Nutrition Lecture 2: Lifecycle Systemic Oral Health and Nutrition Clinical Manifestations
1/81
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lecture given 9/24/2025
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
what are some ways oral health would impede proper nutrition?
dental pain, oral surgery, cleft palate (feeding difficulties), wired jaw, dentures, tooth loss, xerostomia
why is good nutrition important pre-pregnancy?
it is vital to prepare for pregnancy
vitamin deficiencies can increase risk for neural tube defects and cleft lip/palate
obesity increases risk of developing gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, and fetal complication
what factors create an increased risk for cleft lip / cleft palate?
inadequate protein, folate deficiency, vitamin B12 deficiency
what are pre-pregnancy dietary recommendations?
taking prenatal vitamin before conception, folate rich foods to prevent neural tube defects
folate rich foods include: dark green leafy vegetables, broccoli, asparagus, citrus fruits and juices, fortified cereals, legumes, beans, nuts, peas
when does tooth development start in utero?
6th week
when does calcification of primary teeth start in utero?
4 months
what vitamins and minerals are important for fetal bone development?
calcium, phosphorous, vitamin D
what are the dietary recommendations for prenatal period?
balanced / healthful diet, adequate energy and protein, wide variety of foods to reduce risks of deficiencies, foods rich in calcium/phosphorous/vitaminD, adqeuate protein/folic acid/vitaminB12, avoid alcohol
when are humans teeth developing?
from before birth to early adolescence (3rd molars)
t/f extended breastfeeding is a protective factor for childhood caries under 1 year of age
true
what is the dietary recommendation for fluoride consumption for an infant?
low in breastmilk
DRI 0.1mg per day for <6 months of age
DRI 0.5mg per day for 7-12 month of age
sources can be fluoridated water or supplemental
what are the dietary recommendations for breastfeeding moms?
adequate energy and protein intake
what are the dietary recommendations for breastfeeding infants?
infants who are exclusively breastfed or don’t consume at least 1L vitamin D fortified formula should be supplemented with 400IU/d
after 1 year of age it is difficult to conclude between protection and aggravation of caries due to confounding factors like…
dietary patterns, oral hygiene, fluoride
what is the recommended intake of calcium for children 1-3 and 4-8, according to the dietary guidelines for americans?
700mg per day, 1000mg per day
what vitamin is needed in conjuction with calcium to allow for calcium uptake?
vitamin D
children drinking sugar sweetened beverages, >5 oz/day were ____ times more likely to have severe ECC than children drinking less than or equal to 1 oz/day
4.5
what are the dietary recommendations for childhood?
limit sugar containing beverages (milk, juice, soda), in bottles and sippy cups for prolonged periods of time
what are the dietary recommendations for teenage years?
limit availability and use of sweetened beverages such as sodas, flavored waters, and sports drinks
avoid fad diets like juice cleanses
the signs of advanced nutrient deficiencies are usually first seen…
in the oral cavity
what are the dietary recommendations for adults?
balanced, healthful diet and eating pattern
keep weight within a healthy range
avoid fad diets
what factors relating to nutrition does aging affect?
ability to digest and absorb nutrients (intrinsic factor and vitamin B12)
lack of salivary flow (dry mouth)
appetite
hydration status
medication side effects
decreased sense of taste and smell
dentures
what are some functional barriers to good oral health that seniors may experience?
reduced ability to prepare food due to arthritis or impaired vision
reduced ability to chew and swallow due to missing teeth or dentures
what are some psychosocial barriers to good oral health that seniors may experience?
lack of access to food/grocery store (inability to drive, unable to carry groceries, not knowing how to prepare food)
lack of desire for healthy diet (loneliness, depression)
finances
good nutritional status and periodontal diseases
good nutrition can be protective- all nutrients are necessary to create oral tissues and structures, keep oral tissues healthy, enhance immune system to fight infections, and aid in wound healing
poor nutritional status and periodontal diseases
poor nutrition can play a role in modifying the progression and severity of disease
difficulty fighting infection and inflammation
what nutrients are important for healthy periodontium?
vitamin D, A, B complex, C, and protein, iron, zinc, calcium, lipids, fiber, and probiotics
why is vitamin D important for healthy periodontium?
calcium/phosphorus/magnesium absorption, deficiency is linked to periodontal disease, bone metabolism
why is vitamin A important for healthy periodontium?
