AP - exam 3 (respiratory)
CO2
what is a waste product of cellular respiration?
O2
what is supplied to the body during cellular respiration?
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
CO2
what is a waste product of cellular respiration?
O2
what is supplied to the body during cellular respiration?
paranasal sinuses
what has the following functions?
- lighten skull
- secrete mucus
- warm + moisten air
rhinitis
______ is the inflammation of nasal mucosa
pharynx
________ is made of skeletal muscle and connects the nasal cavity + mouth to the larynx + esophagus
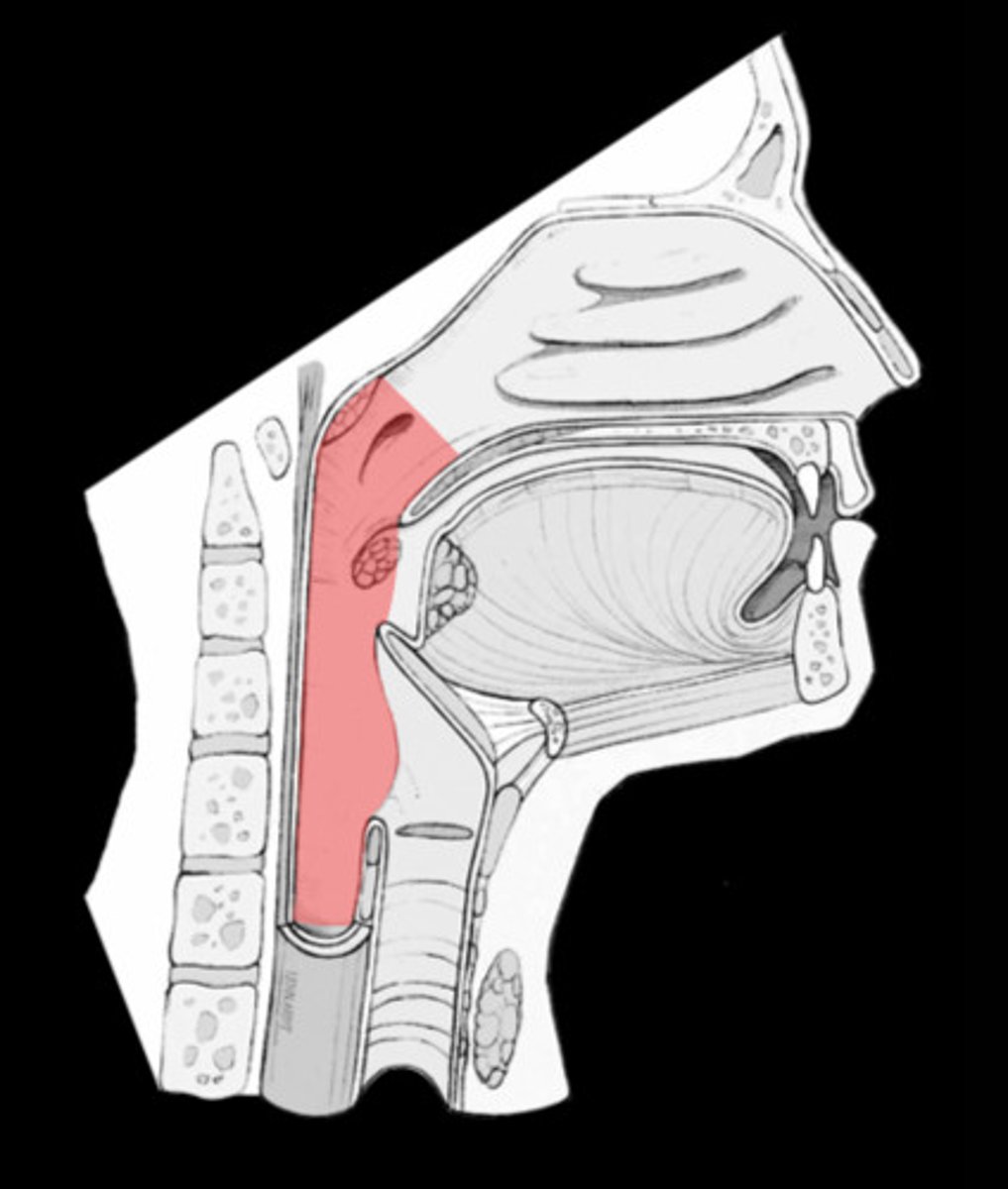
laryngopharynx
what region of the pharynx is the passageway for food + air and is lined with stratified squamous epithelium?
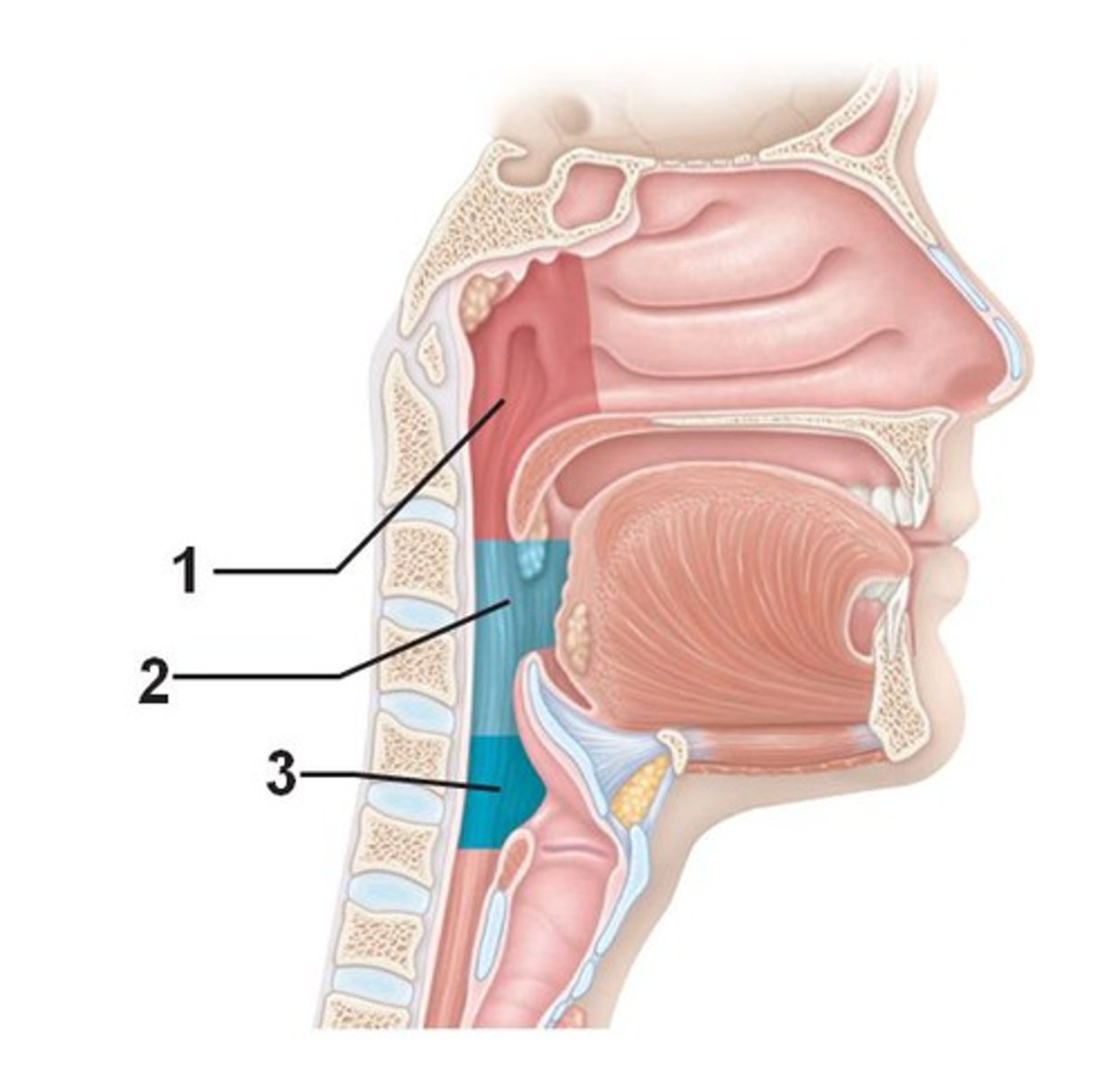
larynx
_____ involves:
- air passage
- channels air + food into proper ways
- voice production -> houses vocal folds (glottis)
trachea
what is known as the windpipe, which is lined with mucosa-ciliated pseudostratified epithelium with goblet cells?
