Hypothyroidism and Thyroiditis
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
14x
Women are ______ more likely to be diagnosed with hypothyroidism
Subclinical
Why type of hypothyroidism is characterized by enough T3/T4 that symptoms are mild and is more common in women?
superior and inferior thyroid arteries
What is the blood supply for the thyroid?
thyroid gland (Hashimoto’s, iodine deficiency, post-thyroidectomy)
A primary hypothyroidism is a dysfunction in the
Pituitary gland (TSH deficiency)
A secondary hypothyroidism is a dysfunction in the
Hypothalamus
A tertiary (central) hypothyroidism is a dysfunction in the
TSH, Free T4, CBC, CMP, maybe antibodies
Patient presents to the clinic with extreme fatigue and depression. She states that she thinks she’s gained 40 pounds in 3 months, but she doesn’t remember the exact timeline, she also reports cold intolerance and menstrual irregularities. On a physical exam you note dry skin, coarse hair, hair loss, and brittle nails. What diagnostic testing do you want?
Combined IV T3/T4, hydrocortisone stress dose, passive rewarming, supportive care (dilute fluids, pressors)
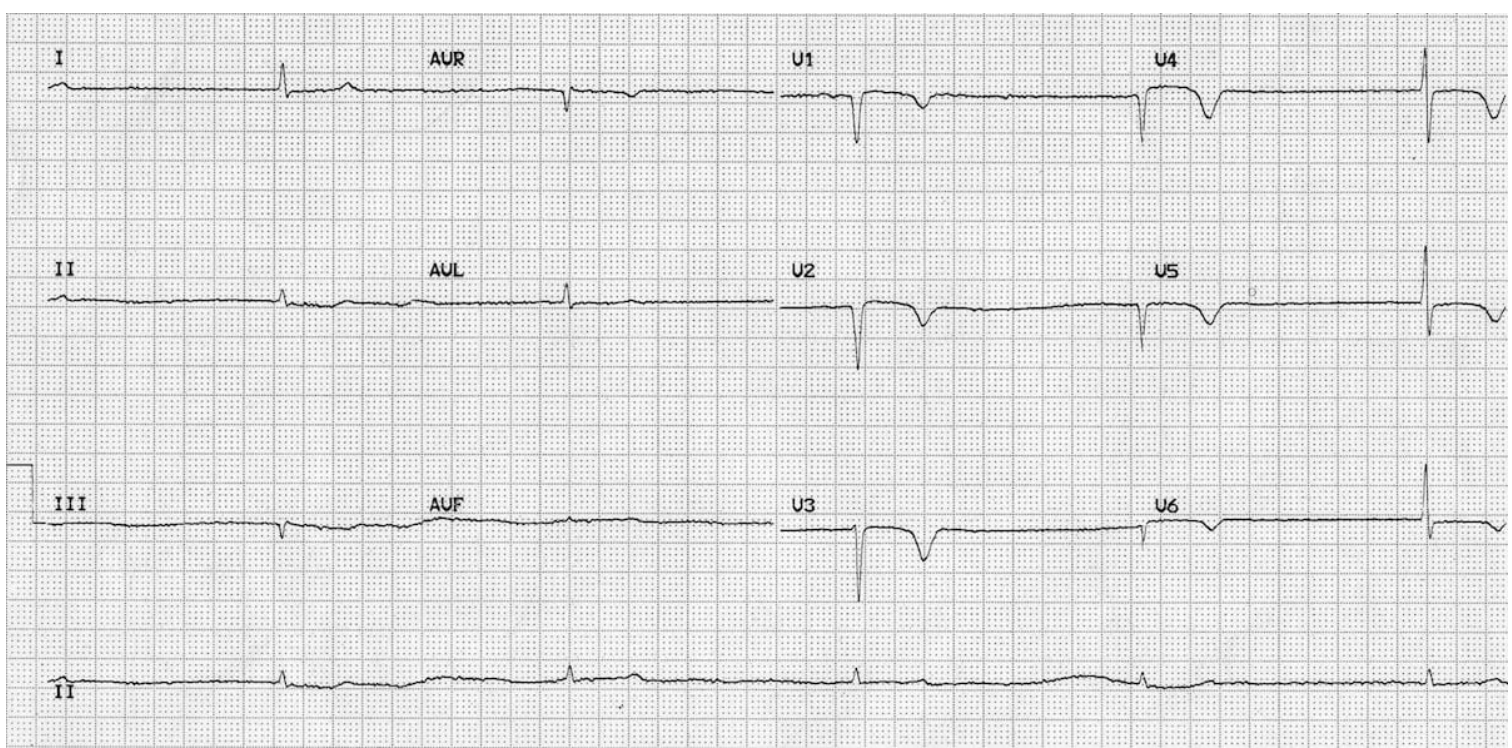
67 y/o woman presents to the ER for altered mental status. PSHx is positive for complete thyroidectomy. Vitals are as follows 94.5 temperature, 30 bpm, 11 RR, and 90/50 bp. Labs show hypoglycemia, hyponatremia, high TSH, extremely low free T4/T3. Your amazing, beautiful, smart ED tech hands you this EKG. What is your treatment plan? Not Tested this is just for me <3
U/S
What imaging is used for evaluating thyroid nodules or goiters?
