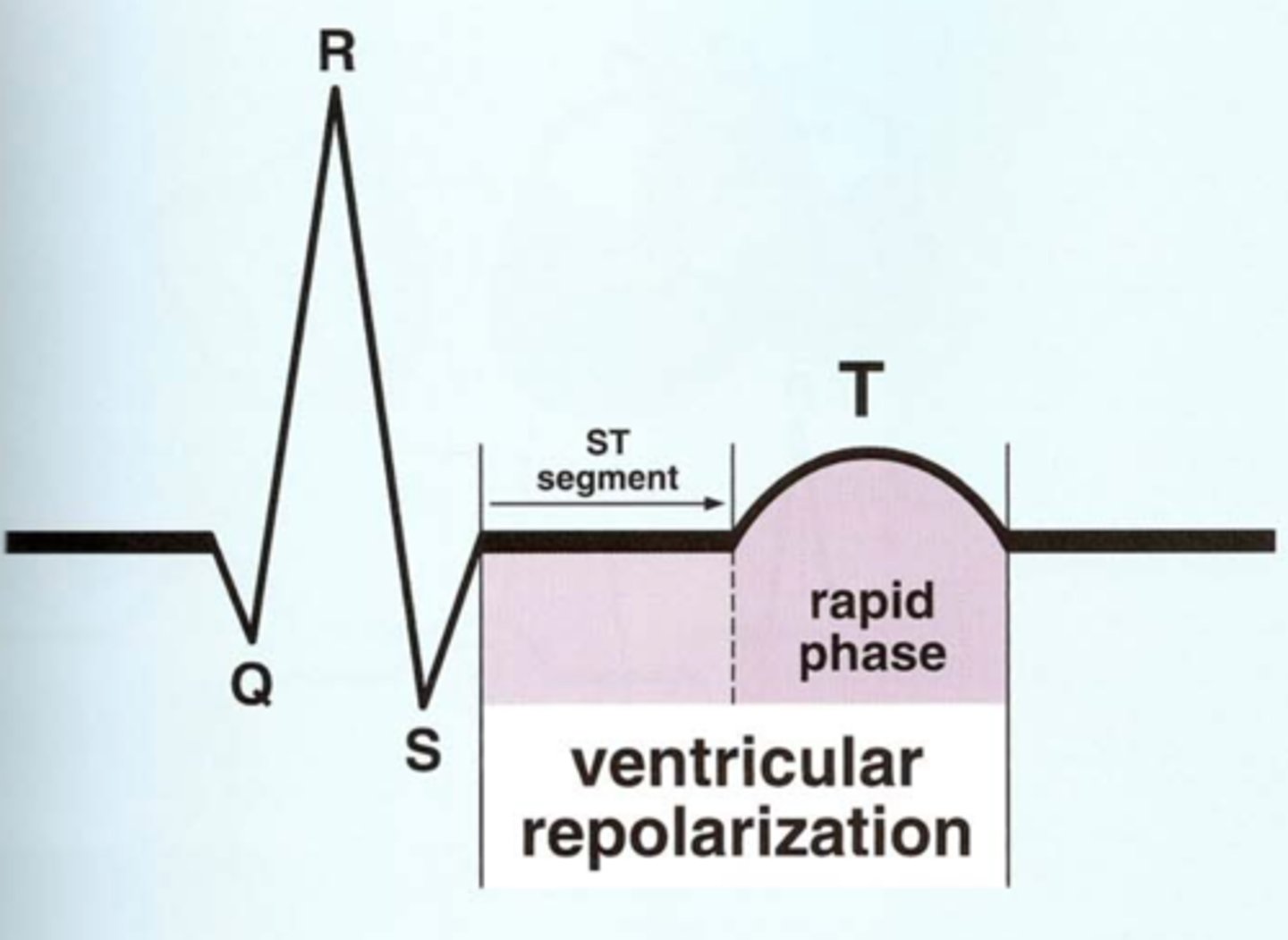
What ions leave the myocytes during repolarization?
Potassium ions
What ions (2) enter myocytes during depolarization?
Sodium and Calcium
**Sodium is fast-moving depolarization
***Calcium lead to slow depolarization of AV node.
ST segment
Represents the 'plateau' or initial phase of ventricular repolarization.
Horizontal baseline that follows the QRS.
Normally level with other areas of baseline.
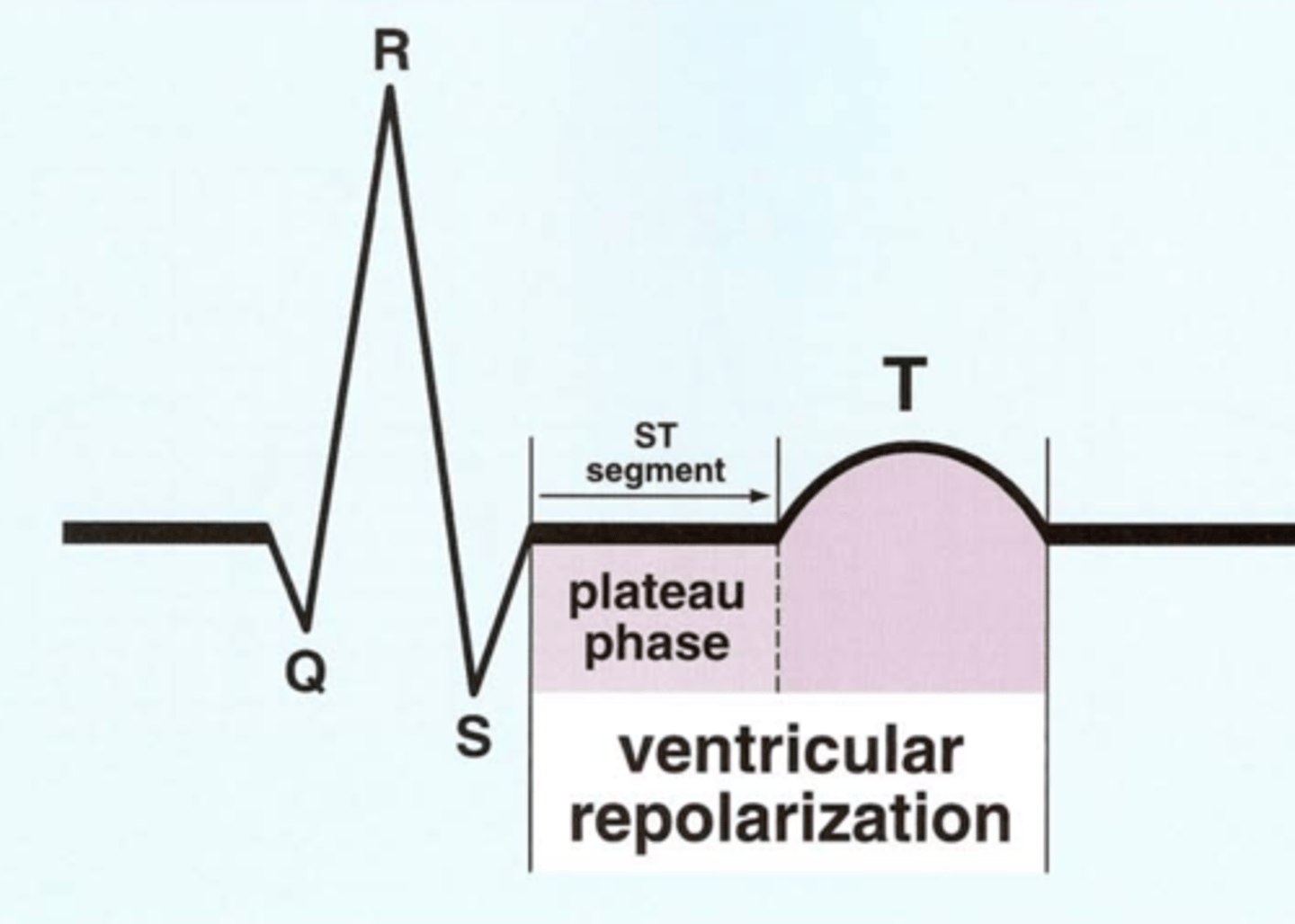
______________ of ventricular myocytes begin immediately after QRS and persist until end of T-wave
Repolarization of ventricular myocytes begin immediately after QRS and persist until end of T-wave
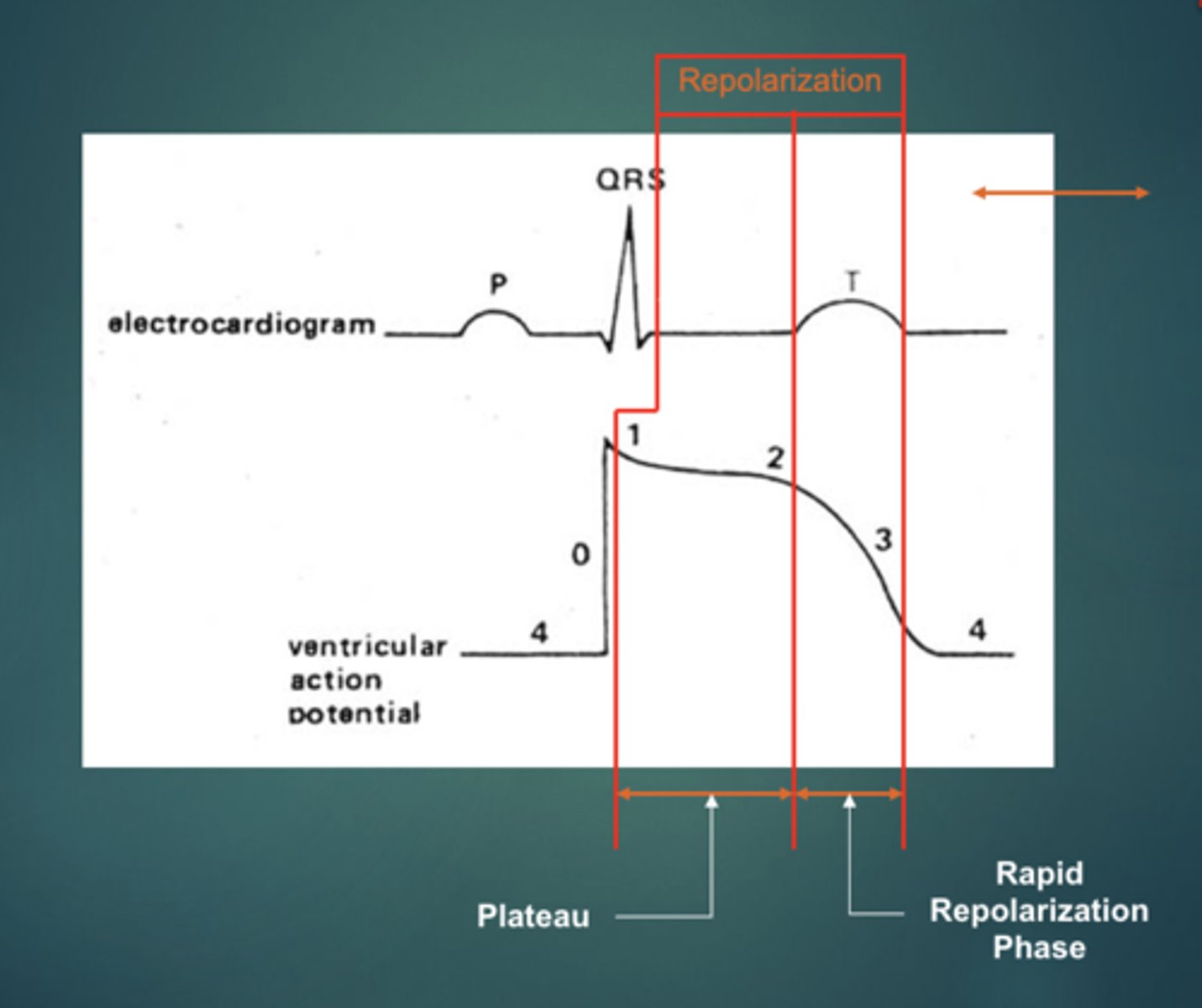
_______ contraction begins with the QRS and persists until the end of the T-wave
Ventricular contraction begins with the QRS and persists until the end of the T-wave
_______ is any initial negative deflection
Q-wave is any initial negative deflection
Normal QT is (?) half of the R-R interval
Normal QT is less than half of the R-R interval
QT interval represents?
Represents the duration of ventricular systole/contraction.
Good indicator of repolarization.
R-wave is any _____ deflection
R-wave is any positive deflection
S-wave is any _____ deflection after R-wave
S-wave is any negative deflection after R-wave.
R¹ wave any _____ deflection after S-wave
R¹ wave any positive deflection after S-wave
_______ is when there is only a single negative deflection.
QS complex is when there is only a single negative deflection.
The _______ and _______ valves lie between the atria and the ventricles, thereby acting to electrically ________ the ventricles from the atria.
The mitral and tricuspid (AV) valves lie between the atria and the ventricles, thereby acting to electrically insulate the ventricles from the atria.