builds and maintains epithelium, enhances immune system, salivary gland function
why is vitamin B complex important for healthy periodontium?
formation of new cells, cofactor for nutrients, periodontal wound healing, collagen synthesis (biotin)
why is protein important for healthy periodontium?
promotes growth maintenance and repair of all tissues
why is vitamin C important for healthy periodontium?
aids in collagen formation, deficiency causes ascorbic acid gingivitis, enhances immune response
why are iron and zinc important for healthy periodontium?
aids in collagen formation, wound healing, regulates inflammation
why is calcium important for healthy periodontium?
builds and maintains alveolar process
why is lipid important for healthy periodontium?
omega 3 fatty acids have anti inflammatory properties
why is fiber important for healthy periodontium?
controls serum glucose and inflammatory response, deficiency is linked to periodontal inflammation
why are probiotics important for healthy periodontium?
strengthens immune system, inhibits colonization of harmful microorganisms
cariogenic
fermentable carbohydrates that are metabolized by oral bacteria cause pH of plaque to drop below 5.5
acidogenic
ability of a food to directly cause pH of plaque to drop below 5.5 within 30 minutes
non-cariogenic
food that contributes favorably to dental health by discouraging acid production
cariostatic
inhibits caries formation
what is the pH range where enamel begins to demineralize?
5.5-5.7
what is the pH where cementum begins to demineralize?
6.7
what is caries risk determined by?
contributing factors like plaque bacteria, fermentable carbohydrates, and frequency of intake of carbohydrates
protective factors like fluoride, oral hygiene, diet, saliva (supersaturated with calcium and phosphate, pH of 7 favors remineralization)
is there a steep or moderate slope of pH drop for simple sugars?
steep
is there a steep or moderate slope of pH drop for starches?
moderate
the more total time plaque is below critical pH, theoretically…
the greater the potential risk of caries
which type of sugar are the main players in the development of caries?
sucrose, fructose, glucose, and maltose
lactose has low cariogenicity except when milk in a bottle at bedtime
what do starches become in the oral cavity?
salivary proteins convert starch to maltose
what are some dietary patterns and food factors that help can contribute to the development of caries?
frequent snacking/drinking sugary beverages, physical form of carbohydrate, retentiveness of a food on the tooth surface, sequence in which foods are eaten
between sticky/starchy/solid foods and sugary beverages, which are most likely to contribute to tooth decay?
sticky, starchy, solid foods
t/f drinking a high sugar beverage alone causes a less rapid drop than when it is had with a meal
false- more rapid alone
what can be eaten before a sweet treat to limit a pH drop?
cheese!
t/f manufacturers can use lots of different names for sugar and when there are multiple used, they are listen on a food label in descending order by weight
true
list some non-cariogenic/cariostatic foods
cheese- limits pH drop, stimulates salivary flow, has proteins/calcium/phosphate which neutralizes plaque acids
fats- caries protective, increases oral clearance
erosion
loss of tooth enamel not due to bacteria
occurs when the pH is between 2.4-4.6
which acids contribute to erosion?
citric, phosphoric, ascorbic, malic, tartaric, carbonic
what are some of the most common acidogenic foods?
diet/regular sports and energy drinks, flavored water, diet/regular soda, fruit juice and drinks, citrus fruit, vinegar, alcohol
t/f is something is acidogenic, it cannot be cariogenic
false- can be both
how can you avoid tooth erosion?
bypass the teeth by drinking out of a straw, avoid acidogenic beverages, rinse mouth with water to neutralize salivary pH to 7, chew gum with xylitol
what can cause vitamin deficiencies?
inadequate intake, impaired absorption, increased requirements, increased metabolic demand, major surgery, chronic disease, problems with utilization, inadequate, food/drug/supplement interactions
list the key nutrients for development and maintenance of the oral cavity
B complex, C, A, D, vitamins
calcium, fluoride, protein
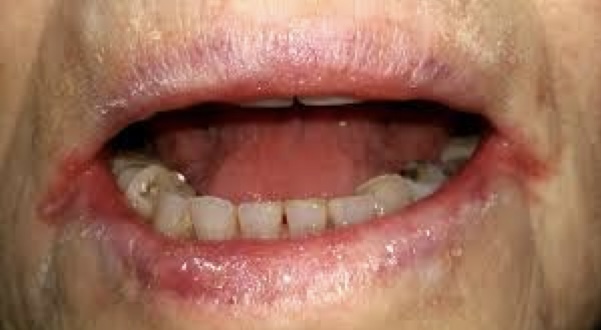
what is this condition and what vitamins is this person likely deficient in?
