Histology 1 Past Exam Questions
1/169
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
170 Terms
What are blood smears stained with?
Giemsa
Which stains selectively elastic tissue?
Resourcin Fuscin
Which stains selectively collagen fibres?
Azan
The epidermis of the cornea:
Stratified squamous non kerantinised epithelium
Two layers of cuboidal cells:
Stratified cuboidal epithelium
Which one is NOT the layer of stratified squamous non kerantised epithelium?
Stratum granulosum
What is the internal lining epithelium of the small intestine?
Simple columnar epithelium
This gland is apocrine:
Mammary Gland
This gland is purely serous:
Parotid Gland
This gland is purely mucous
Eosphageal Gland
This gland is holocrine
Sebaceous gland
These features characterise the serous fluid
The watery fluid rich in proteins
Which cell type is NOT phagocytic?
Plasma cell
Which cell type produces the components of connective tissue?
Histocyte
Which cell type is pluripotent?
Mesenchymal
Which fiber type is the most frequent in the wall of arteries?
Elastic Fibers
Which connective tissue type is the most common in the animal body?
Loose connective tissue
What is the name of the connective tissue layer around cartilages?
Perichondrium
Which tissue produces leptin hormone?
White adipose tissue
Which cell type is present in the hyaline cartilage?
Chondrocyte
Which body part has hyaline cartillage component?
Nose
Which body part has elastic cartilage?
Ear lobe
Which cell type does NOT belong to the bony tissue?
Astrocyte
Which fiber type is the part of the bony matrix?
Collagen fiber
What is giving the firmness of the bony tissue?
The inorganic molecules and ions
Which laminae are remnants of old osteons?
Space filling lamellae
Which structure contains the blood vessels in the bony tissue?
Haversian canal