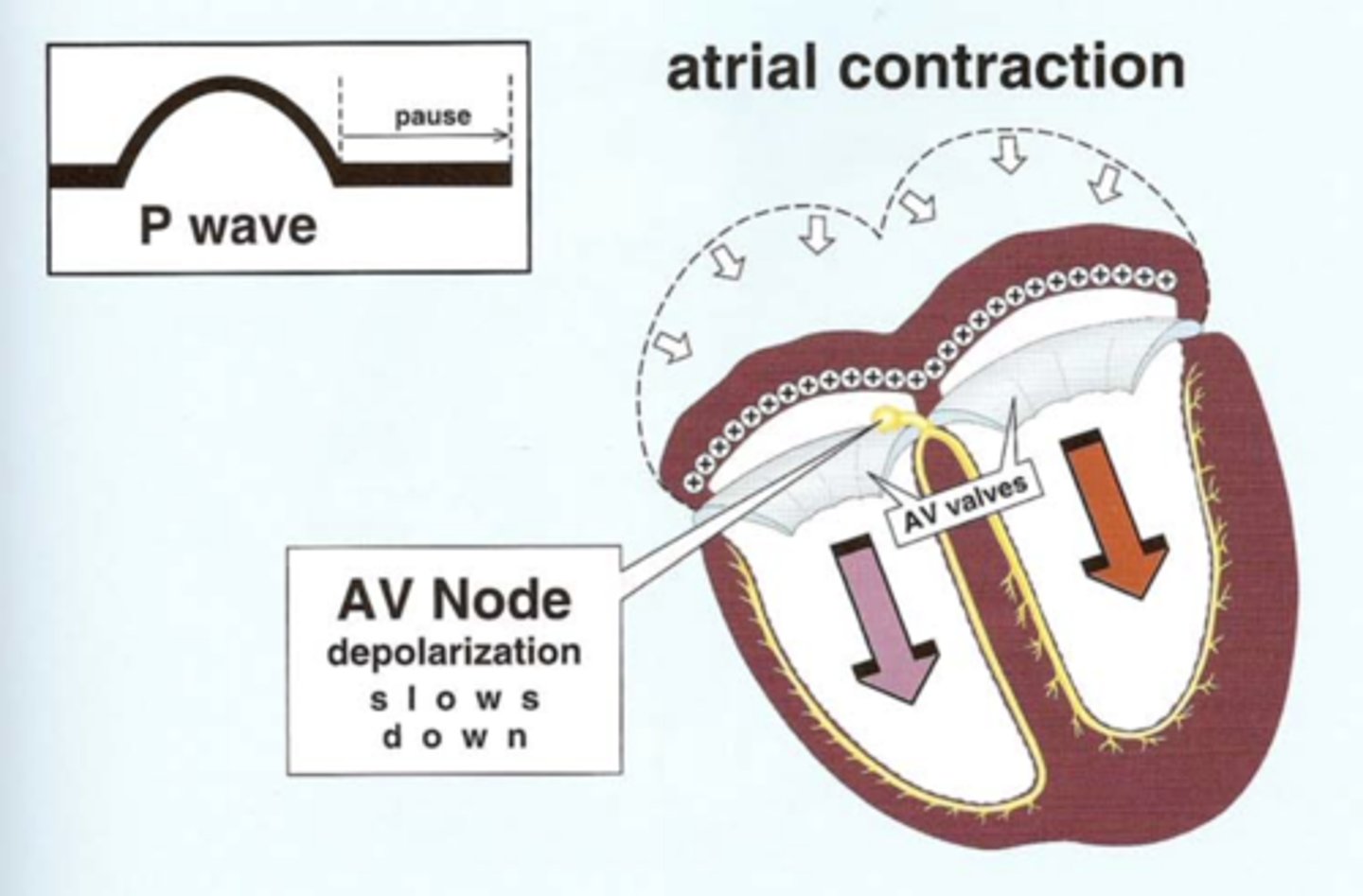
The ___ _____ is the sole pathway to conduct the depolarization stimulus through the fibrous AV valves to the ventricles.
The AV Node is the sole pathway to conduct the depolarization stimulus through the fibrous AV valves to the ventricles.
Depolarization conducts (rapidly or slowly?) through the AV Node, since it is carried by slow moving ___________ ions.
Depolarization conducts slowly through the AV Node, since it is carried by slow moving calcium ions.
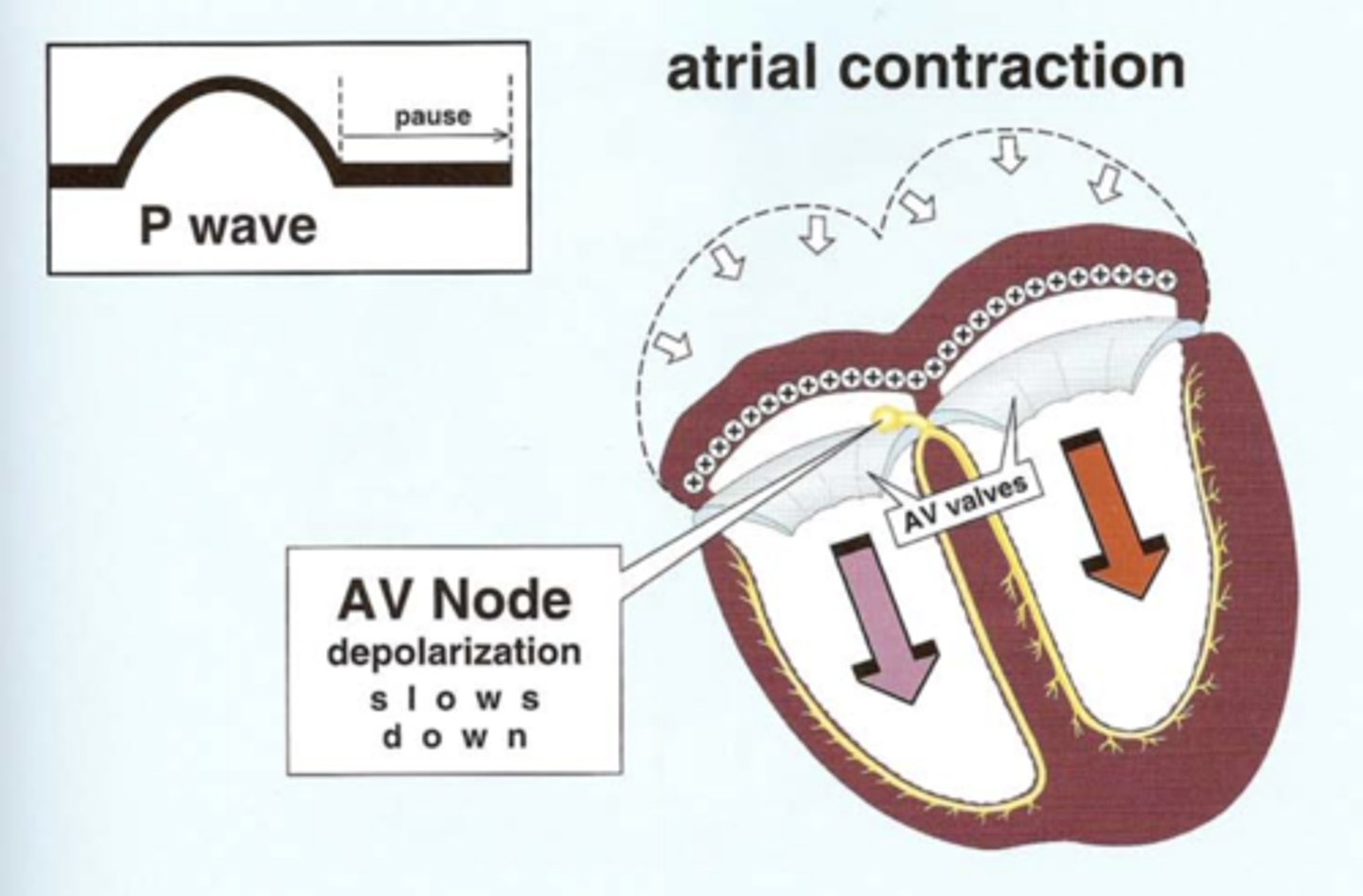
What electrolyte is responsible for ventricular depolarization?
Sodium
What are the two divisions of LBB?
Anterior and posterior divisions.
The ___ _________ represents the time between the beginning of atrial contraction and the beginning of ventricular contraction
The PR Interval represents the time between the beginning of atrial contraction and the beginning of ventricular contraction
? small square = ? mV x ? sec
1 small square = 0.1mV x 0.04sec

? large square = 5mm x 5mm or ? mV x ?sec
1 large square = 5mm x 5mm or 0.5mV x 0.2sec
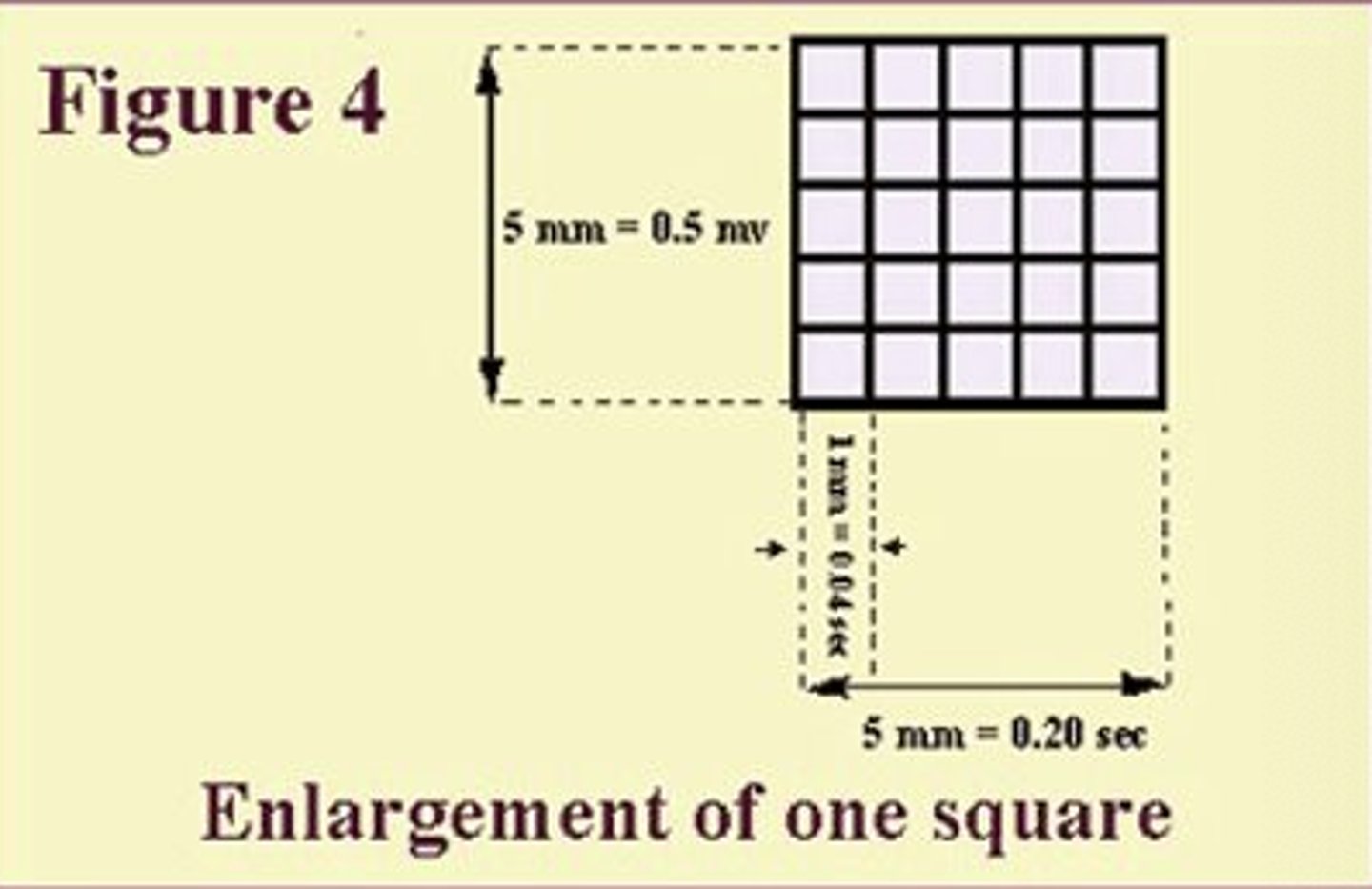
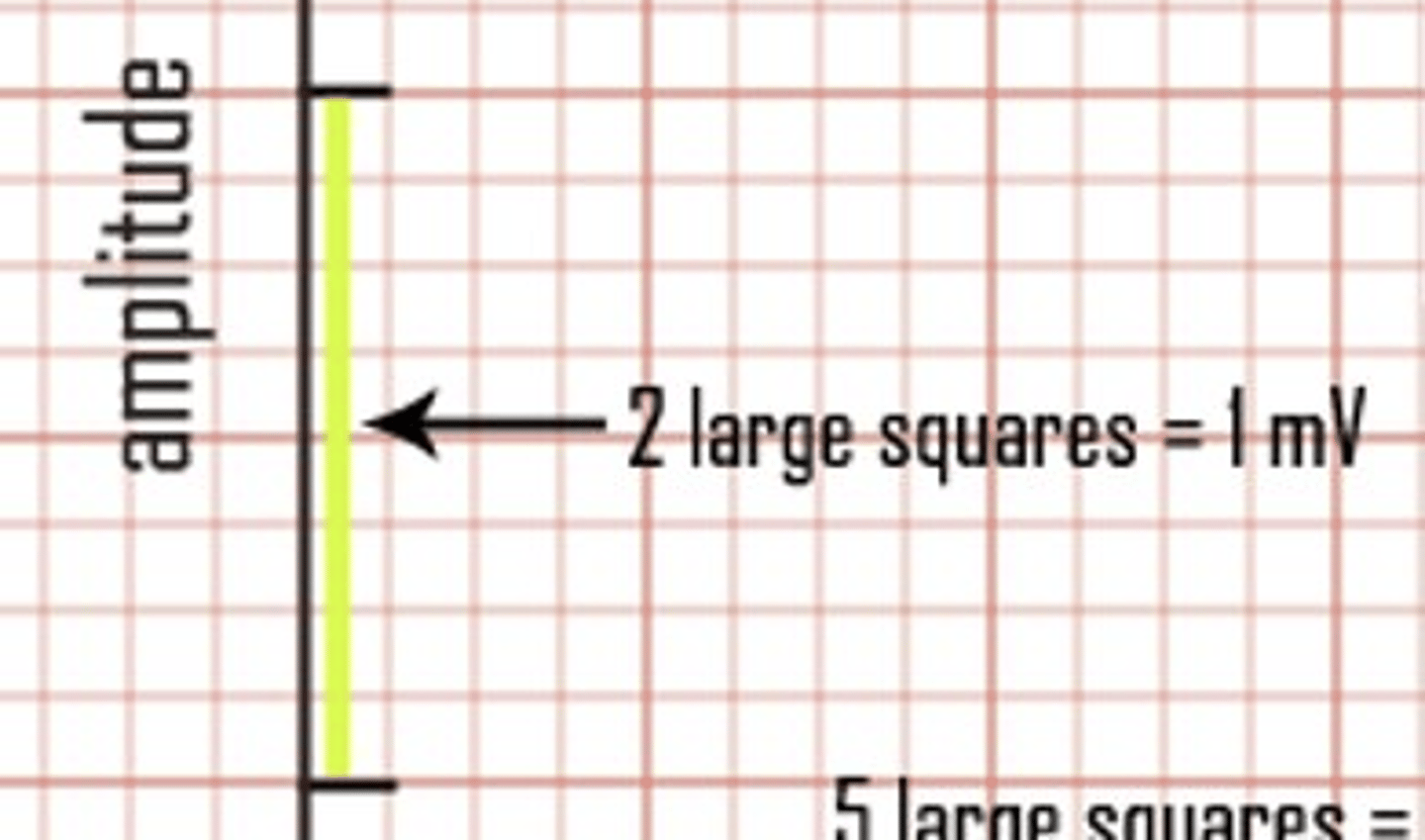
? large squares (vertically) = ?mV
2 large squares = 1mV
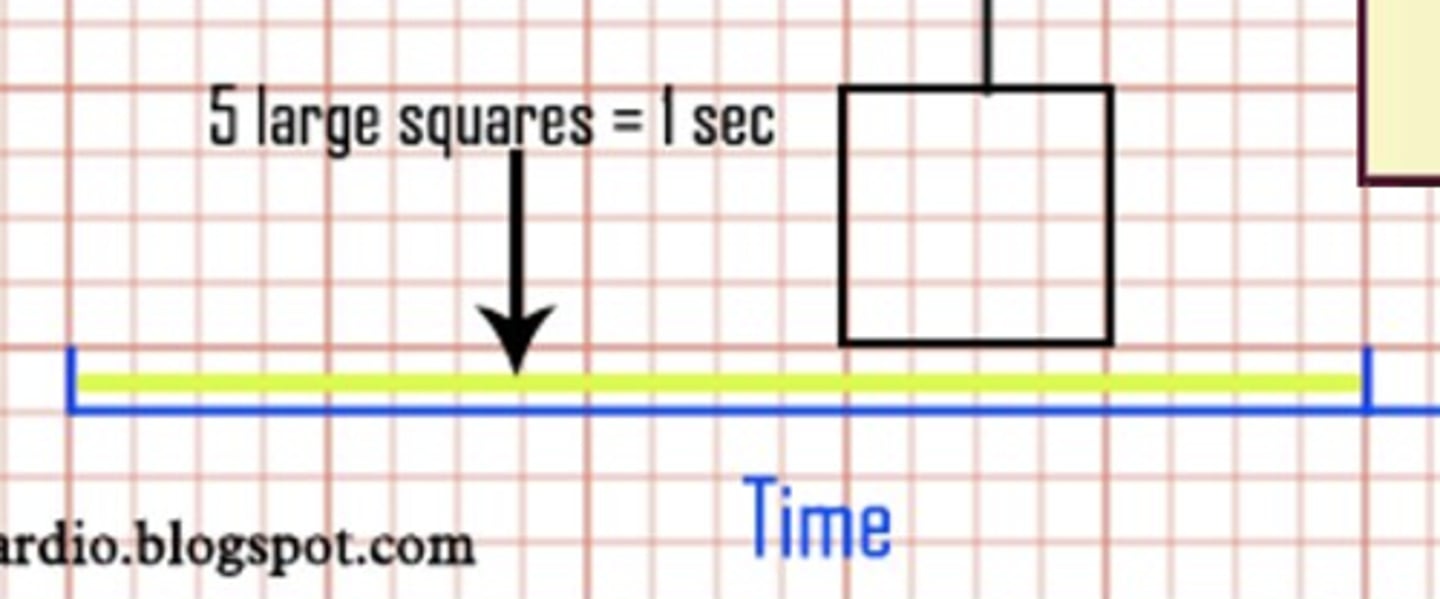
? large squares (horizontally) = 1 sec
5 large squares = 1 sec
Deflections below baseline are ________. When depolarization advances _________ from a positive skin electrode.
