Exam 4- Enzymes that process the genome; DNA replication is semi-conservative; DNA polymerases
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
what are the 3 enzymes involved in polynucleotide synthesis?
- DNA polymerase
- RNA polymerase
- reverse transcriptase
DNA polymerase
- adds one deoxyribonucleoside monophosphate (dNMP) to 3' end of a DNA chain
- requires a DNA template chain and a primer
- primer must have a 3'-OH
RNA polymerase
- adds one ribonucleoside monophosphate (NMP) to 3' end of an RNA chain
- requires a DNA template chain
- can initiate de novo synthesis of RNA
reverse transriptase
- adds one dNMP to 3' end of DNA chain
- requires an RNA template chain and a primer
what is able to digest polynucleotide chains?
nucleases
______ is specific for DNA while ____ is specific for RNA
DNase; RNase
exonuclease
- breaks a phosphodiester bond at ONE END of a polynucleotide chain
- either 5' to 3' or 3 to 5'
endonuclease
- breaks phosphodiester bond WITHIN a polynucleotide chain
- sequence independent/specific
- single strand/ double strand break
excinuclease
breaks 2 phosphodiester bonds within a SINGLE polynucleotide chain
what are restriction endonucleases/enzymes?
- type of endonuclease that only breaks phosphodiester bonds at a specific DNA sequence (restriction sites)
what are palindromic sequences?
Sequences that consist of base pairs that read the same in the opposite direction
true or false: most restrictive enzymes recognize palindromic sequences
true
what is the only enzyme that can link two existing DNA chains by forming a phosphodiester linkage?
DNA ligase
recombinant DNA technology
