Physics - Topic 17 ( Oscillations )
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
( Oscillations )
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Oscillations
Repeated motion of an object from its mean position and between two extreme positions due to a restoring force
Displacement (x)
The instantaneous shortest distance of the moving object from its mean position
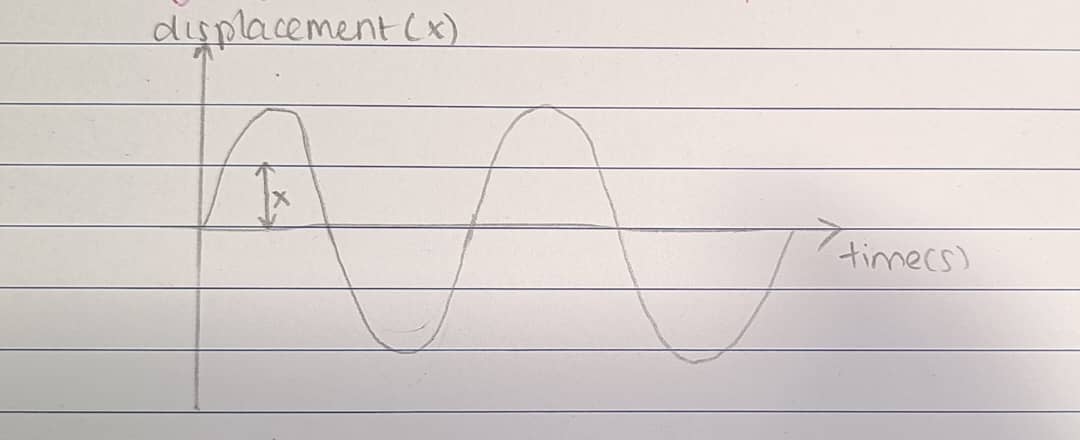
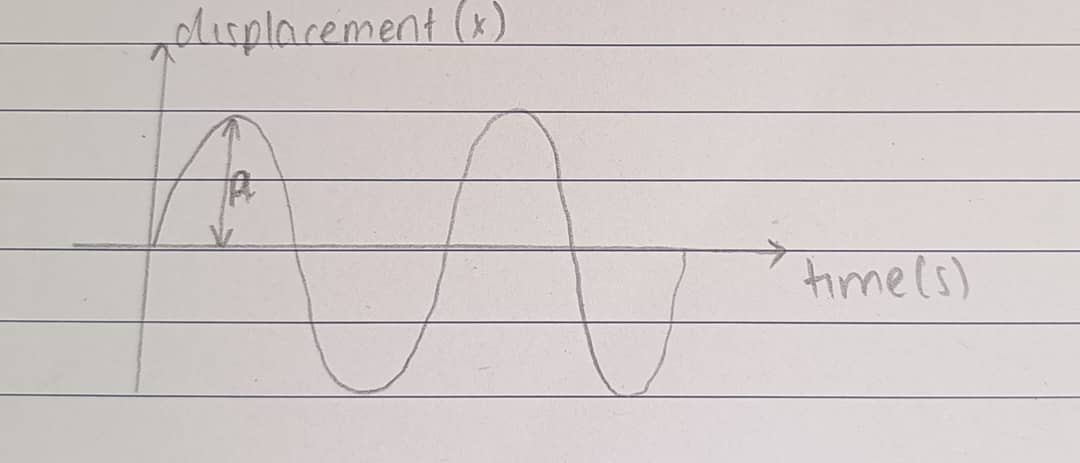
Amplitude (A)
The maximum displacement from the mean position in an oscillatory motion.