Deflections below baseline are negative. When depolarization advances away from a positive skin electrode.
Deflections above baseline are _________
When depolarization advances (toward or away from?) a positive skin electrode
Deflections above baseline are positive
When depolarization advances toward a positive skin electrode
EKG ALWAYS reads from _______ to _______ (electrode) and from ________ to ________ on an axis.
EKG ALWAYS reads from negative to positive (electrode) and from left to right on an axis.
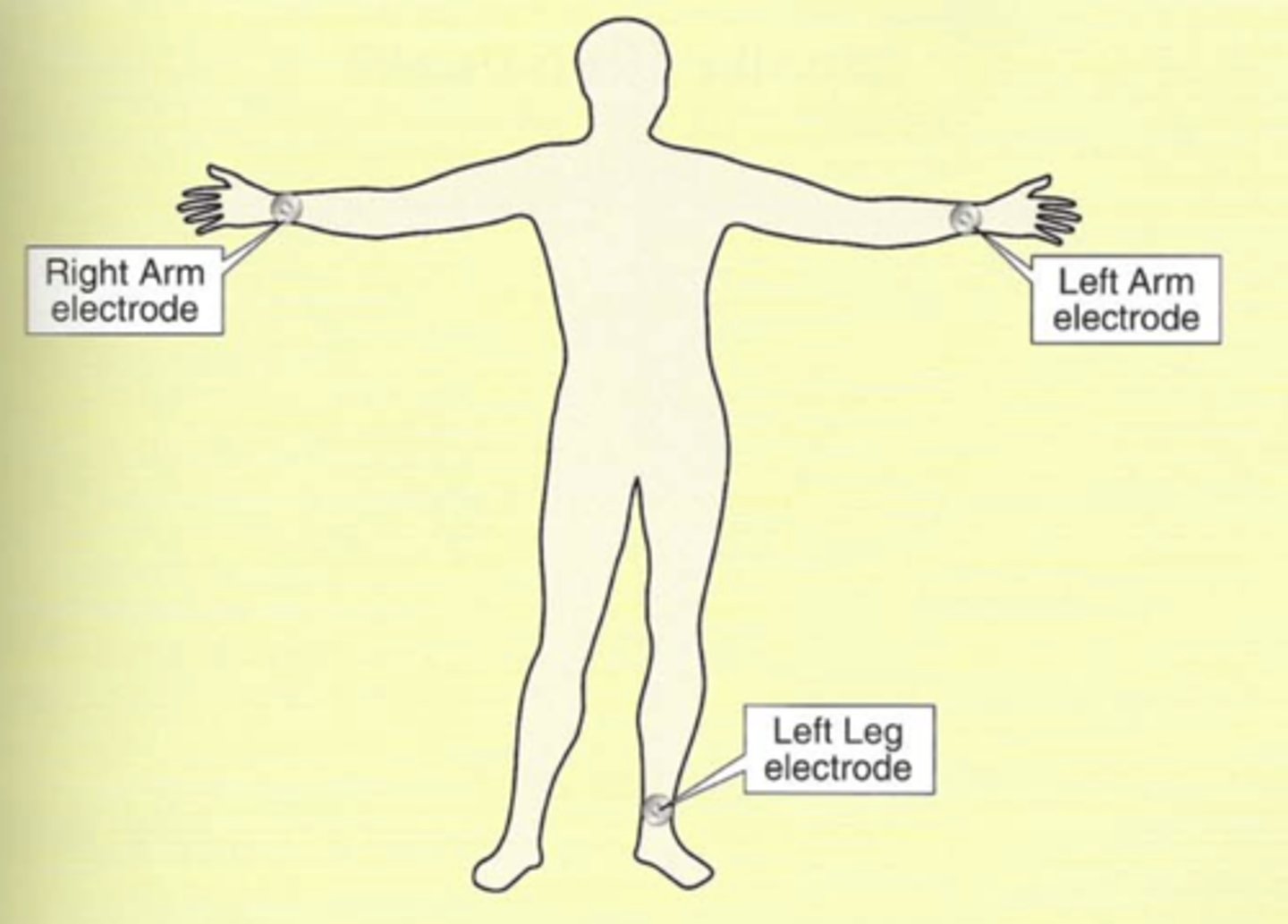
To obtain the _____ leads, electrodes are placed on the ____ arm, the _____ arm, and the _____ leg.
To obtain the limb leads, electrodes are placed on the right arm, the left arm, and the left leg.
A _____ of electrodes is used to record one lead.
A ________ pair is used for each lead.
A pair of electrodes is used to record one lead.
A different pair is used for each lead
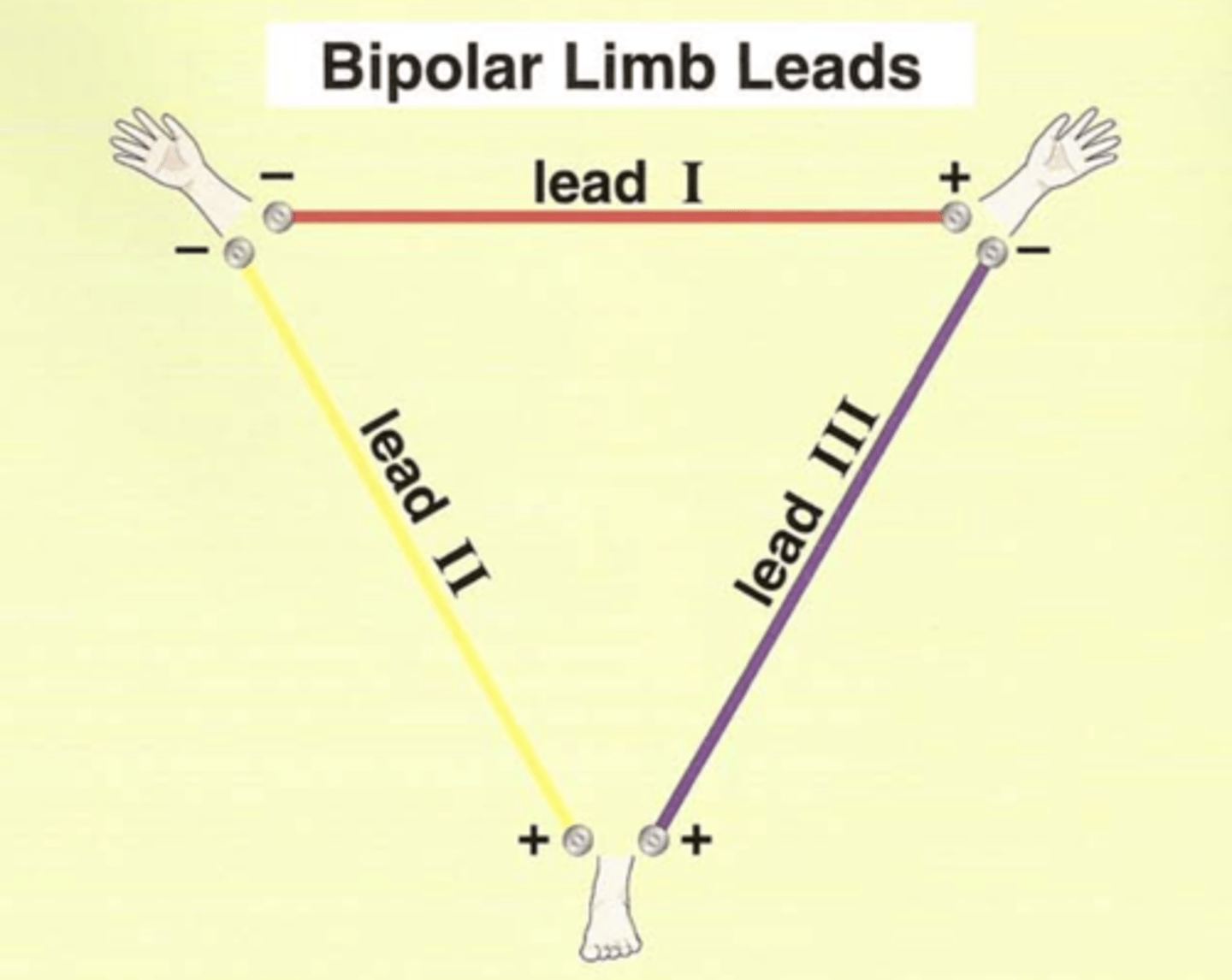
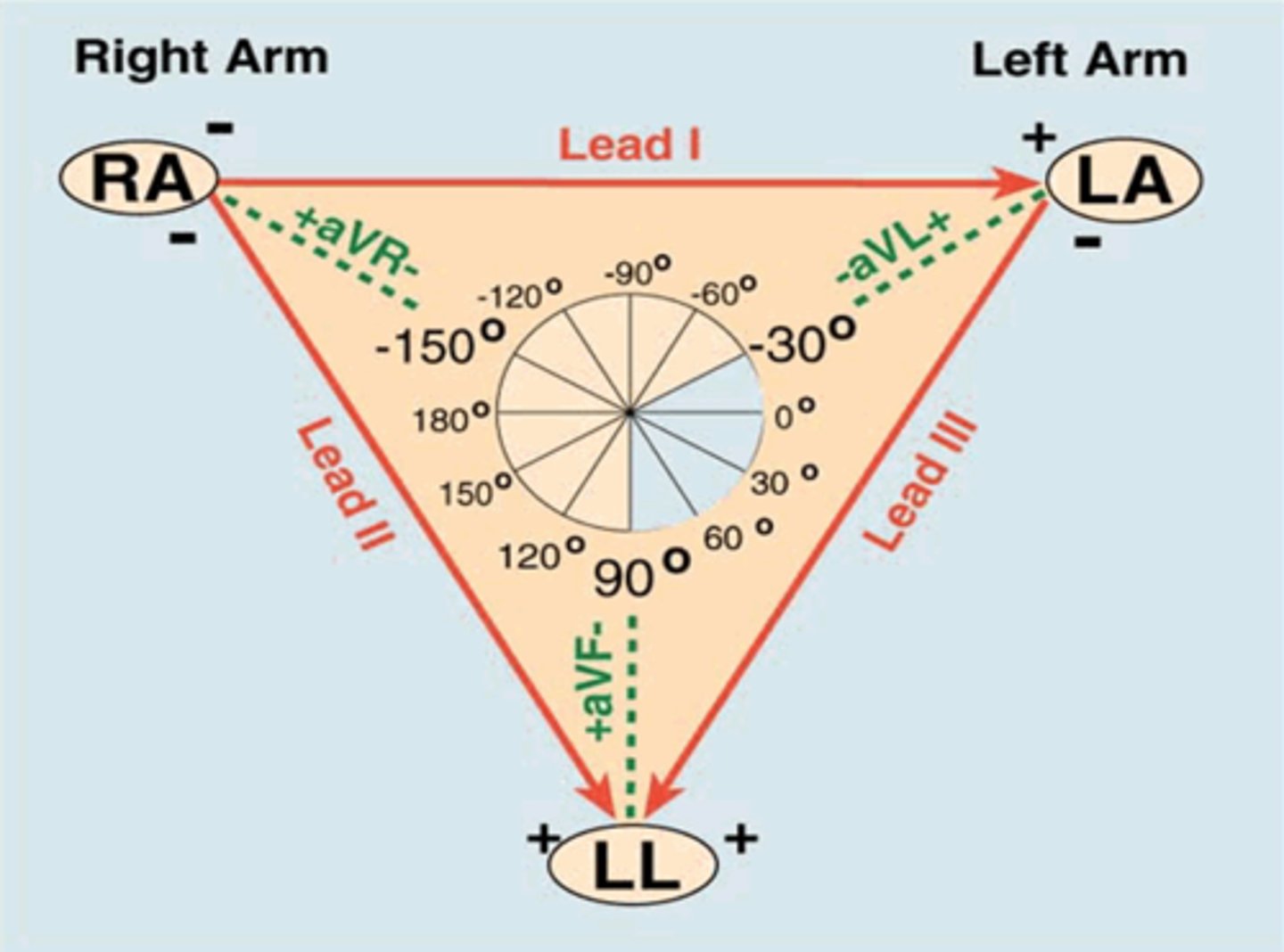
The bipolar limb lead configuration is sometimes called, "___________ _________."