angular cheilitis
B1, B2, B3, B6
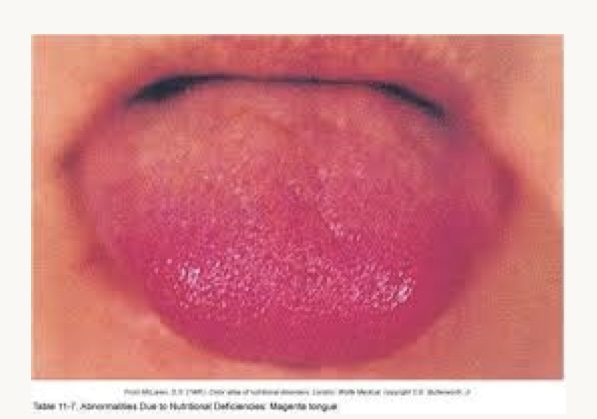
what is this condition and what vitamins is this person likely deficient in?
magenta tongue
B2 (riboflavin)
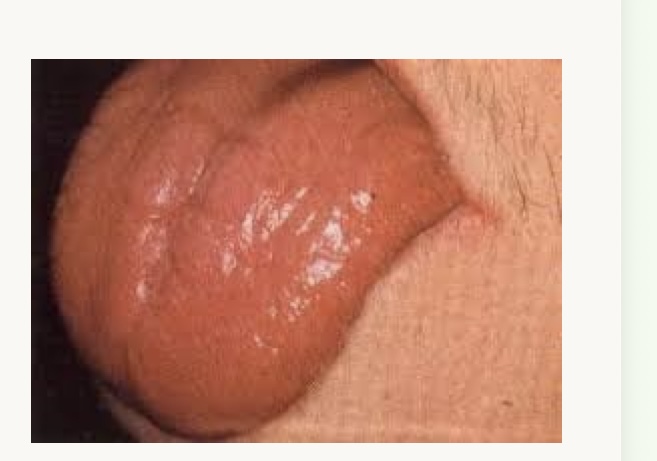
what is this condition and what vitamins is this person likely deficient in?