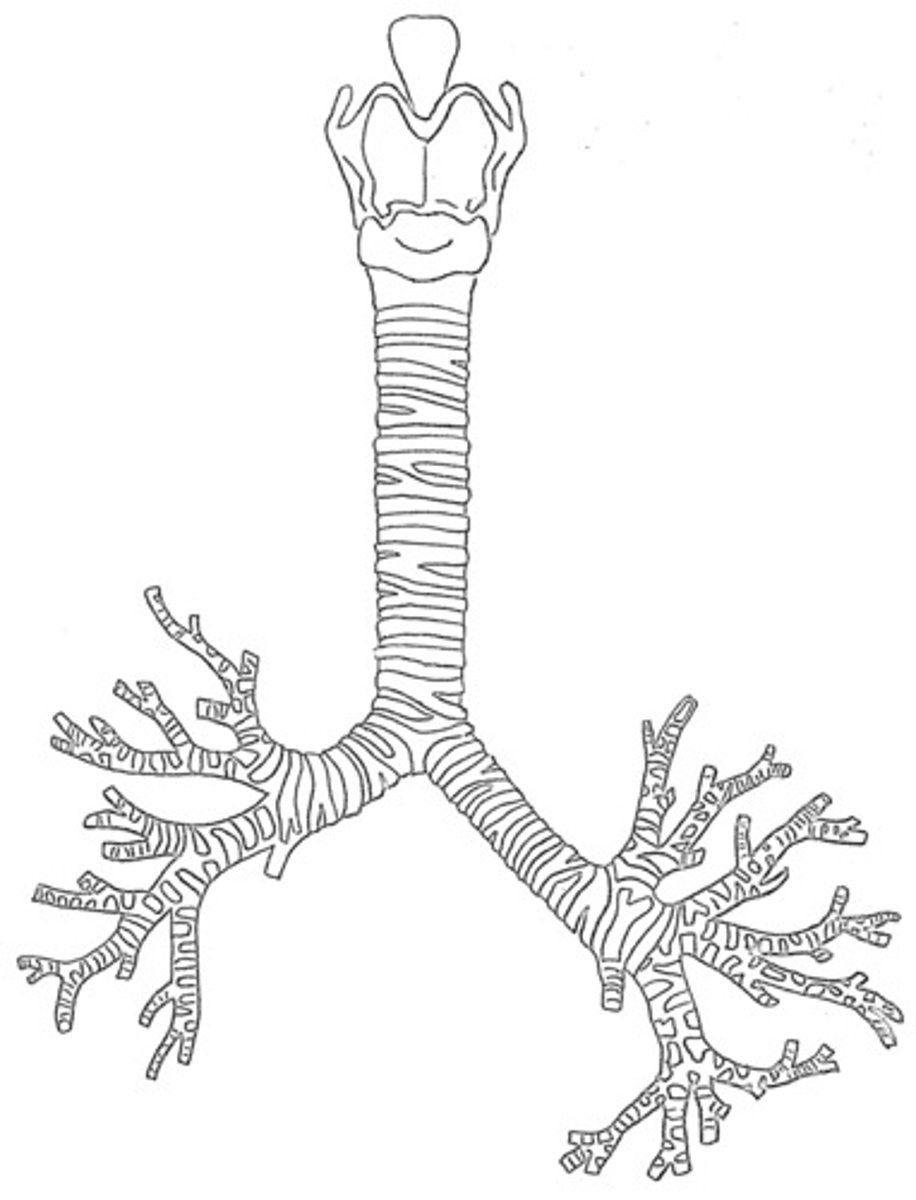
carina
what is the point where the trachea branches into two main bronchi?
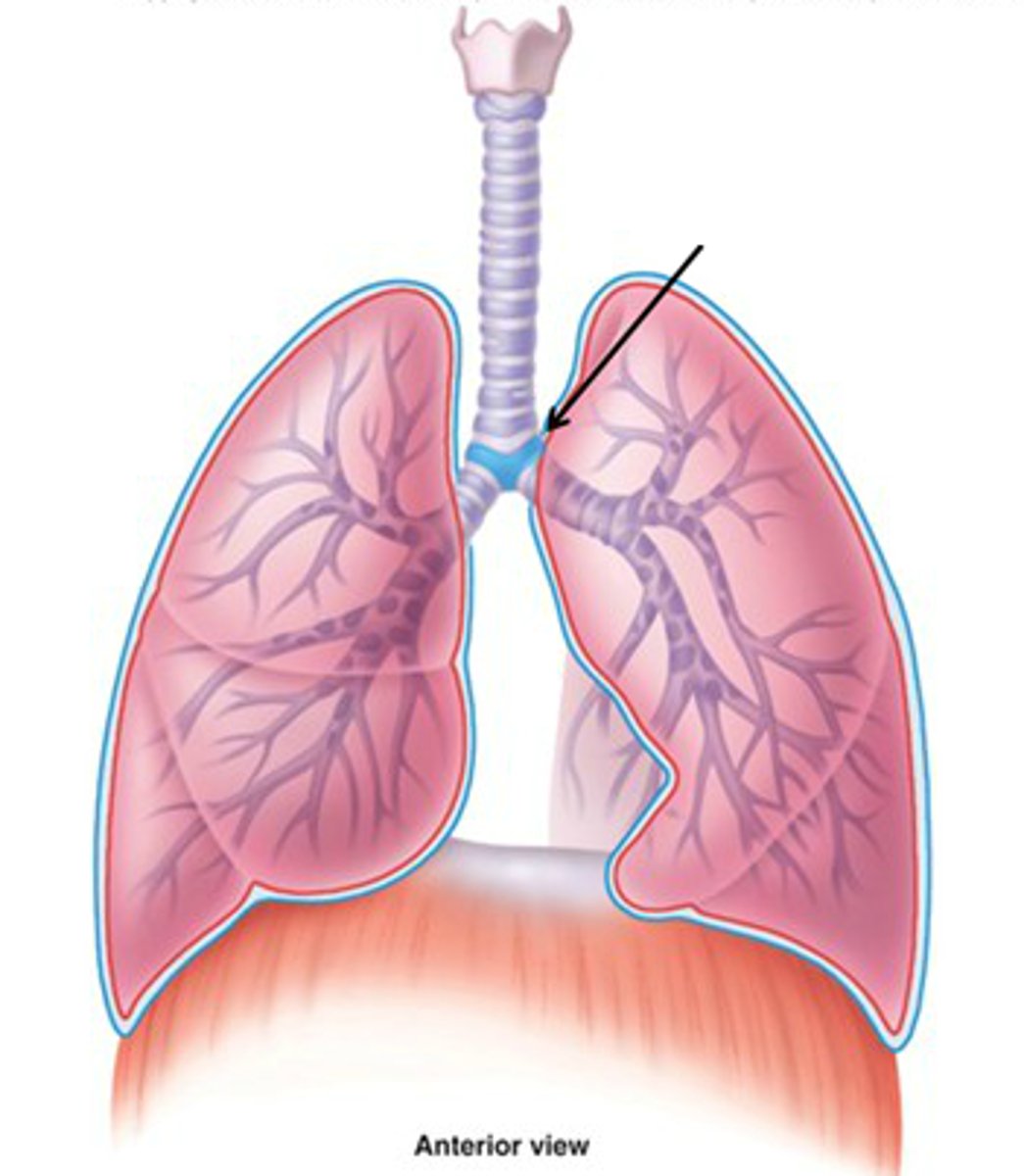
right
which bronchi is wider, shorter, and more vertical than the other?
foreign bodies
what moves more easily toward the right bronchus?
