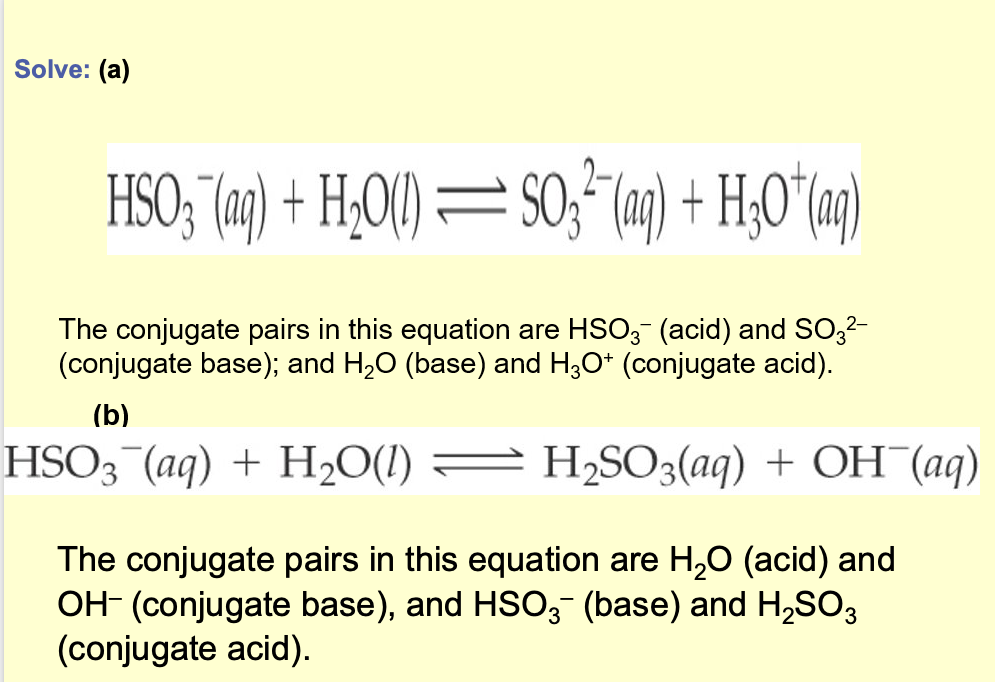Acids and Base equilibria
1/4
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
5 Terms
what happens when an acid dissolve in water ?
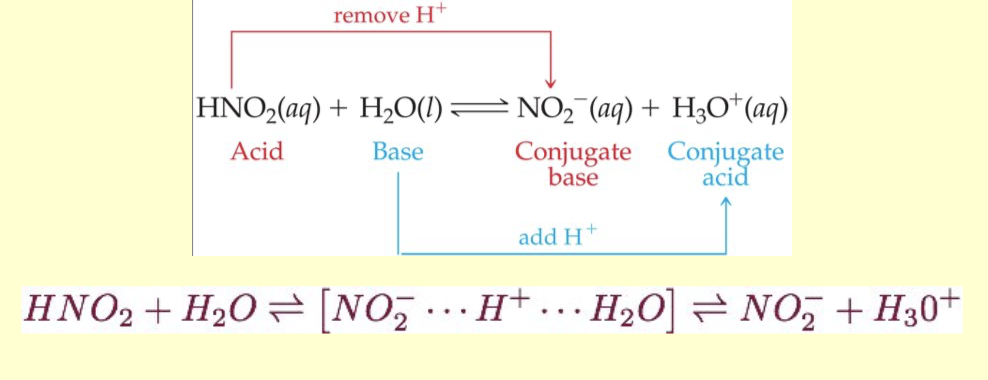
Water acts as a Bronsted Lowry base and abstract a proton H+ from the acid.
Results: Conjugate base of the acid and hydronium ion are formed.
what does conjugare mean ?