red beefy tongue (glossitis)
B12 or B9 folate
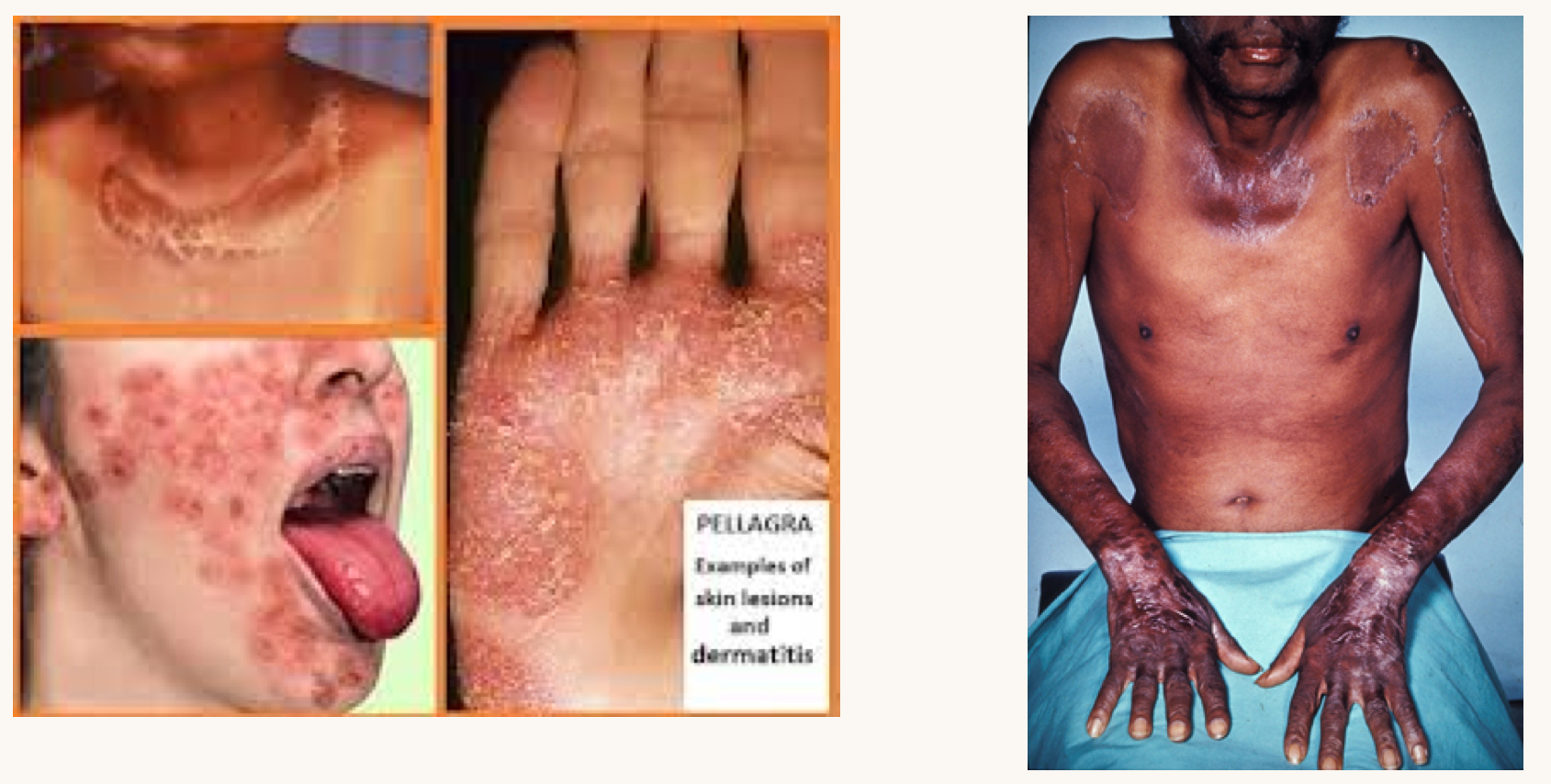
what is this condition and what vitamins is this person likely deficient in?
pellagra
B vitamins (niacin)
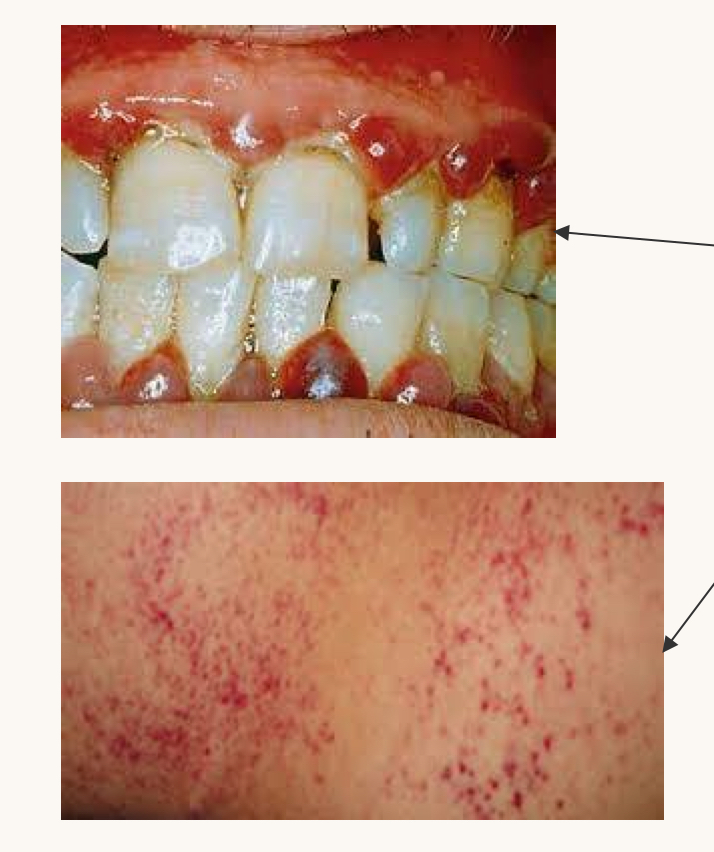
what is this condition and what vitamins is this person likely deficient in?