0.5 mm
the diameter of terminal bronchioles is less than ________
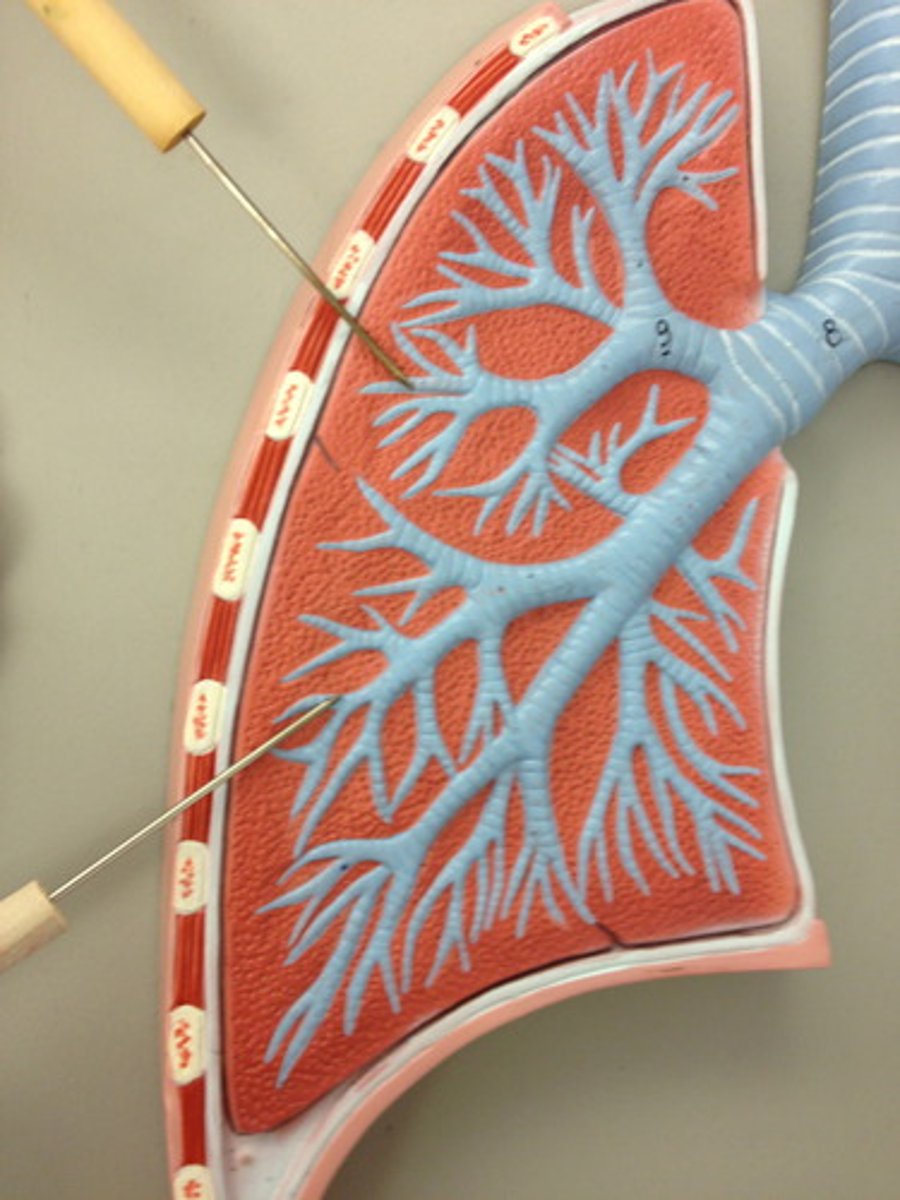
1 mm
the diameter at the start of bronchioles is less than ______
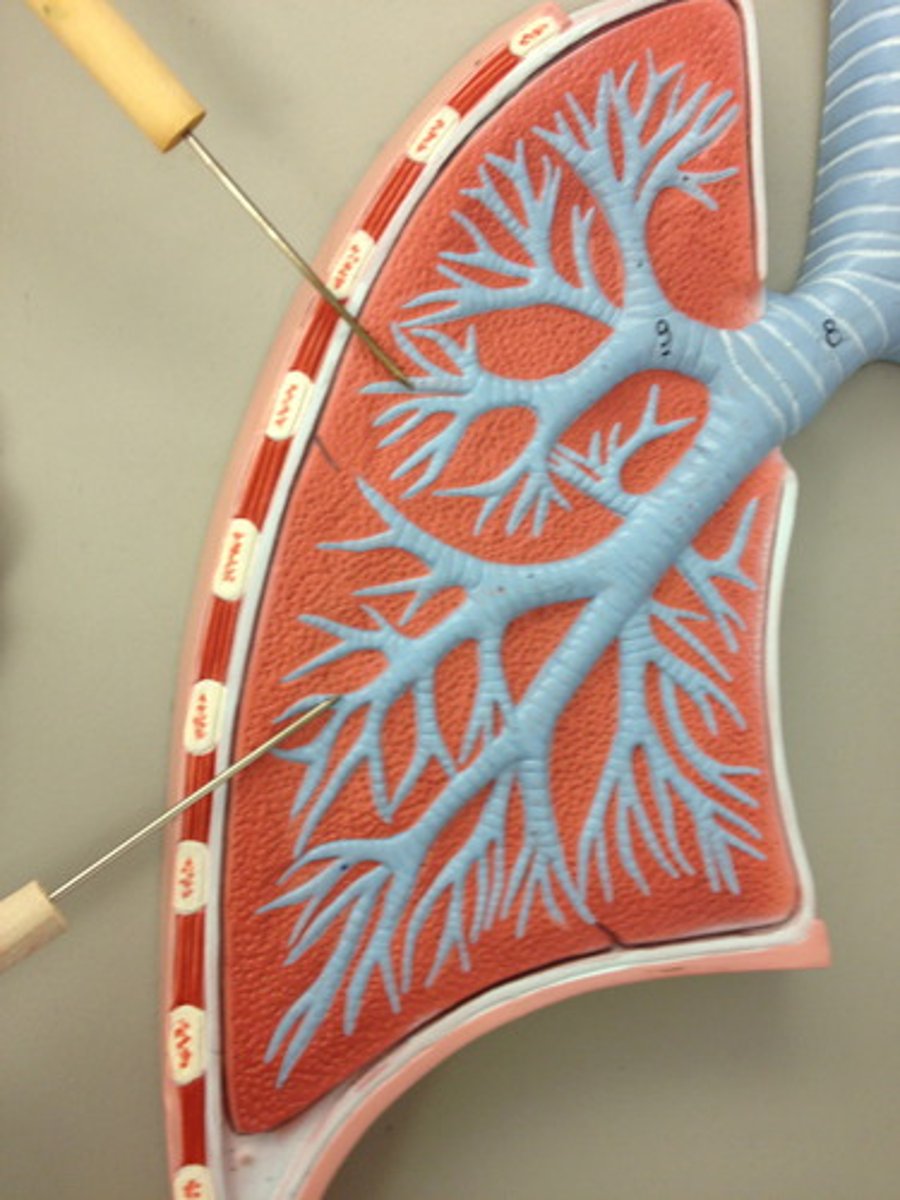
respiratory bronchioles
where does the respiratory zone begin?
300 million
how many alveoli make up most of lung volume?
alveoli
what is the site of gas exchange?