Differentiates causes like thyroiditis or Grave’s
When should you consider radioactive iodine uptake (RAIU)?
Elevated TSH, low T4/T3
Describe the labs in primary hypothyroidism
low/normal TSH, low T4/T3
Describe the labs in secondary hypothyroidism
Hashimoto’s (autoimmune thyroid disease)
If anti-TPO antibodies are positive → what’s the diagnosis babes?

hyponatremia, hyperlipidemia
What are some other diagnostic findings in hypothyroidism?
Levothyroxine (T4), desiccated thyroid extract, lifestyle (optimize iodine intake, avoid excess soy/goitrogens), Liotrix (T3/T4 - controversial)
Treatment options for Hypothyroidism
Levothyroxine (start dose at 1.6 mcg/kg/day - based on IDEAL body weight, lower dose if patient is old or has hx of heart diseae)
What is the drug choice for hypothyroidism?
Increase levothyroxine dose by 30%, monitor every 4 weeks
Concerning treating hypothyroidism in a pregnant patient, what do you need to do
Iodine and selenium supplements, avoid excessive cruciferous veggies (inhibit iodine absorption), increased thyroid demand during pregnancy, decrease stress, exercise
What are some lifestyle changes we can make to help the thyroid?
Congenital hypothyroidism (cretinism)
What is one of the most common preventable cause of intellectuable disability and is apart of the Tx newborn screening?
Levothyroxine NOW
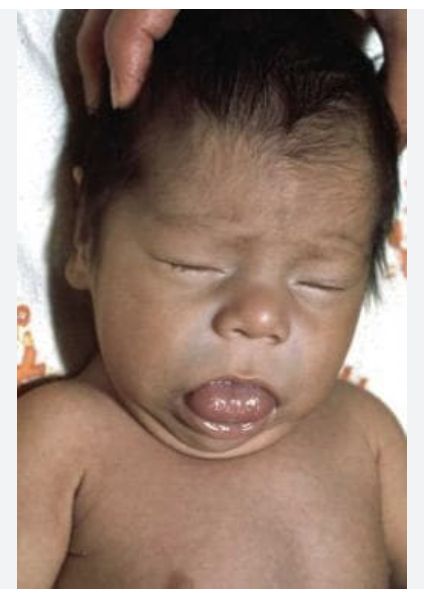
A neonate born just now presents jaundice, puffy face, large tongue. Vitals are stable with the exception of 94.6 temperature. Physical exam shows hypotonia. Lab work shows low T3/4. What is your treatment plan?
iodine deficiency, hashimoto’s, Grave’s, euthyroid, hyper/hypothyroidisn
What are some causes of goiters?
thyroid panel, U/S, FNA biopsy, radioactive testing, CT/MRI
What are some things we are going to order if we see a goiter?
Treat underlying thyroid dysfunction, iodine supplementation
Treatment plan for goiter
Thyroiditis
Inflammation of the thyroid gland that can be caused by autoimmune diseases, infections, radiation, or medications (Amio) - can lead to hypo or hyperthyroidism.
