3.4.3 monopolistic competition
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
characteristics: many sellers
There r numerous firms in the market, each producing slightly differentiated products. These diffs can be based on branding, quality, design, or other factors.
characteristics: product differentiation
Each firm produces a product that is similar but not identical to the products of its competitors. This allows firms to have some control over the price they charge.
characteristics: easy entry + exit
Firms can enter/exit the market relatively easily. There r no significant barriers to entry, such as high start up costs/gov regulations.
characteristics: non-price comp
Firms engage in non-price comp to attract customers. This incl. advertising, product design, branding + customer service.
characteristics: limited price control
While firms have some degree of pricing power due to product differentiation, they face comp from other firms offering similar products. As a result, they can’t significantly raise prices w/o losing customers.
characteristics: imperfect info
Consumers may not have perf info ab all available products, making advertising + branding important tools for firms to differentiate their products.
profit maximising equ in the SR
In the SR a firm maximises its profit by producing the Q of output where MC=MR + setting a price based on its perceived D curve:
Determine the MC + MR for the firm.
Find the Q of output where MC=MR.
Set the price based on the D curve corresponding to that Q.
If the price exceeds ATC at this profit-maximising quantity, the firm will earn econ profit. If the price is less than ATC but greater than AVC, the firm will incur losses but continue to produce in the SR. If the price falls below AVC, the firm will shut down temporarily.
profit maximising equ in the LR
In the LR, firms face competition + have the flexibility to adjust their product characteristics, prices + production lvls:
If a firm is making econ profits, new firms will be attracted to the market due to its attractiveness. This will increase competition.
As more firms enter, the D for each individual firm's product decreases, leading to a decrease in the D curve for each firm.
In the LR, the firm's econ profit will be reduced to 0 as the D curve shifts to the left.
Firms may continue to operate with 0 econ profit, as long as they cover their ATC.
If firms are experiencing losses, some may exit the market + the remaining firms may experience a smaller decrease in D, allowing them to cover their costs.
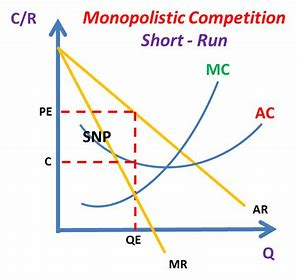
monopolistic diagram SR
At MR=MC, given that AR is above ATC at Q, SNPs r possible (the rectangle).
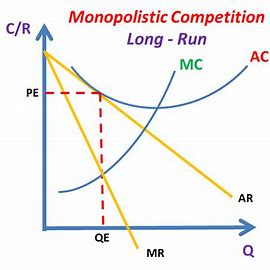
monopolistic diagram LR
In LR, SNP attracts new entrants which shifts D curve for an existing firm to the left.
New entrants only continue until normal profit is available, at which point firms have reached their LR equ.
As choice increases for consumers due to more supply, D for individual firm shifts inwards bc it becomes inelastic