scurvy
vitamin C
manifests as gingival inflammation, petechiae, and poor healing
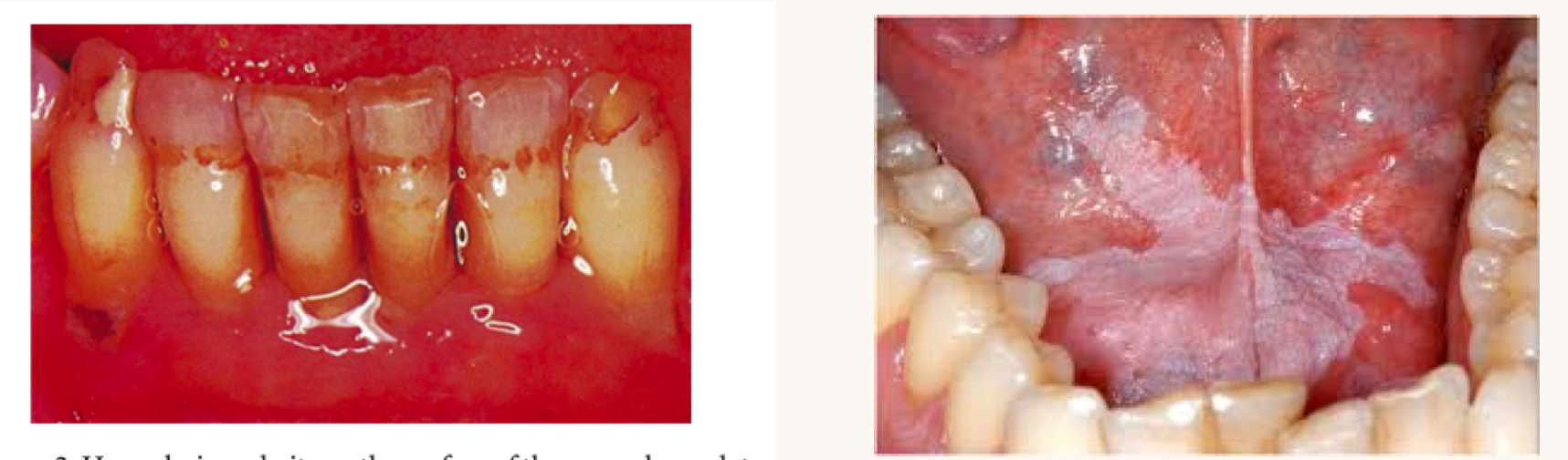
what is this condition and what vitamins is this person likely deficient in?
right is oral leukoplakia
vitamin A
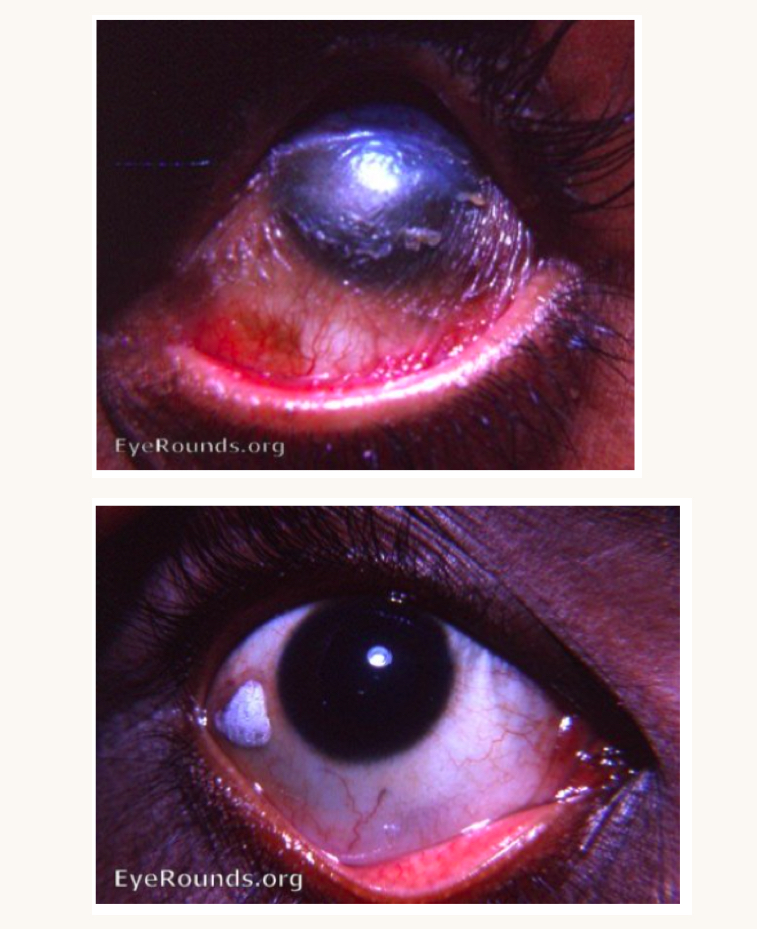
what is this condition and what vitamins is this person likely deficient in?