The bipolar limb lead configuration is sometimes called, "Einthoven's Triangle."
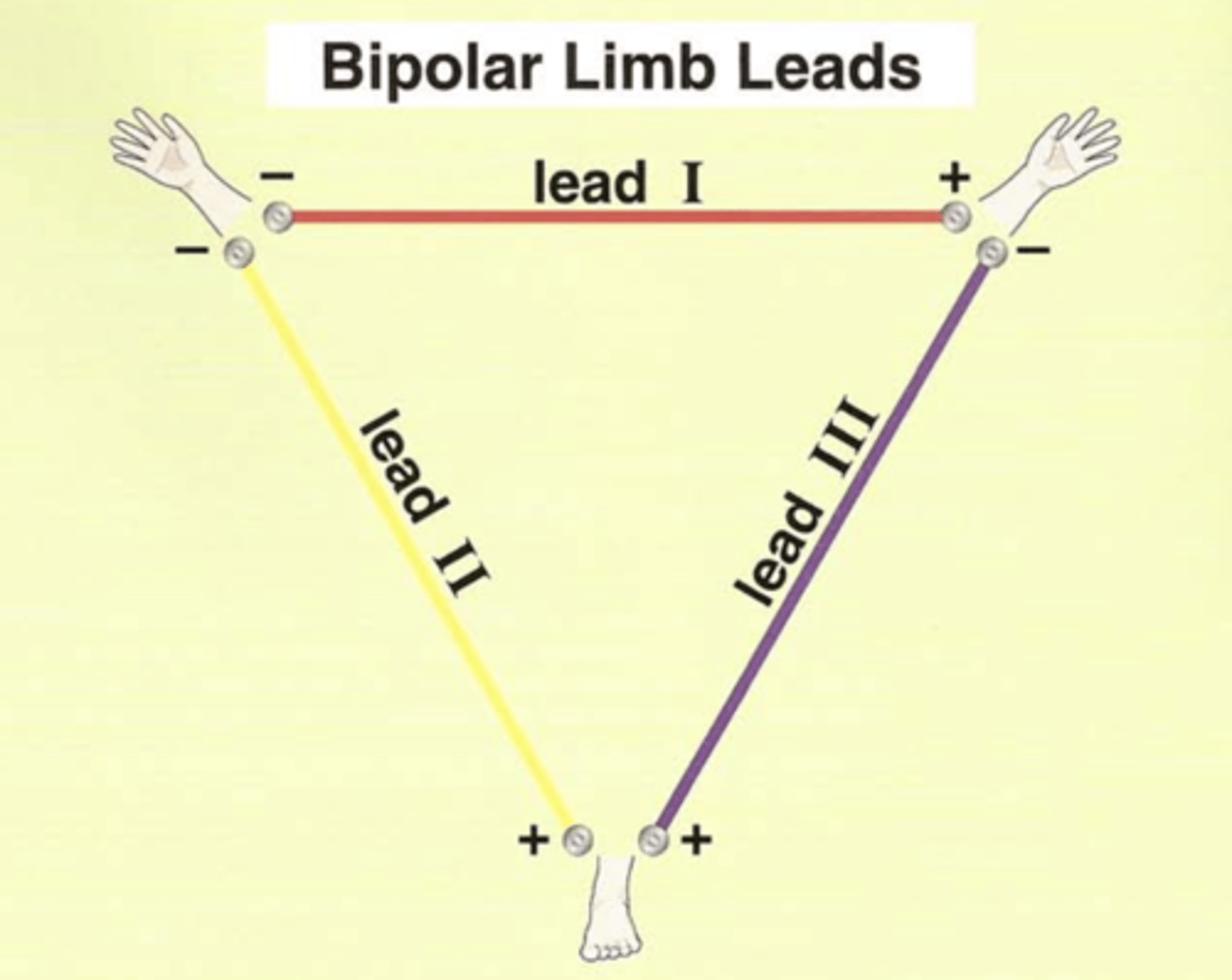
Bipolar limb leads or Einthoven's triangle
Which leads?
I, II, III
Three unipolar or augmented leads?
Are they positive or negative?
aVR, aVL, aVF
Electrode is positive.
Two remaining electrodes serve as a common ground (negative).
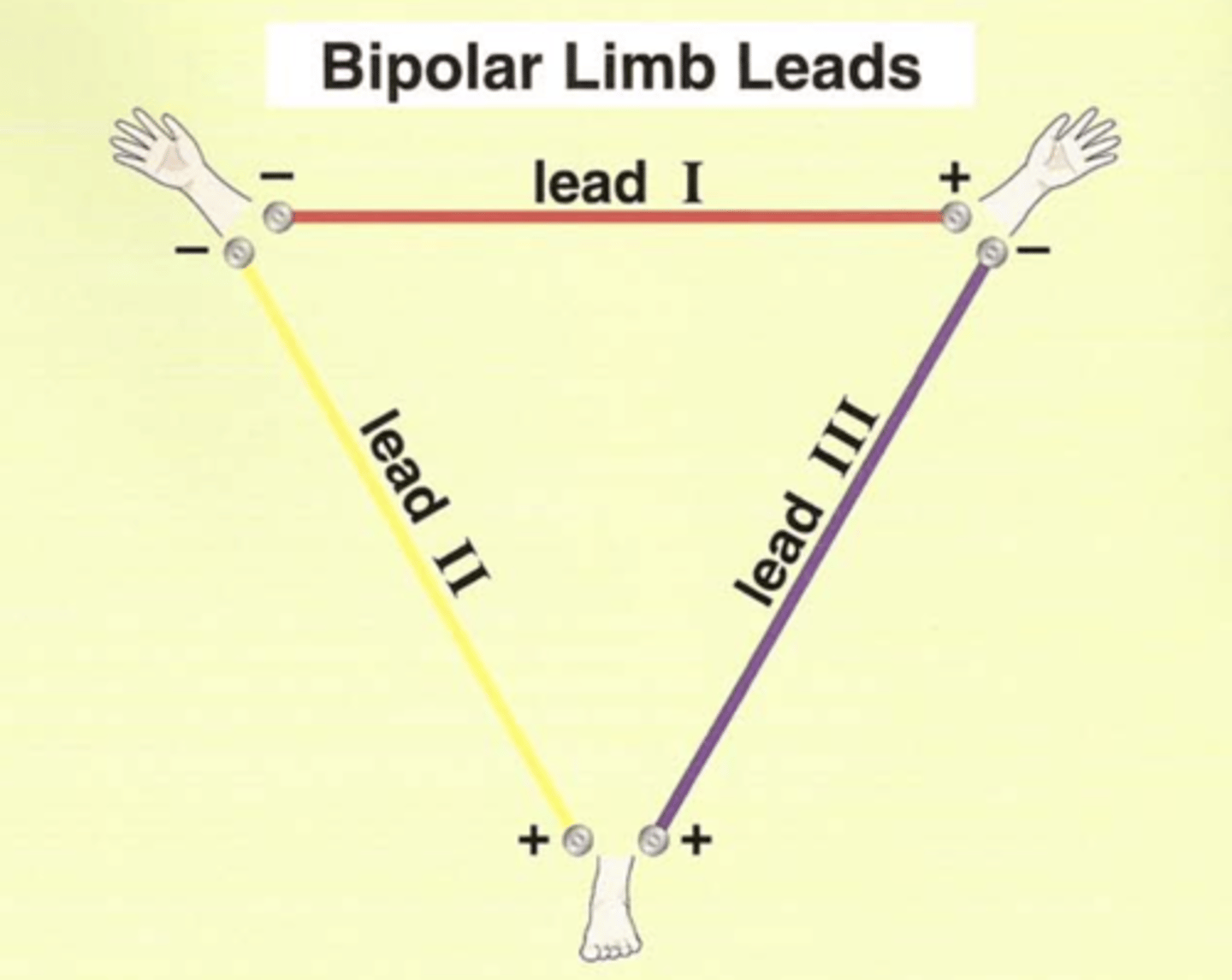
What does aVF stand for?
In this lead, the (right or left?) foot electrode is (positive or negative?).
Combination of leads _____ and ______.
The remaining two are positive or negative?
Augmented/amplified, Voltage, left Foot
Left foot electrode is positive.
Combination of leads II and III.
The remaining two are negative.
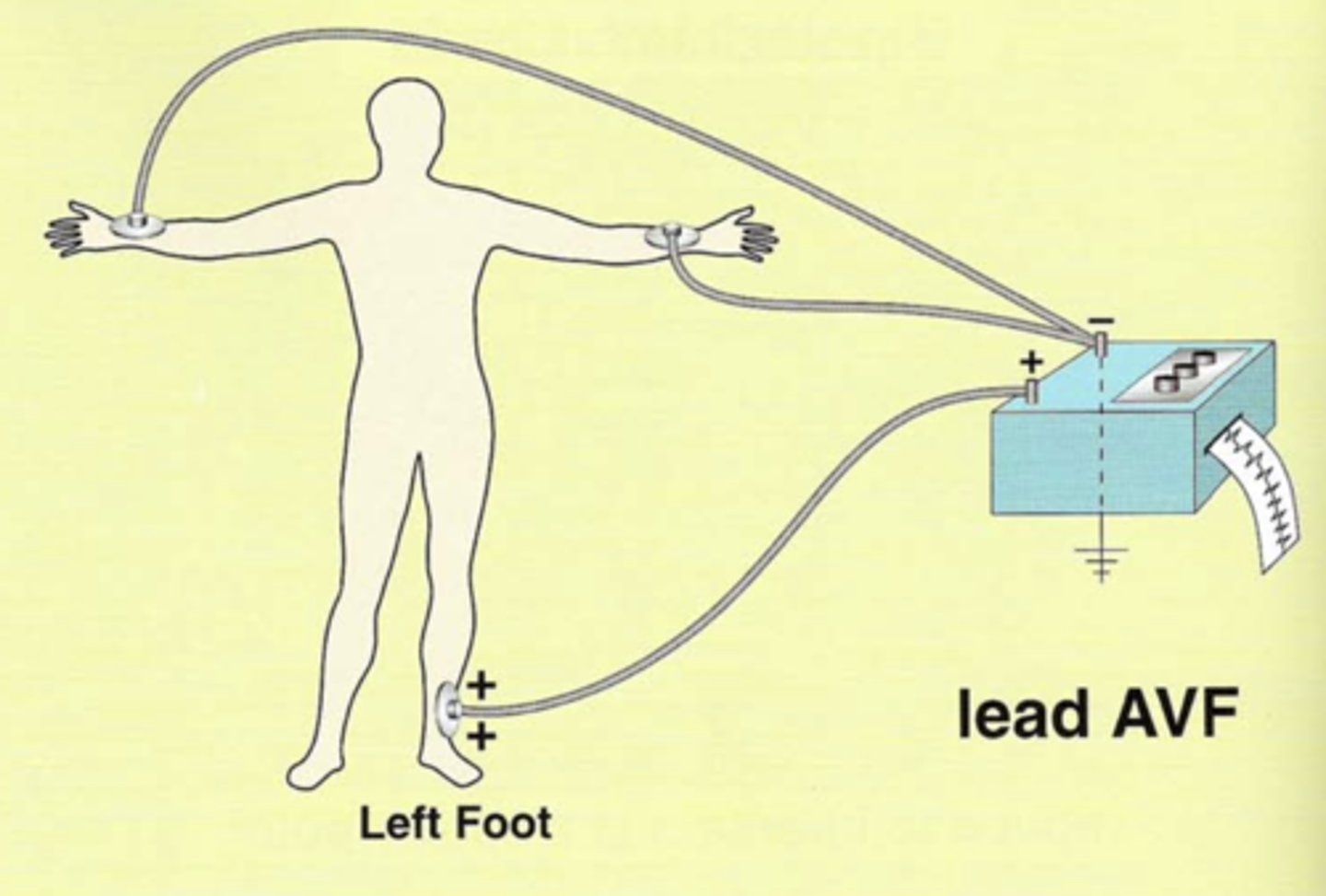
What does aVR stand for?
In this lead, the (right or left?) arm electrode is (positive or negative?).
The remaining two are positive or negative?
Augmented/amplified, Voltage, Right arm
Right arm electrode is positive.
The remaining two are negative.