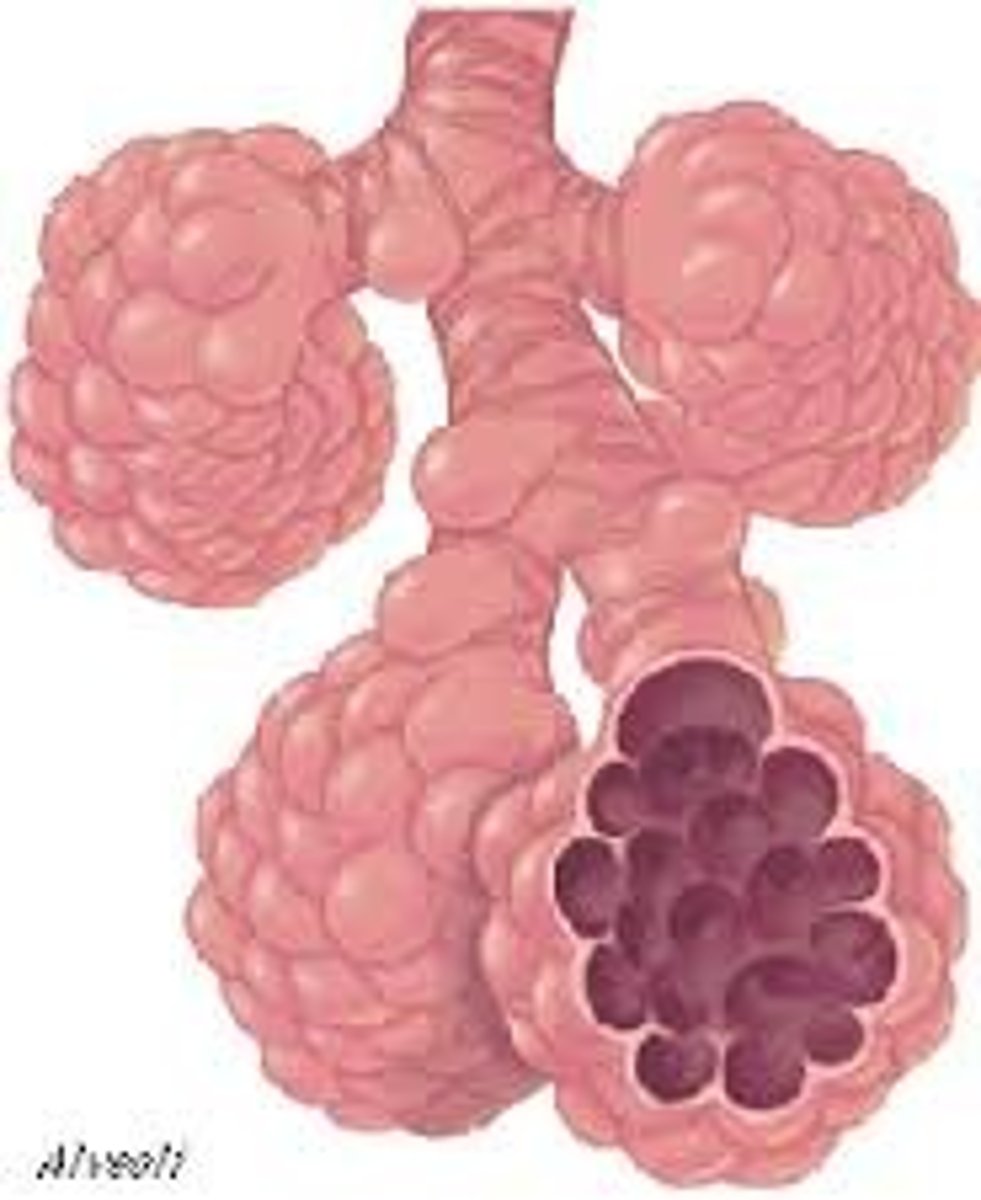
respiratory membrane
_______ is made of alveolar and capillary walls and their fused basement membrane
simple diffusion
how goes gas exchange occur across the respiratory membrane?
type I alveolar cells
what type of alveolar cell found in alveolar walls is found in the single layer of squamous epithelium?
type II alveolar cells
what type of alveolar cell found in alveolar walls are scattered and cuboidal and secretes surfactants and antimicrobial properties?
alveolar macrophages
what keeps alveolar surfaces sterile in the alveolar walls?
left
which lung is smaller?
1. left
2. right
cardiac notch
the left lung contains the _______, which is the concavity for the heart
oblique fissure
the left lung is separated into superior + inferior lobes by the ________