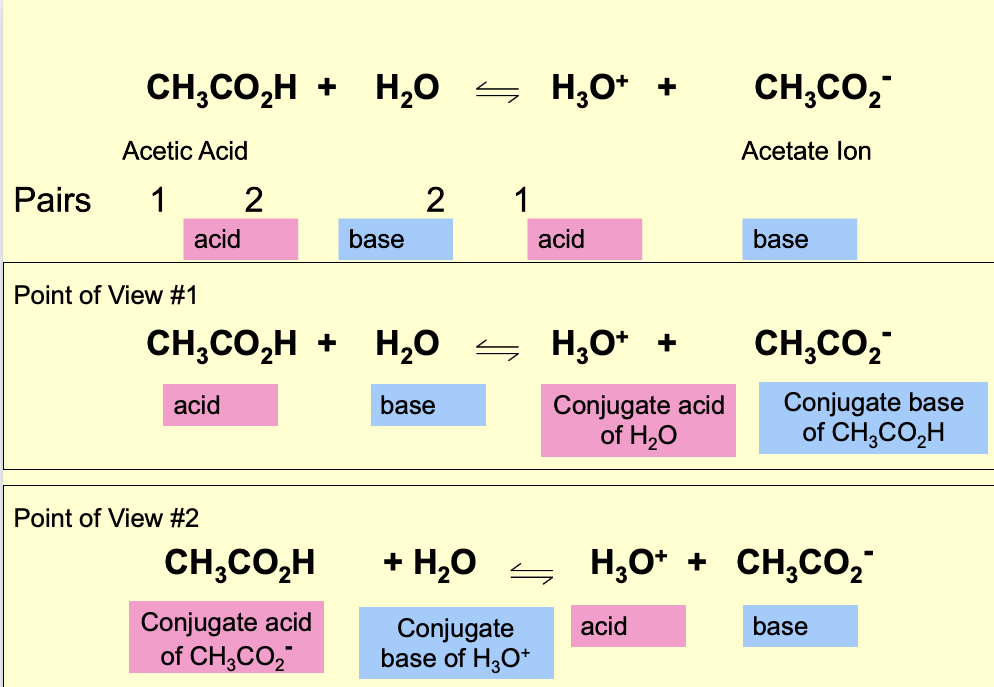
to join together, reactions between acids and bases always yield their conjugate bases and acids.
Identifying Conjugate
Acids and Bases
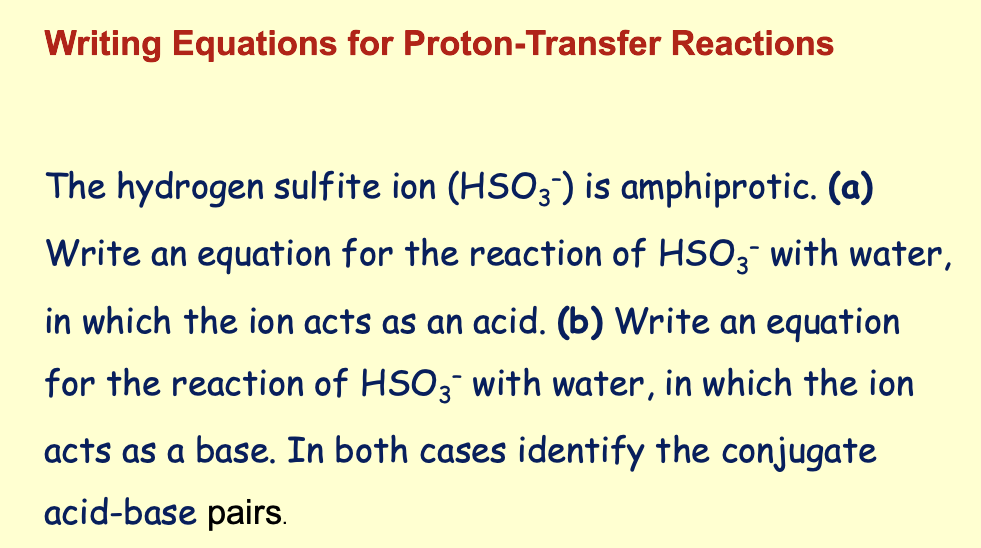
What is the conjugate base of each of the following acids: HCIO 4 , H2S, PH4 + , H CO3-?
What is the conjugate acid of each of the following bases: CN - , SO4 2- , H2O, H CО3- ?
Extra challenge: in which way is HCO3 - different? Can you think of other examples of substances that behave in a similar way?
Solve: (a) HCIO4, less one proton (H*) is CIO4 - The other conjugate bases are HS-, PH3, and CO3 2-
(b) CN- plus one proton (H+) is HCN. The other conjugate acids are HSO4 - , H3O+ and H2 CO3.
Notice that the hydrogen carbonate ion (H CO3-) is amphiprotic: It can act as
either an acid or a base. Another example H2PO4 -.