Dialysis
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
what is the primary purpose of DIALYSIS
managing fluid + electrolyte balance with CKD/AKI
what are the 3 major types of DIALYSIS
1. peritoneal dialysis
2. intermittent hemodialysis
3. continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT)
for either PERITONEAL/INTERMITTENT DIALYSIS, what 3 principles are used to balance fluid + electrolyte levels
1. diffusion
2. osmosis
3. ultrafiltration
what is DIFFUSION
is the movement of solutes (Cr, urea/electrolytes) from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration
what is OSMOSIS
is the movement of fluid from an area of lesser solute concentration to an area of greater solute concentration
what is ULTRAFILTRATION
is the removal of water + fluid
how is ULTRAFILTRATION accomplished
by creating pressure gradients between arterial blood + dialyzer membrane/compartment
what 2 types of DIALYSIS are indicated for AKI cases
1. intermittent hemodialysis
2. CRRT
what setting is CRRT implemented in
critical care settings in patients with AKI
- stabilize patients
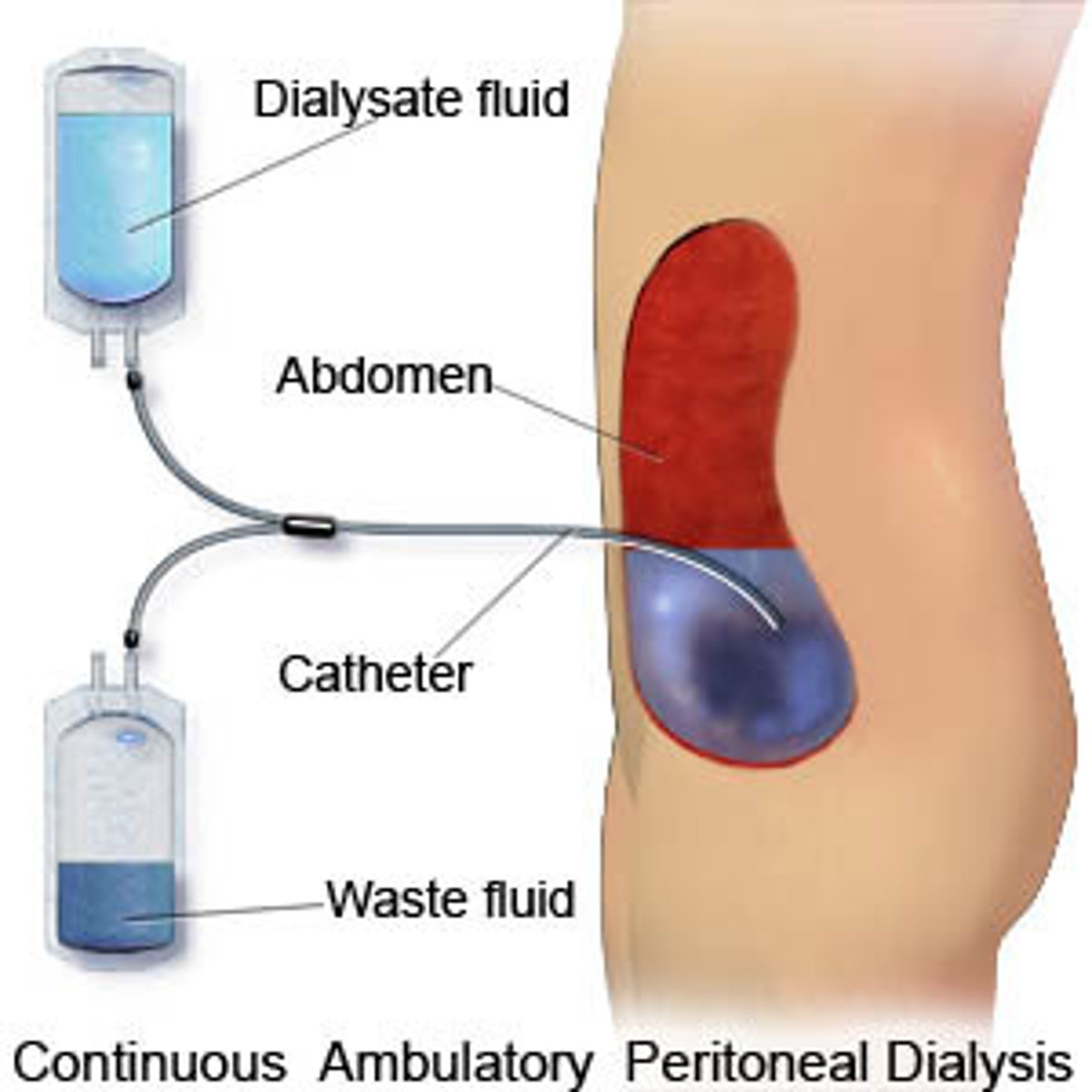
what does PERITONEAL DIALYSIS involve
using the peritoneal cavity as a semipermeable membrane to exchange soluble substances + water between the dialysate fluid + blood vessels in abdominal cavity
what is the duration range for PERITONEAL DIALYSIS
45 minutes to 9 hours
what is the PERITONEAL DIALYSIS exchange range that patients can have anywhere from
4-24 exchanges per day
what are the 3 major steps involved in PERITONEAL DIALYSIS
1. dialysate fluid instilled into peritoneal cavity through an indwelling catheter
2. after dialysate is instilled into peritoneum, there's an equilibrium period when water + solutes pass through semipermeable membrane
3. once equilibrium is complete, peritoneal cavity is drained of excess fluid + solutes that the failing kidney can't remove
what are the 3 phases of PERITONEAL DIALYSIS
1. instillation