night blindess, xeropthalmia, bitot spots
vitamin A
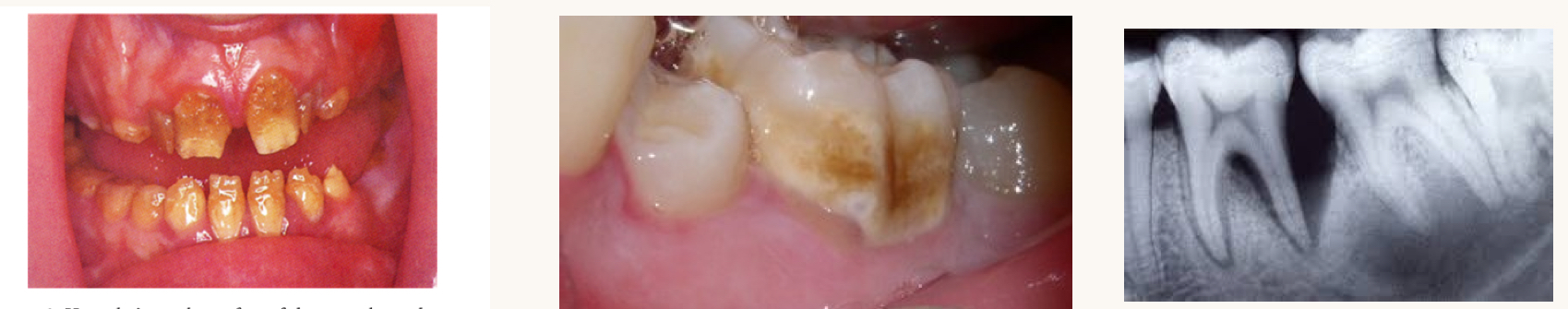
what is this condition and what vitamins is this person likely deficient in?
severe hypoplasia, hypocalcification, alveolar bone loss, delayed tooth eruption
vitamin D
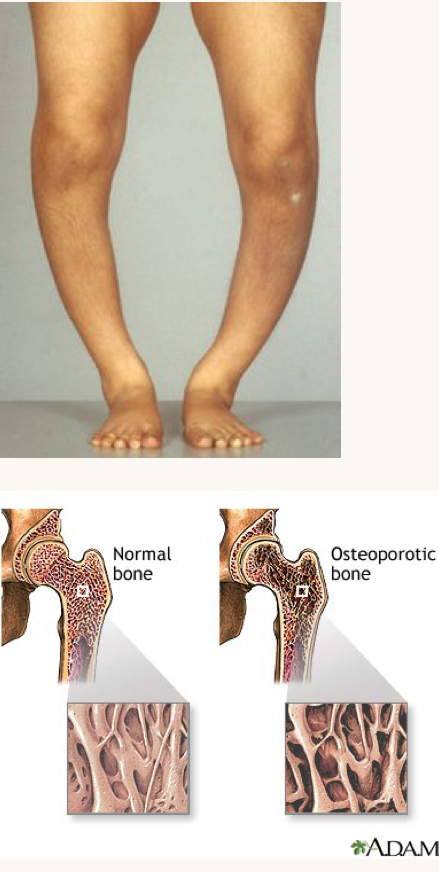
what is this condition and what vitamins is this person likely deficient in?