Suppurative (bacterial, fungal, parasitic), subacute (viral), chronic autoimmune thyroiditis, drug-induced, postpartum
Types of thyroiditis
IV antibiotics, surgical draining of abscess
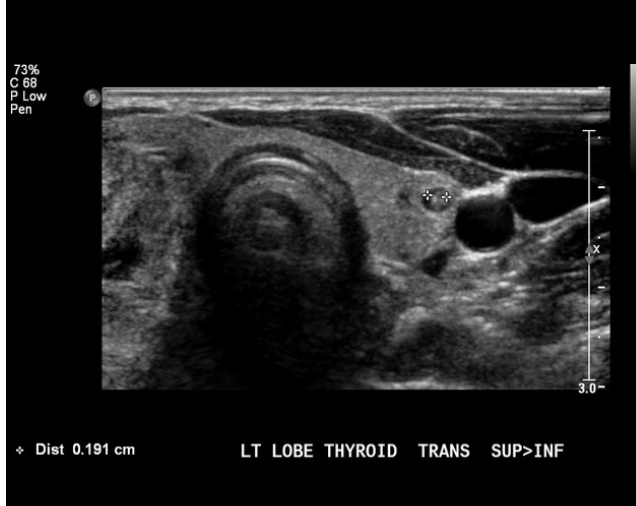
Patient presents to the ED for neck pain and general malaise. Her symptoms started 3 hours ago. Vitals are stable with the exception of a temp of 104.3. Physical exam reveals, a painful, erythematous thyroid. Lab work shows elevated PMNs, elevated ESR and CRP, leukocytosis, TSH is in range. See U/S. What is your management plan?
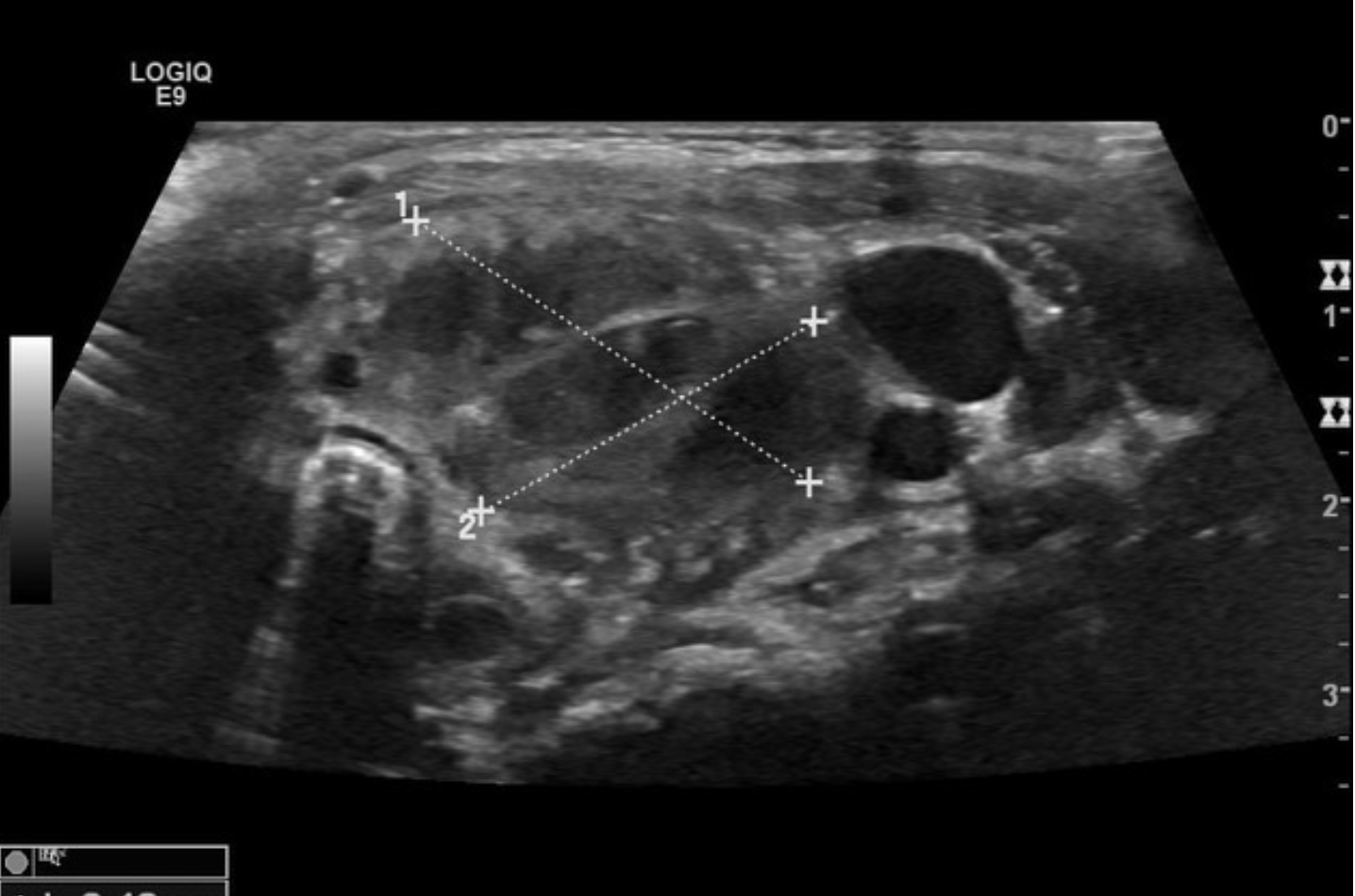
ASA/NSAIDs (if 10/10 pain use prednisone), Beta blockers (she’s in the hyperthyroid stress stage), monitor T3/T4 levels (switch to levothyroxine if they start to fall low)
35 y/o women presents to the clinic for odynophagia starting 2 weeks ago. PMHx is positive for the flu. She states that she has been unable to eat due to pain. She reports that she has been intolerant to heat. Vitals are stable with the exception of a 99.0 F temperature and 120 bpm. Physical exam reveals an enlarged thyroid that is tender on palpation. Labs reveal low TSH, elevated T3/T4, elevated ESR and CRP. See u/s. What is your management plan?
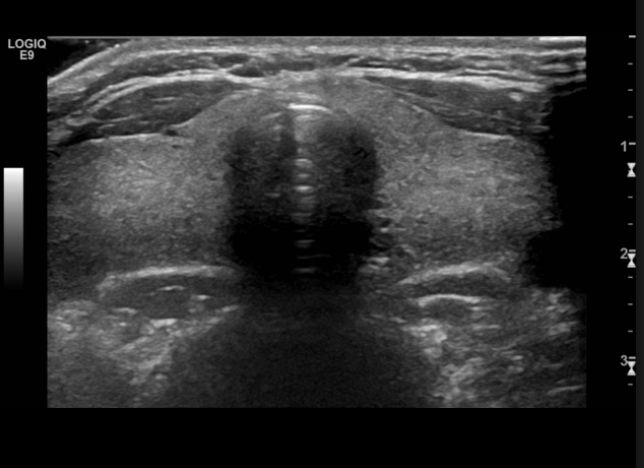
FNA biopsy of nodule, Levothryoxine for hypothyroidism, monitor for other autoimmune diseases