2. equilibration
3. drainage
what are the 2 types of PERITONEAL DIALYSIS
1. automated PD (APD)
2. continuous ambulatory PD (CAPD)
what is the difference between APD vs CAPD
APD: uses an automatic cycling device
CAPD: carried out by patient at home + doesn't require a machine; manually performed
what does AUTOMATED PD (APD) include
use of an automatic cycling device to control the instillation, equilibration + drainage phases
what type of setting can CAPD be completed in
at home
does CAPD require a machine
no, doesn't require a machine + is performed manually
what is involved in CAPD
dialysate left in peritoneal cavity for 6-8 hours allowing for equilibrium then drained out + fresh dialysate instilled
how many times a day is CAPD performed
3-4 times/day
what does fluid removal rely on regarding CAPD
creating an osmotic gradient across membrane using varying concentrations of glucose in dialysate
what patients is PERITONEAL DIALYSIS indicated for
patients with CKD who may/may not be hospitalized
what is the purpose of INTERMITTENT HEMODIALYSIS
control kidney functions (fluid volume, electrolyte balance, acid-base balance + filtration of nitrogenous wastes)
what are 2 steps involved in INTERMITTENT HEMODIALYSIS
1. patient's arterial blood is mechanically circulated through semi-permeable tubing surrounded by a dialysate solution in dialyzer (artificial kidney)
2. as patient's arterial blood is being filtered through dialyzer, "clean" blood is returned to patient's venous circulation
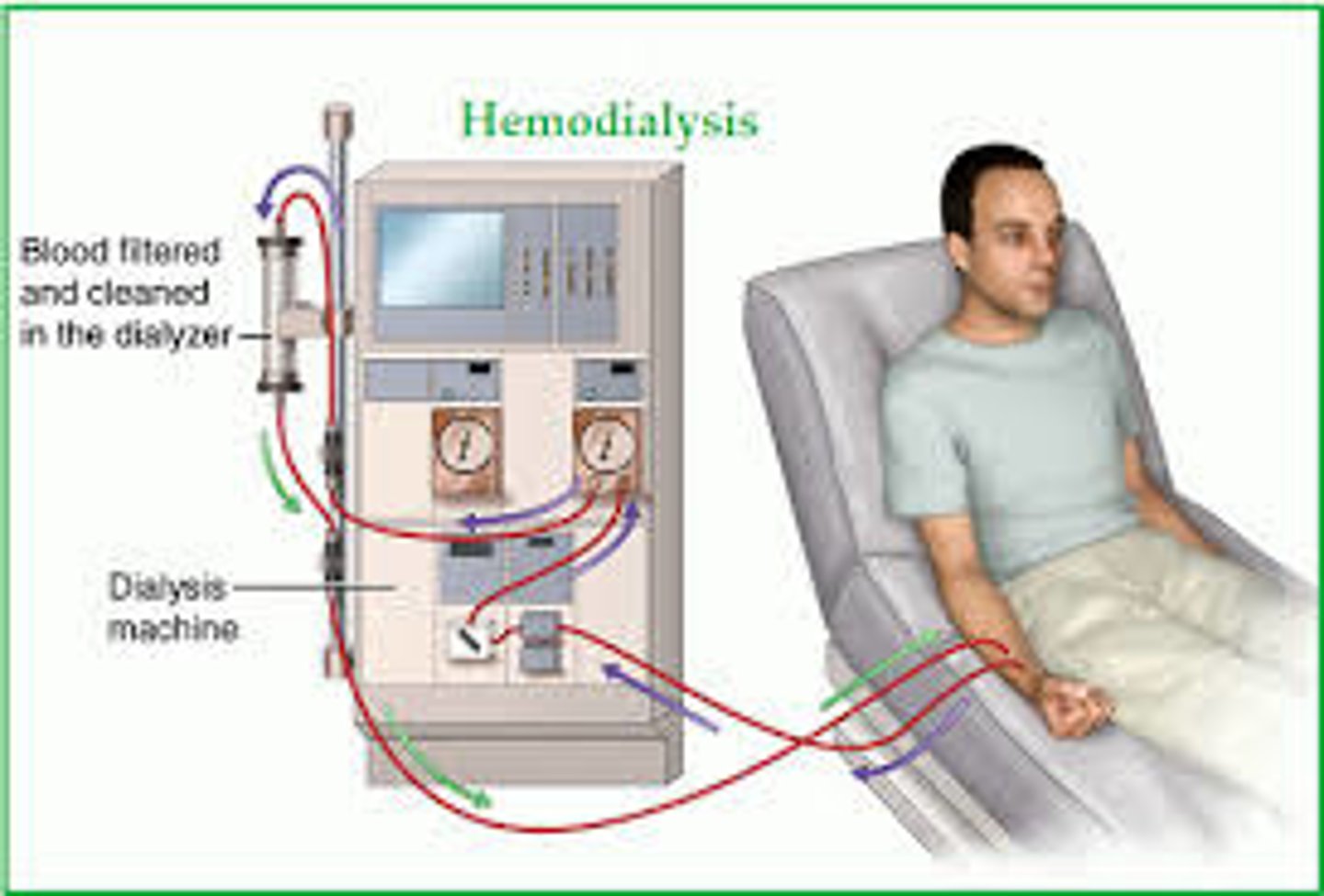
what are patient required to replace per dialysis session regarding INTERMITTENT HEMODIALYSIS
patients required to replaced 2-3L of fluid per dialysis session
why are patients require to replace 2-3L of fluid per dialysis session with INTERMITTENT HEMODIALYSIS
to fully achieve clear waste products + achieve osmotic balance
what does CRRT (Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy) provide