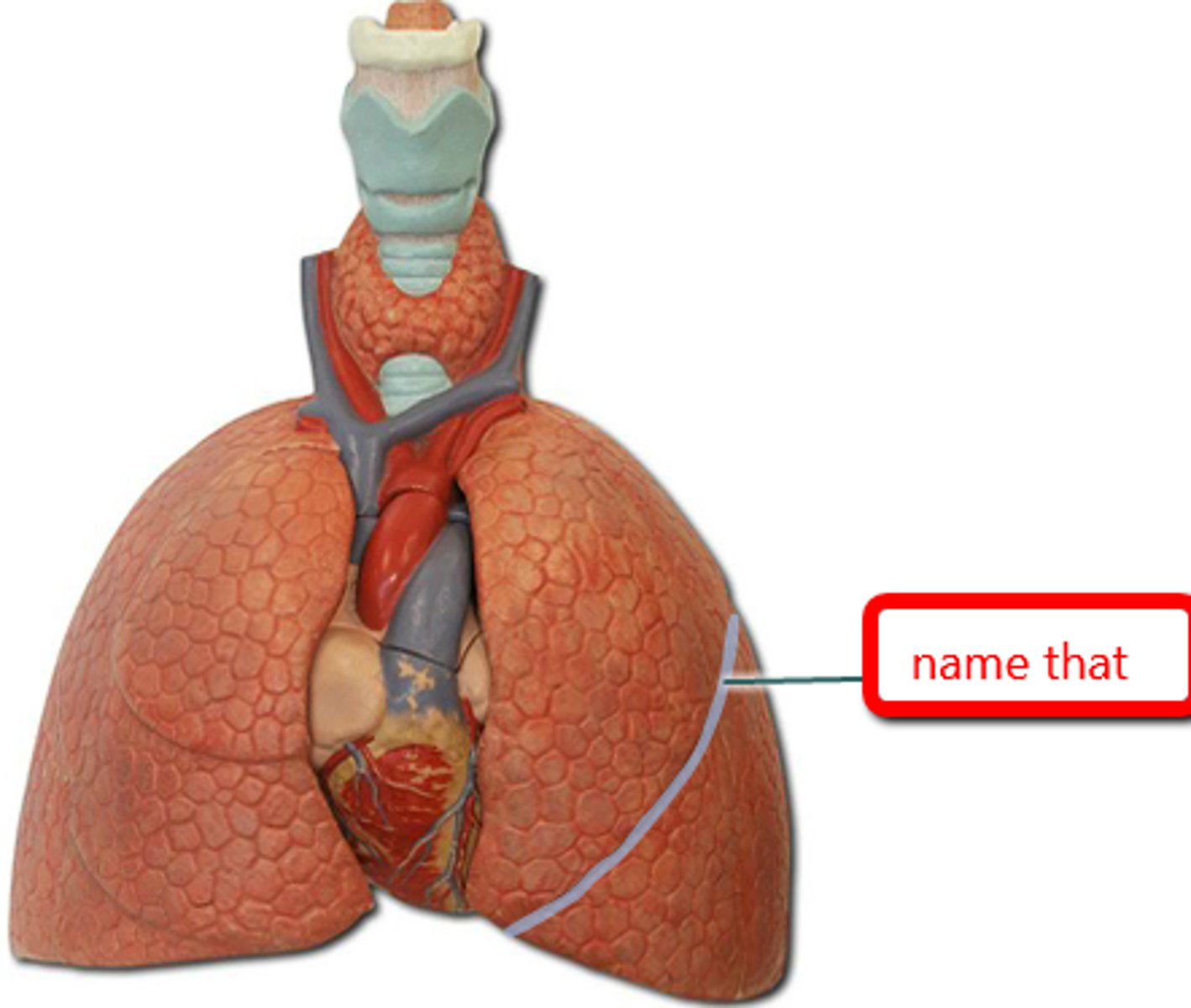
oblique and horizontal fissure
the right lung is separated into superior, middle, inferior lobes by the __________
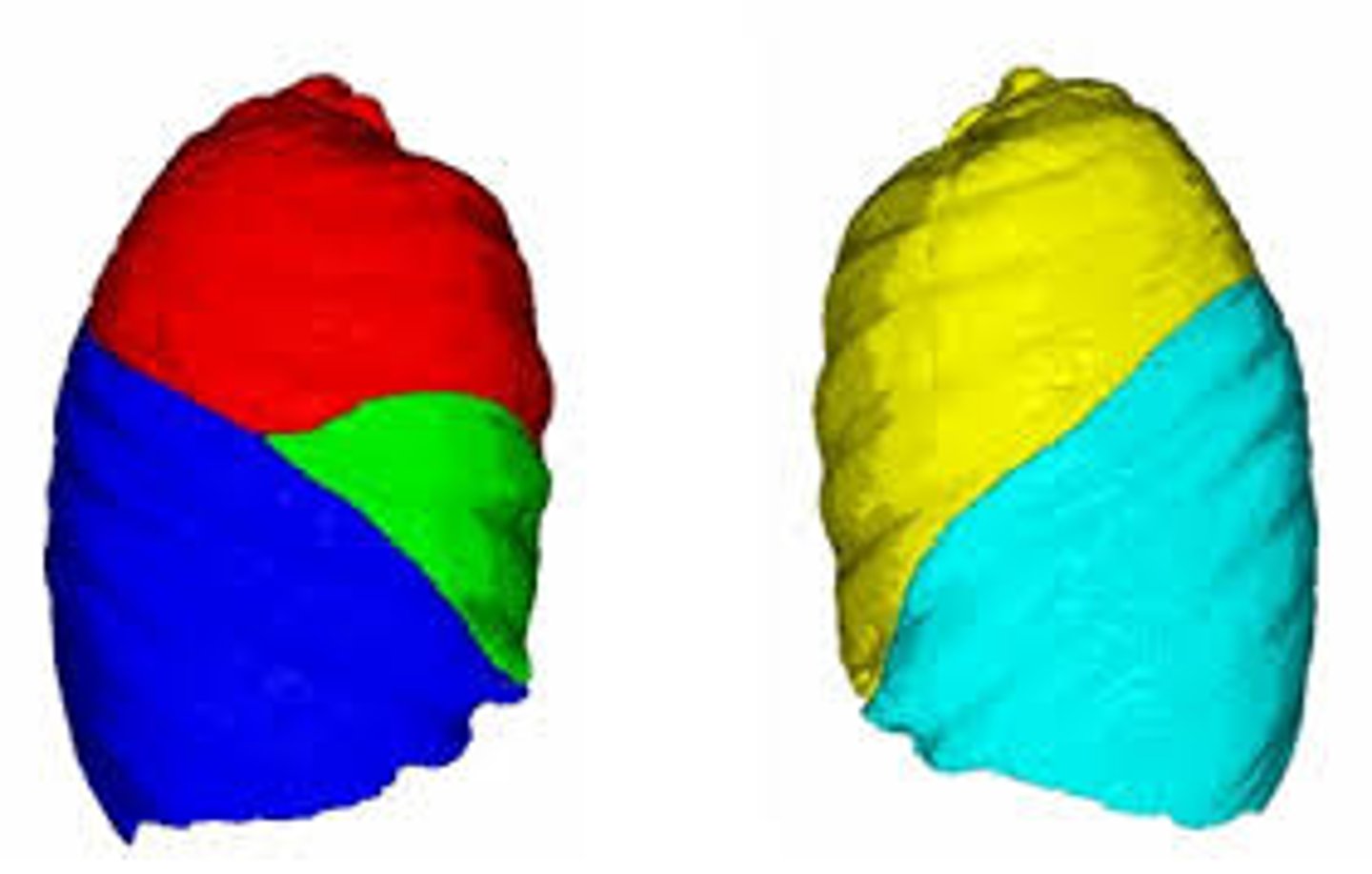
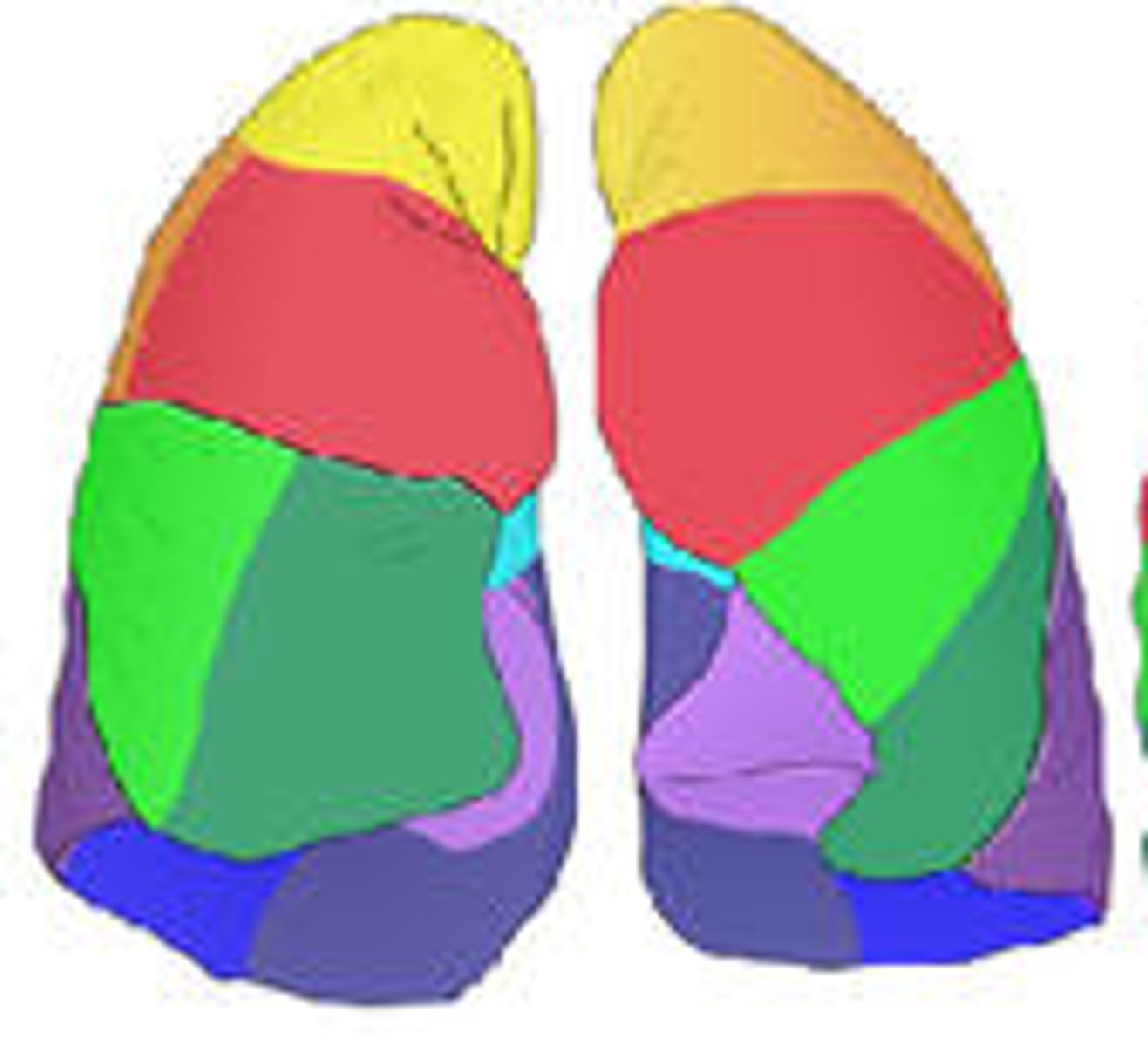
bronchopulmonary segments
if taken by disease, ________, which are separated by connective tissue septa, can be individually removed
(hint: 10 right, 8-10 left)
thin double-layered serosa
what divides the thoracic cavity into two pleural compartments + mediastinum?
parietal pleura
what lines the thoracic wall, is on the superior face of diaphragm, around the heart, and between lungs?
visceral pleura
what covers the external lung surface?
pleural fluid
what fills the pleural cavity and provides. . .?