Where does the chondral ossification begin?
At the diaphysis
What does it mean: indirect ossification?
The future bone develops from hyaline cartilage model
Which cell type is multinucleated in the bony tissue?
Osteoclast
Which features are characteristic of the smooth muscle?
It is built up by spindle shaped cells
Which features are characteristic of the cardiac muscle?
It performs quick contractions and does not fatigue
Which feautures are characteristic of the skeletal muscle?
Impulses for contraction are generated by motor endplates
What is true for the z-line?
It contains anchoring proteins for actin
Which one is the thin filament?
Actin
What is NOT necessary for the skeletal muscle contraction?
Microtubules
What is the role of the troponin-tropmyosin complex?
At rest it prevents the actin myosin binding
What is the muscle spindle?
Sensory nerve specialisation in the skeletal muscle
In which body part do you find skeletal muscle?
In the locomtor organs
What kind of neurons are the pyramidal cells?
Multipolar
Which one is NOT a glial cell type?
Purkinje-cell
Which one is the input process of a neuron?
Dendrite
Which one is NOT characteristic of an excitatory neuron?
Symmentrical synapse
Which synapse type is the most frequent?
Axosomatic
Which synapse type is electronic synapse?
Gap junction
Which one is an inhibitory neurostransmitter?
Gamma-amino butyric acid
Which nerve fiber type is conducting at a highest speed?
Alpha
Which cell organelle is missing from the neuron?
Centriole (It has mitochondrium, golgi complex and endoplasmic reticulum)
Which is NOT a glial cell type of the central nervous system?
Satellite Cell (ependymal, oligodendrocyte and astrocyte all are)
Which glial cell type has mesodermal origin?
Microglial
Which glial cell's process is present in the blood-brain barrier?
Astrocyte
