Nutrition
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Define Autotrophic organisms and the 2 types
Autotrophic - organisms that make their own food from simple inorganic molecules
Photoautotrophic - use light energy to make food via photosynthesis
Chemoautotrophic - use energy from chemical reactions
Define Heterotrophic organisms
organisms that consume complex organic molecules for nutrition
Define Saprotrophic , Parasitic and Holozoic Nutrition carried out by Heterotrophic organisms
Saprotrophic - used by fungi to feed on dead/decaying matter
Parasitic - obtain food from another living organism the host (Endoparasites - live in body of host, Ectoparasites - live on surface)
Holozoic - food is ingested, digested, absorption of nutrients, assimilation and egestion using a specialised disgestive system
Describe nutrition in unicellular organism Ameoba
-Holozoic Nutrition
-food taken in my endocytosis + digested by lysosomal enzymes
-products absorbed into cytoplasm
-remains egested by exocytosis
Describe nutrition in multicellular organism Hydra
-Hydra lives in freshwater
-simple undifferentiated tube like gut with single opening
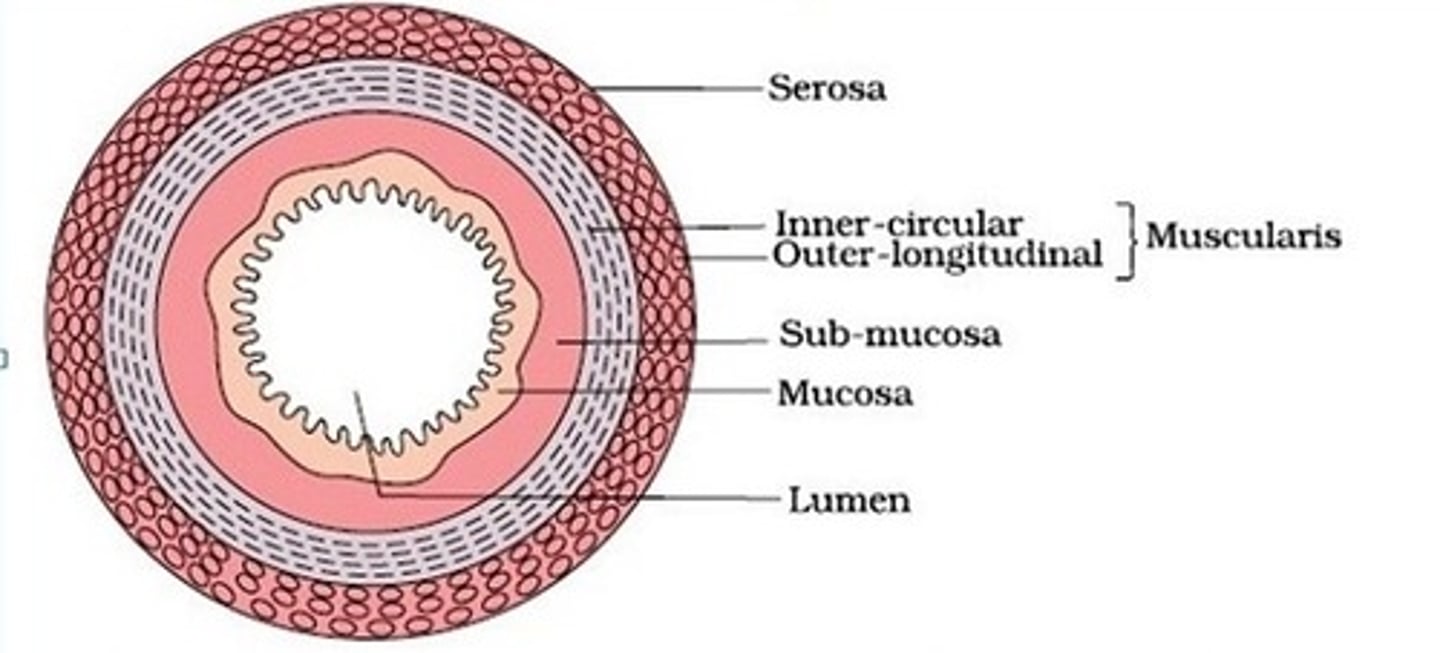
Describe structure + function of Gut wall (in order)
-lumen surrounded by epithelium
-mucosa -> innermost layer of wall where epithelium secrets mucus to lubricate + protect mucosa
-submucosa -> made up of connective tissue containing, blood vessels, nerves and lymph vessels which remove absorbed digestion products
-muscle of mucosa
-circular + longitudinal muscle -> help carry out peristalsis
-serosa -> tough connective tissue which protects gut wall by reducing friction with other organs when gut moves whilst processing food
Explain role of Buccal Cavity
-mechanical digestion of food to increase surface area
-so saliva can mix with food which has amylase to break down starch + glycogen into maltose
-lubricates food for passage down oesophagus
Explain role of Stomach
-food mixes with gastric juice as wall contracts rhythmically to mix it
What is gastric juice made from and where is it secreted from?
-secreted from gastric pits
-contains peptidases, HCL (to lower stomach pH), mucus (lubricates food + protects stomach wall)
Explain role of Duodenum
-first part of small intestine where lipids + proteins are digested
-bile made in liver + stored in gall bladder passes into duodenum to emulsify lipids by breaking down large globules into smaller ones to increase SA
Explain role of Ileum
-lining of epithelium cells with villi for digestive enzyme synthesis
-carbohydrase to digest disaccharides into monosaccharides
-endopeptidases + exopeptidases to digest dipeptides into amino acids
Explain role of Large Intestine
-undigested food + bacteria + dead cells passes through colon where water in absorbed from them to result in semi-solid faeces stored in the rectum
-colon has less villi then ileum
Explain adaptation of Villi
-microvilli increases SA
-good blood supply to maintain conc gradient
-thin diffusion pathway
-permeable
Role of Saliva
-lubricates food
-contains amylase which starts chemical digestion of starch + glycogen into maltose (hydrolysed further by maltase into alpha-glucose)
Role of Pepsin + Trypsin
Pepsin - type of endopeptidase produced in gastric glands as inactive pepsinogen
-endopeptidases hydrolyse peptide bonds in molecules
-exopeptidases hydrolyse terminal peptide bonds
Trypsin - type of endopeptidase produced in pancreas as inactive trypsinogen activated by enterokinase
-digests proteins in duodenum
Role of Bile salt and Lipase
Bile salt - emulsifies lipids
Lipase - breaks down triglycerides into mono + fatty acids
How and where are fatty acids monoglycerides and fat-soluble vitamins absorbed?
by diffusion from lumen -> epithelial cell -> lacteal
(fatty acids have same process instead they are rearranged into triglycerides before passing into lacteal)
How and where are amino acids and disaccharides absorbed?
Amino acids - by active transport from lumen -> epithelial cell
-> by FC diffusion into capillaries
Disaccharides - active transport from lumen -> epithelial cell -> FC diffusion into capillaries
How and where is glucose and minerals absorbed?
Glucose - by co-transport into lumen -> epithelial cell -> FC diffusion into capillaries
Minerals - by FC diffusion into lumen -> epithelial cell -> capillaries
How and where is water and water-soluble vitamins absorbed?
Water - by osmosis into lumen -> epithelial cell -> capillaries
Water-soluble vitamins - by active transport into lumen -> epithelial cell -> FC diffusion into capillaries
How are amino acids + glucose transported to liver?
via hepatic portal vein