- lubrication + surface tension
- assists in expansion + recoil
atmospheric pressure (Patm)
pressure in thoracic cavity always tries to equal to ________
intrapulmonary pressure (Ppul)
__________ is the pressure in alveoli, which fluctuates with breathing
intrapleural pressure (Pip)
______ is the pressure within the pleural cavity, which fluctuates with breathing
negative
intrapleural pressure (Pip) always has a ________ pressure
(hint:
positive
a _________ intrapleural pressure due to fluid accumulation can result in lung collapse
enlarges lungs
negative intrapleural pressure is caused by opposing forces, where the outward force tends to ________
elastic recoil
negative intrapleural pressure is caused by opposing forces, where the _______ (an inward force) collapses lungs by decreasing lung size
surface tension
negative intrapleural pressure is caused by opposing forces, where the inward force of _______ of alveolar fluid reduces alveolar size
transpulmonary pressure
what is the difference between intrapulmonary pressure (Ppul) and intrapleural pressure (Pip), which is the resulting pressure that will keep the airways open, referred to as?
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
what condition involves a group of lung diseases that cause airflow obstruction, where an individual uses respiratory accessory muscles to increase thoracic cage size?
(hint: patients more prone to increase of Pip)
atelectasis
___________ is lung collapse due to plugged bronchioles and collapse of alveoli
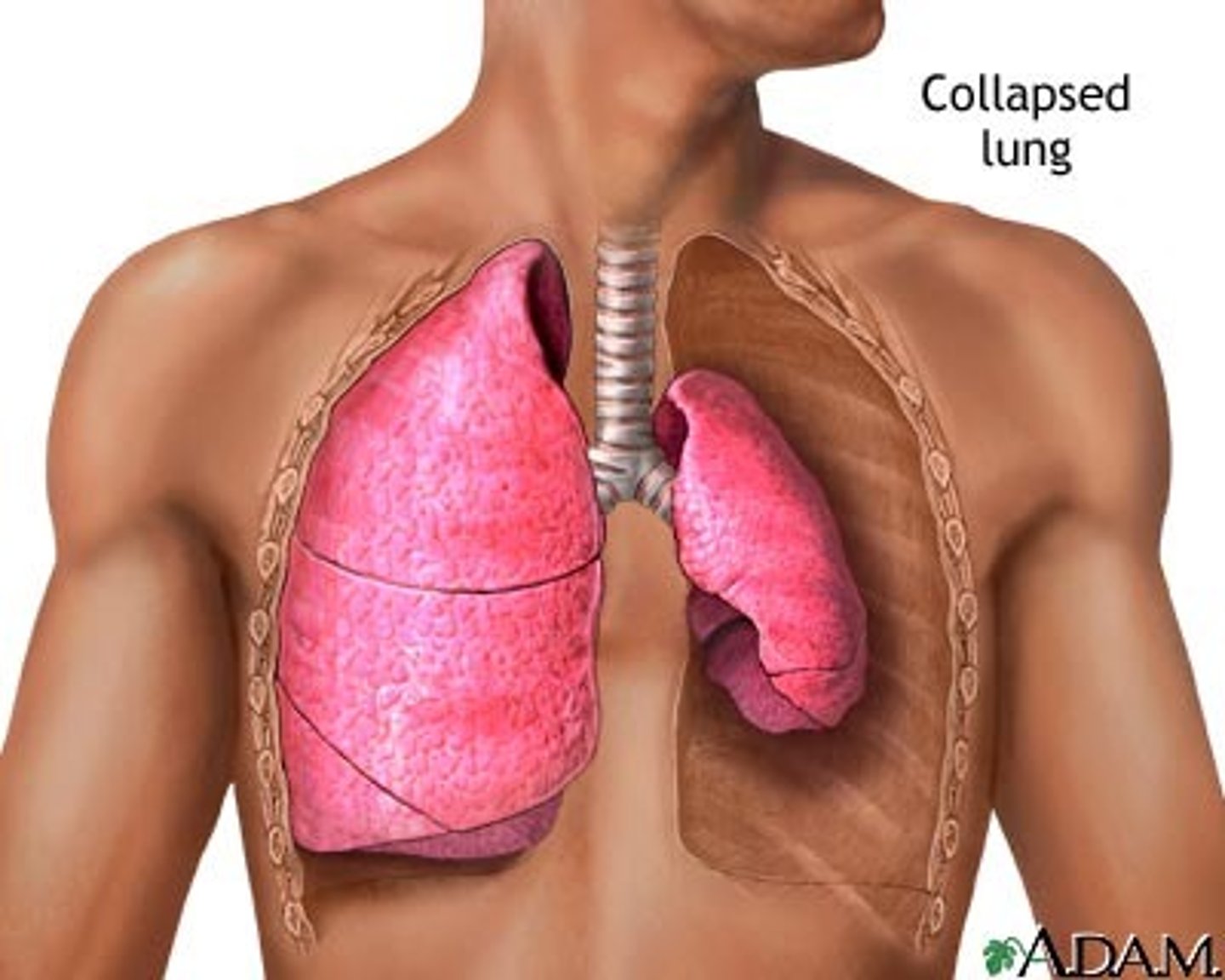
pneumothroax
what condition involves air in the pleural cavity, either from wound in parietal or rupture of visceral pleura?
chest tubes
pneumothorax is treated by removing air with ___________, where then the pleurae heal and the lung reinflates
inspiration
_________ is an active process defined as when gases flow into lungs
expiration
____________ is defined as when gases exit lungs
increases
regarding pulmonary ventilation, when volume __________, pressure decreases
decreases
regarding pulmonary ventilation, when volume __________, pressure increases
diaphragm and external intercostals
during inspiration, the inspiratory muscles such as the __________ contract, leading to an increase in thoracic volume
passive
quiet expiration is normally a _________ process, where inspiratory muscles relax and thoracic cavity volume decreases
active
forced expiration is an __________ process, and uses abdominal (oblique and transverse) and internal intercostal muscles
lung compliance
what is the capacity to change volume in lungs as pressure changes known as?
easier
a higher lung compliance means that lungs are _______ to expand and recoil
infant respiratory distress syndrome
insufficient quantity of surfactant in premature infants can cause ____________, where alveoli collapse after each breath
tidal volume
______ is the amount of air inhaled/exhaled with each breather under resting conditions
inspiratory reserve volume (IRV)
__________ is the amount of air that can be forcefully inhaled after normal TV inspiration
expiratory reserve volume (ERV)
_________ is the amount of air that can be forcefully exhaled after normal TV expiration
residual volume (RV)
________ is the amount of air in lungs after forced expiration
total lung capacity (TLC)
_______ is the maximum amount of air contained in lungs after a maximum inspiratory effort
vital capacity (VC)
________ is the maximum amount of air that can be expired after a maximum inspiratory effort
inspiratory capacity (IC)
_______ is the maximum amount of air that can be inspired after a normal TV expiration
functional residual capacity (FRC)
________ is the volume of air remaining in the lungs after a normal TV expiration
forced expiratory volume (FEV) test
what is the most important pulmonary test in spirometry and done several times?
restrictive disease
what type of condition involves a destruction/less functional lung tissue?