Which blood corpuscle is the most frequent in the mammalian?
Erthrocyte
Which cell type has the most segmented nucleus?
Neutrophil
Which cell type has bactericid properties?
Neutrophil
Which cell type has crystallisation it its specific granules?
Eosinophil
Which blood corpuscle is responsible for blood clotting?
platelet
Which cell type is enlarged with antibody production?
Plasma cell
Which pathogenic micro-organisms are the targets of microphages?
Bacteria
How can we distinguish mammallan and avlan blood smear?
On the basis of the presence or lack of nuclei in the erythrocytes and thrombocytes
Which cell type us multipolar in the red bone marrow?
Myeloid
Where is the site of maturation of erythrocytes?
The red bone marrow
Which developmental line has rubriblast?
Erthrocytic cell line
What is NOT present in the erythroblastic istand?
Osteoblast (macrophage,metarubricyte and reticulocyte all present)
Which developmental line has band forms?
Granulocytic cell line
What kind of organ produces erthropoetin?
Kidney
Which cell type gives rise to platelets?
Megakaryocyte
Which layer is NOT the part of blood vessels?
Tunica Mucosa (tunica media, tunica externa, tunica intima)
Which layer is the thickest in the elastic arteries?
Tunica media
Which blood vessel has several elastic membranes in its wall?
Aorta
Which layer is the thickest in the wall of large calliber veins?
Tunica externa
Which layer of blood vessles is made by the endothelium and subendotheial connective tissue?
Tunica intima
Which layer of the heart is made by cardiac muscle?
Myocardium
Which blood vessel type is containing valves?
Vein
Which organ has fenestrated capillaries?
kidney
Which organ has continuous capillaries?
Brain
Which vessel type belongs to the venous system?
Lymphatic vessels
What kind of tissue forms the endocardium of the heart?