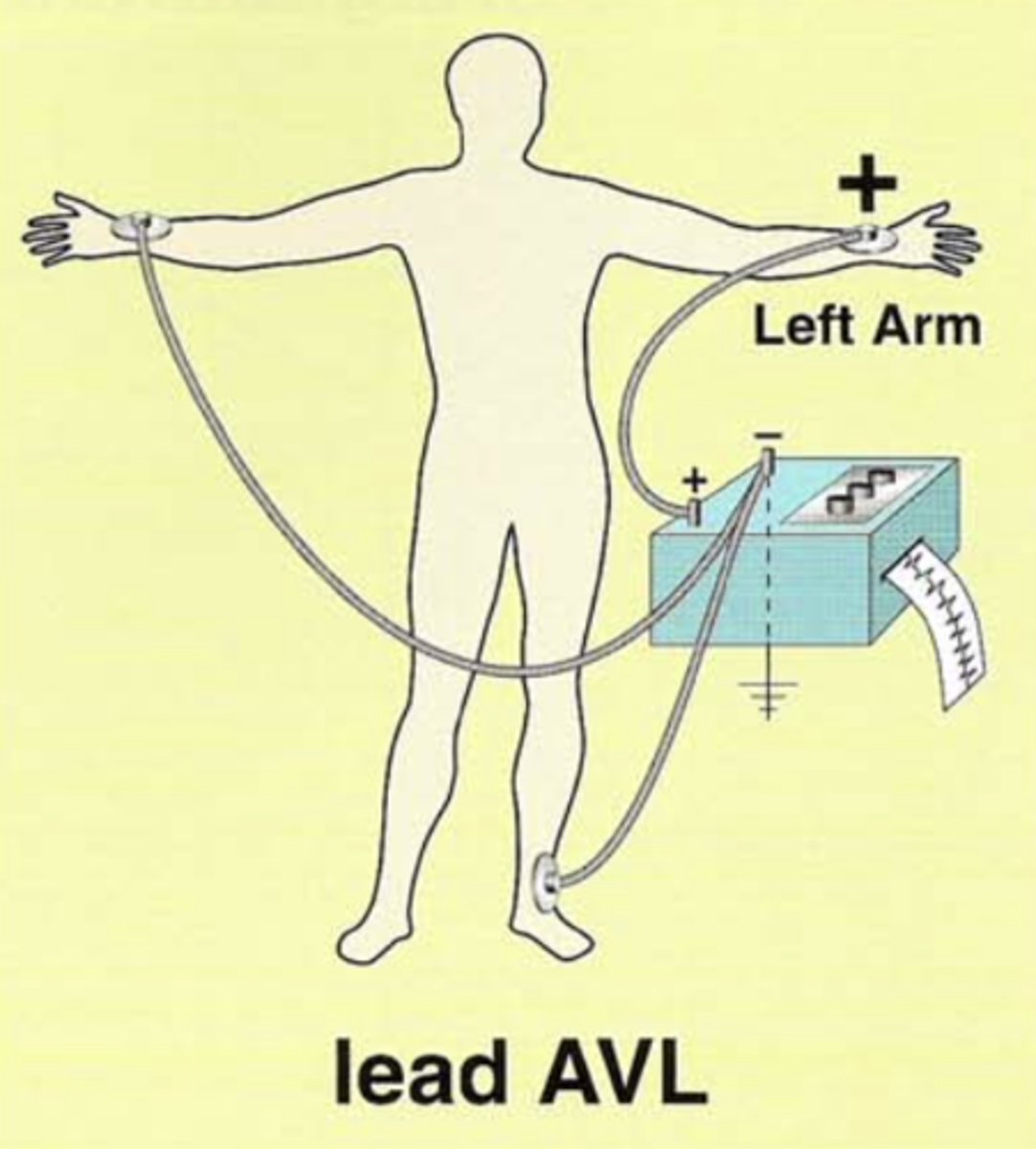
What does aVL stand for?
In this lead, the (right or left?) arm electrode is (positive or negative?).
The remaining two are positive or negative?
Augmented/amplified, Voltage, Left arm
Left arm electrode is positive.
The remaining two are negative.
The augmented limb leads ______ _____ _____ formed by leads I, II, and III.
The augmented limb leads split the angles formed by leads I, II, and III.
Axial reference system
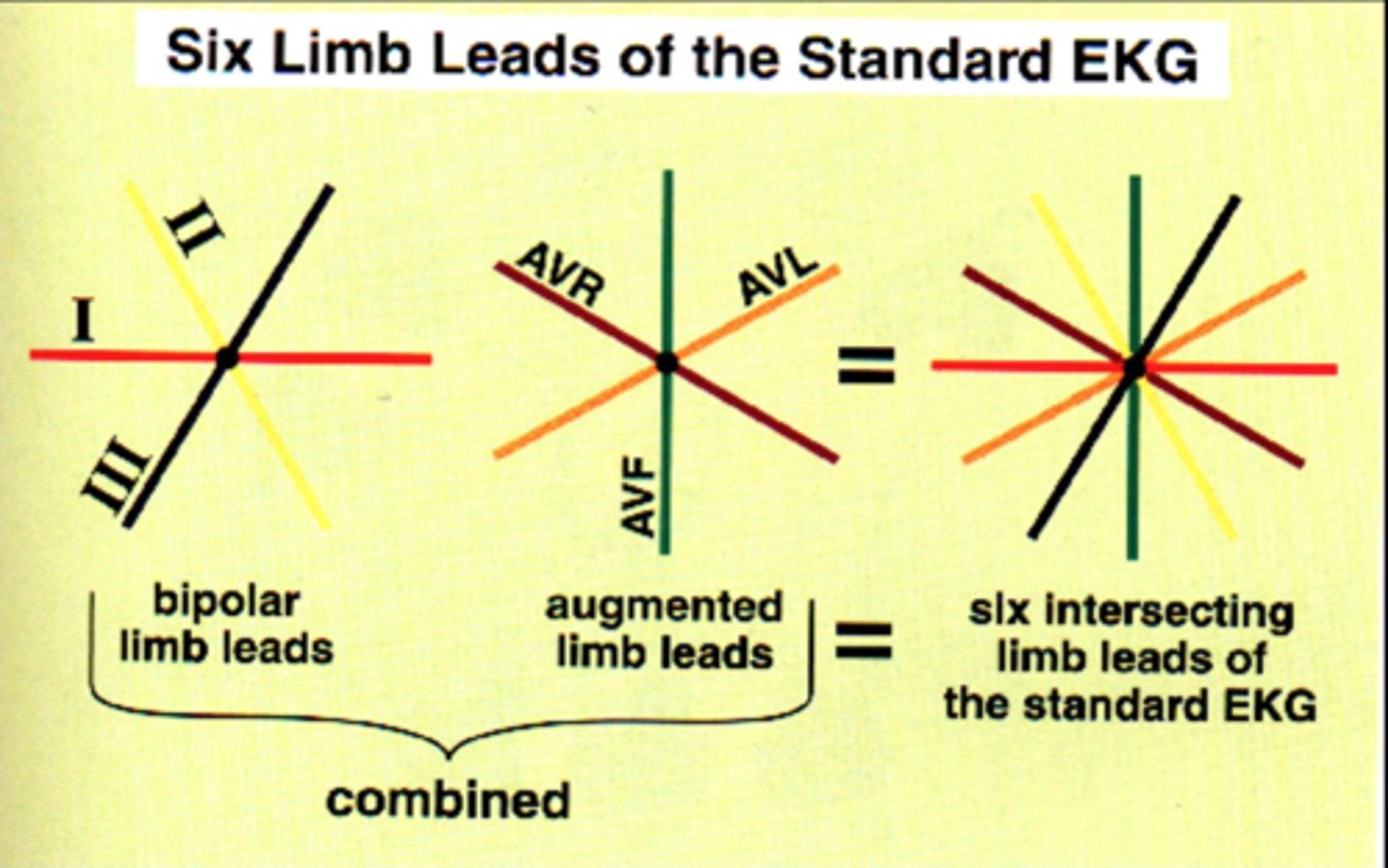
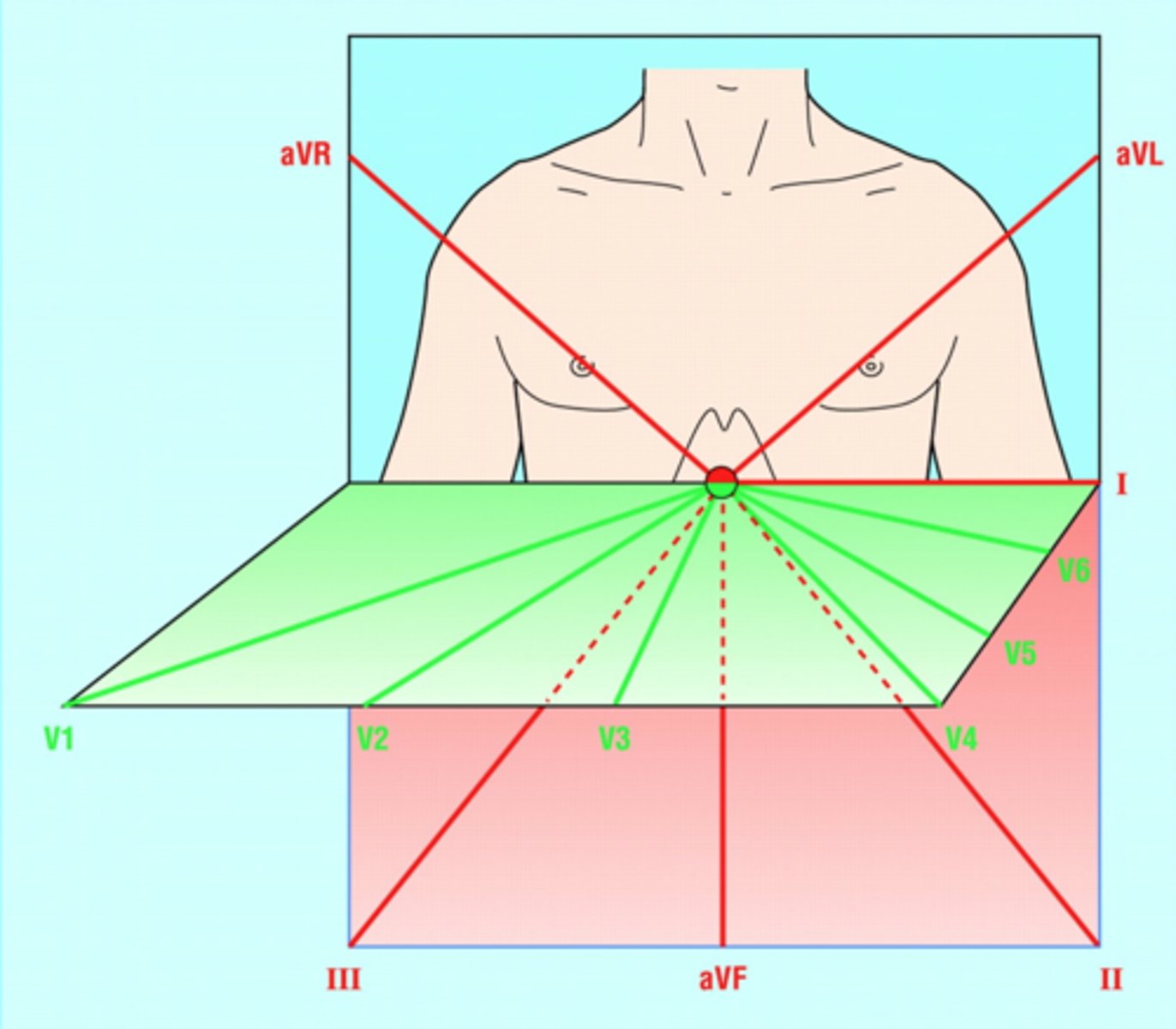
The six limb leads consist of the three bipolar limb leads, ___ , ___ , ___ , and three unipolar/augmented leads, ____ , _____ , _____.
The six limb leads consist of the three bipolar leads, I, II, III, and three augmented leads, aVR, aVL, aVF.