(examples: tuberculosis, fibrosis, cystic)
perfusion
______ is the blood flow reaching alveoli
diameter
regarding perfusion, changes in PO2 in alveoli cause changes in ________ of arterioles
dilate
regarding perfusion, when alveolar O2 is high, arterioles __________
constrict
regarding perfusion, when alveolar O2 is low, arterioles __________
ventilation
_______ is defined as the amount of gas reaching alveoli (air flow)
plasma
regarding transport of respiratory gases by blood, 1.5% of O2 is dissolved in _________
hemoglobin (Hb)
regarding transport of respiratory gases by blood, 98.5% of O2 is loosely bound to each Fe in _________
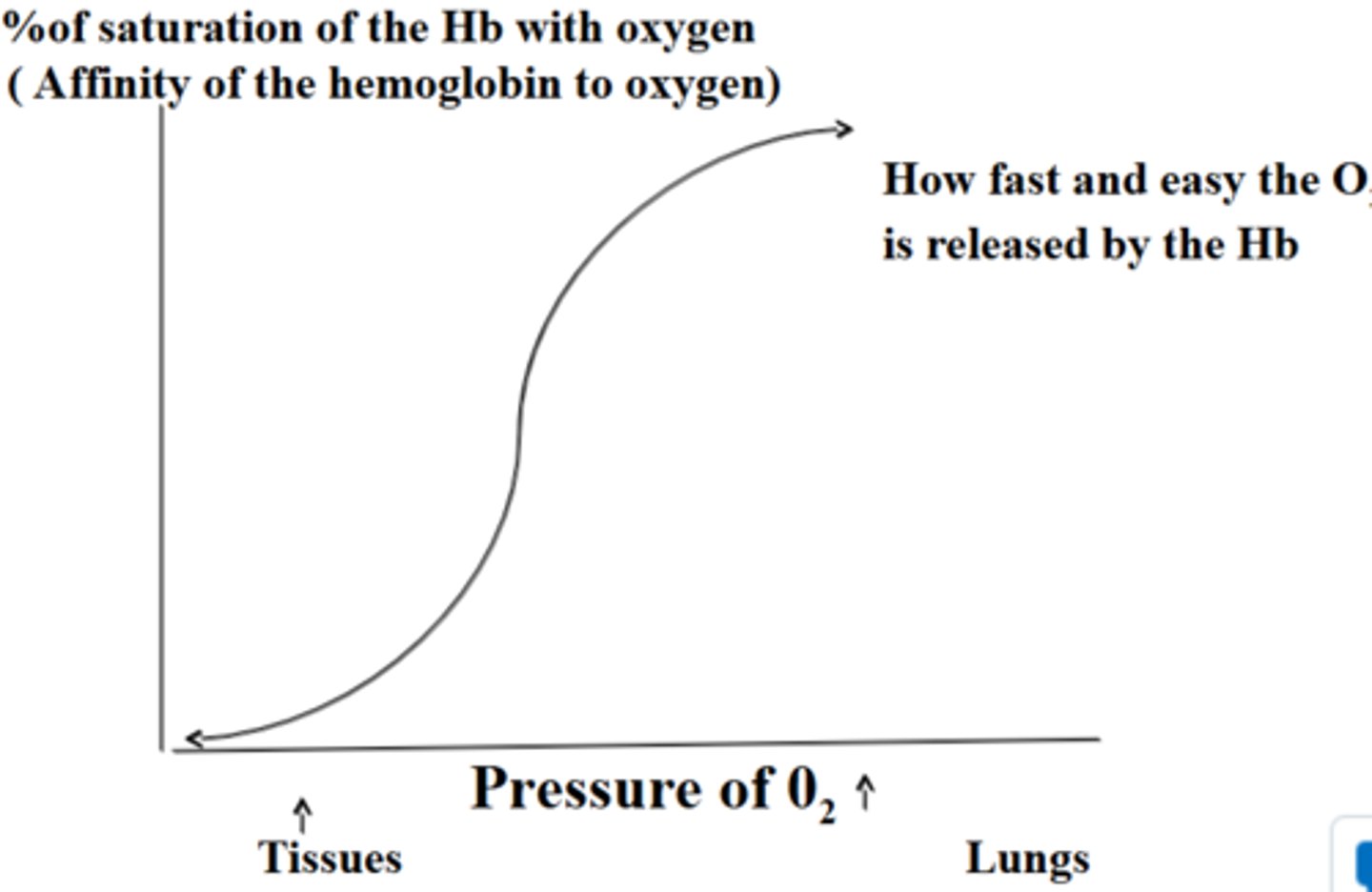
fully saturated
when all 4 heme groups carry O2 in Hb molecule at 100%, it is _________
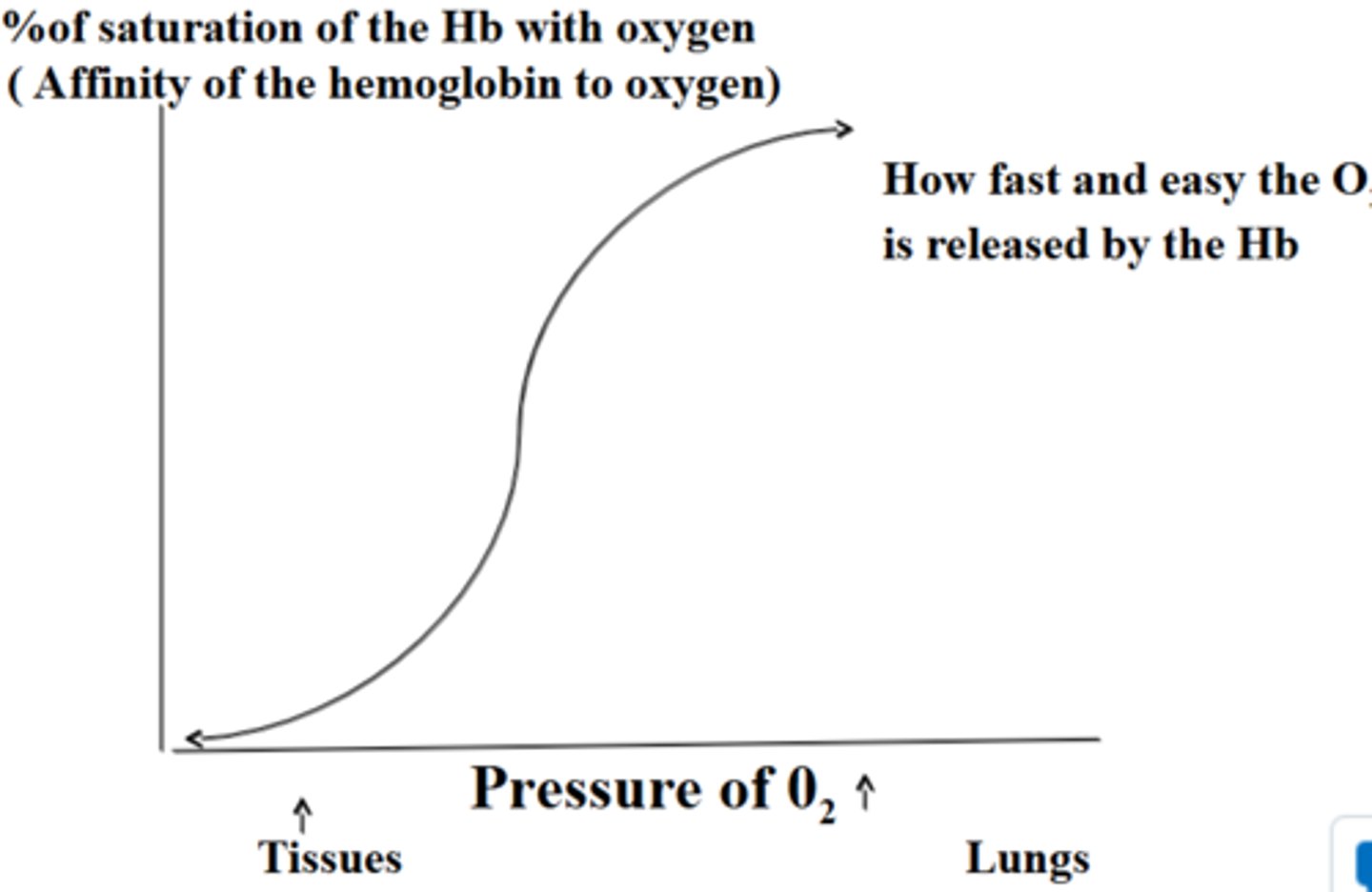
partially saturated
when 1-3 heme groups carry O2 in Hb molecules, it is __________
2,3-bisphosphoglyceric acid (BPG)
one of the factors regulating release of O2 by Hb is the concentration of __________, which is produced by RBC during glycolysis
- levels rise when O2 levels are chronically low
hypozia
what is the inadequate O2 delivery to tissues referred to as?