Endothelium and the subendothelial connective tissue layer
Bowman's capsule:
Simple Squamous Epithelium
Synthesis of Collagen Fibres: Name 1
Fibroblast

Synthesis of Collagen Fibres: Name 2
Tropelastin
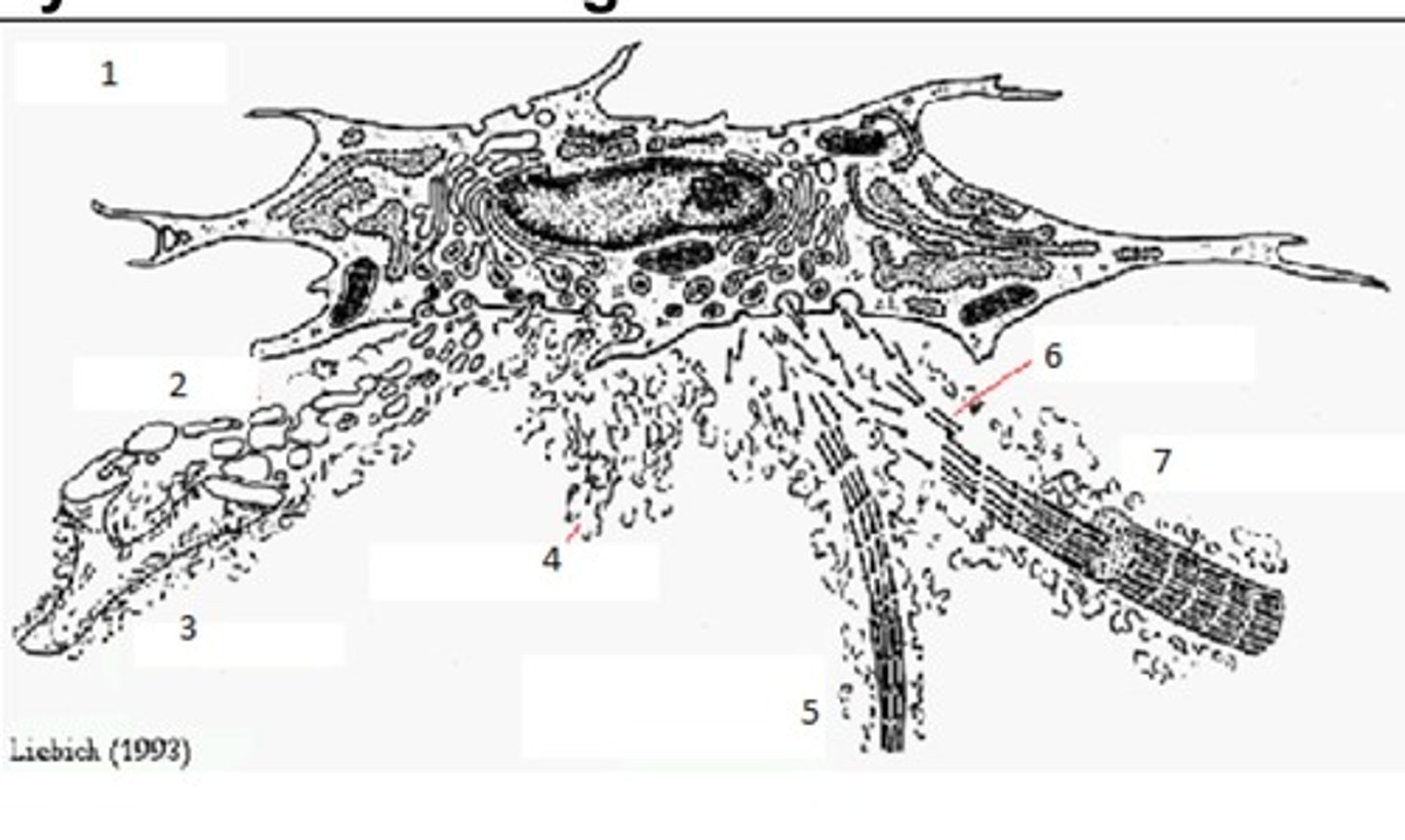
Synthesis of Collagen Fibres: Name 3
Elastic Fibre

Synthesis of Collagen Fibres: Name 4
Ground Substance
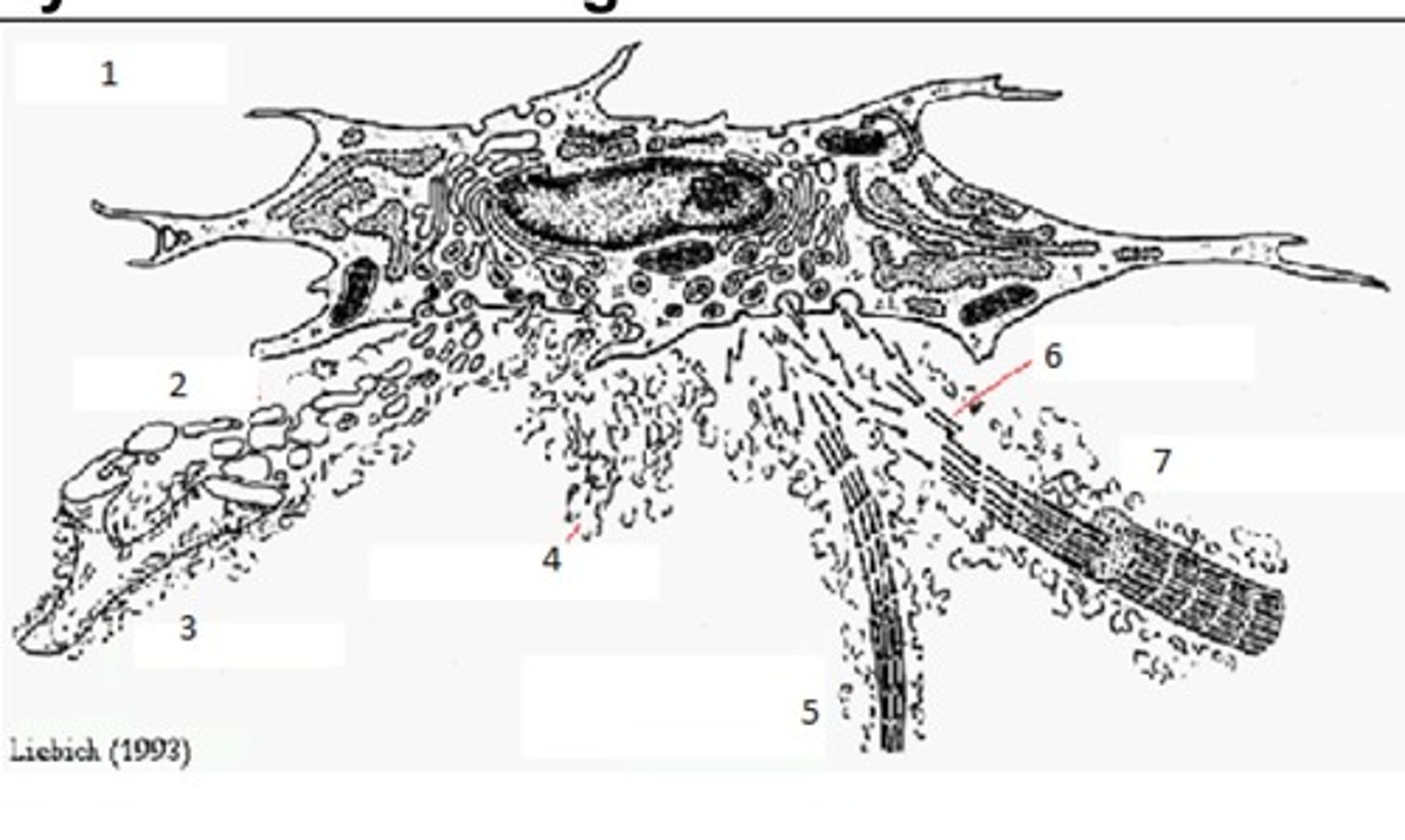
Synthesis of Collagen Fibres: Name 5
Reticular Fibre
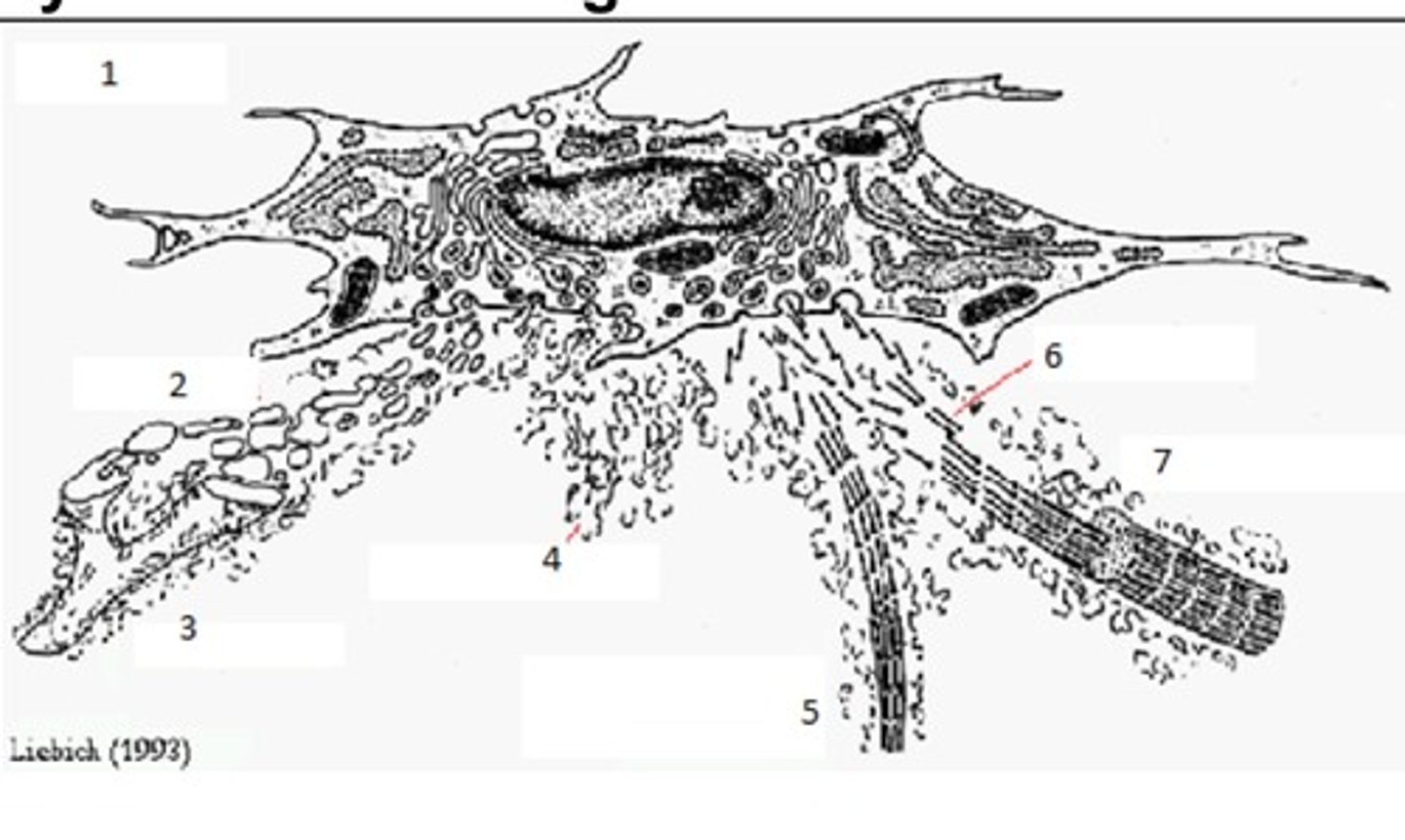
Synthesis of Collagen Fibres: Name 6
Tropocollagen
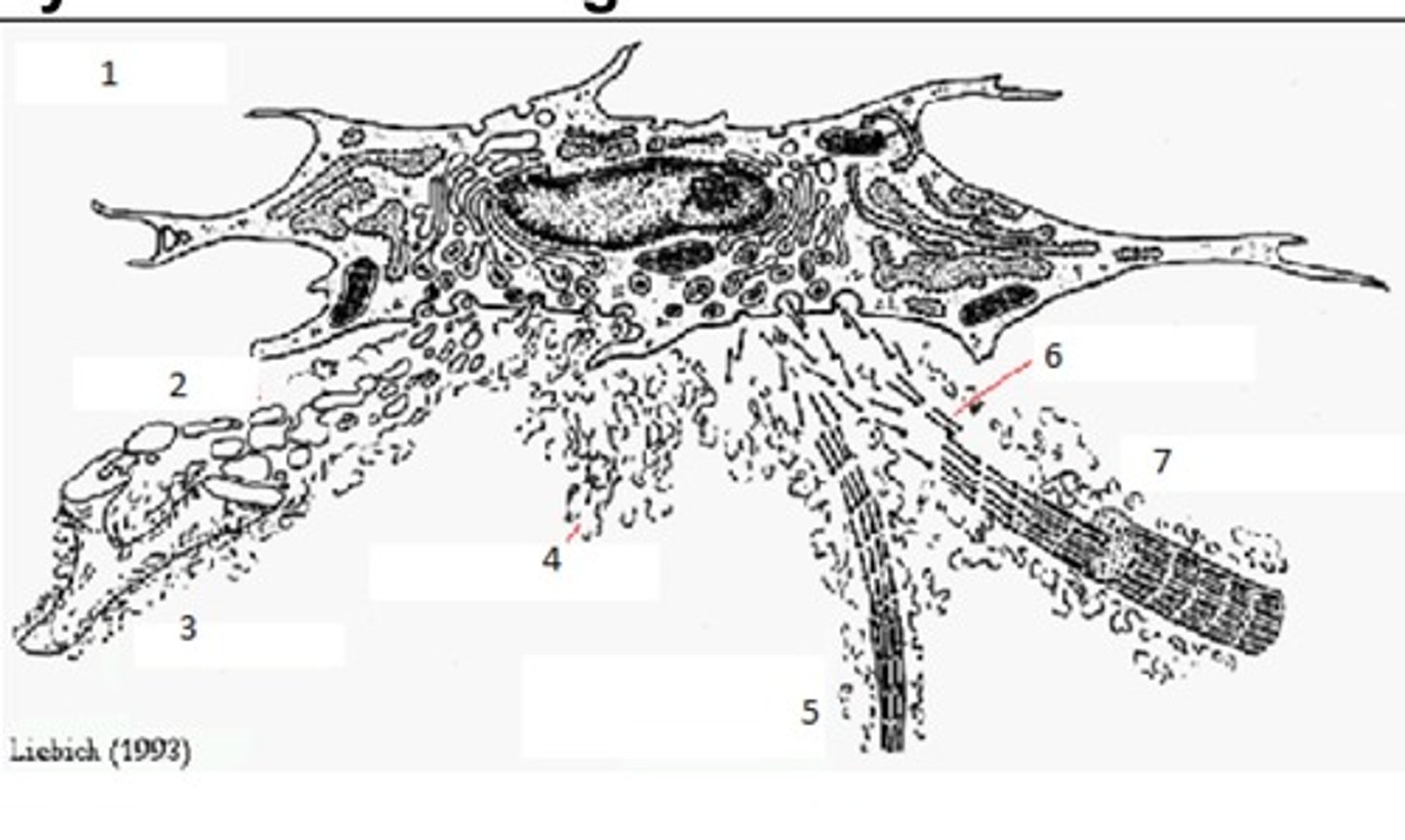
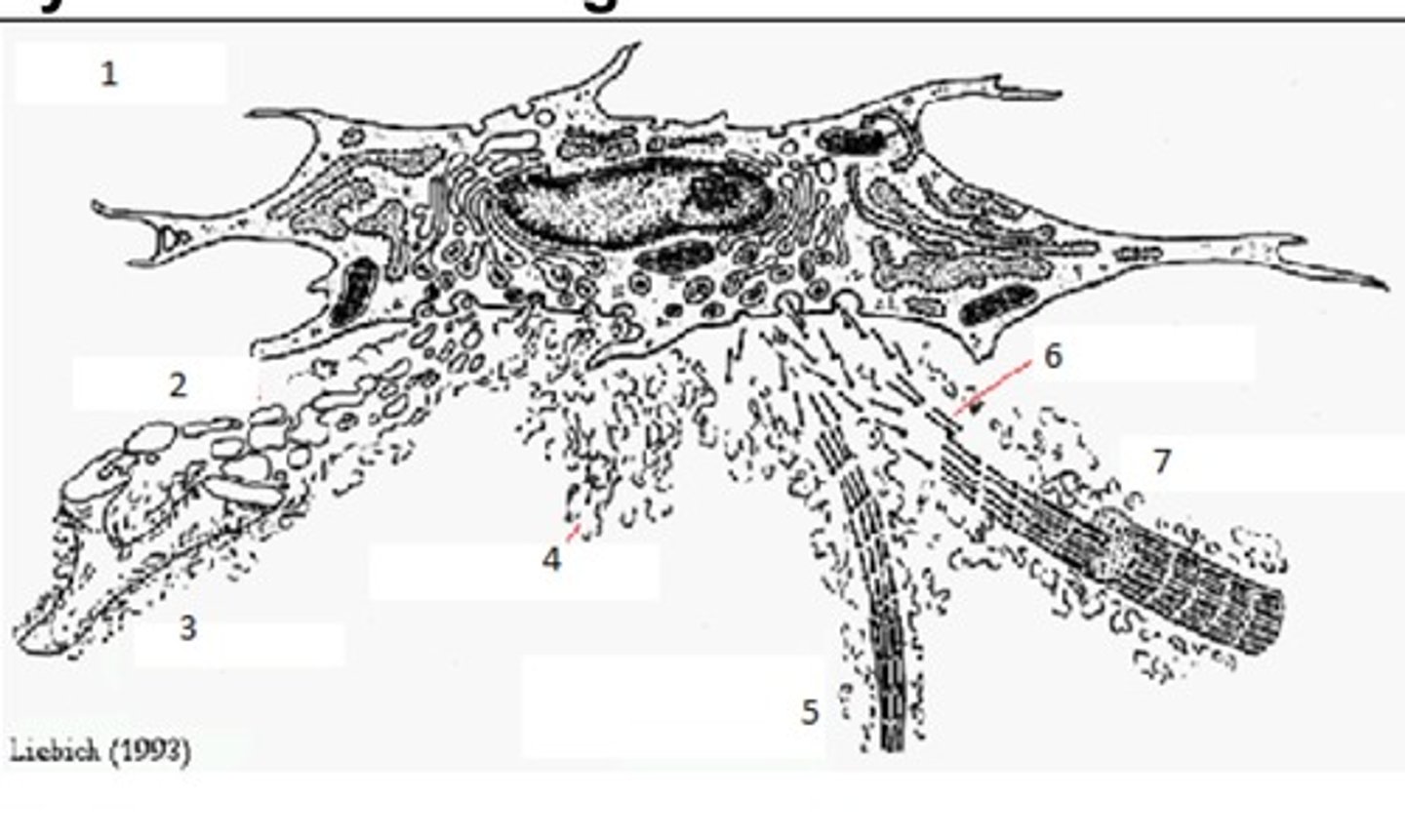
Synthesis of Collagen Fibres: Name 7
Collagen I Fibril
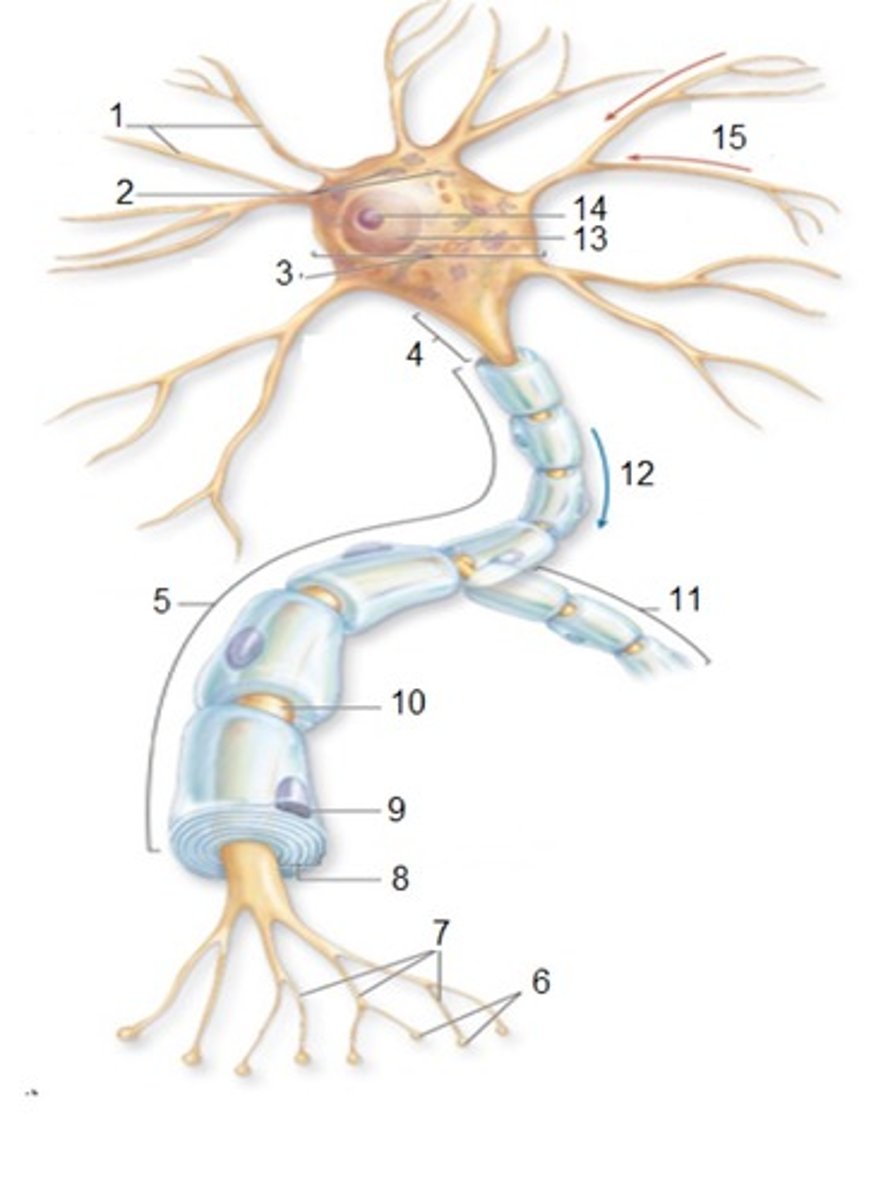
General Neuron Structure: Name 1
Dendrites
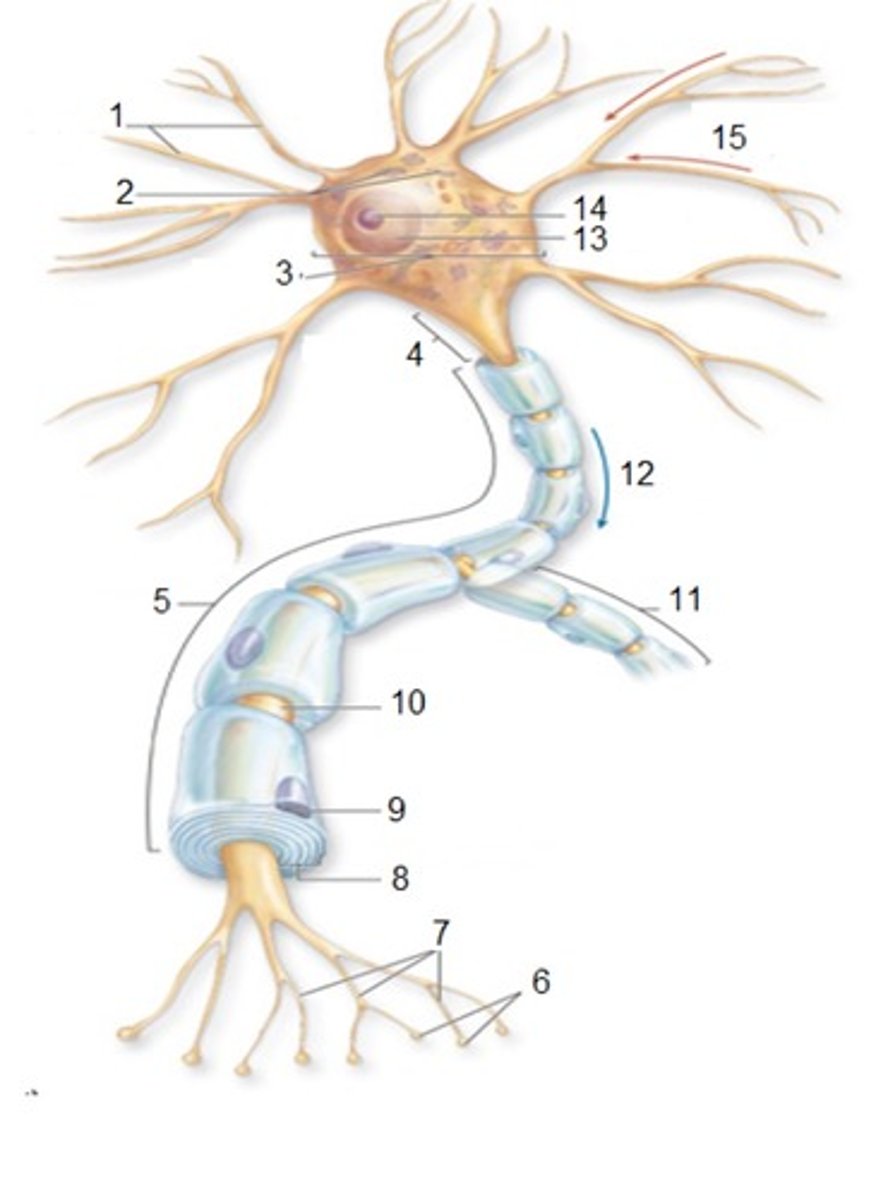
General Neuron Structure: Name 2
Chromatophilic Substances

General Neuron Structure: Name 3
Cell Body
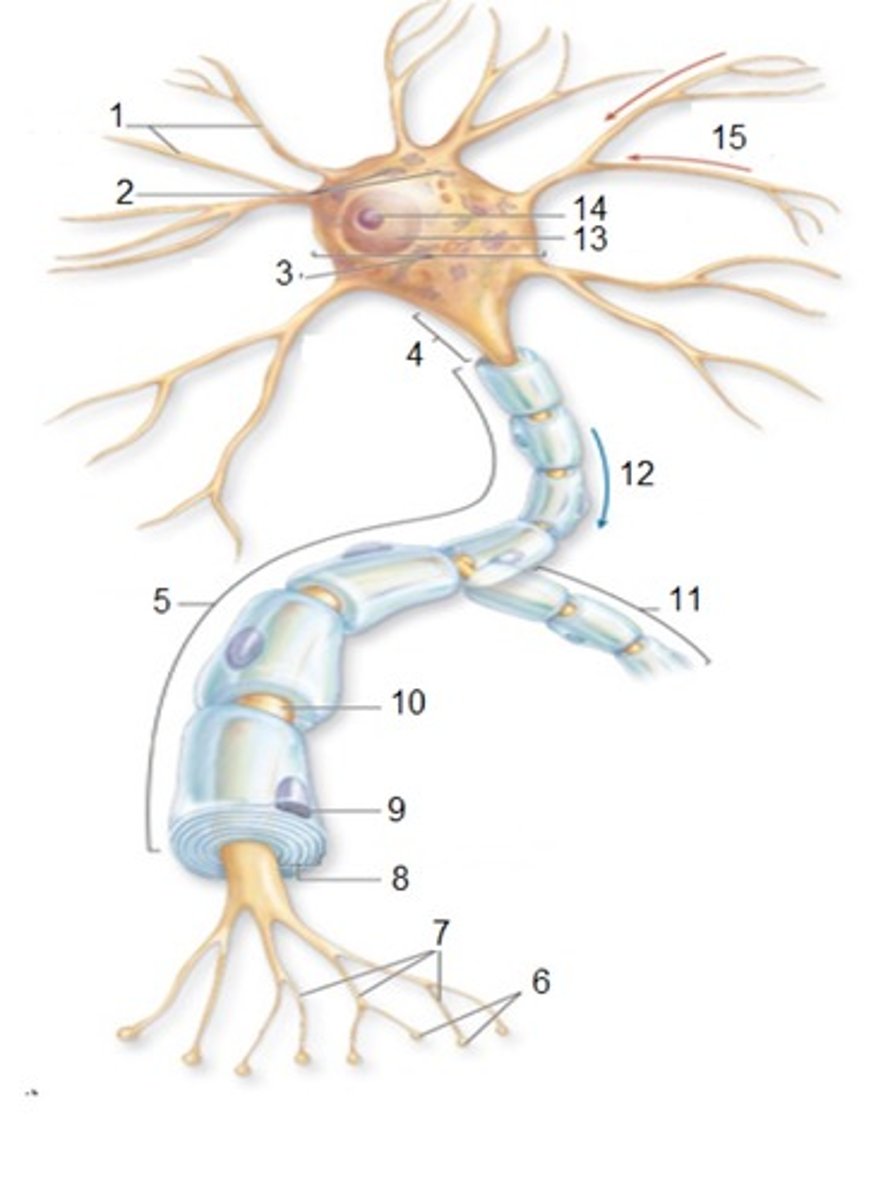