DNA processing new enzymes that can be used to create new combinations of sequences
what does in vitro DNA ligase do?
- joins two DNA molecules together end-to-end
- joins blunt-ends or compatible sticky-ends created by endonucleases
conservative replication
yields an original intact DNA molecule and one entirely newly synthesized DNA
semi-conservative replication
yields two DNA molecules, each with one parental and one newly synthesized strand
dispersive replication
yields two DNA molecules that are hybrids (or mixtures) of parental and newly synthetized DNA
explain the meselson and stahl experiment
1. E.coli grown in heavy N15; a band forms at the bottom of the tube
2. switches to N14 medium, allowing one round of replication and division
3. only one band in the middle of the tube= part old DNA and part new= NOT conservative
4. repeated step 2; one band in the middle and one at the top of the tube= semi-conservative model true
what does a DNA polymerase with roman numerals represent?
they are from bacteria
what does a DNA polymerase with greek letters represent?
they are from eukaryotes
DNA polymerase _____ DNA synthesis
catalyzes
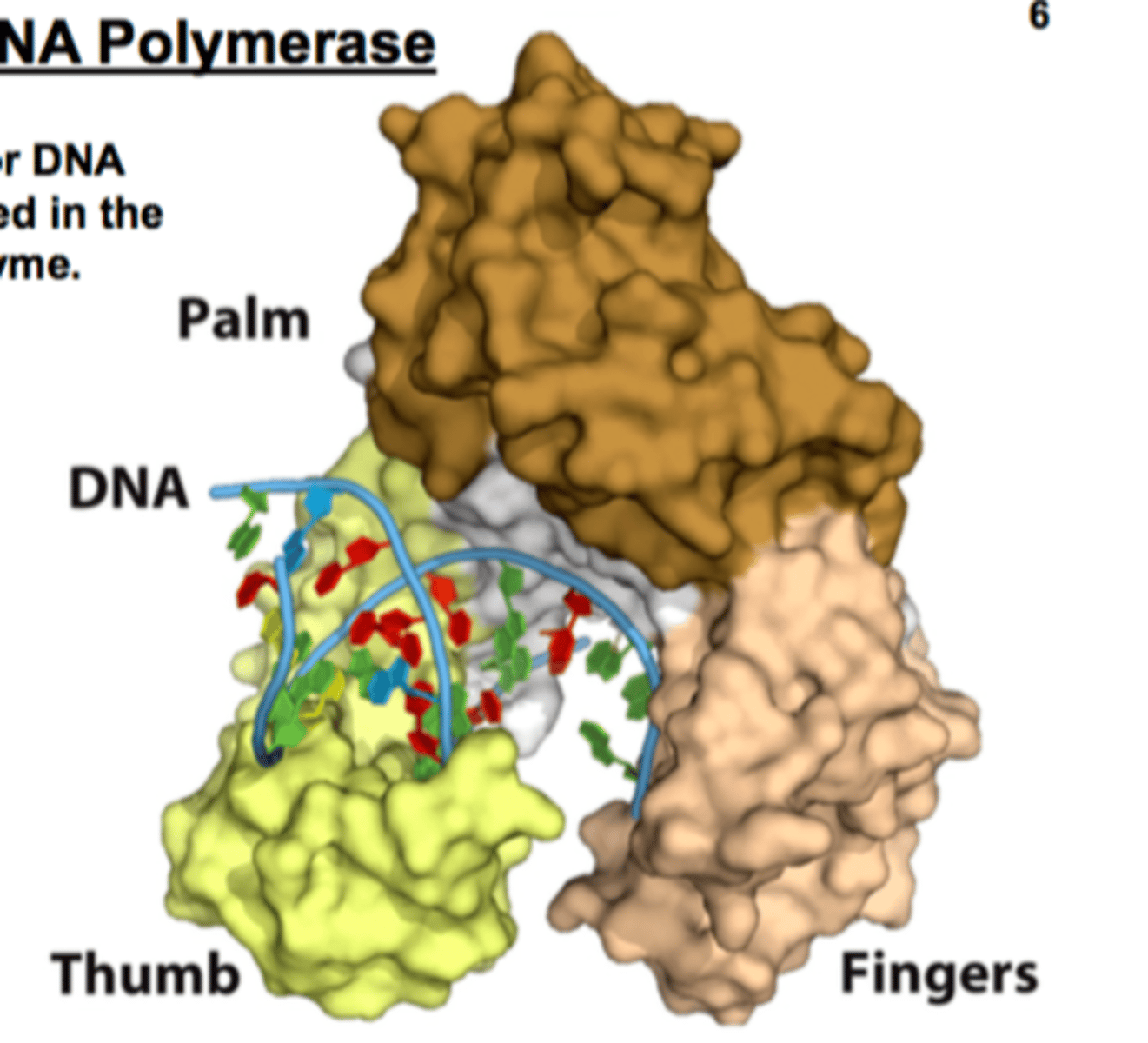
where is the catalytic site for DNA synthesis located?
the palm of the enzyme
Describe the mechanism of DNA polymerase
1. DNA polymerase, the enzyme, catalyzes the extension of a DNA strand one dNMP at a time
2. DNA synthesis starts; The Mg2+ ions facilitates attack of the 3'-hydroxyl group of the primer on the α phosphate of the nucleotide triphosphate
3. the other Mg2+ ion facilitates displacement of the pyrophosphate
4. bond breaks and releases B and y as a pyrophosphate