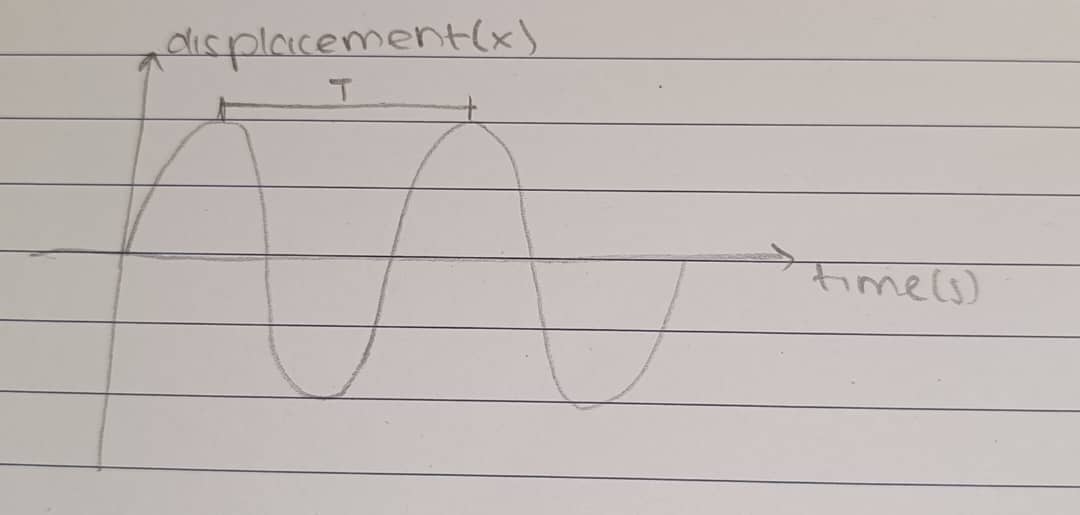
Period (T)
Is the time taken for one complete oscillation.
Frequency (F)
Is the number of oscillations per unit time
f = 1 / T, where T is the period.
Angular frequency (w)
Is the rate of change of angular displacement
w = 2πF.
Phase difference
A measure of how much one wave is out of step with another wave
Phase difference = 2πt / T, where T is period and t is time lag between the waves
Time lag is the time difference between corresponding points on 2 or more waves