anemic hypoxia
what type of hypoxia involves too few RBCs and abnormal/too little Hb?
ischemic hypoxia
what type of hypoxia involves impaired/blocked circulation?
histotoxic hypoxia
what type of hypoxia involves cells unable to use O2, as in metabolic poisons?
hypoxemic hypoxia
what type of hypoxia involves abnormal ventilation, such as pulmonary disease?
carbon monoxide poisoning
what type of hypoxia involves CO having 200x greater affinity for Hb than oxygen, especially resulting from fire?
7-10%
what percentage of CO2 is dissolved in plasma?
20%
what percentage of CO2 is bound to globin of hemoglobin to make carbaminohemoglobin?
70%
what percentage of CO2 is transported as bicarbonate ions (HCO3-) in plasma?
carbonic acid
CO2 combines with water to form ___________, which quickly dissociates; this occurs primarily in RBCs, where carbonic anhydrase reversibly + rapidly catalyzes the reaction
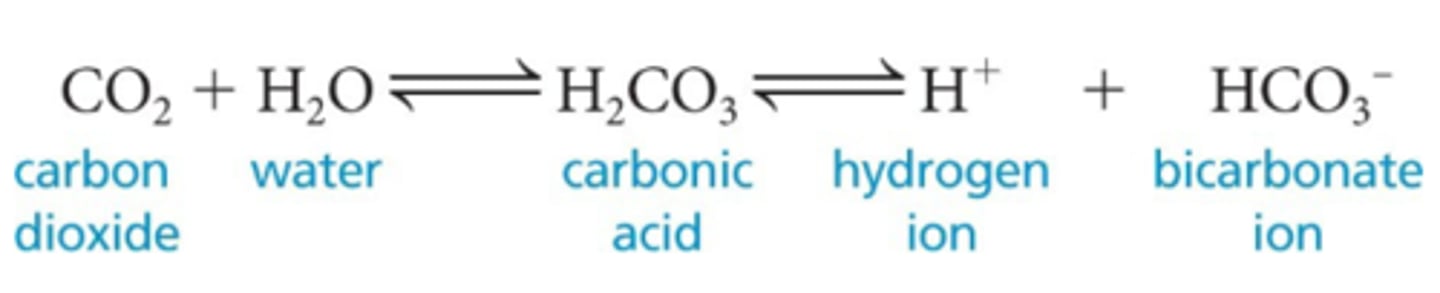
more solube
CO2 is 20 times ____________ in plasma than oxygen
haldane effect
________ states that if more O2 enters the blood in the lungs, more CO2 is removed from blood
bohr effect
________ states that if PCO2 and H+ increase in capillary blood, then the Hb-O2 bond weakens and more oxygen is released
slow, shallow breathing
what type of breathing rate would increase CO2 in blood (respiratory acidosis), leading to a drop in pH because the reaction in the image goes to the right and more H+ form?
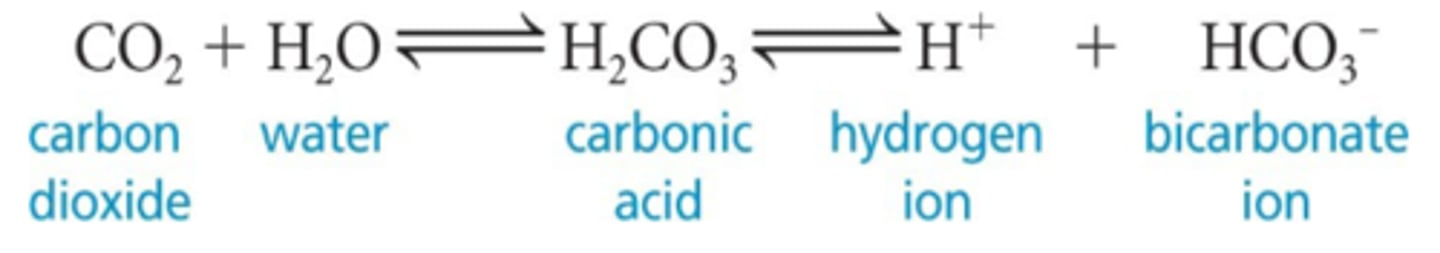
rapid, deep breathing
what type of breathing rate would decrease CO2 in blood (respiratory alkalosis), leading to a rise in pH because the reaction in the image goes to the left and more CO2 forms using the H+?
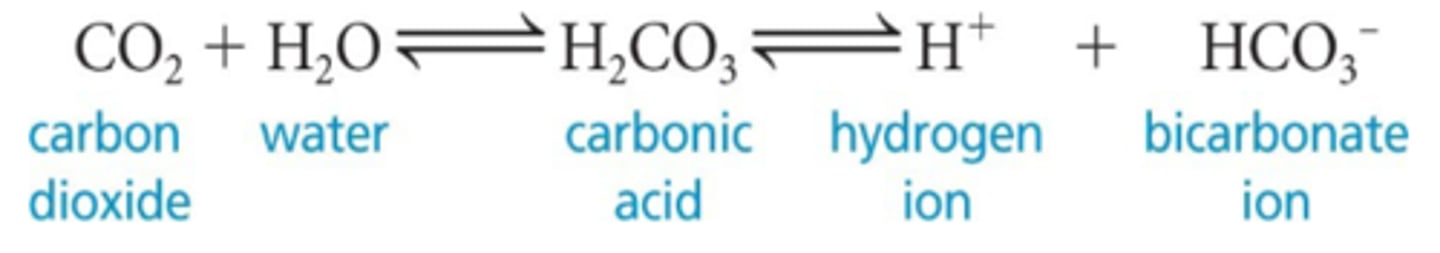
dorsal respiratory group (DRG)
what is the rhythm-generating center in the medulla, which sets eupnea at 12-15 bpm?
ventral respiratory group (VRG)
what center in the medulla has inspiratory and expiratory centers that function only when breathing demands increase + accessory muscles become involved?
(aka forced respiration)
apneustic center
what type of pontine respiratory center in the medulla promotes inhalation?
pneumotaxic center
what type of pontine respiratory center in the medulla inhibits the apneustic center + promotes active/passive exhalation?
hyperventilation
what is the increase of depth and rate of breathing that exceeds body's need to remove CO2 referred to as?
hypoventilation
_______ involves the increase of blood CO2 concentration and decrease of pH, producing respiratory acidosis
inflation relfex
_________ involves the stretch receptors in pleurae and airways stimulated by lung inflation
hypothalamic controls
_________, for example, involves breath holding that occurs in anger or gasping with pain
cortical controls
__________, for example, involves voluntary breath holding
brain stem
what reinstates breathing when blood CO2 is too high after voluntary breath holding?
emphysema
_______ involves. . .
- permanent enlargement of alveoli
- destruction of alveolar walls
- decreased lung elasticity
- results from smoking, COPD, a-1 antitrypsin deficiency
tuberculosis
what infectious disease is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, with symptoms of fever, night sweats, weight loss, racking cough, coughing of blood?