rickets, osteopenia, osteoporosis
vitamin D
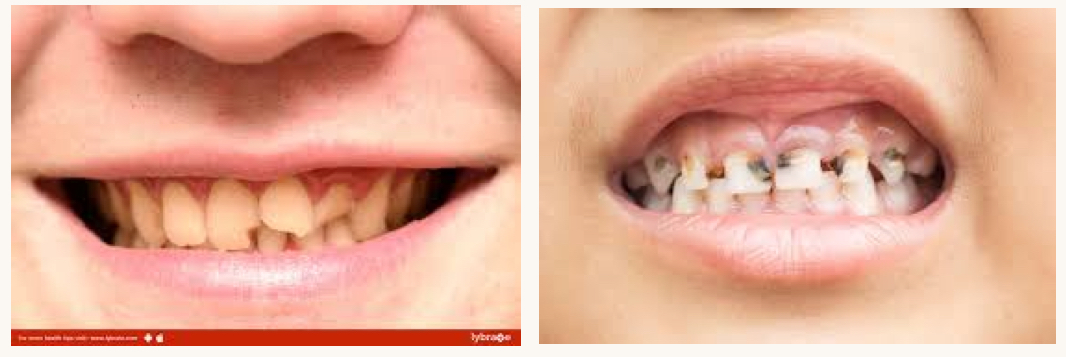
what is this condition and what mineral is this person likely deficient in?
brittle bones leading to chips/fractures, increased risk of decay and caries
calcium
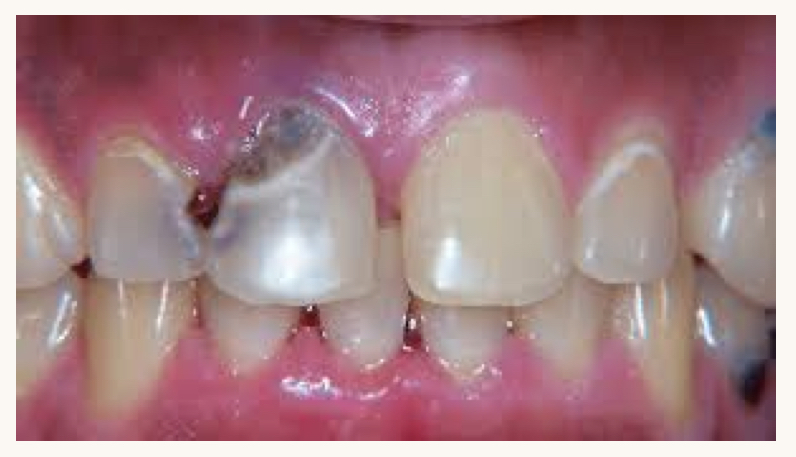
what is this condition and what mineral is this person likely deficient in?
fluoride deficiency
fluoride
excess fluoride can causes fluorosis
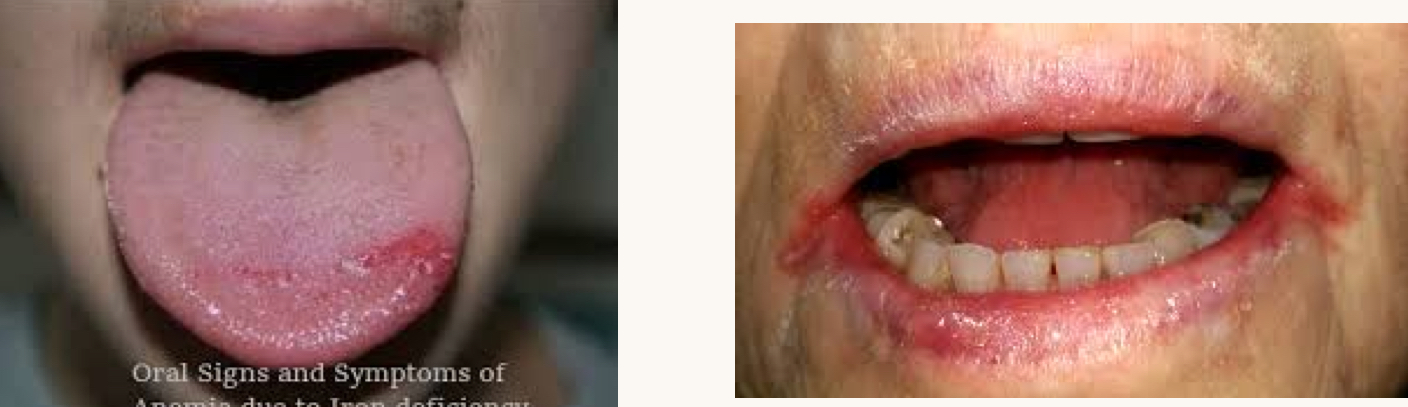
what is this condition and what mineral is this person likely deficient in?