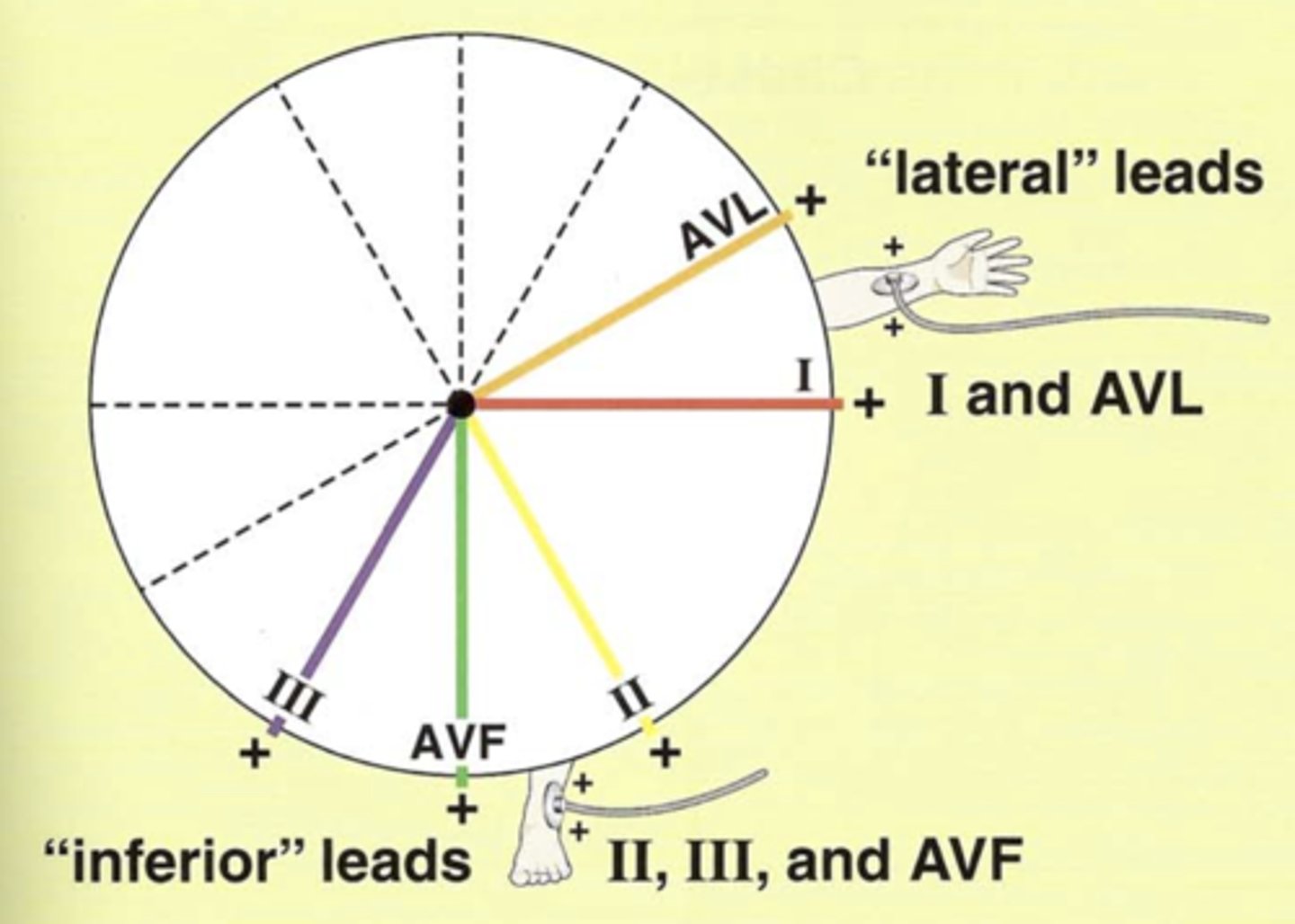
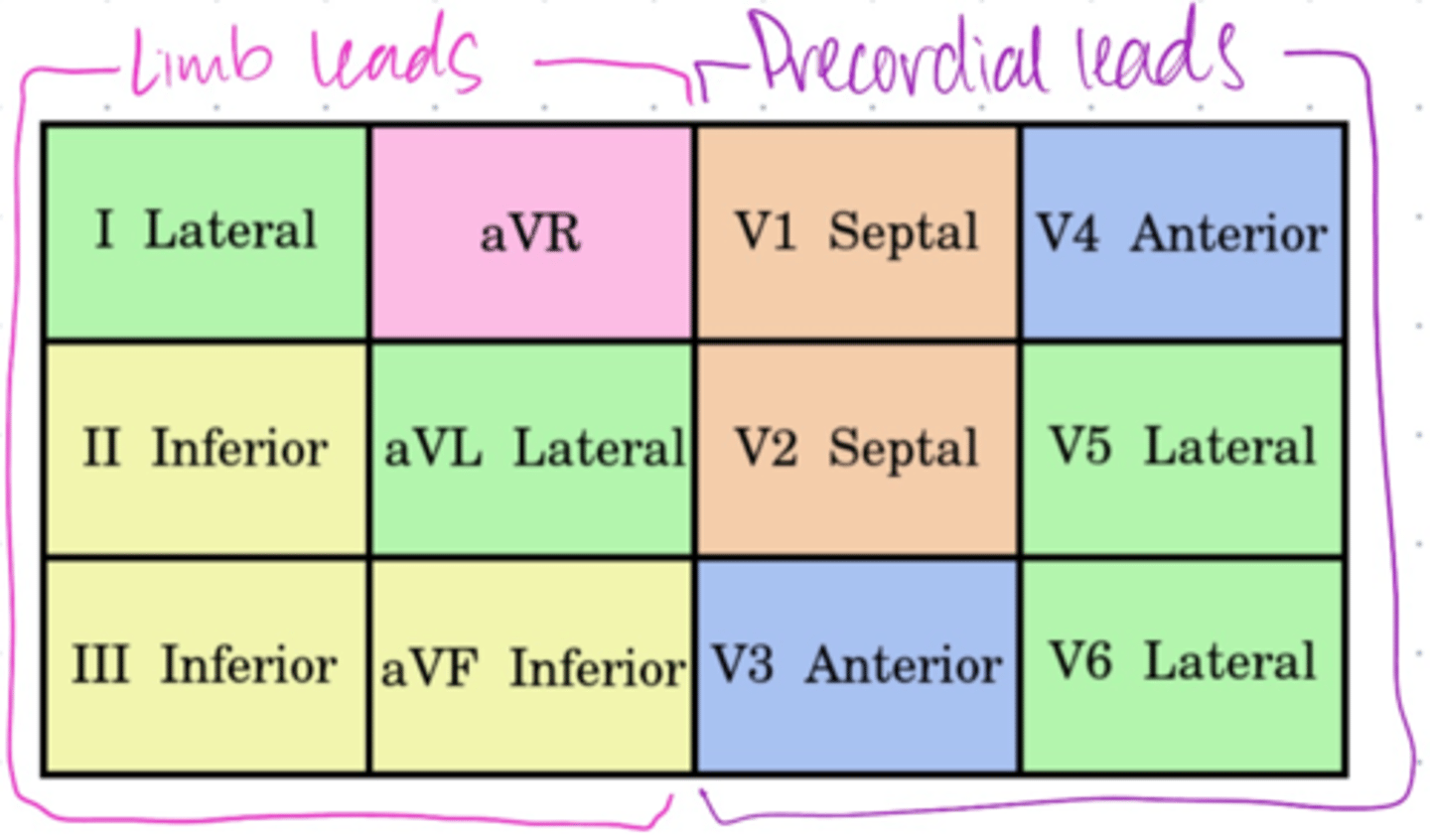
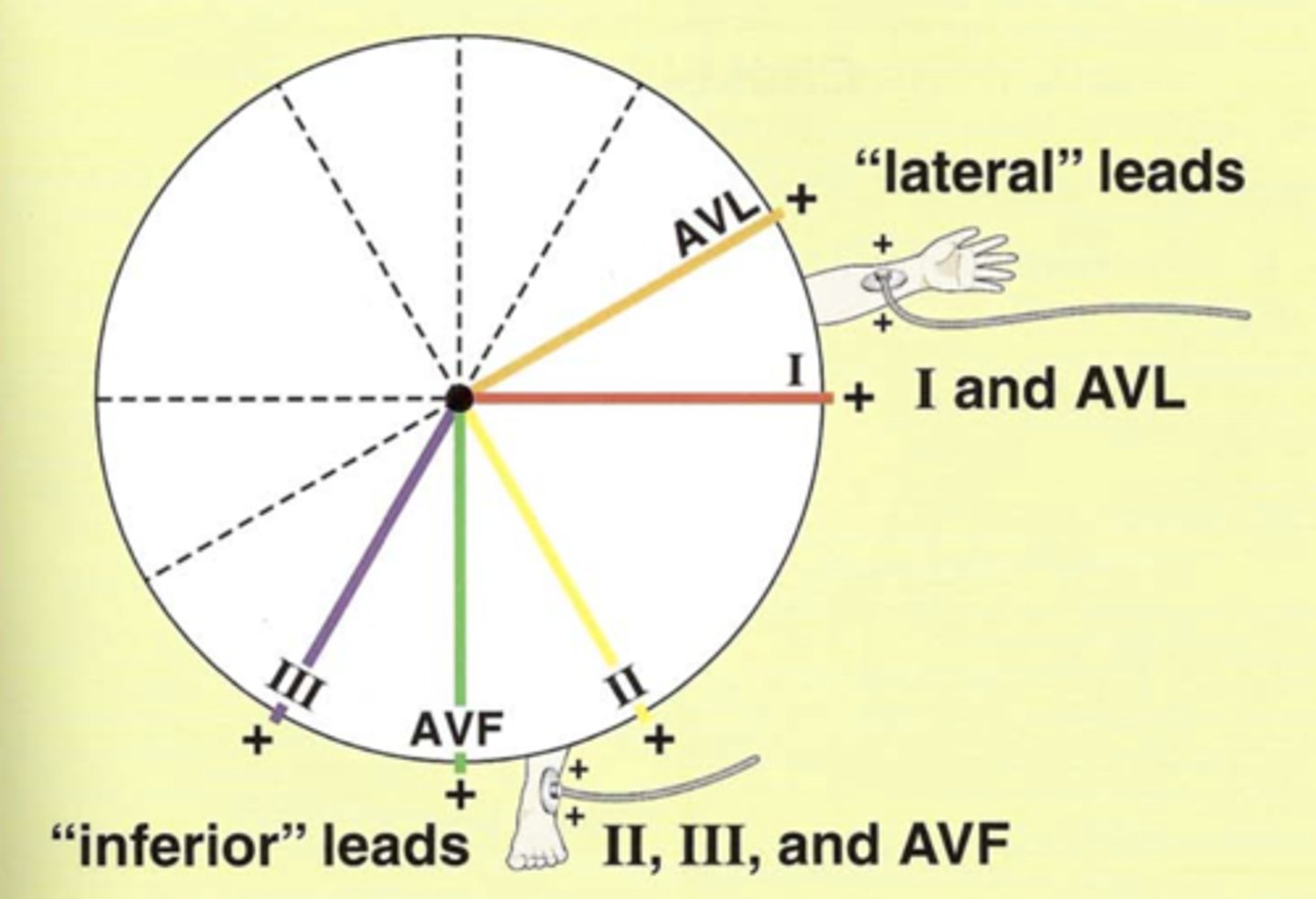
Lateral leads in frontal plane (2)
Have a _____ electrode positioned laterally on ____ _____.
I and aVL
Have positive electrode positioned laterally left arm.
**LAteral leads, Left Arm**
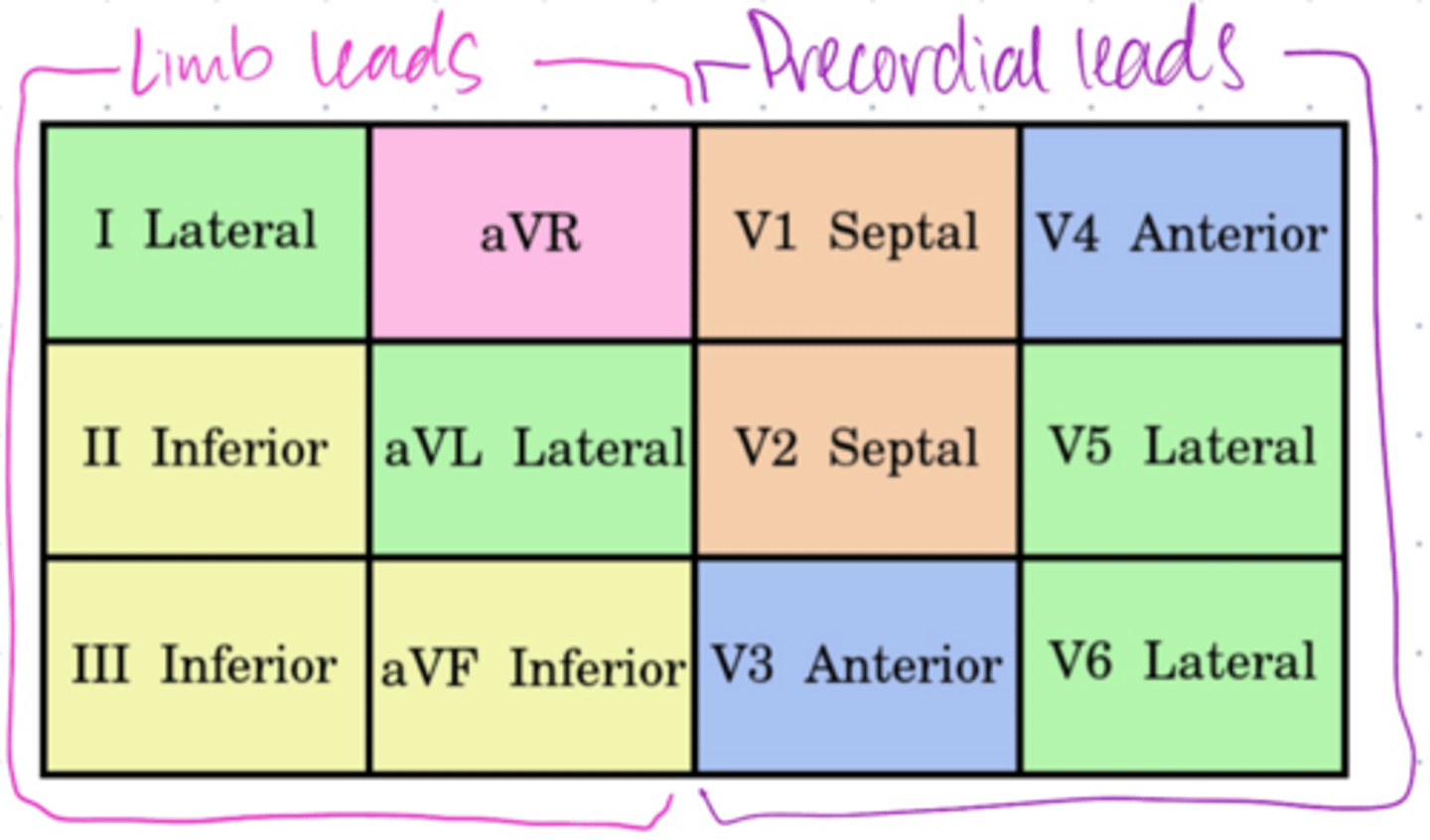
Inferior leads (3)
Have ______ electrode on ____ foot.
II, III, and aVF
Have positive electrode on left foot.
______ leads allow you to determine if depolarization is moving toward/away from the patient's _____ side and inferiorly toward the ______ foot.
Limb leads allow you to determine if depolarization is moving toward/away from the patient’s Left side and inferiorly toward the Left foot.