Simple Harmonic Motion
Oscillatory motion given that acceleration is proportional to the negative displacement to the negative displacement with acceleration being to the mean position
a= - w2x, where a is acceleration and x is displacement.
Velocity & Displacement Equation of S.H.M
V = ±w√(A² - x²), where v is velocity, A is the amplitude, x is the displacement, and w is the angular frequency.
Displacement X = X0sin wt
Graphs of S.H.M displacement, velocity & acceleration
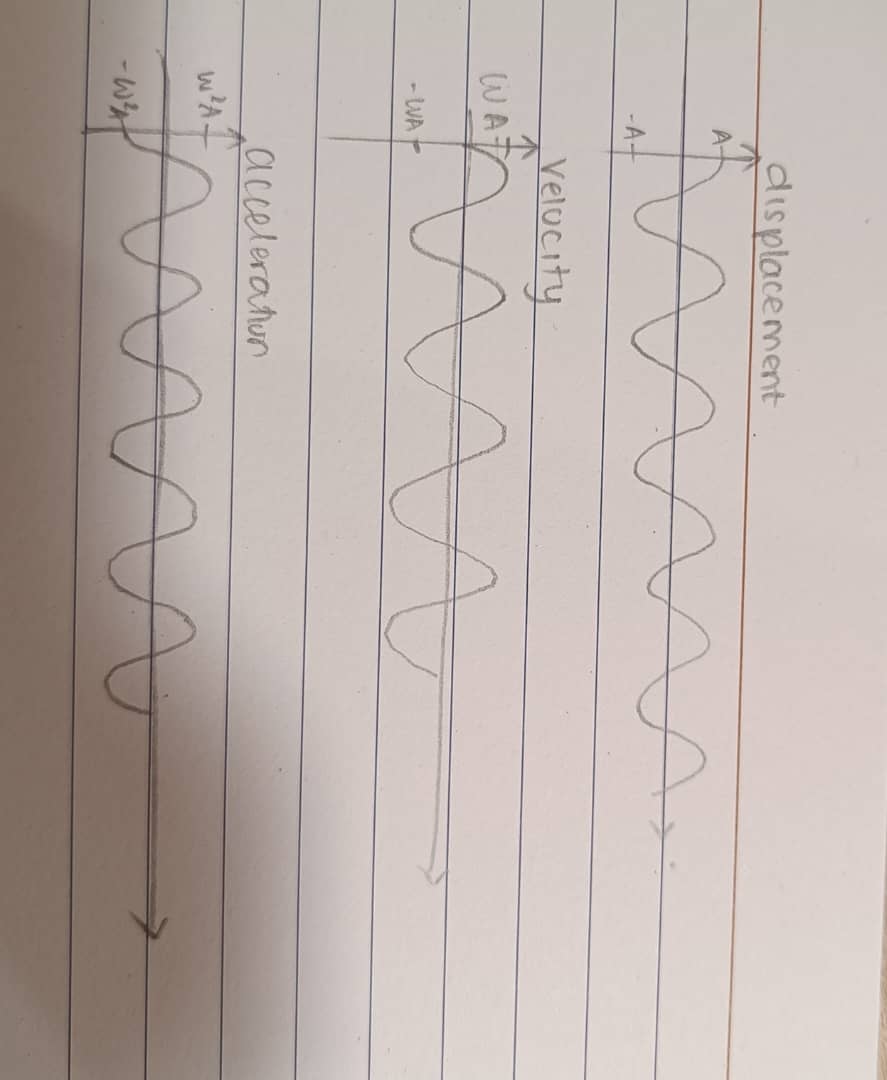
Energy in S.H.M
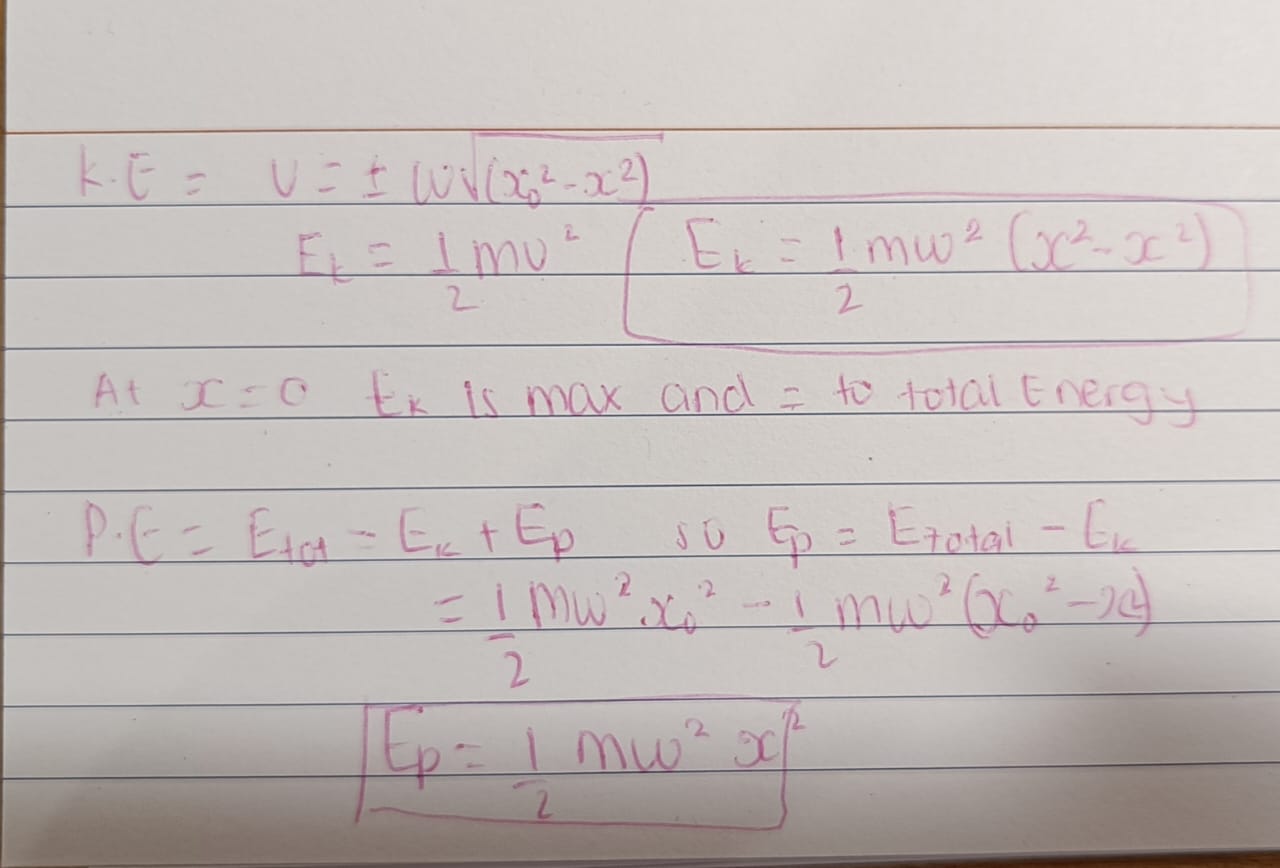
Total Energy
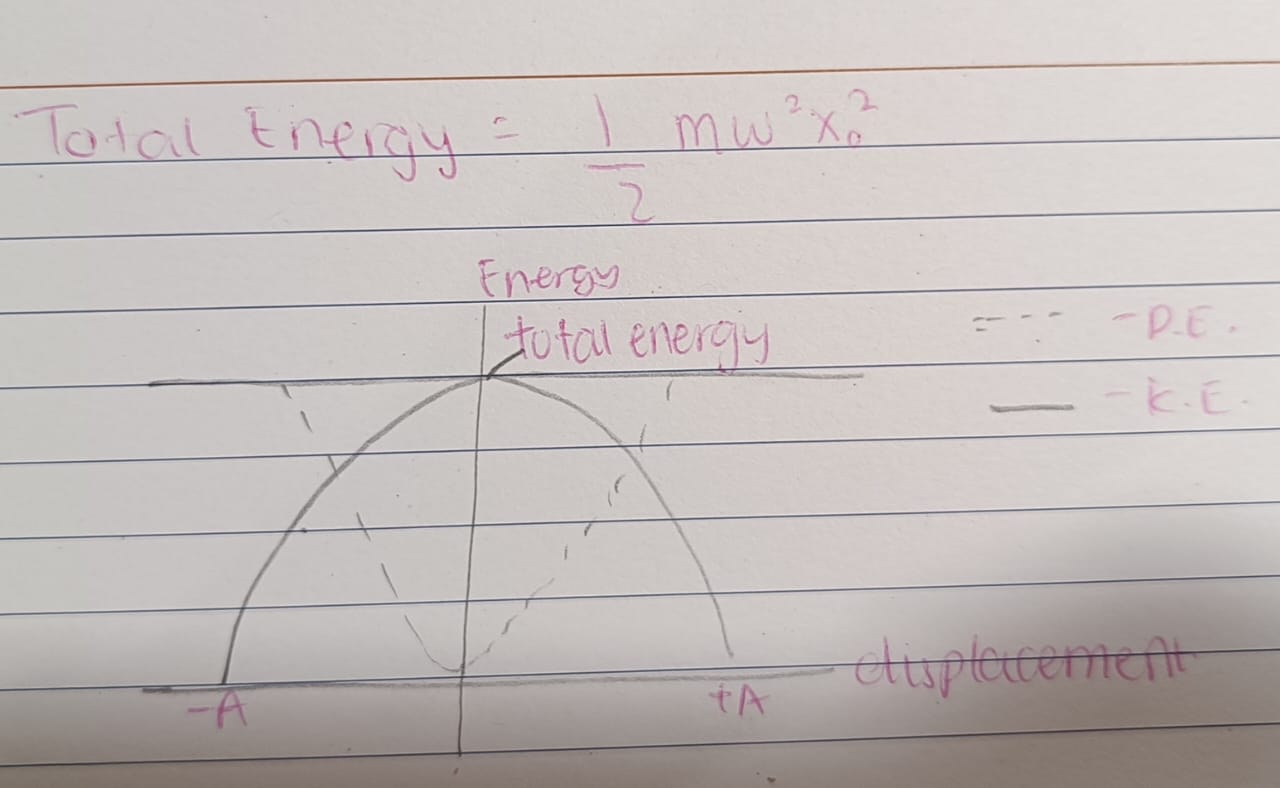
Damping
Loss of energy and reduction in amplitude from an oscillating system caused by force acting in the opposite direction to the motion
Light Damping
The system oscillated about the equilibrium position with decreasing amplitude over a period of time
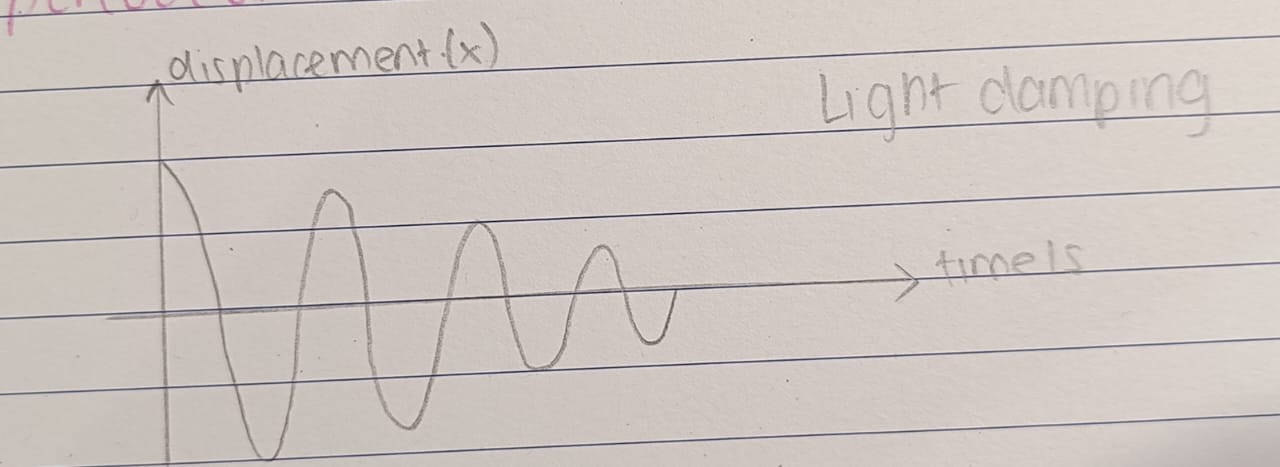
Critical damping