pale/swollen tongue, angular cheilitis
iron deficiency
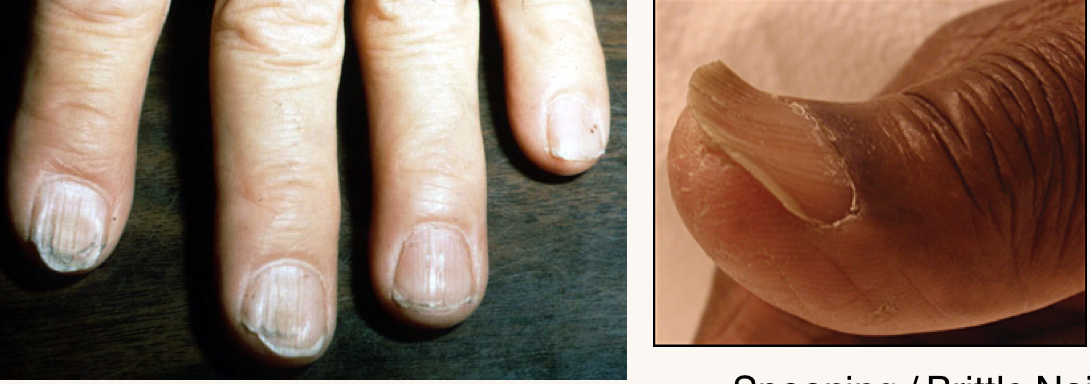
what is this condition and what mineral is this person likely deficient in?
spooning/brittle nails, pica (not pictured)
iron deficiency
if someone is complaining of altered taste, what are they likely deficient in?
zinc
what dietary factors are correlated with oral candidosis?
deficiencies in iron, B1, B2, B9, vitamin C, K, and zinc
also excess carbohydrates
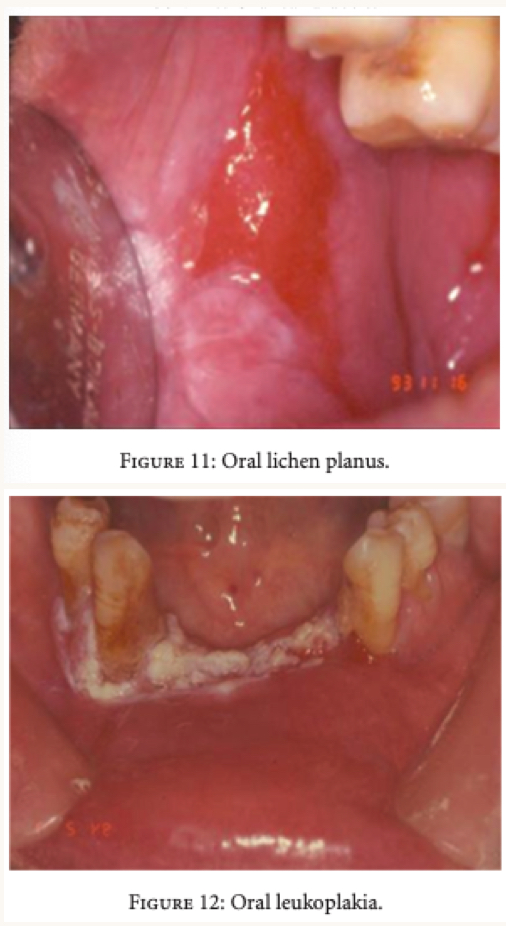
what nutrient deficiencies are related with these oral lesions?
deficiencies in B9, B12, vitamin C, A
what are some nutritional risk symptoms and their nutritional deficiencies that would be evident on the face?
malar pigmentation- riboflavin, niacin, B6
bitemporal wasting- protein
pale- iron
what are some nutritional risk symptoms and their nutritional deficiencies that would be evident on the lips?
cheilosis- riboflavin, niacin
angular fissures- riboflavin, niacin, B6, iron
what are some nutritional risk symptoms and their nutritional deficiencies that would be evident on the gingiva?
spongy, bleeding, abnormal redness- vitamin C
what are some nutritional risk symptoms and their nutritional deficiencies that would be evident on the tongue?
glossitis- riboflavin, niacin, B6, folate, B12, iron
pale, atrophic, smooth/slick- niacin, folate, B12, iron
magenta color- riboflavin