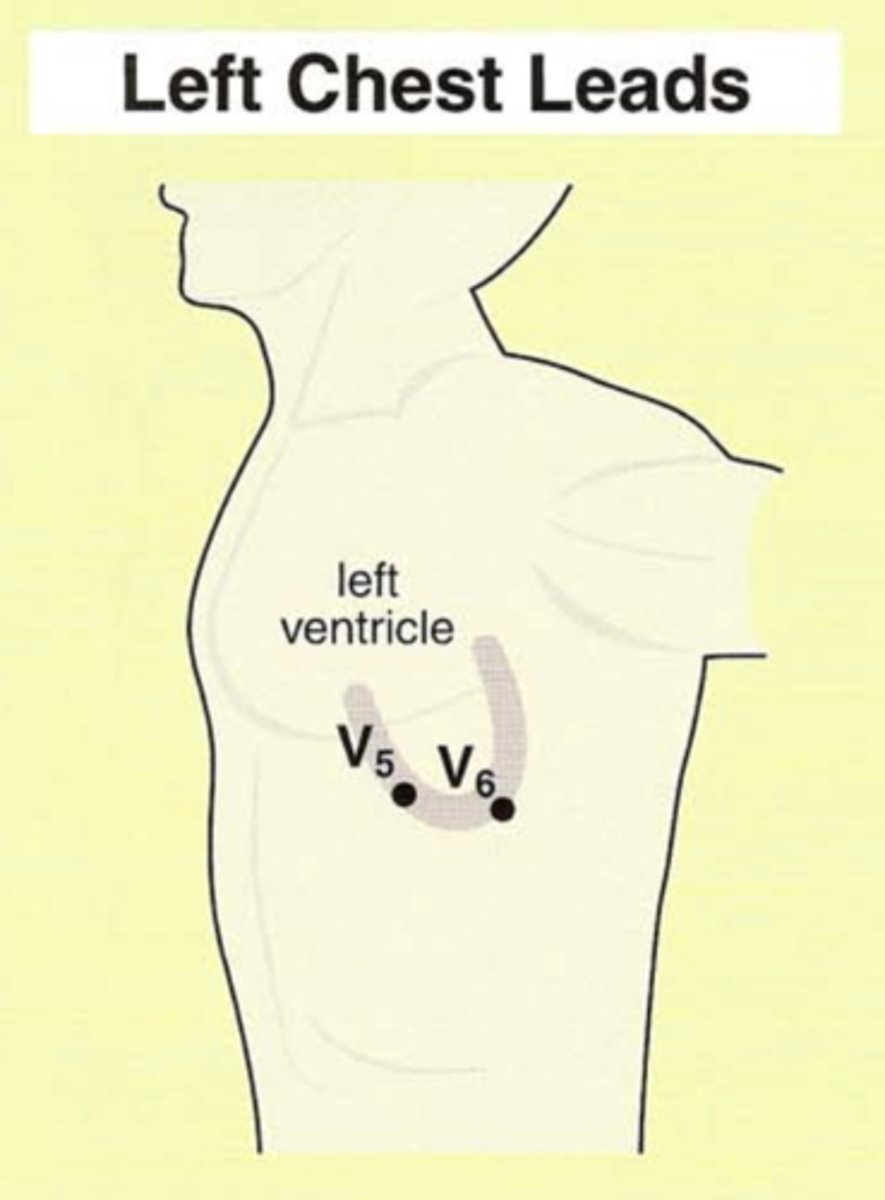
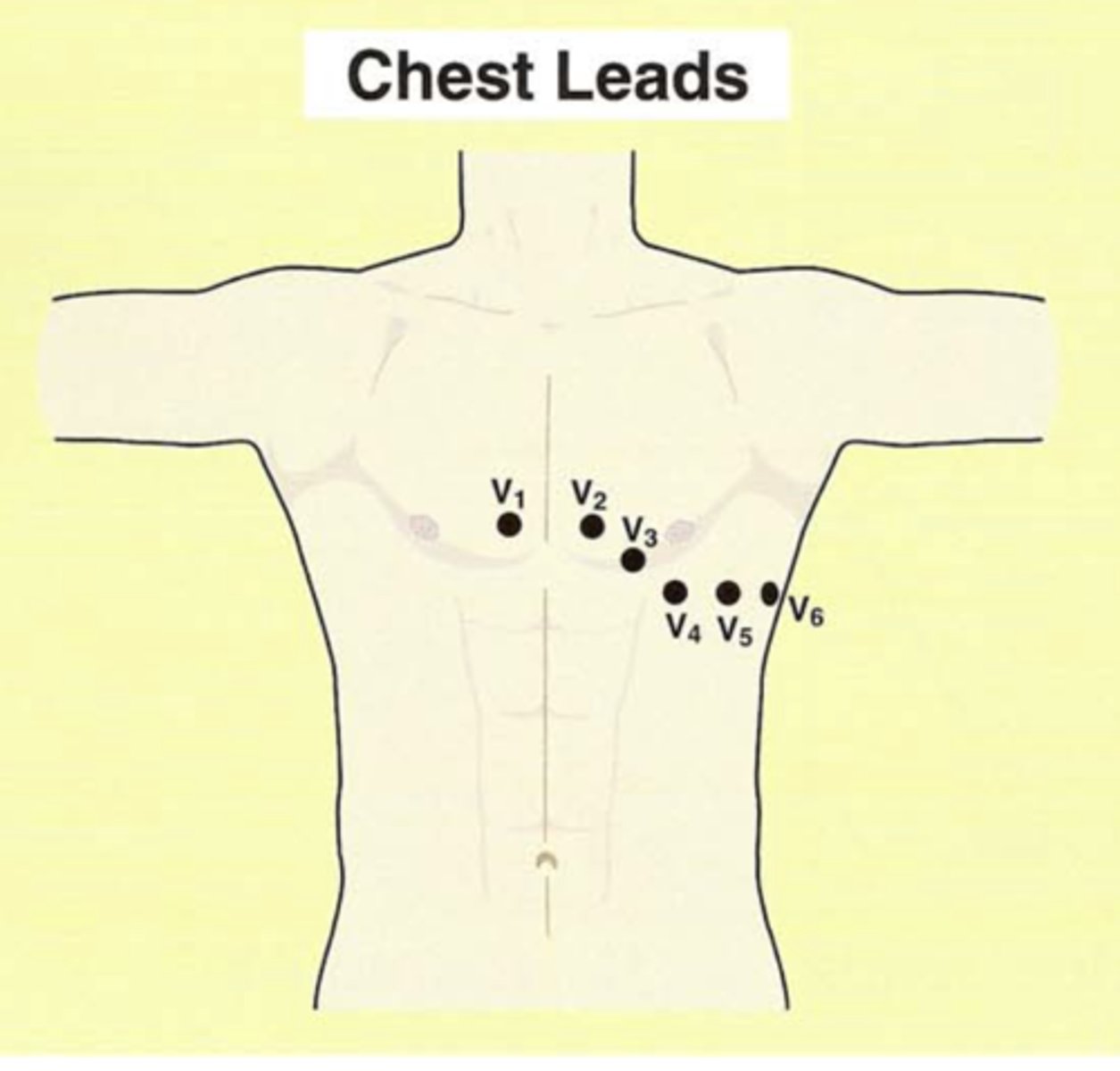
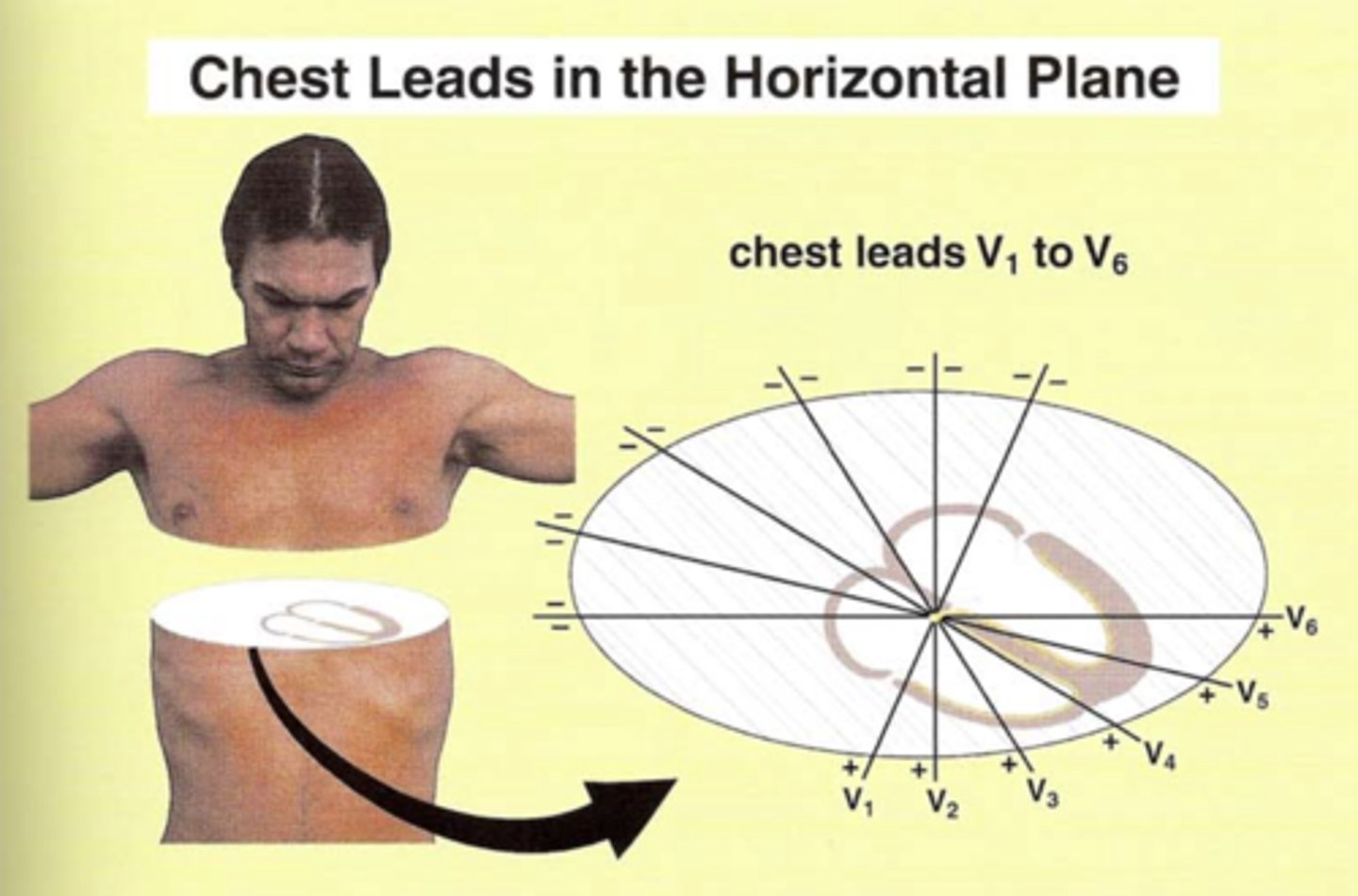
What are the chest leads (precordial leads)?
They are all ________ electrodes.
V1, V2, V3, V4, V5, V6
They are all positive electrodes.
Depolarization moving toward chest lead produces ____________ deflection on EKG.
Depolarization moving toward chest lead produces positive deflection on EKG.
Chest leads look at the heart in the ________ plane.
Each lead (positive or negative?) is oriented through (what node) and projects through the patient's back (positive or negative?)
Chest leads look at the heart in the horizontal plane.
Each lead (positive) is oriented through AV node and projects through the patient’s back (negative)
All six limb leads meet to form (how many?) intersecting leads that lie in a flat “______” plane.
All six limb leads meet to form six intersecting leads that lie in a flat “frontal” plane.
What is R wave progression?
A pattern of progressively increasing R wave (or R wave:S wave ratio) amplitude moving right to left in the precordial leads.
In leads V1-V6.
**V6 might be smaller than V5 because V6 is further from the left ventricle d/t lungs.
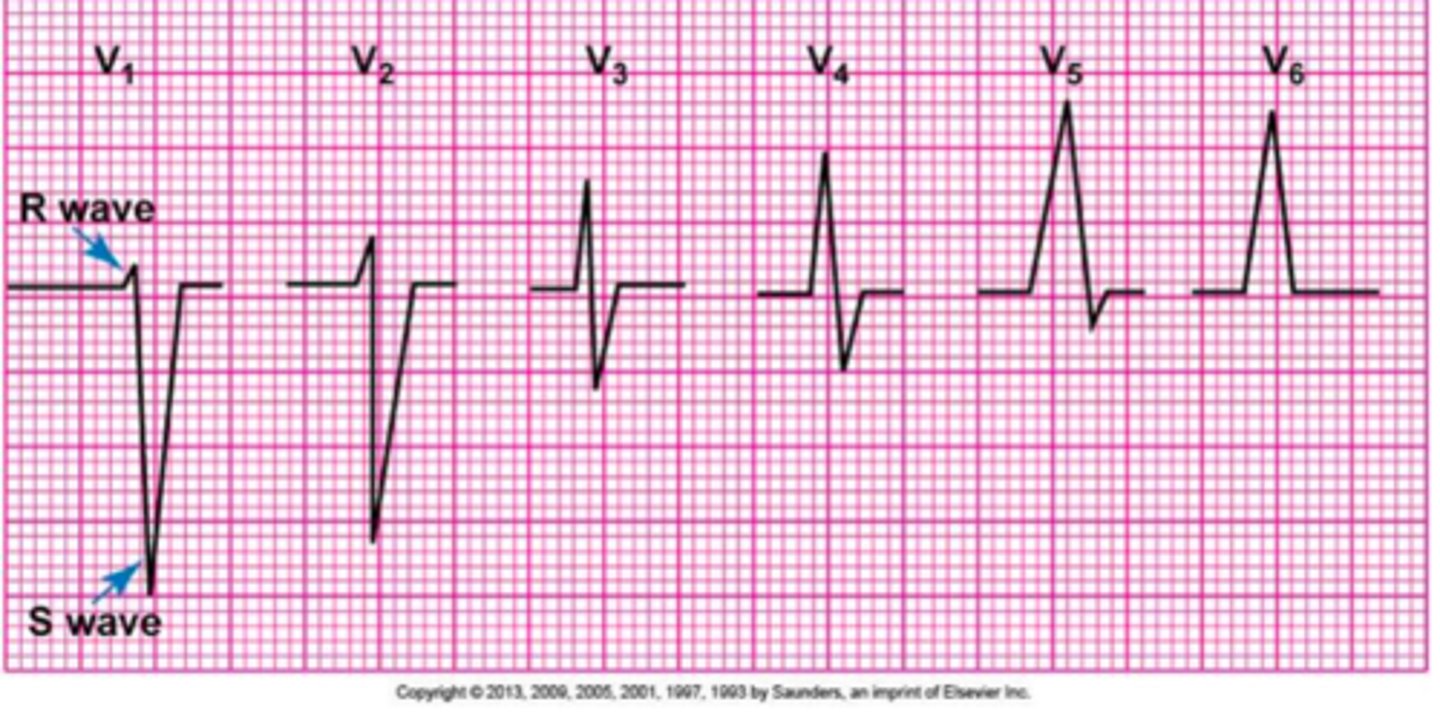
QRS in V1 and V2 mostly positive or negative?