General Neuron Structure: Name 4
Axon Hilock
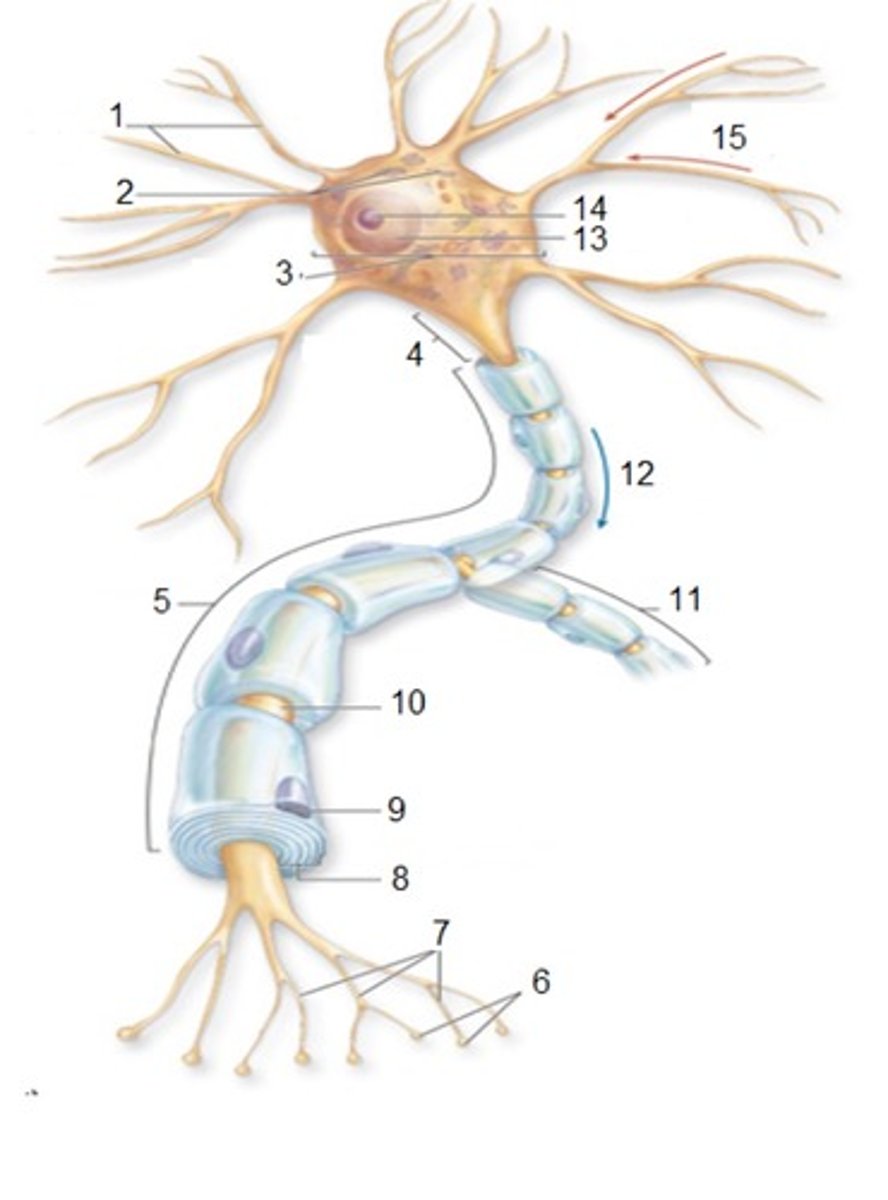
General Neuron Structure: Name 5
Axon

General Neuron Structure: Name 6
Synaptic Knobs
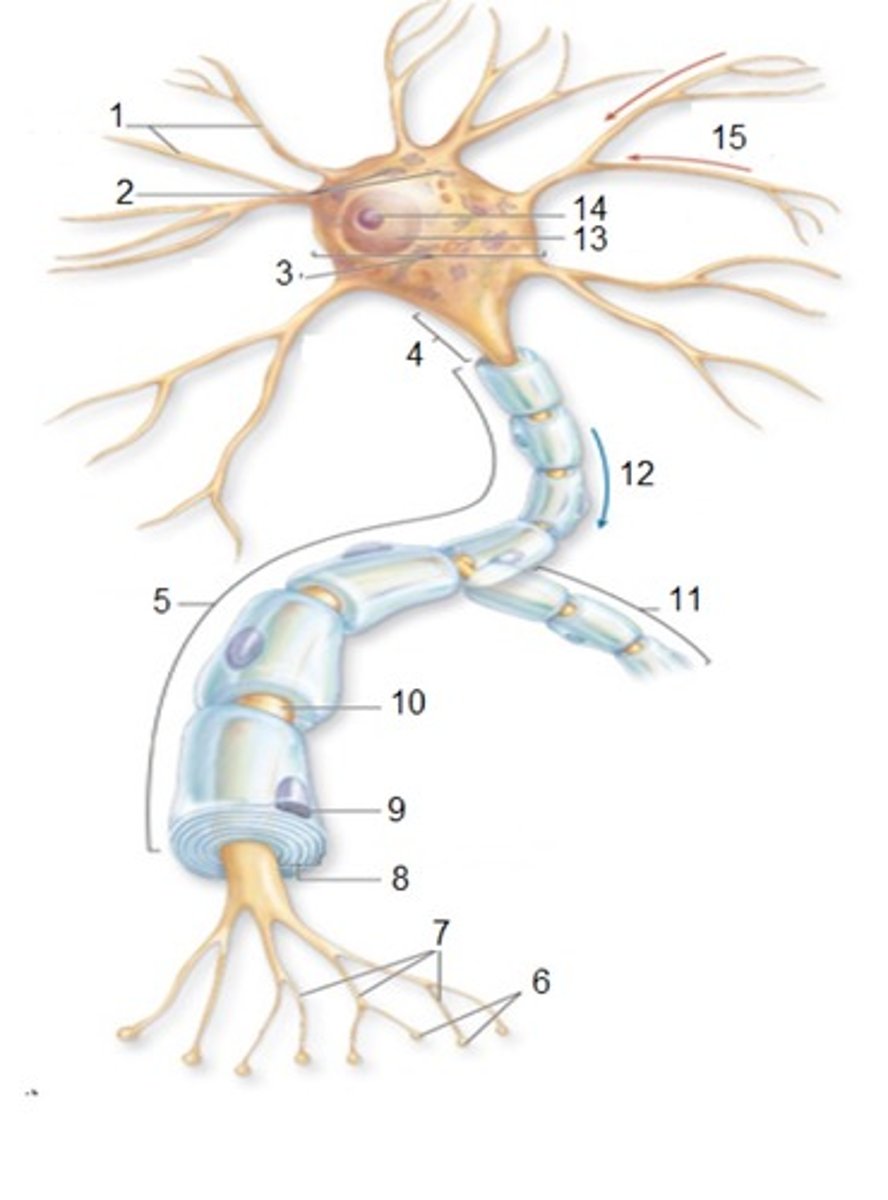
General Neuron Structure: Name 7
Telodendria
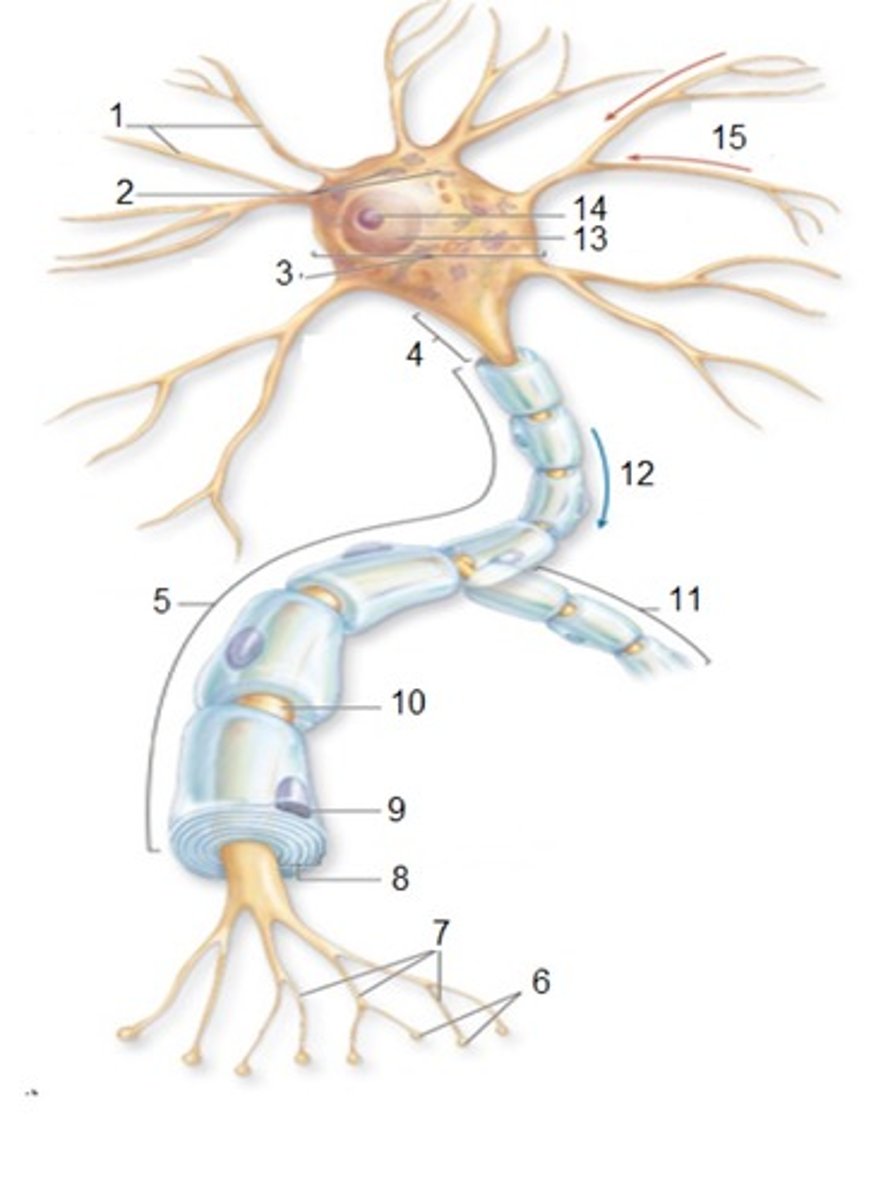
General Neuron Structure: Name 8
Myelin Sheath

General Neuron Structure: Name 9
Neurlemmocyte
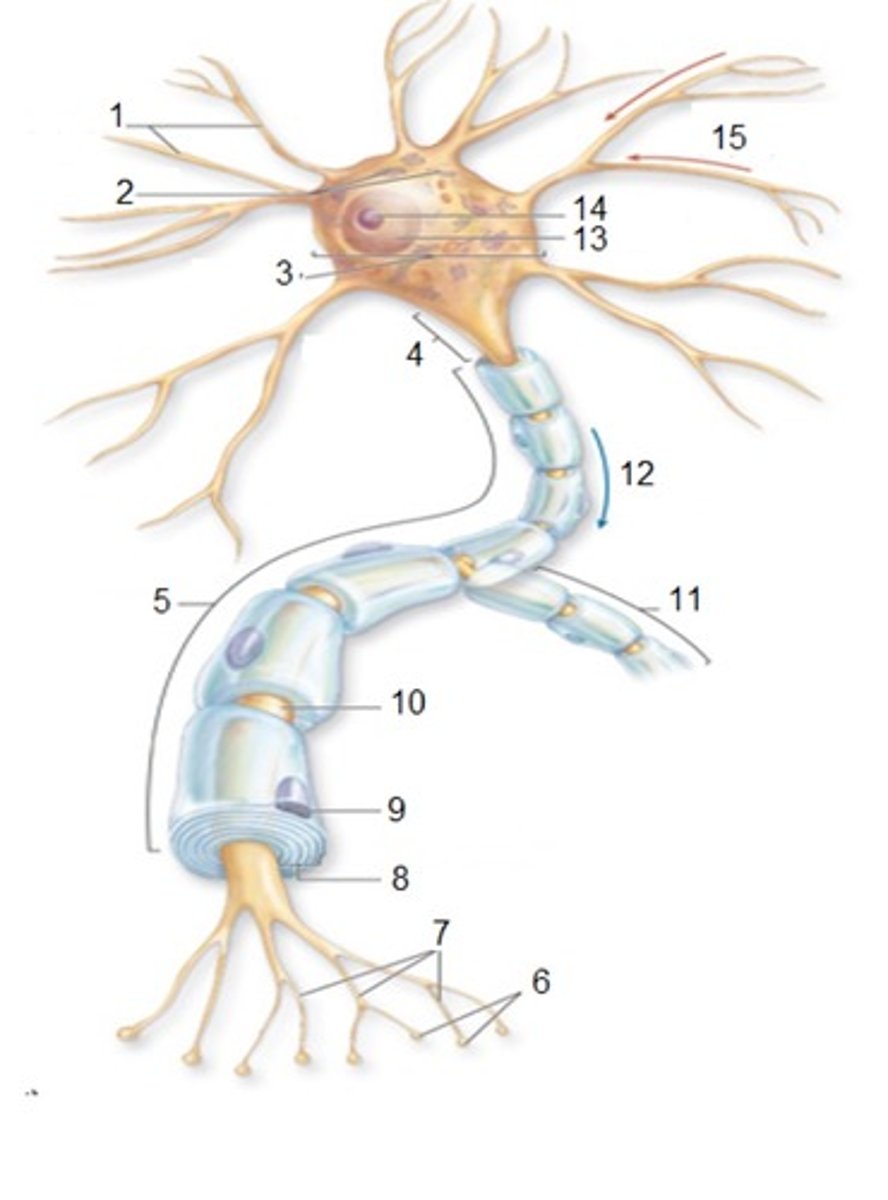
General Neuron Structure: Name 10
Node of Ranvier
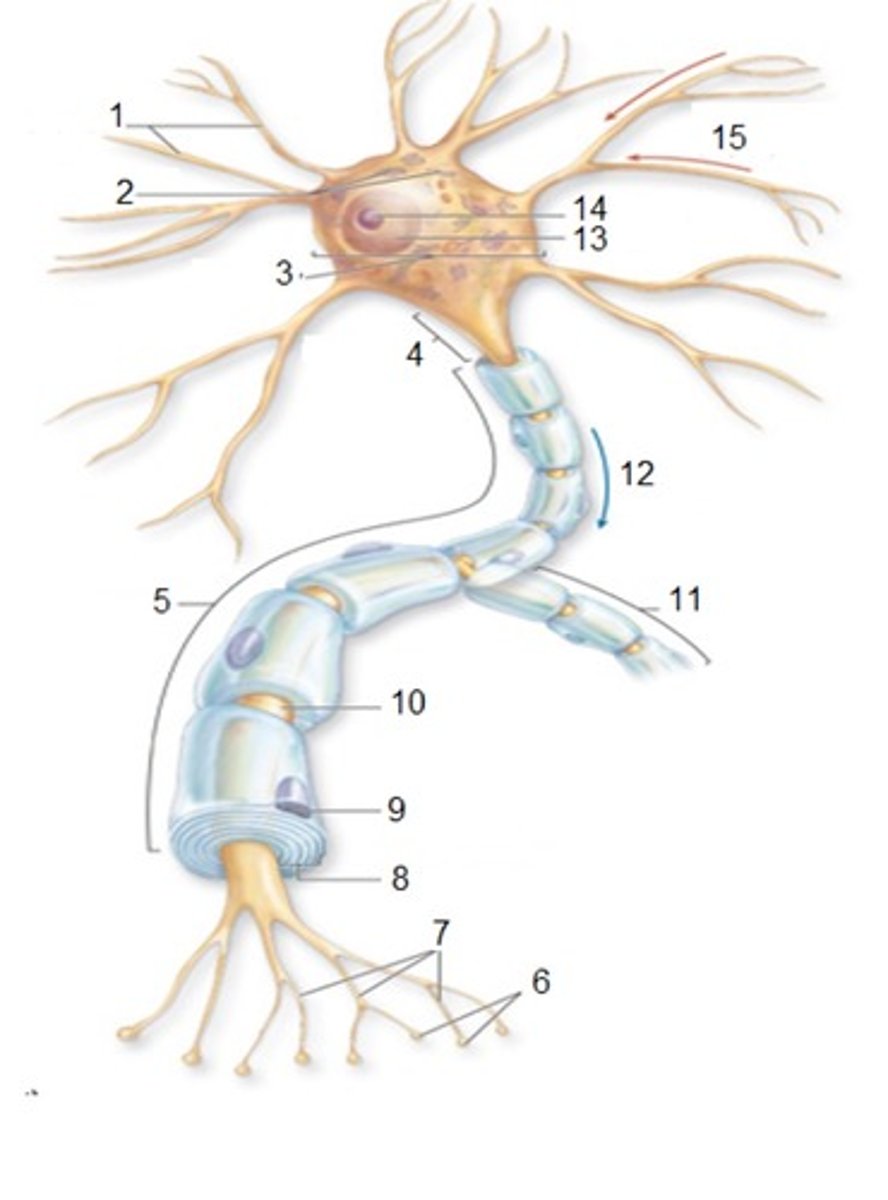
General Neuron Structure: Name 11
Axon Collateral
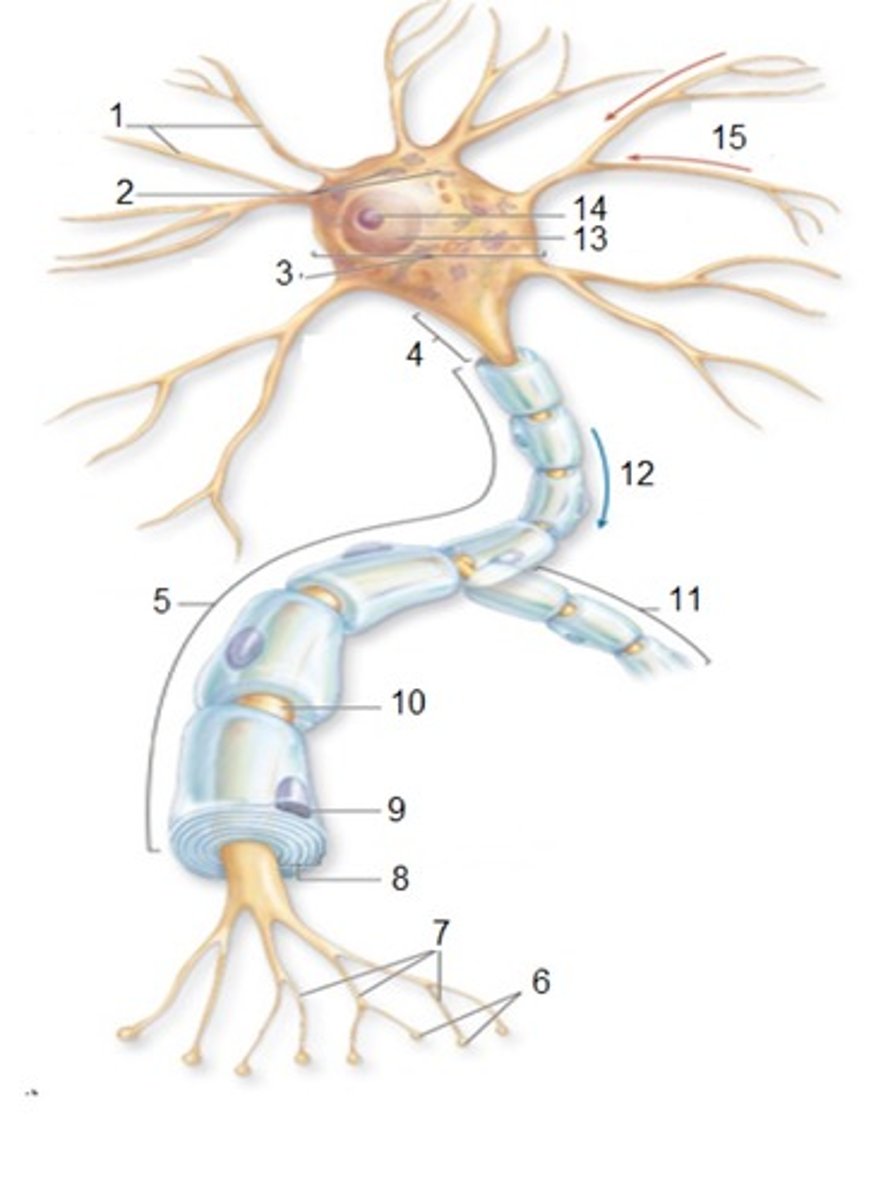
General Neuron Structure: Name 12
Output
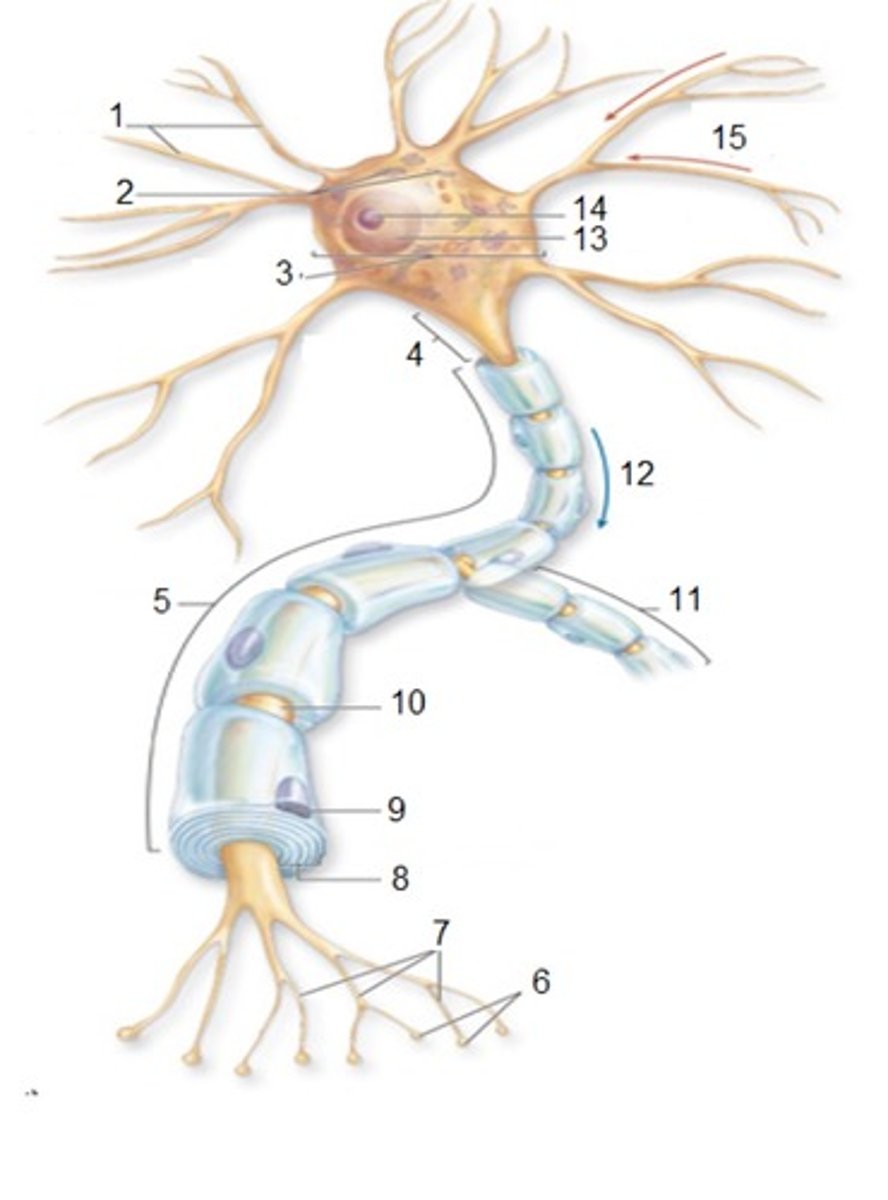
General Neuron Structure: Name 13
Nucleus
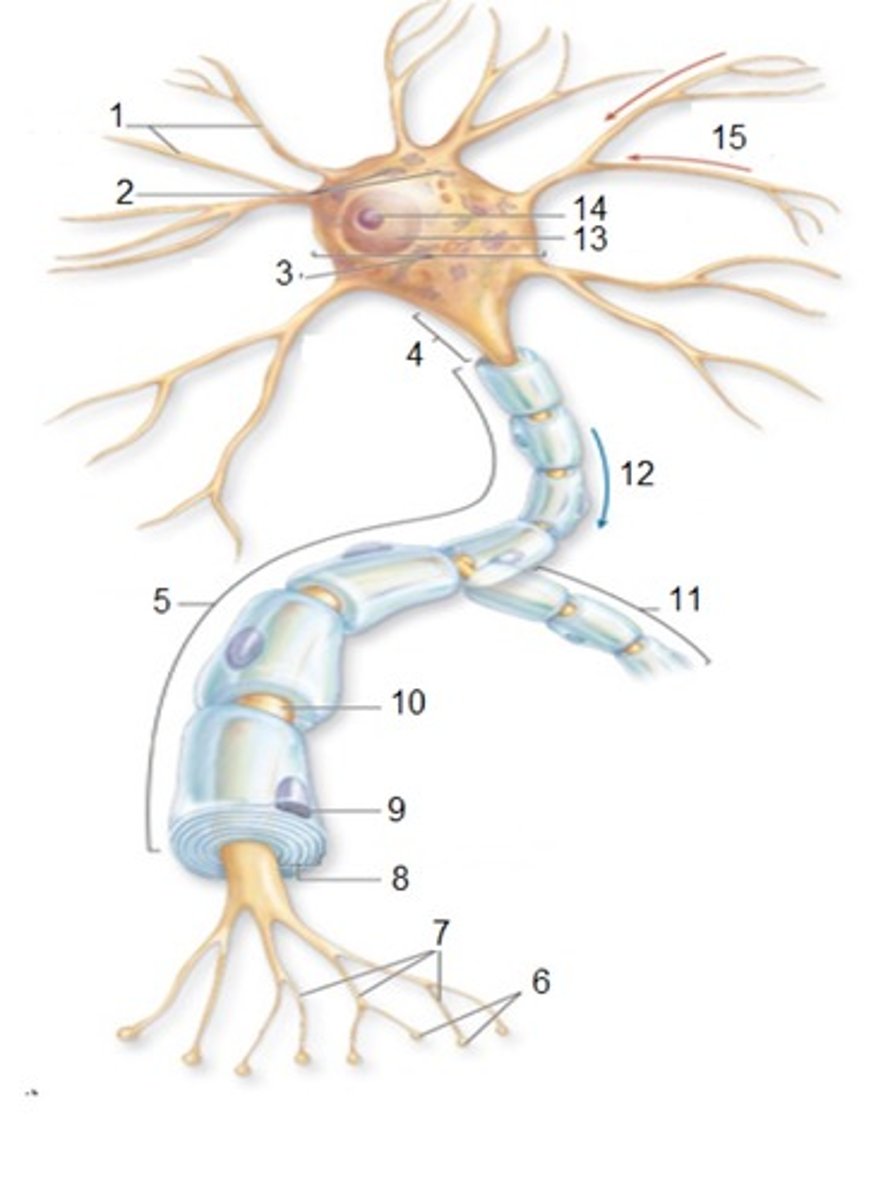
General Neuron Structure: Name 14
Nucleolus
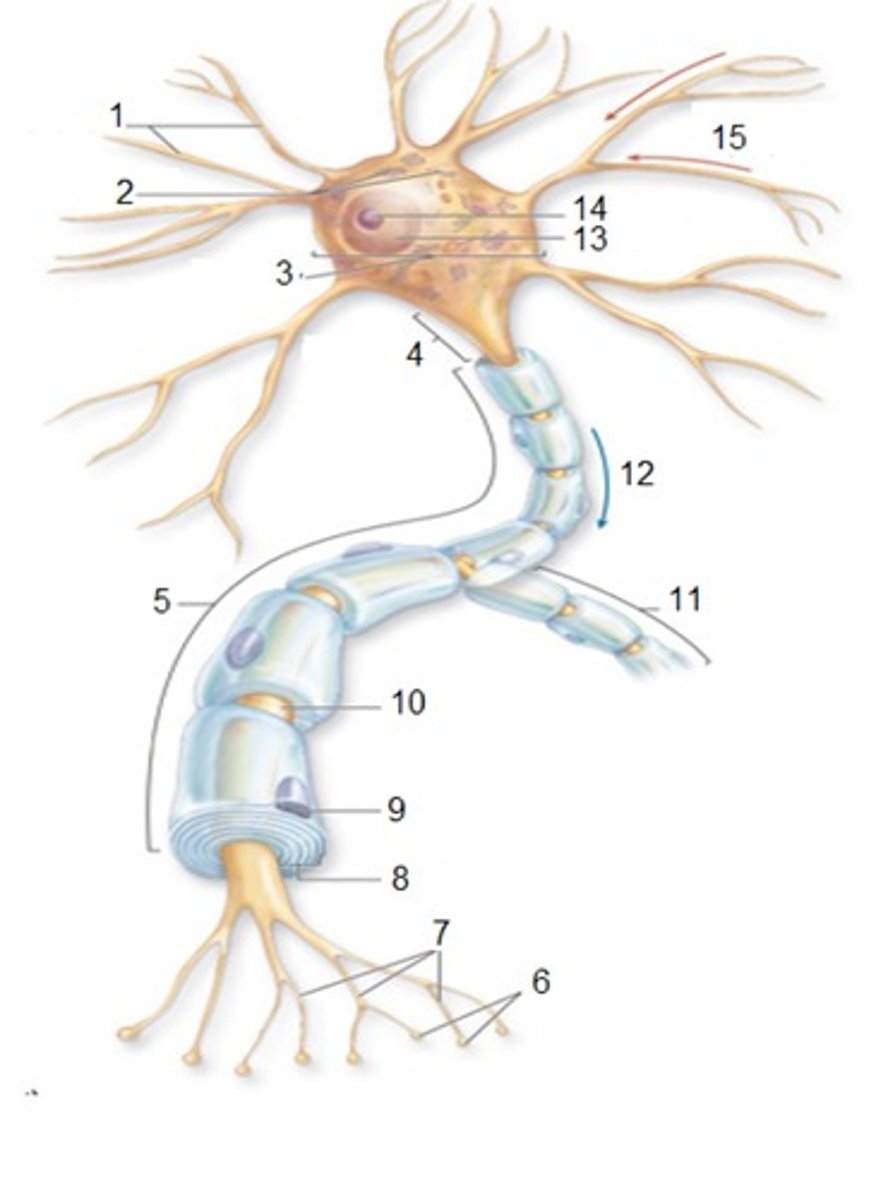
General Neuron Structure: Name 15
Input