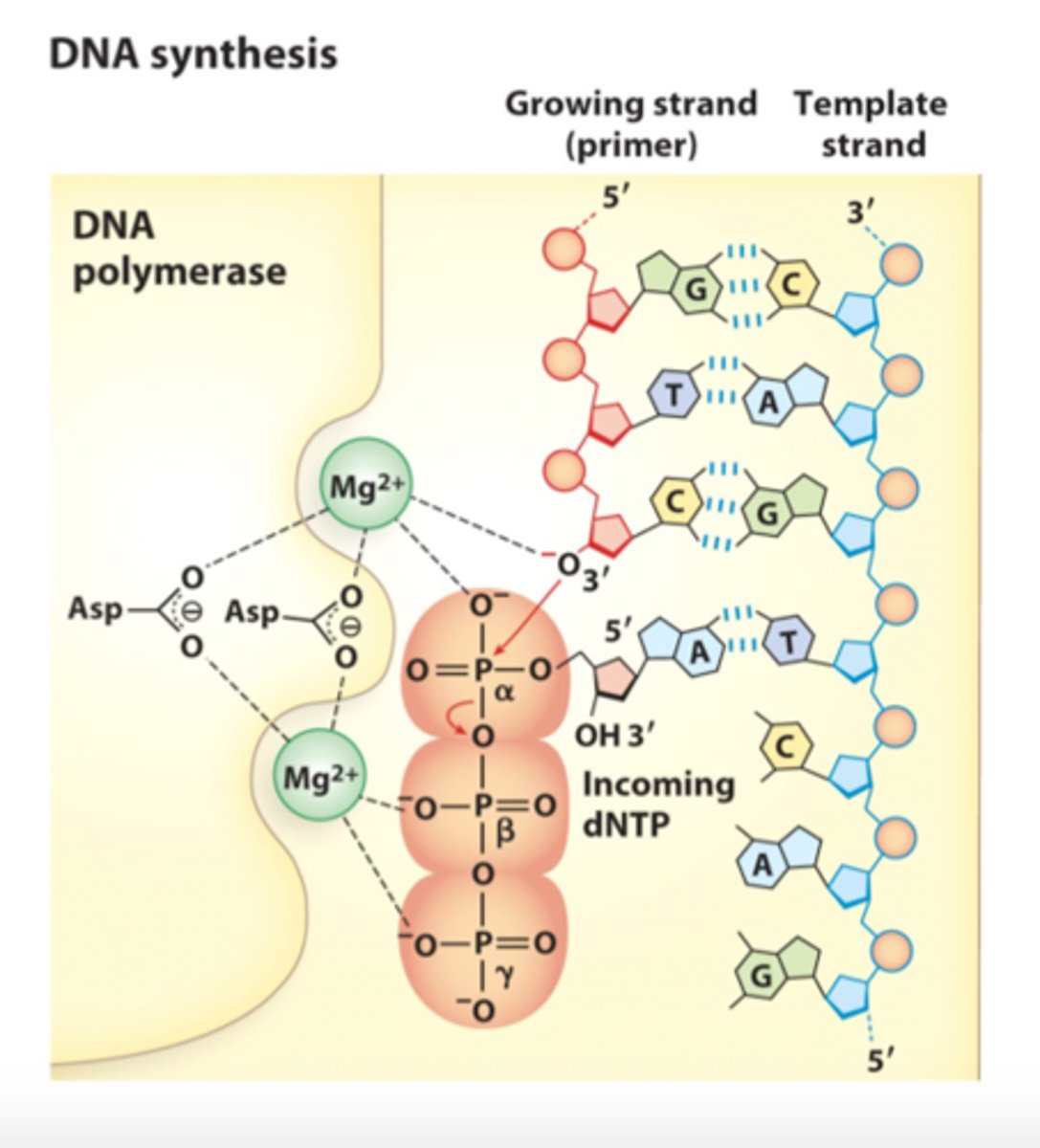
what makes sure that Mg2+ is where it needs to be at the catalytic site?
aspartate
an error in replication can introduce a _____ into the genome. It will be permanent and inherited by subsequent _____ cells
mutation; daughter
what is the average E. coli mutation rate?
- 1 bp in 10^9-10^10 bp
- an error occurs only per 1,000-10,000 replications
how are errors in replication fixed in all polymerases?
- DNA polymerase active site restricts base paring to watson-crick-franklin bp
- "geometry"; if base pairs do not fit into the active site, there is presynthetic error control and they start over
True or false: all polymerases go through proofreading
false
what are the 2 active sites for high-fidelity DNA polymerases?
- a catalytic site for DNA synthesis
- a 3' to 5' exonuclease site for removing mis-incorporated nucleotides
process of proofreading (think of a keyboard and backspace)
1. polymerase mispairs
2. repositions mispaired 3' terminus into 3' to 5' exonuclease site
3. exonuclease hydrolyses mispaired group
4. 3' terminus repositions back to polymerase site
5. polymerase incorporates the correct nucleotide
what are the 2 main prokaryotic DNA polymerases?
DNA polymerase I, DNA polymerase III
what are the cellular roles of DNA polymerase I and III?
genomic replication and DNA repair
compare and contrast DNA polymerase I and III in terms of proofreading, 5'-3' exonuclease, polymerization rate and processivity
- proofreading: both can
- 5'-3' exonuclease: I can, III can't
- polymerization rate: I is lower, III is higher
- processivity: I is lower, III is higher