Negative
(Think about r-wave progression)
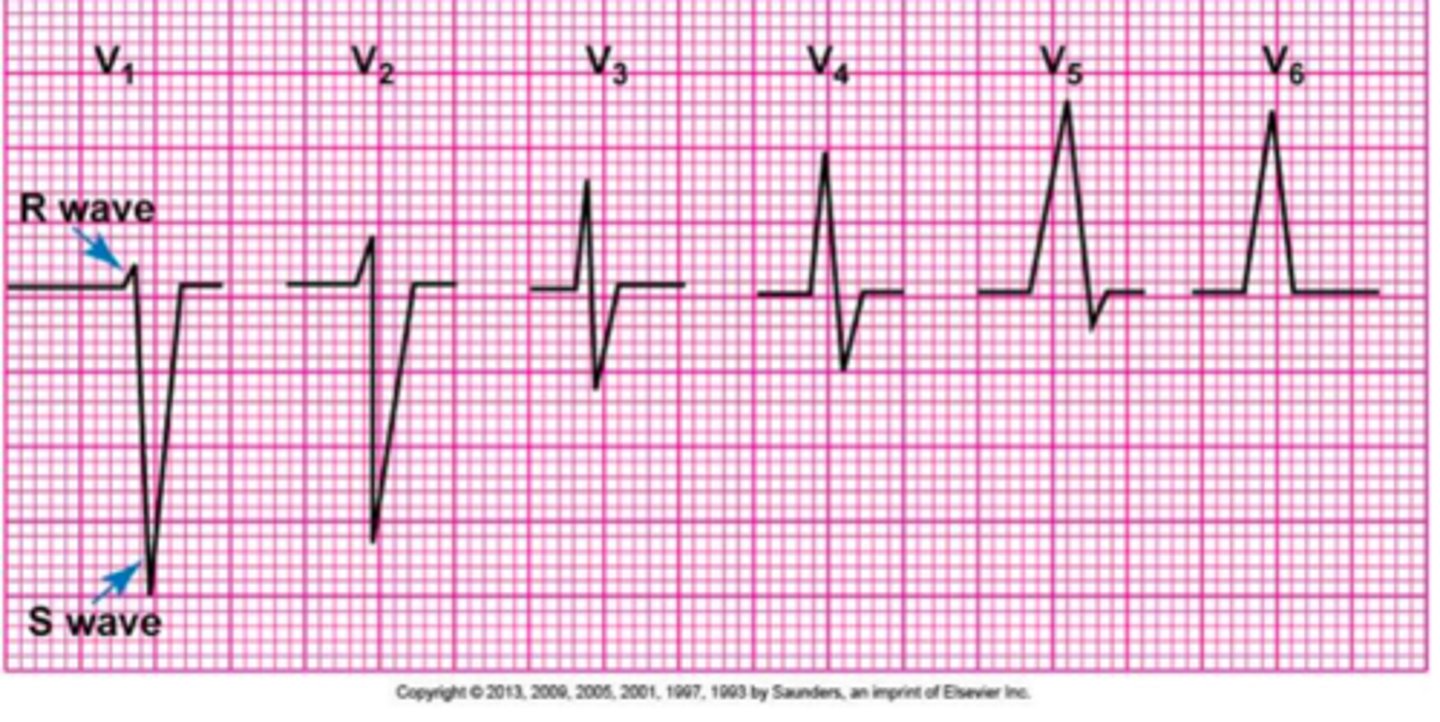
QRS in V5 and V6 are mostly positive or negative?
Positive
(Think about r-wave progression)
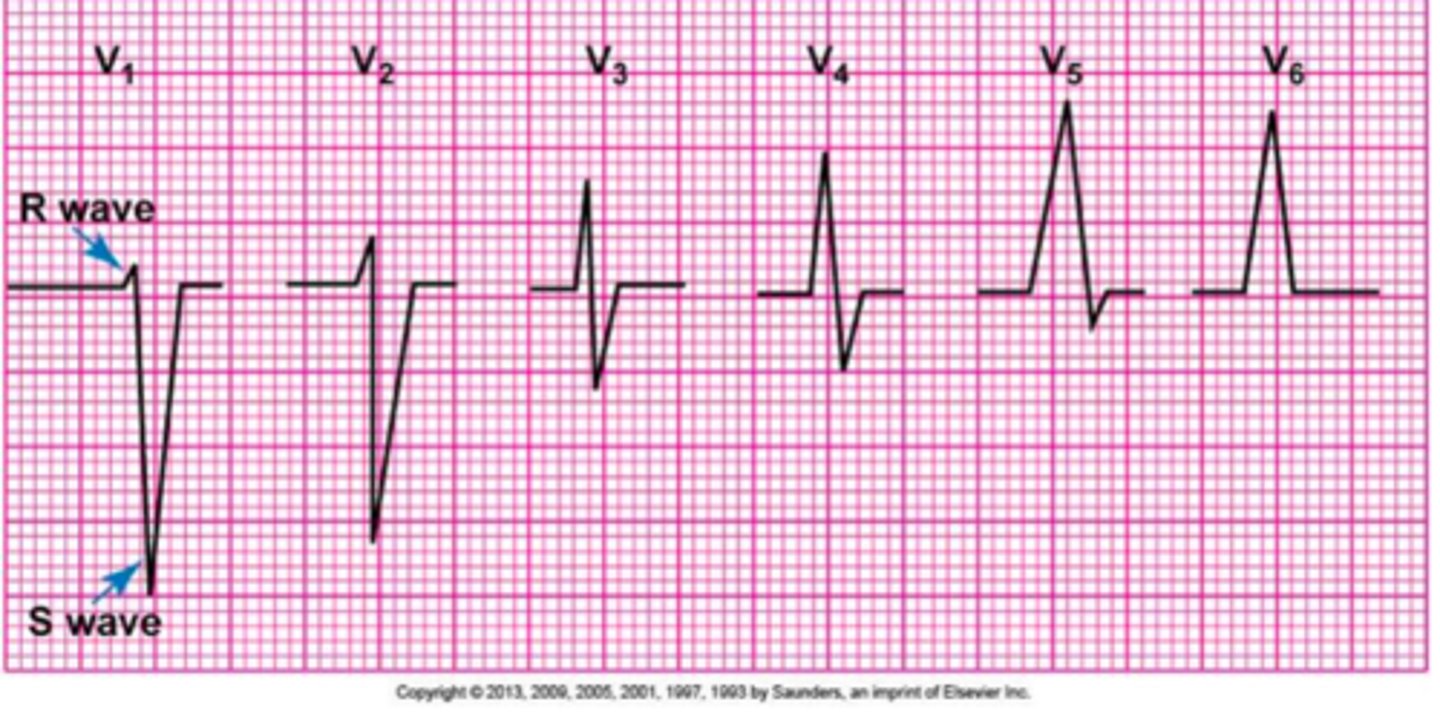
QRS in leads V3-V4 are mostly positive or negative or ....?
Should be mostly isoelectric.
(Think about r-wave progression)
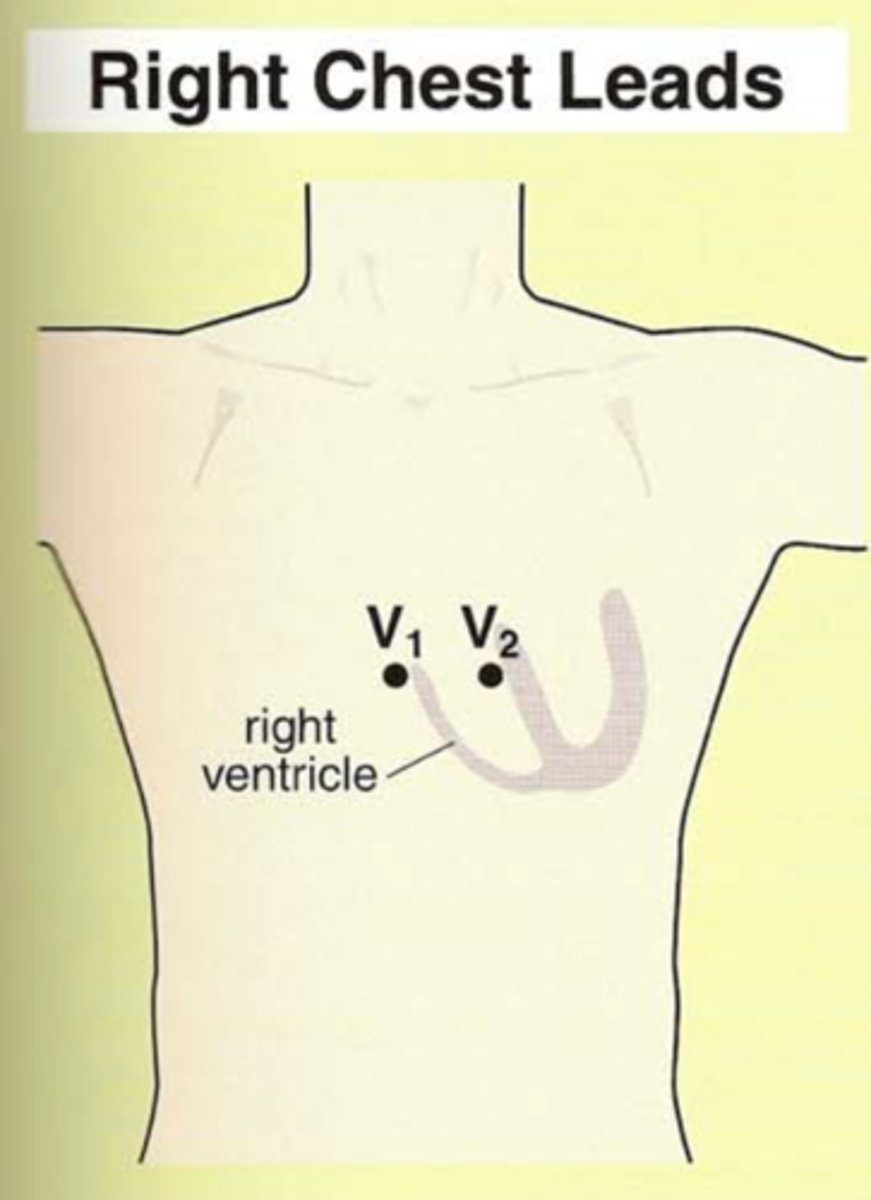
Where are V1 and V2 oriented?
Over right side of heart
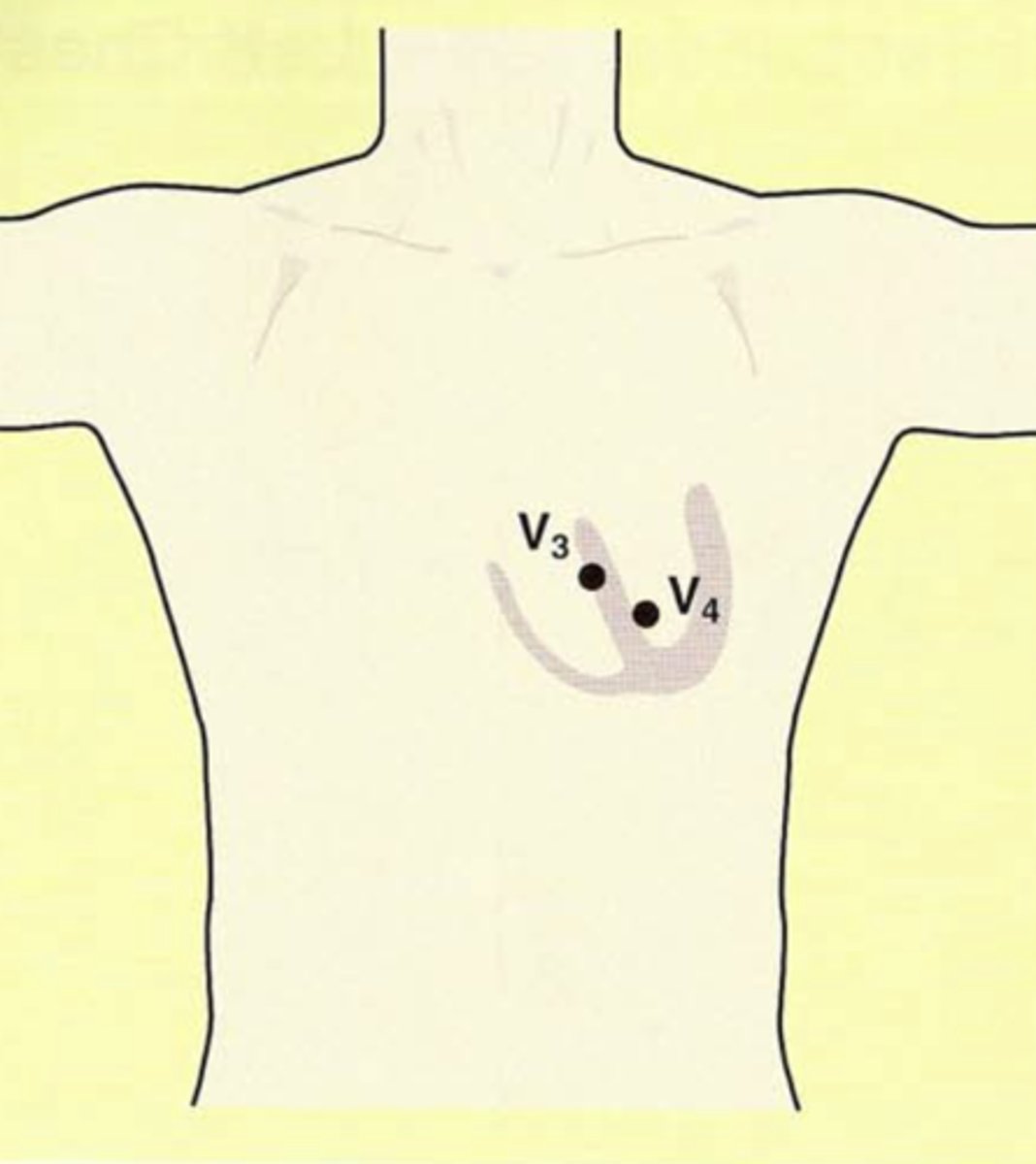
Where are V3 and V4 oriented?
over the intraventricular septum
Where are leads V5 and V6 oriented?
Over the left side of the heart