a continuous mechanism that balances fluid + electrolytes and small + medium solutes from the body in a manner that mimics the natural function of the patient's native kidney
what is CRRT beneficial for
patients with positive fluid balance
what are 6 predictable outcomes with CRRT
1. hemodynamic stability
2. continuous control of fluid status
3. control of acid-base status + electrolyte, calcium + phosphate balance
4. provision of protein-rich nutrition with excellent uremic control
5. prevention of intracerebral water fluctuations
6. minimal risk of infection
what are the 6 types of CRRT
1. slow continuous ultrafiltration (SCUF)
2. continuous veno-venous hemofiltration (CVVH)
3. continuous veno-venous hemodialysis
4. continuous veno-venous hemodiafiltration (CVVHDF)
5. continuous high-flux dialysis (CVVHFD)
6. continuous plasma-filtration adsorption (CPFA)
what is slow continuous ultrafiltration ONLY USED FOR
fluid control
what 2 types of MODES does slow continuous ultrafiltration have
1. arteriovenous modes
2. venovenous modes
what does continuous venovenous hemofiltration include
convective blood purification through a high-permeability membrane
what MODE is available with continuous venovenous hemofiltration
arteriovenous mode
what does continuous venovenous hemodialysis include
diffusive purification of blood through a low-permeability dialyzer
what is continuous venovenous hemodialysis ONLY USED FOR
small molecule clearance
what does continuous venovenous hemodiafiltration include
diffusive + convective blood purification with a highly permeable membrane
what does continuous high-flux dialysis include
diffusive + convective blood purification with a highly permeable membrane
- accessory pump to control ultrafiltration
what does continuous plasma-filtration adsorption include
a highly permeable plasma filter filters plasma, allowing it to pass through a bed of adsorbent material (carbon/resins)
what is MAINTAINED during continuous plasma-filtration adsorption
fluid balance