45 y/o female presents with worsening symptoms of hypothyroidism (weight gain, cold intolerance, muscle weakness, etc). PMHx is positive for Hashimoto’s. Family Hx is positive for Grave’s. She states that she was feeling pretty good last week as she loss some weight and was full of energy, but she notes she didn’t sleep as well and her heart pounding. On a physical exam you note a mass in her neck. Labs show elevated anti TPO and TG antibodies. What is your treatment plan?
genetic susceptibility and environmental factors, radiation exposure, dietary iodine supplementation (Wolff-Chaikoff), amio, some cancer meds
Risk factors for hashimoto’s thyroiditis
goiterous autoimmune (usually asymptomatic), atrophic autoimmune
Types of hashimoto’s thyroiditis
thyroid is under stress due to follicular disruption so it releases all of the thyroid hormone it has
Why do you get transient hyperthyroidism (Hashitoxicosis) early on in the course of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis?
Postpartum thyroiditis
An autoimmune inflammation of the thyroid occurring within 1 year of being postpartum that is characterize by a phase of transient hyperthyroidism and a phase of hypothyroidism.
Anti-TPO elevated, TSH/T4 - depends on phase
Labs for postpartum thyroiditis
symptom management (beta blockers), monitor TSH/T4
Management plan for postpartum thyroiditis - hyperthyroid phase
levothyroxine if symptomatic, monitor TSH/T4
Management plan for postpartum thyroiditis - hypothyroid phase