Equine infectious diseases
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
what are the two ways that impact fertility?
infectious and non-infectious
what does equid herpesvirus -1 (EHV-1) cause?
abortions if later than 5 months in gestation
red bag placenta
neonatal foal death
how does EHV-1 affect mares?
infects white blood cells and endothelium
where does EHV-1 establish latency?
latency in leucocytes and trigeminal ganglia
what is red bag placenta?
early placental separation and the foal has no nutrients or oxygen
what are the clinical signs of equine arteritis virus (EAV/EVA)?
flu like with high temperature and increased respiratory rate
conjunctivitis
limb oedema (swollen legs)
what does EAV/EVA cause?
abortions between 3-10 months
how is EAV spread?
shed in semen
how to treat EAV?
symptomatic treatment one at a time and recovery over 1 month
is EAV notifiable?
yes and exotic in the UK
where is EVA harboured in stallions?
in the accessory glands
what happens when EVA is transmitted from stallions to mares through sexual contact?
mated mares develops respiratory tract infection
can mares transfer EVA to other mares?
yes via respiratory transmission and if pregnant will cause abortions
Are stallions infected by EVA always infected?
always seropositive - always have the disease even if no clinical signs or not shedding
how to limit stallions spreading EVA?
castration as stallions do not transmit through respiratory
what is equine herpesvirus 3?
equine coital exanthema
distal reproductive tract
what are the symptoms of equine herpesvirus 3?
vesicles which lead to ulcerated nodules on the penis and clitoris
how is equine herpesvirus 3 transmitted?
sexually transmitted through reciprocal contact
how is equine herpesvirus 3 treated?
it is self limiting
susceptible to antibiotics which may be required if secondary bacterial infection occurs
what are the two ways for prevention of diseases?
biosecurity and quarantine
which viruses have vaccines available?
equine viral arteritis and equine herpes virus 1 both have inactivated virus as vaccines which cause no disease but an immune response
what causes contagious equine metritis (CEM)?
taylorella congenitalis
what is the structure of taylorella congenitalis?
gram negative, coccobacillus, slow growing, partial anaerobe
what does CEM cause?
subfertility
early return to oestrus due to loss of pregnancy
inflammation of the reproductive tract
smelly mucous discharge
where can the CEM bacteria live in mares and stallions?
mares = clitoral fossa and clitoral sinuses
stallions = penis sheath, urethral fossa and sinus and distal urethra
how is CEM transmitted?
sexually transmitted through reciprocal contact
how is CEM controlled?
susceptible to local and systemic antibiotics and topical washes
what does klebsiella pneuomoniae and E.coli cause?
placentitis - inflammation of the placenta
placental separation and abortion
how does an umbilical cord torsion cause reproductive issues?
it twists and prevents nutrients getting to the foal
how does twins cause reproductive issues?
dangerous for mare and foal as the placenta can only expand to a certain size and so mare is under stress and foals are unlikely to survive
how does degenerate endometrium in aged mares pose a problem?
difficult to get pregnant and maintain pregnancy as nutrient transfer is less efficient and more difficult
what does poor perineal conformation cause?
pneumovagina
suck air into vagina and causes infection
what is mare reproductive loss syndrome caused by?
spiny caterpillars
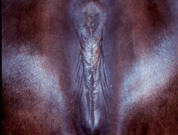
what is good perineal conformation?
perineum vertical
clean vulva and tract

what is poor perineal conformation?
sunken rectum
faecal/bacterial contamination of tract
what causes poor perineal confirmation?
loss of fatty deposits behind the anus and vagina
what does poor perineal confirmation cause (2)?
defecating over the vulva and infections enter the endometrium
sunken over the pelvic bone can cause air sucking
how can you prevent infections due to poor perineal confirmation?
caslicks surgery
what is caslicks surgery?
stitching part of the vulva to prevent a wide opening
how do pregnant mares give birth with caslicks surgery?
it is cut open before foaling and it won’t hurt due to being fibrous tissue
what does retained foetal membranes cause?
can be fatal due to uterine infections which develop
high temp, lethargic and potentially colic
may lead to laminitis