The system does not oscillate and is the amount of damping required such that the system returns to equilibrium position in shortest time possible

Heavy / Over damping
Damping is so great that the displaced object never oscillates but takes time return to its equilibrium position
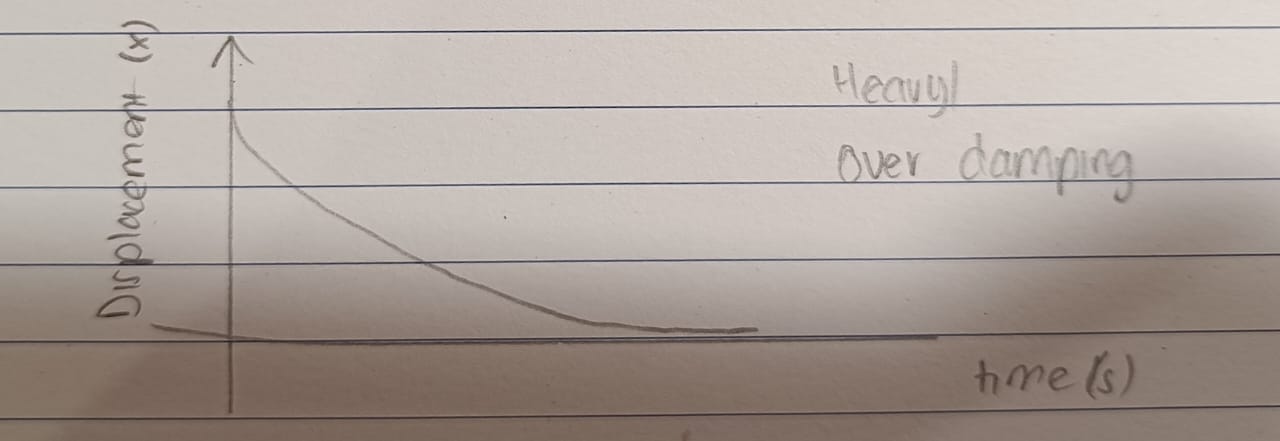
Natural frequency ( f0)
The unforced frequency of oscillation of a freely oscillating object
Resonance
Increase in an oscillation amplitude due to forced oscillation’s frequency equal to the natural frequency